
a
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700
www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703
© Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
OP400
Quad Low-Offset, Low-Power
Operational Amplifier
REV. A
FEATURES
Low Input Offset Voltage 150 V Max
Low Offset Voltage Drift, Over ≠55 C to +125 C
1.2 pV/ C Max
Low Supply Current (Per Amplifier) 725 A Max
High Open-Loop Gain 5000 V/mV Min
Input Bias Current 3 nA Max
Low Noise Voltage Density 11 nV/
˜Hz at 1 kHz
Stable With Large Capacitive Loads 10 nF Typ
Pin Compatible to LM148, HA4741, RM4156, and LT1014
with Improved Performance
Available in Die Form
PIN CONNECTIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OP400 is the first monolithic quad operational amplifier
that features OP77 type performance. Precision performance no
longer has to be sacrificed to obtain the space and cost savings
offered by quad amplifiers.
The OP400 features an extremely low input offset voltage of
less than 150
mV with a drift of under 1.2 mV/C, guaranteed
over the full military temperature range. Open-loop gain of the
OP400 is over 5,000,000 into a 10 k
W load, input bias current is
under 3 nA, CMR is above 120 dB, and PSRR is below 1.8
mV/V.
On-chip zener-zap trimming is used to achieve the low input
offset voltage of the OP400 and eliminates the need for offset
nulling. The OP400 conforms to the industry-standard quad
pinout which does not have null terminals.
The OP400 features low power consumption, drawing less than
725
mA per amplifier. The total current drawn by this quad
amplifier is less than that of a single OP07, yet the OP400 offers
significant improvements over this industry standard op amp.
Voltage noise density of the OP400 is a low 11 nV/
˜
Hz at 10 Hz,
which is half that of most competitive devices.
The OP400 is pin-compatible with the LM148, HA4741,
RM4156, and LT1014 operational amplifiers and can be used
to upgrade systems using these devices. The OP400 is an ideal
choice for applications requiring multiple precision operational
amplifiers and where low power consumption is critical.
14-PIN HERMETIC DIP
(Y-Suffix)
14-PIN PLASTIC DIP
(P-Suffix)
16-PIN SOL
(S-Suffix)
Figure 1. Simplified Schematic (One of Four Amplifiers is Shown)

≠2≠
OP400≠SPECIFICATIONS
REV. A
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
OP400A/E
OP400F
OP400G/H
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Input Offset
Voltage
V
OS
40
150
60
230
80
300
mV
Long-Term Input
Voltage Stability
0.1
0.1
0.1
mV/mo
Input Offset
Current
I
OS
VCM =
V
0.1
1.0
0.1
2.0
0.1
3.5
nA
Input Bias
Current
I
B
VCM =
V
0.75
3.0
0.75
6.0
0.75
7.0
nA
Input Noise
Voltage
e
n p-p
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
0.5
0.5
0 5
mV p-p
Input Noise
Voltage Density
1
e
n
f
O
= 10 Hz
1
22
36
22
36
22
f
O
= 1000 Hz
1
11
18
11
18
11
nV/
˜Hz
Input Noise
Current
i
n p-p
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
15
15
15
pAp-p
Input Noise
Current Density
i
n
f
O
= 10 Hz
0.6
0.6
0.6
pA/
˜Hz
Input Resistance
Differential Mode R
IN
10
10
10
M
W
Input Resistance
Common Mode
R
INCM
200
200
200
G
W
Large Signal
Voltage Gain
A
VO
V
O
=
±10 V
R
L
= 10 k
W
5000
12000
3000
7000
3000
7000
R
L
= 2 k
W
2000
3500
1500
3000
1500
3000
V/mV
Input Voltage
Range
3
IVR
±12 ±13
±12 ±13
±12 ±13
V
Common Mode
Rejection
CMR
VCM = 12 V
120
140
115
140
110
135
dB
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
PSRR
V
S
= 3 V
to 18 V
0.1
1.8
0.1
3.2
0.2
5 6
mV/V
Output Voltage
Swing
V
O
R
L
= 10 k
W
±12 ±12.6
±12 ±12.6
±12 ±12.6
V
R
L
= 2 k
W
±11 ±12.2
±11 ±12.2
±11 ±12.2
Supply Current
Per Amplifier
I
SY
No Load
600
725
600
725
600
725
mA
Slew Rate
SR
0.1
0.15
0.1
0.15
0.1
0.15
V/
ms
Gain Bandwidth
Product
GBWP
A
V
= 1
500
500
500
kHz
Channel
Separation
CS
V
O
= 20 V p-p
123
135
123
135
123
135
dB
f
O
= 10 Hz
2
Input
Capacitance
C
IN
3.2
3.2
3.2
pF
Capacitive Load
Stability
A
V
= 1
No Oscillations
10
10
10
nF
NOTES
1
Sample tested
2
Guaranteed but not 100% tested.
3
Guaranteed by CMR test
(@ V
S
= 15 V, T
A
= 25 C, unless otherwise noted.)

