
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
11
16
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
AD1868
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
S
V
O
L
V
O
R
V
S
18-BIT
DAC
�
+
�
+
V
REF
V
REF
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
Single Supply
Dual 18-Bit Audio DAC
AD1868*
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700
Fax: 617/326-8703
FEATURES
Dual Serial Input, Voltage Output DACs
Single +5 V Supply
0.004% THD+N (typ)
Low Power: 50 mW (typ)
108 dB Channel Separation (min)
Operates at 8 Oversampling
16-Pin Plastic DIP or SOIC Package
APPLICATIONS
Portable Compact Disc Players
Portable DAT Players and Recorders
Automotive Compact Disc Players
Automotive DAT Players
Multimedia Workstations
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD1868 is a complete dual 18-bit DAC offering excellent
performance while requiring a single +5 V power supply. It is
fabricated on Analog Devices' ABCMOS wafer fabrication pro-
cess. The monolithic chip includes CMOS logic elements, bipo-
lar and MOS linear elements, and laser-trimmed thin-film
resistor elements. Careful design and layout techniques have re-
sulted in low distortion, low noise, high channel separation, and
low power dissipation.
The DACs on the AD1868 chip employ a partially segmented
architecture. The first three MSBs of each DAC are segmented
into seven elements. The 15 LSBs are produced using standard
R-2R techniques. The segments and R-2R resistors are laser
trimmed to provide extremely low total harmonic distortion.
The AD1868 requires no deglitcher or trimming circuitry. Low
noise is achieved through the use of two noise-reduction capacitors.
Each DAC is equipped with a high performance output ampli-
fier. These amplifiers achieve fast settling and high slew rate,
producing
�
1 V signals at load currents up to
�
1 mA. The
buffered output signal range is 1.5 V to 3.5 V. Reference volt-
ages of 2.5 V are provided, eliminating the need for "False
Ground" networks.
A versatile digital interface allows the AD1868 to be directly
connected to all digital filter chips. Fast CMOS logic elements
allow for an input clock rate of up to 13.5 MHz. This allows for
operation at 2
�
, 4
�
, 8
�
, or 16
�
the sampling frequency for each
channel. The digital input pins of the AD1868 are TTL and
+5 V CMOS compatible.
*Protected by U.S. Patent Numbers: 3,961,326; 4,141,004; 4,349,811;
4,857,862; and patents pending.
The AD1868 operates on +5 V power supplies. The digital sup-
ply, V
L
, can be separated from the analog supply, V
S
, for re-
duced digital feedthrough. Separate analog and digital ground
pins are also provided. In systems employing a single +5 volt
power supply, V
L
and V
S
should be connected together. In bat-
tery operated systems, operation will continue even with reduced
supply voltage. Typically, the AD1868 dissipates 50 mW.
The AD1868 is packaged in either a 16-pin plastic DIP or a 16-
pin plastic SOIC package. Operation is guaranteed over the tem-
perature range of �35
�
C to +85
�
C and over the voltage supply
range of 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Single-supply operation @ +5 V.
2. 50 mW power dissipation (typical).
3. THD+N is 0.004% (typical).
4. Signal-to-Noise Ratio is 97.5 dB (typical).
5. 108 dB channel separation (minimum).
6. Compatible with all digital filter chips.
7. 16-pin DIP and 16-pin SOIC packages.
