1
Features
n Built-in quartz with digital trimming for frequency tuning
and temperature compensation facilities
INTEL and MOTOROLA interface compatibility
15 ns typical access time at 5.0 V
tandby current at 3.0 V
Integrated battery switch-over
Battery voltage range, 2.0
4.0 V
No busy state
No external components required
BCD format
12 or 24 hour data format
Time to 1/100 of a second
To external time reference synchronisation
50 Hz or nearest s/min synchronisation
Tri-state bus capability when power fail (
= 0)
User RAM
Temperature range - 40 to +85 C
Package SO28
PFI
O
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
1.2
A typical s
Wide supply voltage range, 2.0
V
5.5 V
V
Frequency measurements
Time set lock mode
Week number calculation
Clock counts up to 99 years
Leap year correction
Output programmable interrupts
Alarm interrupt, programmable up to one month
Timer interrupt, programmable up to 24 hours
Power fail input
Power fail output or Reset output
m
�
�
�
�
DD
BAT
PFI
PFO
Description
The V3025 is a low power CMOS real time clock with an
integrated battery switch-over. The standby current is typically
2.5
A and the access time is 50 ns. The interface is a
multiplexed address and data 8 bits bus. Multiplexing of
address and data is handled by the input line /D. There are no
busy flags in the V3025, internal time update cycles are invisible
to the user's software. Time data can be read from the V3025 in
12 or 24 hour data formats. An external signal puts the V3025 in
standby mode. Even in standby, the V3025 pulls the
pin
active low on an internal alarm interrupt. Calendar functions
include leap year correction and week number calculation. The
V3025 can be synchronized to an external 50 Hz signal or to the
nearest second or minute. The integrated battery switch-over
supply the real time clock part by
as long as
is higher
than
. When
decreases under
, the output
comes active and the real clock is supplied by the battery or the
supercap.
m
A
IRQ
PFO
V
V
V
V
V
DD
DD
BAT
DD
BAT
Very Low Power 8-Bit 32 kHz RTC Module with
Digital Trimming, User RAM and Battery Switch-over
Applications
n Industrial controllers
Alarm systems with periodic wake up
PABX and telephone systems
Point of sale terminals
Automotive electronics
n
n
n
n
n Personal Computers
Pin Assignment
Fig. 2
SO28
SYNC
PFI
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
A/D
IRQ
V
SS
V
BAT
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
RD
WR
CS
V
DD
V3025
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
OUT
PFO
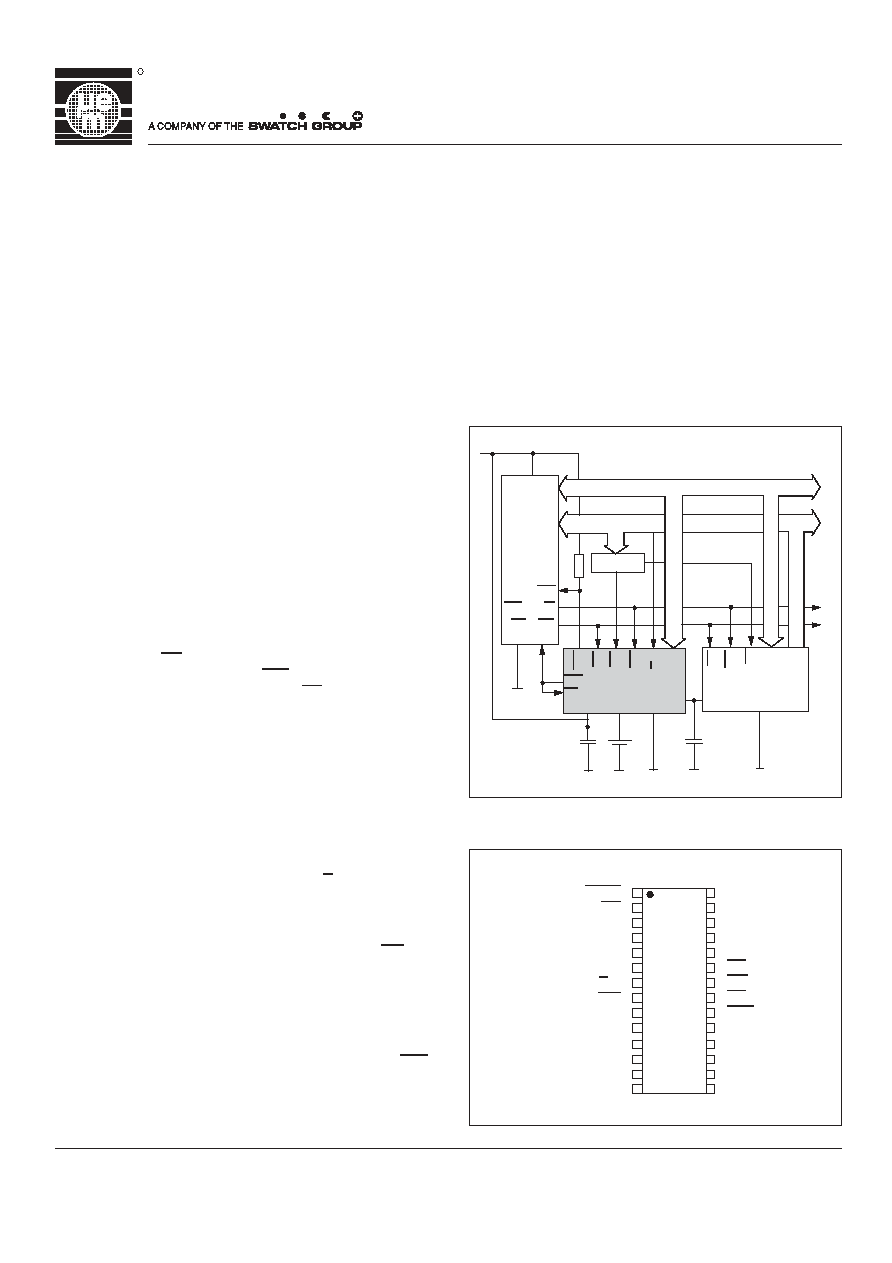
Typical Operating Configuration
Fig. 1
V
DD
V
SS
Data Bus
Address Bus
CPU
Decoder
R
IRQ
IRQ
PFO
PFI
WR
WR
A/D
AD
0-7
RD
WR
RD
RD
CS
CS
DS
or
or
R/W
T
o
Other
P
eripherals
100 nF
100 nF
3.6 V
V3025
in SO-28
RAM
Data
Address
V
DD
V
DD
V
BAT
V
SS
V
OUT
V
DD
V
SS
V3025
R
EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN SA

1)
2)
3)
4)
With
= 0 (V ) all I/O pads can be tri-state, tested.
