 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: DS1085 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

1 of 21
122002
FEATURES
ß User-Programmable Frequency Synthesizer
ß Programmable From 8.1kHz to 133MHz
ß Dual Synchronous Outputs
ß 8.2MHz to 133MHz Reference Oscillator
Output
ß 8.1kHz to 133MHz Main Oscillator Output
ß Three Resolution Options
ß 2-Wire Serial Interface
ß 0.75% Absolute Accuracy
ß Nonvolatile (NV) Frequency Settings
ß Single 5V Supply
ß No External Timing Components
ß Power-Down Mode
PIN ASSIGNMENT
PIN DESCRIPTION
OUT1
- Main Oscillator Output
OUT0
- Reference Oscillator Output
V
CC
- Power-Supply Voltage
GND
- Ground
CTRL1
- Control Pin for OUT1
CTRL0
- Control Pin for OUT0
SDA
- 2-Wire Serial Data Input/Output
SCL
- 2-Wire Serial Clock
ORDERING INFORMATION
DEVICE
PACKAGE
STEP
SIZE
OSCILLATOR
OUTPUT RANGE
DS1085Z-10
150mil SO
10kHz
8.1kHz to 133MHz
DS1085Z-25
150mil SO
25kHz
8.1kHz to 133MHz
DS1085Z-50
150mil SO
50kHz
8.1kHz to 133MHz
DESCRIPTION
The DS1085 is a dual-output frequency synthesizer requiring no external timing components for
operation. It can be used as a standalone oscillator or as a dynamically programmed, processor-controlled
peripheral device. An internal master oscillator can be programmed from 66MHz to 133MHz with three
resolution options of 10kHz, 25kHz, and 50kHz. A programmable, 3-bit prescaler (divide-by-1, 2, 4, or 8)
permits the generation of a reference oscillator output (OUT0) from the master, ranging from 8.2MHz to
133MHz. A second independent prescaler and a 1-to-1025 divider allows the generation of a main
oscillator output (OUT1) from 8.1kHz to 133MHz. The two outputs, although synchronous with the
master, can be independently programmed. The combination of programmable master oscillator,
prescalers, and dividers allows the generation of thousands of user-specified frequencies. All master
oscillator, prescaler, and divider settings are stored in NV (EEPROM) memory, providing a default value
on power-up that allows it to be used as a standalone oscillator. A 2-wire serial interface allows in-circuit,
on-the-fly programming of the master oscillator, prescalers (P0 and P1), and divider (N). This allows
dynamic frequency modification, if required, or, for fixed-frequency applications, the DS1085 can be
used with factory- or user-programmed values.
DS1085
EconOscillator Frequency Synthesizer
www.maxim-ic.com
SO (150mil)
SCL
CTRL0
CTRL1
OUT1
OUT0
V
CC
GND
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
SDA
EconOscillator is a trademark of Dallas Semiconductor.
DS1085
2 of 21
External control inputs, CTRL1 and CTRL0, enable or disable the two oscillator outputs. Both outputs
feature a synchronous enable that ensures no output glitches when the output is enabled and a constant