8. No deglitcher required.
9. No external adjustments required.

REV. A
�2�
AD1868�SPECIFICATIONS
(typical at T
A
= +25 C and +5 V supplies unless otherwise noted)
Min
Typ
Max
Units
RESOLUTION
18
Bit
DIGITAL INPUTS
V
IH
2.4
V
V
IL
0.8
V
I
IH
, V
IH
= V
L
1.0
�
A
I
IL
, V
IL
= DGND
1.0
�
A
Maximum Clock Input Frequency
13.5
MHz
ACCURACY
Gain Error
�
1
% of FSR
Gain Matching
�
1
% of FSR
Midscale Error
�
15
mV
Midscale Error Matching
�
10
mV
Gain Linearity Error
�
3
dB
DRIFT (0
�
C to +70
�
C)
Gain Drift
�
100
ppm/
�
C
Midscale Drift
�
100
�
V/
�
C
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
0 dB, 990.5 Hz
AD1868N
0.004
0.008
%
AD1868N-J
0.004
0.006
%
�20 dB, 990.5 Hz
AD1868N
0.020
0.08
%
AD1868N-J
0.020
0.08
%
�60 dB, 990.5 Hz
AD1868N
2.0
5.0
%
AD1868N-J
2.0
5.0
%
CHANNEL SEPARATION 1 kHz, 0 dB
108
NIL*
dB
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (with A-Weight Filter)
95
97.5
dB
D-RANGE (with A-Weight Filter)
86
92
dB
OUTPUT
Voltage Output Pins (V
O
L, V
O
R)
Output Range (
�
3%)
�
1
V
Output Impedance
0.1
Load Current
�
1
mA
Bias Voltage Pins (V
B
L, V
B
R)
Output Voltage
+2.5
V
Output Impedance
350
POWER SUPPLY
Specification, V
L
and V
S
4.75
5
5.25
V
Operation, V
L
and V
S
3.5
5.25
V
+I, V
L
and V
S
= 5 V
10
14
mA
POWER DISSIPATION
50
70
mW
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specification
0
25
70
�
C
Operation
�35
85
�
C
Storage
�60
100
�
C
*Above 115 dB.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD1868 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
V
L
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 V to 6 V
V
S
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0 V to 6 V
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
�
0.3 V
Digital Inputs to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . �0.3 to V
L
Soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +300
�
C, 10 sec
*Stresses greater than those listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.

AD1868
REV. A
�3�
Typical Performance of the AD1868
�30
�40
�50
�60
�70
�80
�90
�100
0.5
2.5
4.5
6.5
8.5
10.5
12.5
14.5
FREQUENCY � kHz
THD +N � dB
�20dB
�60dB
0dB
16.5
18.5
20.5
Figure 1. THD+N vs. Frequency
�20
�30
�40
�50
�60
�70
�80
�90
4.4
4.6
4.8
5.0
5.2
5.4
VOLTAGE SUPPLY
THD +N � dB
�60dB
�20dB
0dB
Figure 3. THD+N vs. Supply Voltage
�60
�80
�100
140
THD +N � dB
�50
�30
�10
10
30
50
70
90
110
130
�20
�40
60dB
�
20dB
�
0dB
TEMPERATURE � �C
Figure 5. THD+N vs. Temperature
150
140
130
120
110
100
FREQUENCY � Hz
CHANNEL SEPARATION � dB
10
3
10
4
Figure 2. Channel Separation vs. Frequency
8
6
4
2
0
�2
�4
�6
0
INPUT AMPLITUDE � dB
GAIN LINEARITY ERROR � dB
�100
�80
�60
�40
�10
�20
0�C
25�C
70�C
Figure 4. Gain Linearity Error vs. Input Amplitude
90
80
70
60
50
40
SUPPLY MODULATION FREQUENCY � Hz
PSRR � dB
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
Figure 6. Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency

AD1868
REV. A
�4�
PIN CONFIGURATION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
11
16
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
AD1868
TOP VIEW
(Not To Scale)
V
S
V
S
V
O
R
V
O
L
V
B
L
DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONS
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
Total harmonic distortion plus noise (THD+N) is defined as
the ratio of the square root of the sum of the squares of the am-
plitudes of the harmonics and noise to the amplitude of the fun-
damental input frequency. It is usually expressed in percent (%)
or decibels (dB).