OP400
≠3≠
REV. A
SPECIFICATIONS
(continued)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ V
S
= 15 V, ≠55 C < T
A
= 125 C for OP400A, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Input Offset Voltage
VoS
70
270
mV
Average Input Offset Voltage Drift
TCV
OS
0.3
12
mV/C
Input Offset Current
I
OS
V
CM
= 0 V
01
2.5
nA
Input Bias Current
I
B
V
CM
= 0 V
1.3
5.0
nA
Large Signal Voltage Gain
A
VO
V
O
=
±10 V R
L
= 10 k
W 3000
9000
V/mV
R
L
= 2 k
W
1000
2300
Input Voltage Range
*
IVR
±12
±12.5
V
Common Mode Rejection
CMR
V
CM
=
±12 V
115
130
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSRR
V
O
= 3 V to 18 V
0.2
3.2
mV/V
Output Voltage Swing
VO
R
L
= 10 k
W
±12
±12.4
R
L
= 2 k
W
±11
±12
V
Supply Current Per Amplifier
I
SY
No Load
600
775
mA
Capacitive Load Stability
A
V
= 1
8
nF
No Oscillations
NOTE
*
Guaranteed by CMR test
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
OP400A/E
OP400F
OP400G/H
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Input Offset
Voltage
V
OS
60
220
80
350
110
400
mV
Average Input Offset
Voltage Drift
TCV
OS
0 3
1.2
0.3
2.0
0.6
2.5
mV/C
Input Offset
Current
I
OS
V
CM
= 0 V
E, F, G Grades
0.1
2.5
0.1
3.5
0.2
6.0
H Grade
0.2
12.0
nA
Input Bias
Current
I
B
V
CM
= 0 V
E, F, G Grades
0.1
2.5
0.1
3.5
1.0
12.0
H Grade
1.0
20.0
nA
Large-Signal
Voltage Gain
A
VO
V
CM
= 0 V
R
L
= 10 k
W
3000
10000
2000
5000
2000
5000
R
L
= 2 k
W
1500
2700
1000
2000
1000
2000
V/mv
Input Voltage
Range
IVR
*
±12 ±12.5
±12 ±12.5
±12 ±12.5
V
Common-Mode
Rejection
CMR
V
CM
=
±12 V
115
135
110
135
105
130
dB
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
PSRR
V
S
=
±3 V
to
±18 V
0.15
3.2
0.15
5.6
0.3
10.0
mV/V
Output Voltage
Swing
V
O
R
L
= 10 k
W
±12 ±12.4
±12 ±12.4
±12 ±12.6
V
R
L
= 2 k
W
±11 ±12
±11 ±12
±11 ±12.2
Supply Current
Per Amplifier
I
SY
No Load
600
775
600
775
600
775
mA
Capacitive Load
10
10
10
nF
Stability
No Oscillations
NOTE
*
Guaranteed by CMR test.
(@ V
S
= 15 V, ≠25 C < TA S 85 C for OP400E/F, 0 C S T
A
< 70 C for OP400G,
≠40 C < T
A
< +85 C for OP400H, unless otherwise noted.)
≠4≠
OP400
REV. A
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
OP400 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
DIE SIZE 0.181 0.123 inch, 22,263 sq. milts
(4.60 3.12 mm, 14.35 sq. mm)
ORDERING INFORMATION
T
A
= 25 C
Package
Operating
V
OS
Max
CerDIP
Temperature
(mV)
14-Lead
Plastic
Range
150
OP400AY
MIL
150
OP400EY
IND
230
OP400FY
IND
300
OP400GP
COM
300
OP400GS
COM
300
OP400HP
XIND
300
OP400HS
XIND
NOTES
1
For devices processed in total compliance to MIL-STD-883, add/883after part
number. Consult factory for 883 data sheet.
2
Burn-in is available on commercial and industrial temperature range parts in
CerDIP, plastic DIP, and TO-can packages.
For Military processed devices, please refer to the standard
microcircuit drawing (SMD) available at
www.dscc.dla.mil/programs/milspec/default.asp
SMD Part Number
ADI Equivalent
5962-8777101M3A
OP400ATCMDA
5962-8777101MCA
OP400AYMDA
OP400GBC
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Limit
Unit
Input Offset Voltage
V
OS
230
mA Max
Input Offset Current
V
OS
V
CM
= 0 V
2
nA Max
Input Bias Current
I
B
V
CM
= 0 V
6
nA Max
Large Signal
A
VO
V
O
=
±10 V R
L
= 10 k
W
3000
Voltage Gain
Rig 2 k
W
1500
V/mV Min
Input Voltage Range
*
IVR
*
±12
V Min
Common Mode Rejection
CMR
V
CM
=
±12 V
115
dB Min
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSRR
V
S
=
±3 V to ±18 V
3.2
mV/V Max
Output Voltage Swing
V
O
R
L
= 10 k
W
R
L
= 2 k
W
±12
V Min
Supply Current Per Amplifier
I
SY
No Load
725
mA Max
NOTE
*
Guaranteed by CMR test.
Electrical tests are performed at wafer probe to the limits shown Due to variations in assembly methods and normal yield loss, yield after packaging is not guaranteed
for standard product dice. Consult factory to negotiate specifications based on dice lot qualification through sample lot assembly and testing.
1. OUT A
8. OUT C
2. ≠IN A
9. ≠IN C
3. +INA
10. +IN C
4. V+
11. V-
5. +IN B
12. +IND
6. ≠IN B
13. ≠IN D
7. OUT B
14. OUT D
DICE CHARACTERISTICS
WAFER TEST LIMITS
(@ V
S
= 15 V, T
A
= 25 C, unless otherwise noted.)