time interval (for a given frequency setting) from an enable signal to the first output transition. These
inputs also can be configured to disable the master oscillator, putting the device into a low-power mode
for power-sensitive applications.
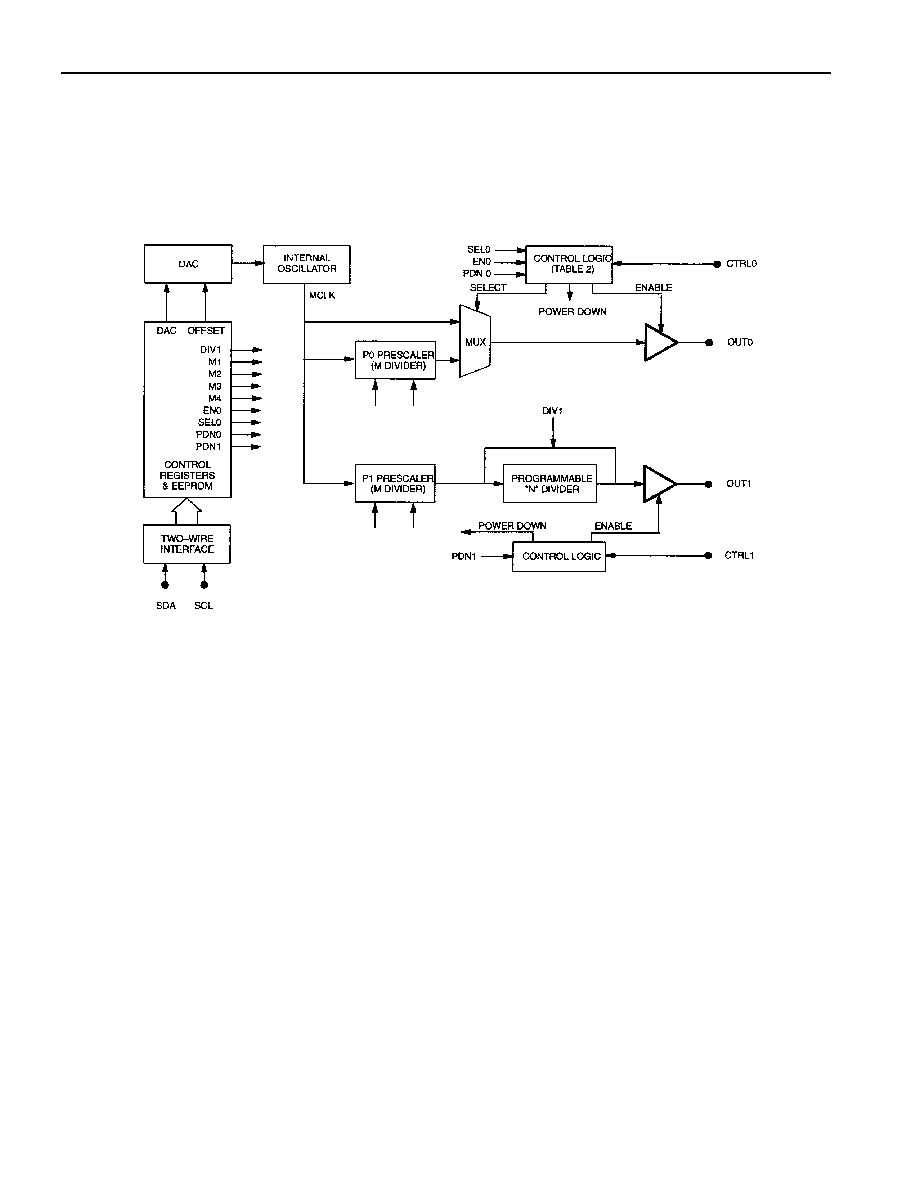
Figure 1. DS1085 BLOCK DIAGRAM
OVERVIEW
A block diagram of the DS1085 is shown in Figure 1. The DS1085 consists of five major components:
ß Master oscillator control DAC
ß Internal master oscillator (66MHz to 133MHz)
ß Prescalers (divide-by-1, 2, 4, or 8)
ß Programmable divider (divide-by-1 to 1025)
ß Control registers
The internal master oscillator provides the reference clock (MCLK), which is fed to the prescalers and
programmable dividers. The frequency of the oscillator can be user-programmed over a two-to-one range
in increments equal to the step size, by means of a 10-bit control DAC. The master oscillator range is
66MHz to 133MHz, which is larger than the range possible with the 10-bit DAC resolution and available
step sizes. Therefore, an additional register (OFFSET) is provided that can be used to select the range of
frequency over which the DAC is used (see Table 1).
0M0
0M1
1M0
1M1

DS1085
3 of 21
Table 1. DEVICE COMPARISONS BY PART NUMBER
PART NUMBER
STEP SIZE (kHz)
DAC SPAN (MHz)
OFFSET SIZE (MHz)
DS1085Z-10
10
10.24
5.12
DS1085Z-25
25
25.60
6.40
DS1085Z-50
50
51.20
6.40
For further description of use of the OFFSET register, see the REGISTER FUNCTIONS section.
The master clock can be routed directly to the outputs (OUT0 and OUT1) or through separate prescalers
(P0 and P1). In the case of OUT1, an additional programmable divider (N) can be used to generate
frequencies down to 8.1kHz.
The prescaler (P0) divides MCLK by 1, 2, 4, or 8 before routing MCLK to the reference output (OUT0)
pin.
The prescaler (P1) divides MCLK by 1, 2, 4, or 8 before routing MCLK to the programmable divider (N),
and, ultimately, the main output (OUT1) pin.
The programmable divider (N) divides the prescaler output (P1) by any number selected between two and
1025 (10 bits) to provide the main output (OUT1), or it can be bypassed altogether by use of the DIV1
register bit. The value of N is stored in the DIV register.
The control registers are user-programmable through a 2-wire serial interface to determine operating
frequency (values of DAC, OFFSET, P0, P1, and N) and modes of operation. Once programmed, the
register settings are nonvolatile and only need reprogramming if it is desired to reconfigure the device.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN
NAME
DESCRIPTION
1
OUT1
This main oscillator output frequency is determined by the control
register settings for the oscillator (DAC and OFFSET), prescaler P1
(mode bits 1M0 and 1M1), and divider N (DIV).