D-Range Distortion
D-range distortion is the ratio of the amplitude of the signal at
an amplitude of �60 dB to the amplitude of the distortion plus
noise. In this case, an A-weight filter is used. The value speci-
fied for D-range performance is the ratio measured plus 60 dB.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
The signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the amplitude
of the output when a full-scale output is present to the ampli-
tude of the output with no signal present. It is expressed in
decibels (dB) and measured using an A-weight filter.
Gain Linearity
Gain linearity is a measure of the deviation of the actual output
amplitude from the ideal output amplitude. It is determined by
measuring the amplitude of the output signal as the amplitude
of that output signal is digitally reduced to a lower level. A per-
fect D/A converter exhibits no difference between the ideal and
actual amplitudes. Gain linearity is expressed in decibels (dB).
Midscale Error
Midscale error is the difference between the analog output and
the bias when the twos complement input code representing
midscale is loaded in the input register. Midscale error is ex-
pressed in mV.
ORDERING GUIDE
THD + N
Package
Model
@ F
S
SNR
Option*
AD1868N
0.008%
95 dB
N-16
AD1868R
0.008%
95 dB
R-16
AD1868N-J
0.006%
95 dB
N-16
AD1868R-J
0.006%
95 dB
R-16
*N = Plastic DIP; R = SOIC.
PIN DESIGNATIONS
1
1
V
L
Digital Supply (+5 Volts)
1
2
LL
Left Channel Latch Enable
1
3
DL
Left Channel Data Input
1
4
CK
Clock Input
1
5
DR
Right Channel Data Input
1
6
LR
Right Channel Latch Enable
1
7
DGND
Digital Common
1
8
V
B
R
Right Channel Bias
1
9
V
S
Analog Supply (+5 Volts)
10
V
O
R
Right Channel Output
11
NRR
Right Channel Noise Reduction
12
AGND
Analog Common
13
NRL
Left Channel Noise Reduction
14
V
O
L
Left Channel Output
15
V
S
Analog Supply (+5 Volts)
16
V
B
L
Left Channel Bias
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The AD1868 is a complete, voltage output dual 18-bit digital
audio DAC which operates with a single +5 volt supply. As
shown in the block diagram, each channel contains a voltage
reference, an 18-bit DAC, an output amplifier, an 18-bit input
latch, and an 18-bit serial-to-parallel input register.
The voltage reference section provides a reference voltage and a
false ground voltage for each channel. The low noise bandgap
circuits produce reference voltages that are unaffected by
changes in temperature, time, and power supply.
The output amplifier uses both MOS and bipolar devices and
incorporates an NPN class-A output stage. It is designed to pro-
duce high slew rate, low noise, low distortion, and optimal fre-
quency response.
Each 18-bit DAC uses a combination of segmented decoder
and R-2R architecture to achieve good integral and differential
linearity. The resistors which form the ladder structure are fab-
ricated with silicon-chromium thin film. Laser trimming of
these resistors further reduces linearity error, resulting in low
output distortion.
The input registers are fabricated with CMOS logic gates.
These gates allow fast switching speeds and low power con-
sumption, contributing to the fast digital timing, low glitch, and
low power dissipation of the AD1868.

AD1868
REV. A
�5�
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
11
16
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
AD1868
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
S
V
O
L
V
O
R
V
S
18-BIT
DAC
�
+
�
+
V
REF
V
REF
Functional Block Diagram
ANALOG CIRCUIT CONSIDERATIONS
GROUNDING RECOMMENDATIONS
The AD1868 has two ground pins, designated as AGND (Pin
12) and DGND (Pin 7). The analog ground, AGND, serves as
the "high quality" reference ground for analog signals and as a
return path for the supply current from the analog portion of the
device. The system analog common should be located as close
as possible to Pin 12 to minimize any voltage drop which may
develop between these two points, although the internal circuit
is designed to minimize signal dependence of the analog return
current.
The digital ground, DGND, returns ground current from the
digital logic portion of the device. This pin should be connected
to the digital common node in the system. As shown in Figure
7, the analog and digital grounds should be joined at one point
in the system. When these two grounds are remotely connected
such as at the power supply ground, care should be taken to
minimize the voltage difference between the DGND and AGND
pins in order to ensure the specified performance.