Typical Performance Characteristics≠OP400
≠5≠
REV. A
TPC 1. Warm-Up Drift
TPC 4. Input Offset Current
vs. Temperature
TPC 7. Noise Voltage Density
vs. Frequency
TPC 2. Input Offset Voltage
vs. Temperature
TPC 5. Input Bias Current vs.
Common-Mode Voltage
TPC 8. Current Noise Density
vs. Frequency
TPC 3. Input Bias Current
vs. Temperature
TPC 6. Common-Mode Rejection
vs. Frequency
TPC 9. 0.1 Hz to10 Hz Noise

≠6≠
OP400
REV. A
TPC 10. Total Supply Current
vs. Supply Voltage
TPC 13. Power Supply
Rejection vs. Temperature
TPC 16. Closed-Loop Gain
vs. Frequency
TPC 11. Total Supply Current
vs. Temperature
TPC 14. Open-Loop Gain vs.
Temperature
TPC 17. Maximum Output
Swing Frequency
TPC 12. Power Supply Rejection
vs. Frequency
TPC 15. Open-Loop Gain and
Phase Shift vs. Frequency
TPC 18. Total Harmonic
Distortion vs. Frequency

OP400
≠7≠
REV. A
TPC 19. Overshoot vs.
Capacitive Load
TPC 22. Large-Signal
Transient Response
TPC 20. Short Circuit vs. Time
TPC 23. Small-Signal
Transient Response
TPC 21. Channel Separation
vs. Frequency
TPC 24. Small-Signal Transient
Response C
LOAD
= 1nF
Figure 2. Noise Test Schematic