2
OUT0
The reference output is taken from the output of the reference select mux.
Its frequency is determined by the control register settings for prescaler
P0 (mode bits 0M0 and 0M1) (see Table 2).
3
V
CC
Power Supply
4
GND
Ground
5
CTRL0
A multifunction control input pin that can be programmed to function as
a mux select, output enable, and/or a power-down. Its function is
determined by the user-programmable control register values of EN0,
SEL0, and PDN0 (see Table 2).
6
CTRL1
A multifunction control input pin that can be programmed to function as
an output enable and/or a power-down. Its function is determined by the
user-programmable control register value of PDN1 (see Table 3).
7
SDA
I/O pin for the 2-wire serial interface used for data transfer.
8
SCL
Input pin for the 2-wire serial interface used to synchronize data
movement over the serial interface.

DS1085
4 of 21
Table 2. DEVICE MODE USING OUT0
EN0
(BIT)
SEL0
(BIT)
PDN0
(BIT)
CTRL0
(PIN)
OUT0
(PIN)
CTRL0
FUNCTION
DEVICE
MODE
1
High-Z
Power-Down***
0
0
0
0
High-Z
Power-Down*
Active
1
MCLK/M
0
1
0
0
MCLK
Mux Select
Active
1
High-Z
1
0
0
0
MCLK
Output Enable
Active
1
High-Z
1
1
0
0
MCLK/M
Output Enable
Active**
1
High-Z
Power-Down
X
0
1
0
MCLK
Power-Down
Active
1
High-Z
Power-Down
X
1
1
0
MCLK/M
Power-Down
Active
*This mode is for applications where OUT0 is not used, but CTRL0 is used as a device shutdown.
**Factory default setting.
***See standby (power-down) current specification for power-down current range.
Table 3. DEVICE MODE USING OUT1
PDN1
(BIT)
CTRL1
(PIN)
CTRL1
FUNCTION
OUT1 (PIN)
DEVICE MODE
0
0
OUT CLK
0
1
Output Enable
High-Z
Active*
1
0
OUT CLK
Active
1
1
Power-Down
High-Z
Power-Down
*Factory default setting.
NOTE:
Both CTRL0 and CTRL1 can be configured as power-downs. They are internally "OR" connected so
either of the control pins can be used to provide a power-down function for the whole device, subject to
appropriate settings of the PDN0 and PDN1 register bits (see Table 4).
Table 4. SHUTDOWN CONTROL WITH PDN0 AND PDN1
PDN0
(BIT)
PDN1
(BIT)
SHUTDOWN CONTROL
0
0
NONE
0
1
CTRL1
1
0
CTRL0
1
1
CTRL1 OR CTRL0
DS1085
5 of 21
REGISTER FUNCTIONS
The user-programmable registers can be used to determine the mode of operation (MUX), operating
frequency (DAC, OFFSET, DIV), and bus settings (ADDR). The functions of the registers are described
in this section, but details of how these registers are programmed can be found in a later section. The
register settings are nonvolatile, with the values being stored automatically or as required in EEPROM
when the registers are programmed through the SDA and SCL pins.
DAC WORD
(Address 08h)
MSB
LSB MSB
LSB
d9
d8
d7
d6
d5
d4
d3
d2
d1
d0
X
X
X
X
X
X
First Data Byte
Second Data Byte
X = Don't care.
The DAC word (d0≠d9) controls the frequency of the master oscillator. The resolution of this register
depends on the step size of the device. The absolute frequency of the device also depends on the value of
the OFFSET register (see Table 5 and 6).
Table 5. DEFAULT DAC SETTINGS
DS1085Z-10
DS1085Z-25
DS1085Z-50
Frequency
DAC
Offset
Frequency
DAC
Offset
Frequency
DAC
Offset
97.1MHz
500
OS
104.6MHz
600
OS
101.8MHz
500
OS
For any given value of OFFSET the master oscillator frequency can be derived as follows:
Frequency = Min Frequency + DAC x Step Size
where: Min frequency is the lowest frequency shown in Table 6 for the corresponding offset.
DAC is the value of the DAC register (0≠1023).
Step size is the step size of the device (10kHz, 25kHz, or 50kHz).
OS is the decimal, integer value of the five MSBs of the RANGE register.
OFFSET BYTE
(Address 0Eh)
MSB
LSB
X
X
X
O4
O3
O2
O1
O0
X = Don't care.
The OFFSET byte (O0≠O4) determines the range of frequencies that can be obtained within the absolute
minimum and maximum range of the oscillator. Correct operation of the device is not guaranteed for
values of OFFSET not shown in Table 6.