POWER SUPPLIES AND DECOUPLING
The AD1868 has three power supply input pins. V
S
(Pins 9 and
15) provides the supply voltages which operate the analog por-
tion of the device including the 18-bit DACs, the voltage refer-
ences, and the output amplifiers. The V
S
supplies are designed
to operate with a +5 V supply. These pins should be decoupled
to analog common using a 0.1
�
F capacitor. Good engineering
practice suggests that the bypass capacitors be placed as close as
possible to the package pins. This minimizes the inherent induc-
tive effects of printed circuit board traces.
V
L
(Pin 1) operates the digital portions of the chip including the
input shift registers and the input latching circuitry. V
L
is also
designed to operate with a +5 V supply. This pin should be by-
passed to digital common using a 0.1
�
F capacitor, again placed
as close as possible to the package pin. Figure 7 illustrates the cor-
rect connection of the digital and analog supply bypass capacitors.
An important feature of the AD1868 audio DAC is its ability to
operate at reduced power supply voltages. This feature is very
important in portable battery operated systems. As the batteries
discharge, the supply voltage drops. Unlike any other audio
DAC, the AD1868 can continue to function at supply voltages
as low as 3.5 V. Because of its unique design, the power require-
ments of the AD1868 diminish as the battery voltage drops, fur-
ther extending the operating time of the system.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
S
V
O
L
V
O
R
AD1868
POWER
SUPPLY
0.1�F
0.1�F
4.7�F
4.7�F
V
S
Figure 7. Recommended Circuit Schematic
NOISE REDUCTION CAPACITORS
The AD1868 has two noise reduction pins designated as NRL
(Pin 13) and NRR (Pin 11). It is recommended that external
noise reduction capacitors be connected from these pins to
AGND to reduce the output noise contributed by the voltage
reference circuitry. As shown in Figure 7, each of these pins
should be bypassed to AGND with a 4.7
�
F or larger capacitor.
The connections between the capacitors, package pins and
AGND should be as short as possible to achieve the lowest
noise.
USING V
B
L AND V
B
R
The AD1868 has two bias voltage reference pins, designated as
V
B
R (Pin 8) and V
B
L (Pin 16). These pins supply a dc reference
voltage equal to the center of the output voltage swing. These
bias voltages replace "False Ground" networks previously required
in single-supply audio systems. At the same time, they allow dc-
coupled systems, improving audio performance.
Figure 8a illustrates the traditional approach used to generate
False Ground voltages in single-supply audio systems. This cir-
cuit requires additional power and circuit board space.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
16-BIT
LATCH
16-BIT
DAC
SERIAL
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
AD1851
I
OUT
�V
S
DGND
NC
CLK
LE
DATA
+V
L
NC = NO CONNECT
+V
S
TRIM
MSB
ADJ
I
OUT
AGND
SJ
R
F
V
OUT
NC
Figure 8a. Schematic Using False Ground

AD1868
REV. A
�6�
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
S
AD1868
+ 5V
V
O
L
+5V
10
V
B
L
V
O
R
V
O
L
V
O
R
V
S
V
B
R
Figure 8b. Circuitry Using Voltage Biases
The AD1868 eliminates the need for "False Ground" circuitry.
V
B
R and V
B
L generate the required bias voltages previously
generated by the "False Ground." As shown in Figure 8b, V
B
R
and V
B
L may be used as the reference point in each output
channel. This permits a dc-coupled output signal path. This
eliminates ac-coupling capacitors and improves low frequency
performance. It should be noted that these bias outputs have
relatively high output impedance and will not drive output
currents larger than 100
�
A without degrading the specified
performance.
DISTORTION PERFORMANCE AND TESTING
The THD+N figure of an audio DAC represents the amount of
undesirable signal produced during reconstruction and playback
of an audio waveform. Therefore, the THD+N specification
provides a direct method to classify and choose an audio DAC
for a desired level of performance.