≠8≠
OP400
REV. A
Figure 3. Burn-In Circuit
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The OP400 is inherently stable at all gains and is capable of
driving large capacitive loads without oscillating. Nonetheless,
good supply decoupling is highly recommended. Proper supply
decoupling reduces problems caused by supply line noise and
improves the capacitive load driving capability of the OP400.
Total supply current can be reduced by connecting the inputs of
an unused amplifier to ≠V. This turns the amplifier off, lowering
the total supply current.
APPLICATIONS
Dual Low-Power Instrumentation Amplifier
A dual instrumentation amplifier that consumes less than 33 mW
of power per channel is shown in Figure 1. The linearity of the
instrumentation amplifier exceeds 16 bits in gains of 5 to 200
and is better than 14 bits in gains from 200 to 1000. CMRR is
above 115 dB (G = 1000). Offset voltage drift is typically 0.4
mV/C over the military temperature range which is comparable
to the best monolithic instrumentation amplifiers. The band-
width of the low-power instrumentation amplifier is a function
of gain and is shown in Table I.
Table I. Gain Bandwidth
Gain
Bandwidth
5
150 kHz
10
67 kHz
100
7.5 kHz
1000
500 Hz
The output signal is specified with respect to the reference
input, which is normally connected to analog ground. The refer-
ence input can be used to offset the output from ≠10 V to +10 V
if required.
Figure 4. Dual Low-Power Instrumentation Amplifier

OP400
≠9≠
REV. A
BIPOLAR CURRENT TRANSMITTER
In the circuit of Figure 5, which is an extension of the standard
three op amp instrumentation amplifier, the output current is
proportional to the differential input voltage. Maximum output
current is
±5 mA with voltage compliance equal to ±10 V when
using
±15 V supplies. Output impedance of the current transmit-
ter exceeds 3 M
W and linearity is better than 16 bits with gain
set for a full scale input of
±100 mV.
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT INSTRUMENTATION
AMPLIFIER
The output voltage swing of a single-ended instrumentation
amplifier is limited by the supplies, normally at
±15 V, to a
maximum of 24 V p-p. The differential output instrumentation
amplifier of Figure 6 can provide an output voltage swing of
48 V p-p when operated with
±15 V supplies. The extended
output swing is due to the opposite polarity of the outputs. Both
outputs will swing 24 V p-p but with opposite polarity, for a
total output voltage swing of 48 V p-p. The reference input can
be used to set a common-mode output voltage over the range
±10 V. PSRR of the amplifier is less than 1 mV/V with CMRR
(G = 1000) better than 115 dB. Offset voltage drift is typically
0.4
mV/C over the military temperature range.
Figure 6. Differential Output Instrumentation Amplifier
Figure 5. Bipolar Current Transmitter
≠10≠
OP400
REV. A
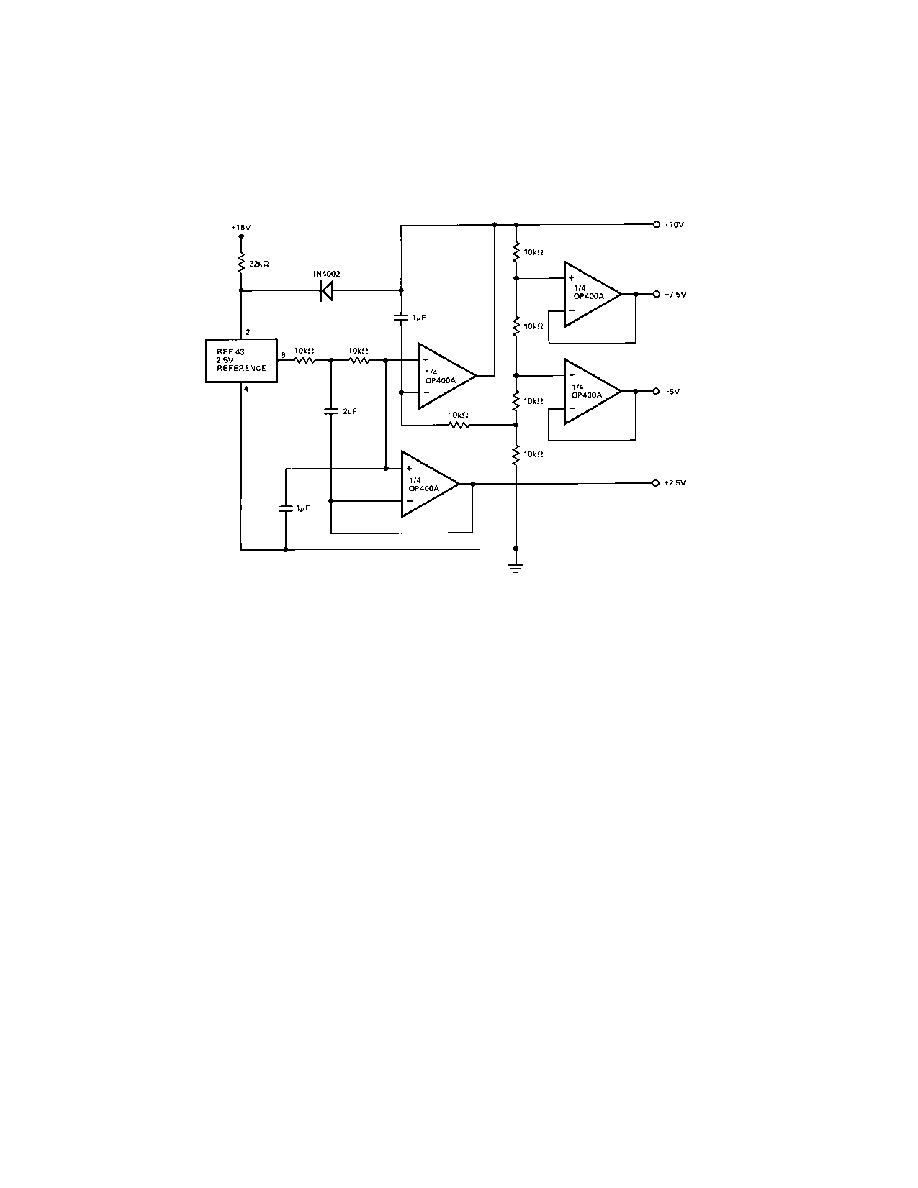
MULTIPLE OUTPUT TRACKING VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
Figure 7 shows a circuit that provides outputs of 10 V, 7.5 V, 5 V,
and 2.5 V for use as a system voltage reference. Maximum
output current from each reference is 5 mA with load regulation
under 25
mV/mA. Line regulation is better than 15 mV/V and
output voltage drift is under 20
mV/C. Output voltage noise
from 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz is typically 75
mV p-p from the 10 V output
and proportionately less from the 7.5 V, 5 V, and 2.5 V outputs.
Figure 7. Multiple-Output Tracking Voltage Reference

