1
S2204
QUAD GIGABIT ETHERNET DEVICE
July 16, 1999 / Revision C
S2204
Æ
QUAD GIGABIT ETHERNET DEVICE
DEVICE
SPECIFICATION
MAC
(ASIC)
S2004
QUAD
GIGABIT
ETHERNET
INTERFACE
MAC
(ASIC)
MAC
(ASIC)
MAC
(ASIC)
TO SERIAL BACKPLANE
S2204
GE INTERFACE
SERIAL BP DRIVER
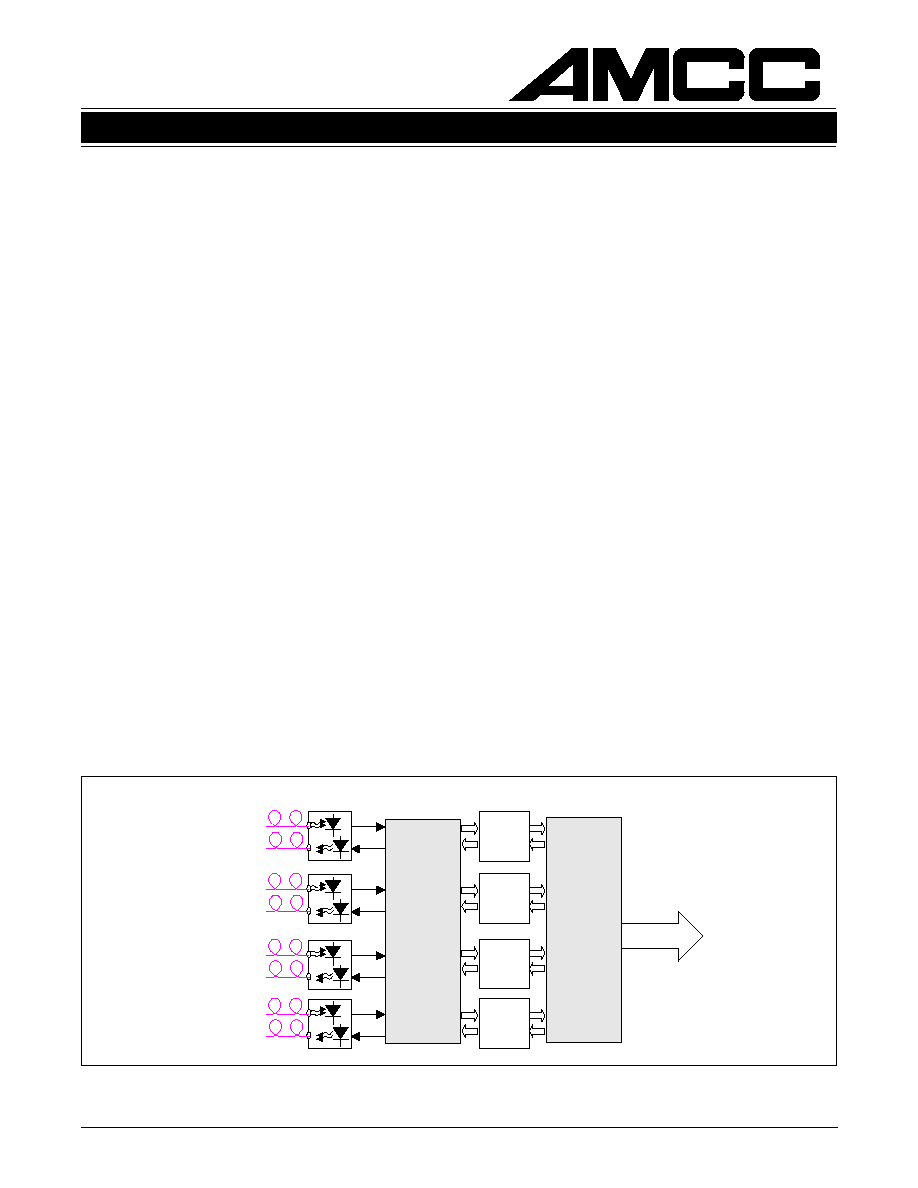
Figure 1. Typical Quad Gigabit Ethernet Application
FEATURES
∑ 1250 MHz (Gigabit Ethernet) operating rate
- 1/2 Rate Operation
∑ Quad Transmitter with phase-locked loop (PLL)
clock synthesis from low speed reference
∑ Quad Receiver PLL provides clock and data
recovery
∑ Internally series terminated TTL outputs
∑ Low-jitter serial PECL interface
∑ Individual local loopback control
∑ JTAG 1149.1 Boundary scan on low speed I/O
signals
∑ Interfaces with coax, twinax, or fiber optics
∑ Single +3.3V supply, 2.5 W power dissipation
∑ Compact 23mm x 23mm 208 TBGA package
APPLICATIONS
∑ Ethernet Backbones
∑ Workstation
∑ Frame buffer
∑ Switched networks
∑ Data broadcast environments
∑ Proprietary extended backplanes
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The S2204 facilitates high-speed serial transmission
of data in a variety of applications including Gigabit
Ethernet, serial backplanes, and proprietary point to
point links. The chip provides four separate trans-
ceivers which can be operated individually for a data
capacity of >4 Gbps.