Figure 1 illustrates the typical THD+N versus frequency perfor-
mance of the AD1868. It is evident that the THD+N perfor-
mance of the AD1868 remains stable at all three levels through
a wide range of frequencies. A load impedance of at least 2 k
is
recommended for best THD+N performance.
Analog Devices tests and grades all AD1868s on the basis of
THD+N performance. During the distortion test, a high speed
digital pattern generator transmits digital data to each channel
of the device under test. Eighteen-bit data is latched into the
DAC at 352.8 kHz (8
�
F
S
). The test waveform is a 990.5 Hz
sine wave with 0 dB, �20 dB, and �60 dB amplitudes. A 4096-
point FFT calculates total harmonic distortion + noise,
signal-to-noise ratio, and D-range. No deglitchers or external
adjustments are used.
DIGITAL CIRCUIT CONSIDERATIONS
INPUT DATA
The AD1868 digital input port employs five signals: Data Left
(DL), Data Right (DR), Latch Left (LL), Latch Right (LR) and
Clock (CLK). DL and DR are the serial inputs for the left and
right DACs, respectively. Input data bits are clocked into the in-
put register on the rising edge of CLK. The falling edges of LL
and LR cause the last 18 bits which were clocked into the serial
registers to be shifted into the DACs, thereby updating the re-
spective DAC outputs. For systems using only a single latch sig-
nal, LL and LR may be connected together. For systems using
only one DATA signal, DR and DL may be connected together.
Data is transmitted to the AD1868 in a bit stream composed of
18-bit words with a serial, twos complement, MSB first format.
Left and right channels share the Clock (CLK) signal.
Figure 9 illustrates the general signal requirements for data
transfer for the AD1868.
CLK
DL
DR
LL
LR
MSB
MSB
LSB
LSB
Figure 9. Control Signals

AD1868
REV. A
�7�
TIMING
Figure 10 illustrates the specific timing requirements that must
be met in order for the data transfer to be accomplished prop-
erly. The input pins of the AD1868 are TTL and 5 V CMOS
compatible.
The maximum clock rate of the AD1868 is specified to be at
least 13.5 MHz. This clock rate allows data transfer rates of 2
�
,
4
�
, 8
�
, and 16
�
F
S
(where F
S
equals 44.1 kHz). The applica-
tions section of this data sheet contains additional guidelines for
using the AD1868.
LSB
(18th BIT)
>15ns
CLK
> 74./ ns
>10ns
>30ns
>30ns
DATA
LATCH
ENABLE (LE)
>60ns
>40ns
>40ns
>30ns
BITS CLOCKED
TO SHIFT REGISTER
2nd BIT
MSB
1st BIT
NEXT
WORD
>10ns
INTERNAL DAC INPUT REGISTER
UPDATED WITH 18 MOST RECENT BITS
Figure 10. Input Signal Timing
APPLICATIONS OF THE AD1868
The AD1868 is a high performance audio DAC specifically de-
signed for portable and automotive digital audio applications.
These market segments have technical requirements fundamen-
tally different than those found in the high-end or home-use
market segments. Portable equipment must rely on components
which require low amounts of power to offer reasonable playing
times. Also, battery voltages drop as the end of the discharge
cycle is approached. The AD1868's ability to operate from a
single +5 V supply makes it a good choice for battery-operated
gear. As the battery voltage drops, the power dissipation of the
AD1868 drops. This extends the usable battery life. Finally, as
the battery supply voltage drops, the bias voltages and signal
swings also drop, preventing signal clipping and abrupt degra-
dation of distortion. Figure 3 illustrates that THD+N perfor-
mance of the AD1868 remains constant through a wide range
of supply voltages.