OP400
≠11≠
REV. A
Revision History
Location
Page
Data Sheet changed from REV. 0 to REV. A.
Edits to FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Edits to ORDERING INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Edits to PIN CONNECTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Edits to GENERAL DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1, 2
Edits to PACKAGE TYPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
14-Lead Hermetic DIP Package
(Y-Suffix)
14
1
7
8
0.310 (7.87)
0.220 (5.59)
PIN 1
0.005 (0.13) MIN 0.098 (2.49) MAX
0.100 (2.54)
BSC
15
0
0.320 (8.13)
0.290 (7.37)
0.015 (0.38)
0.008 (0.20)
SEATING
PLANE
0.200
(5.08)
MAX
0.785 (19.94) MAX
0.150
(3.81)
MIN
0.200 (5.08)
0.125 (3.18)
0.023 (0.58)
0.014 (0.36)
0.070 (1.78)
0.030 (0.76)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
14-Lead Plastic DIP Package
(P-Suffix)
14
1
7
8
PIN 1
0.795 (20.19)
0.725 (18.42)
0.280 (7.11)
0.240 (6.10)
0.100 (2.54)
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.210 (5.33)
MAX
0.022 (0.558)
0.014 (0.356)
0.160 (4.06)
0.115 (2.93)
0.070 (1.77)
0.045 (1.15)
0.130
(3.30)
MIN
0.195 (4.95)
0.115 (2.93)
0.015 (0.381)
0.008 (0.204)
0.325 (8.25)
0.300 (7.62)
16-Lead SOL Package
(S-Suffix)
SEATING
PLANE
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0040 (0.10)
0.0192 (0.49)
0.0138 (0.35)
0.1043 (2.65)
0.0926 (2.35)
0.050 (1.27)
BSC
16
9
8
1
0.4193 (10.65)
0.3937 (10.00)
0.2992 (7.60)
0.2914 (7.40)
PIN 1
0.4133 (10.50)
0.3977 (10.00)
0.0125 (0.32)
0.0091 (0.23)
8
0
0.0291 (0.74)
0.0098 (0.25)
45
0.0500 (1.27)
0.0157 (0.40)

C00304≠0≠4/02(A)
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
≠12≠