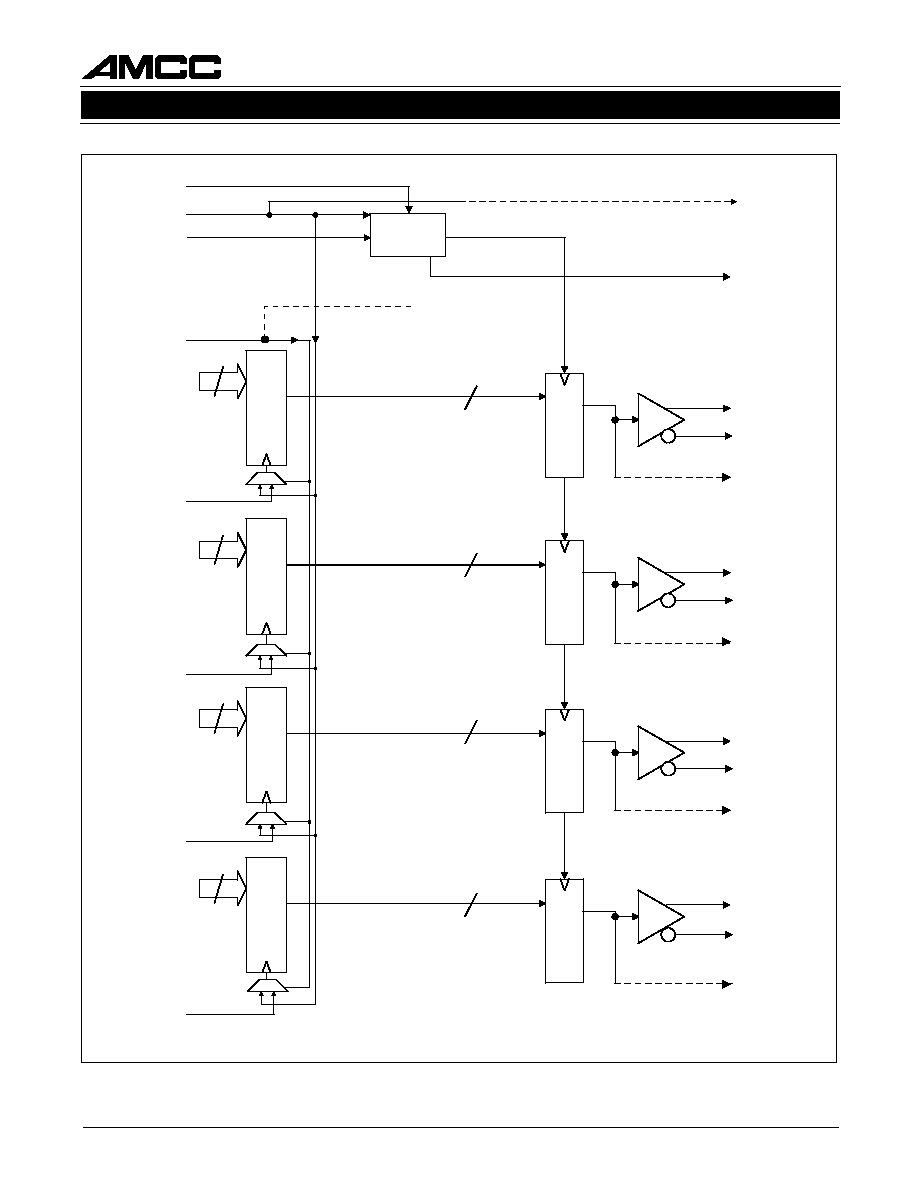
Each bi-directional channel provides parallel to serial
and serial to parallel conversion, clock generation/
recovery, and framing. The on-chip transmit PLL
synthesizes the high-speed clock from a low-speed
reference. The on-chip quad receive PLL is used for
clock recovery and data re-timing on the four inde-
pendent data inputs. The transmitter and receiver
each support differential PECL-compatible I/O for
copper or fiber optic component interfaces with ex-
cellent signal integrity. Local loopback mode allows
for system diagnostics. The chip requires a 3.3V
power supply and dissipates 2.5 watts.
Figure 1 shows the S2204 and S2004 in a Gigabit
Ethernet application. Figure 2 combines the
S2204 with a crosspoint switch to demonstrate a
serial backplane application. Figure 3 is the input/
output diagram. Figures 4 and 5 show the transmit
and receive block diagrams, respectively.