Automotive equipment rely on components which are able to
consistently perform in a wide range of temperatures. In addi-
tion, due to the limited space available in automotive applica-
tions, small size is essential. The AD1868 is able to satisfy both
of these requirements. The device has guaranteed specified per-
formance between 0
�
C and +70
�
C, and the 16-pin DIP or 16-
pin SOIC package is particularly attractive where overall size is
important.
Since the AD1868 provides dc bias voltages, the entire signal
chain can be dc-coupled. This eliminate ac-coupling capacitors
from the signal path, improving low frequency performance and
lowering system cost and size.
In summary, the AD1868 is an excellent choice for battery op-
erated portable or automotive digital audio systems. In the fol-
lowing sections, some examples of high performance audio
applications featuring the AD1868 are described.
AD1868 with Sony CXD2550P Digital Filter
Figure 11 illustrates an 18-bit CD player design incorporating
an AD1868 DAC, a Sony CXD2550P digital filter and 2-pole
antialias filters. This high performance, single supply design op-
erates at 8
�
F
S
and is suitable for portable and automotive ap-
plications. In this design, the CXD2550P filter transmits left
and right channel digital data to the AD1868. The left and
right latch signals, LL and LR, are both provided by the word
clock signal (LRCKO) of the digital filter. The digital data is
converted to low distortion output voltages by the output
amplifiers on the AD1868. Also, no deglitching circuitry or
external adjustments are required. Bypass capacitors, noise
reduction capacitors and the antialias filter details are omitted
for clarity.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
AD1868
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
11
12
13
14
15
16
18
17
TEST
SLOT
LRCK0
CXD2550P
9
10
V
DD
BCKO
DATAR
DATAL
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
7
AGND
V
S
LEFT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
RIGHT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
+5V POWER
SUPPLY
8Fs/4Fs
INIT
V
SS
V
S
V
O
R
V
O
L
V
B
L
V
S
Figure 11. AD1868 with Sony CXD2550P Digital Filter

AD1868
REV. A
�8�
ADDITIONAL APPLICATIONS
In addition to CD player designs, the AD1868 is suitable for
similar applications such as DAT, portable musical instru-
ments, Laptop and Notebook personal computers, and PC au-
dio I/O boards. The circuit techniques illustrated are directly
applicable in those applications.
Figures 12, 13, and 14 show connection diagrams for the
AD1868 with popular digital filter chips from NPC and
Yamaha. Each application operates at 8
�
F
S
operation. Please
refer to the appropriate sections of this data sheet for additional
information.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
O
L
V
O
R
V
S
AD1868
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
21
22
23
24
25
26
28
27
BCKO
9
20
V
SS
1
DOR
DOL
WCKO
LEFT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
RIGHT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
+5V POWER
SUPPLY
10
19
11
18
12
17
13
16
14
15
V
DD
OW18
OW20
LOW
PASS
FILTER
LOW
PASS
FILTER
COB
V
L
V
SS
2
V
S
SM5813
Figure 12. AD1868 with NPC SM5813 Digital Filter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
S
V
O
L
V
O
R
AD1868
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
BCKO
SM5818AP
V
SS
DOR
DOL
WDCO
LEFT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
RIGHT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
+5V POWER
SUPPLY
LOW
PASS
FILTER
LOW
PASS
FILTER
V
DD
V
S
Figure 13. AD1868 with NPC SM5818AP Digital Filter

AD1868
REV. A
�9�
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
V
S
AD1868
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
YM3434
V
SS
DRO
DLO
LEFT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
RIGHT
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
+5V POWER
SUPPLY
LOW
PASS
FILTER
LOW
PASS
FILTER
V
DD
2
ST
BCO
WCO
16/18
V
B
R
V
B
L
V
DD
1
V
S
V
O
L
V
O
R
Figure 14. AD1868 with Yamaha YM3434 Digital Filter
OTHER DIGITAL AUDIO COMPONENTS AVAILABLE FROM ANALOG DEVICES
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
16-BIT
LATCH
16-BIT
DAC
SERIAL
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
AD1856
DGND
NC
CLK
LE
DATA
NC = NO CONNECT
TRIM
MSB
ADJ
AGND
SJ
�V
S
+V
L
�V
L
+V
S
I
OUT
V
OUT
R
F
I
OUT
AD1856 16-Bit Audio DAC
Complete, No External Components Required
16-Pin DIP or SOIC Package
Standard Pinout
Low Cost
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
18-BIT
LATCH
18-BIT
DAC
SERIAL
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
AD1860
DGND
NC
CLK
LE
DATA
NC = NO CONNECT
TRIM
MSB
ADJ
AGND
SJ
�V
S
+V
L
�V
L
+V
S
I
OUT
V
OUT
R
F
I
OUT
AD1860 18-Bit Audio DAC
Complete, No External Components Required
102 dB SNR Minimum
16-Pin DIP or SOIC Package
Standard Pinout

AD1868
REV. A
�10�
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
16-BIT
LATCH
16-BIT
DAC
SERIAL
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
AD1851
I
OUT
�V
S
DGND
NC
CLK
LE
DATA
+V
L
NC = NO CONNECT
+V
S
TRIM
MSB
ADJ
I
OUT
AGND
SJ
R
F
V
OUT
NC
AD1851 16-Bit PCM Audio DAC
107 dB SNR Minimum
16
�
F
S
Capability
�
5 V Supply
REFERENCE
AD1864
�V
S
AGND
R
F
TRIM
MSB
I
OUT
DGND
+V
S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
TRIM
SJ
V
OUT
�V
L
DL
LL
MSB
I
OUT
AGND
R
F
SJ
V
OUT
+V
L
DR
LR
CK
REFERENCE
18-BIT
LATCH
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
LATCH
�
+
�
+
AD1864 Dual 18-Bit Audio DAC
Complete, No External Components
High Performance
Low Crosstalk
24-Pin DIP
THD+N = 0.004% (typical)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
18-BIT
LATCH
18-BIT
DAC
SERIAL
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
AD1861
DGND
NC
CLK
LE
DATA
NC = NO CONNECT
TRIM
MSB
ADJ
AGND
SJ
�V
S
+V
L
+V
S
I
OUT
V
OUT
R
F
I
OUT
NC
AD1861 18-Bit PCM Audio DAC
107 dB SNR Minimum
16
�
F
S
Capability
�
5 V Supply
REFERENCE
AD1865
�V
S
AGND
R
F
TRIM
MSB
I
OUT
DGND
+V
S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
TRIM
SJ
V
OUT
NC
DL
LL
MSB
I
OUT
AGND
R
F
SJ
V
OUT
+V
L
DR
LR
CK
REFERENCE
18-BIT
LATCH
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
LATCH
�
+
�
+
NC = NO CONNECT
AD1865 Dual 18-Bit Audio DAC
107 dB SNR Minimum
16
�
F
S
Capability
THD+N = 0.004% (typical)
�
5 V Supply

AD1868
REV. A
�11�
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
INPUT
&
DIGITAL
OFFSET
AD1862
�V
S
CLK
LE
DATA
AGND
R
F
TRIM
NR
2
ADJ
NR
1
I
OUT
DGND
20-BIT
DAC
�V
S
+V
L
�V
L
+V
S
AD1862 20-Bit, Low Noise Audio DAC
110 dB SNR Minimum
THD+N = 0.0019% (typical)
�
1 dB Gain Linearity
16-Pin Plastic DIP
AD1868
REV. A
�12�
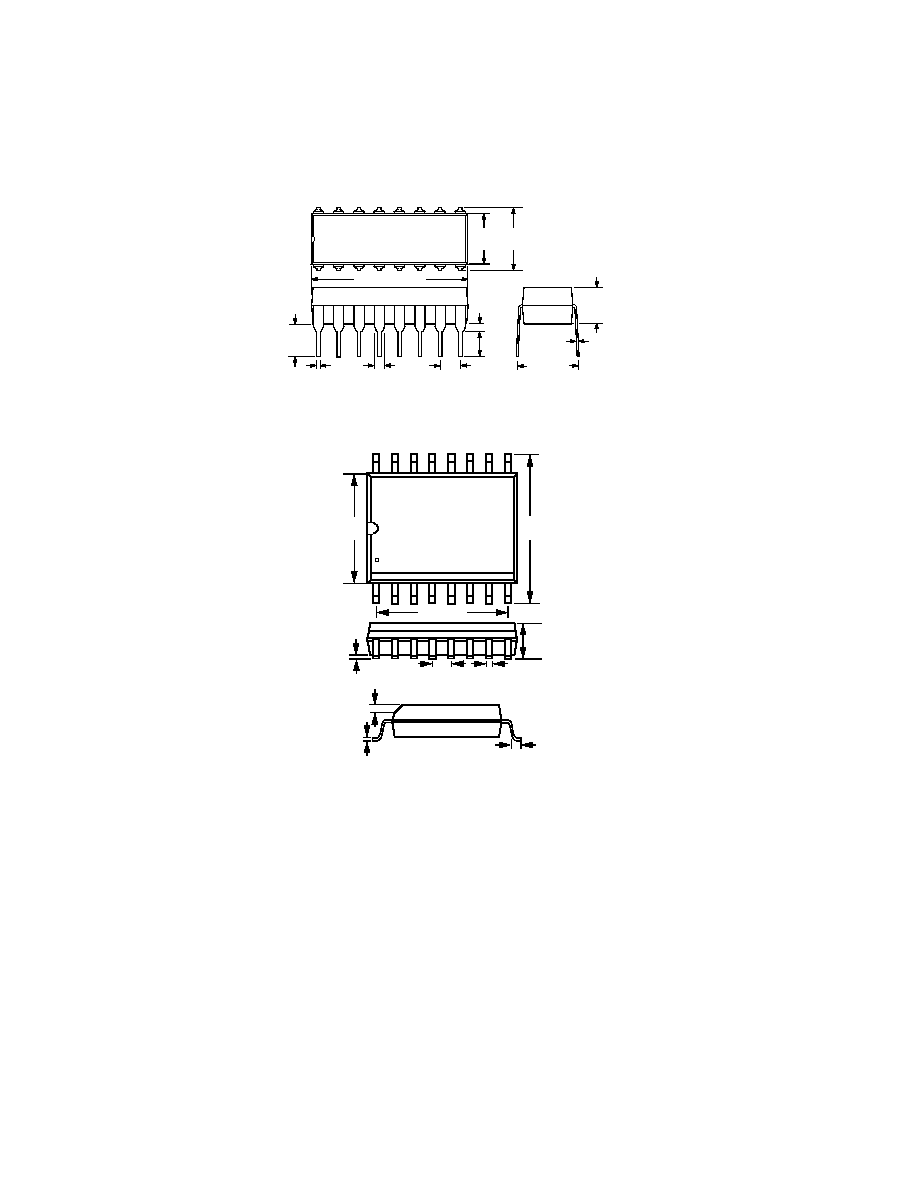
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
C1478�7�10/90
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
Plastic DIP (N) Package
0.125
(3.18)
MIN
0.035
(0.89)
0.18
(4.57)
0.3 (7.62)
0.87 (22.1) MAX
0.25
(6.35)
0.31
(7.87)
0.18
(4.57)
MAX
0.011
(0.28)
1
8
9
16
0.018 (0.46)
0.033 (0.84)
0.1 (2.54)
Plastic SOIC (R) Package
0.042 (1.07)
0.013 (0.32)
0.019 (0.49)
0.050
(1.27)
REF
0.104
(2.65)
0.012
(0.3)
1
8
9
16
0.413 (10.50)
0.419
(10.65)
0.299
(7.60)
0.030
(0.75)