With
= 1 (V
),
= 1 (V
) and all other I/O pads fixed to V
or to V : same standby current, not tested.
All other inputs to V
and all outputs open.
At a given temperature.
See Fig. 5
PFO
PFO
CS
SS
SUP
DD
SUP
SS
DD
Stresses above these listed maximum ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. Exposure beyond specified
operating conditions may affect device reliability or cause
malfunction.
2
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 1
Parameter
Maximum voltage at V
and V
Max. voltage at remaining pins
Min. voltage on all pins
DD
BAT
Maximum storage temperature
Minimum storage temperature
Maximum electrostatic discharge
to MIL-STD-883C method 3015
Maximum soldering conditions
Shock resistance
V
SUPmax
V
SUP
V
min
T
STOmin
T
STOmax
V
Smax
T
Smax
V
+ 7.0V
SS
V
+ 0.3V
DD
V
- 0.3V
SS
-55 C
0
+125 C
O
1000V
250 C x 10s
5000 g.
0.3ms, / sine
O
1
2
Symbol Conditions
Handling Procedures
This device has built-in protection against high static voltages
or electric fields; however, anti-static precautions must be taken
as for any other CMOS component. Unless otherwise specified,
proper operation can only occur when all terminal voltages are
kept within the supply voltage range. Unused inputs must
always be tied to a defined logic voltage level.
Operating Conditions
T
A
V
DD
V
BAT
-40
+85
O
C
Parameter
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Units
Operating temperature
Main supply votage
Battery supply voltage
2.0
5.0
V
V/ s
m
nF
5.5
6
100
V
SUP
dv/dt
Logic supply voltage
Supply voltage dv/dt
(power-up & down)
Decoupling capacitor
2
5.5
V
V
4
2
Table 2
Electrical Characteristics
V
= 5.0V � 10%, V
= 3 V, V
= 0 V, T = -40 to +85 C, unless otherwise specified
DD
BAT
SS
A
O
Table 3
Standby current
1)
Dynamic current
2)
IRQ (open drain)
Inputs and Outputs
Output low voltage
Input logic low
Output low voltage
Input logic high
Output logic low
Output logic high
PFI activation voltage
PFI hysteresis
Input leakage
Output tri-state leakage
Oscillator Characteristics
Starting voltage
Frequency tolerance
Frequency stability
Temperature stability
Aging
Accuracy versus switch-over
Start-up time
Frequency Characteristics
I
DD1
I
DYN
V
OL
V
OL
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
V
H
V
PFL
I
IN
I
TS
V
STA
V
STA
T
STA
Df/f
f
sta
t
sta
t
ag
ppm/V
ppm
T
+25 C
A
�
O
T = +25 C addr. 10 hex = 00 hex
A
O
210
4)
251
ppm
2.0
V
5.5 V
�
�
DD
3)
1
5
addr. 10 hex = 00 hex
T = + 25 C, first year
A
o
see Fig. 6
Parameter
Symbol
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
T = +25 C
A
0
V <V <V
SS
IN
DD
CS = 1
T = +25 C
A
0
T = +25 C
A
0
I
= 6 mA
OL
I
= 6 mA
OH
0.2 V
SUP
V
V
V
V
V
0.8 V
SUP
0.4
2.4
0.5 V
DD
100
mV
nA
nA
5
1000
5
1000
2
V
V
s
2.5
1
I
= 6 mA
OL
I
= 1 mA, V
= 2 V
OL
DD
0.4
0.4
V
V
V
= 3 V, V
= 0 V,
= 0
DD
BAT
PFI
V
= 5.5 V,
= 0
DD
PFI
1.2
2.5
1.3
10
15
10
1.5
mA
mA
mA
CS
RD
= 4 MHz,
= V ,
SS
WR = V
DD
�5
ppm/year
150
Pullup on SYNC
I
LS
V
= 0.8 V
ILS
mA
20
A
SW
V
= 3 V, 10 pulses of V
BAT
DD
switching between 2 to 5 V in 70 ms
0.2
ppm
Standby current
1)
I
DD2
I
BAT
V
= 0 V,
= 0
DD
PFI
mA
40
V3025
R

3
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
t
starts from
(
) or
, whichever activates last
Typically, t
= 5 + 0.9 C
in ns; where C
(external parasitic capacitance) is in pF
t
starts from
(
) or
, whichever deactivates first
t
ends at
(R/ ) or
, whichever deactivates first
t
starts from
(R/ ) or
, whichever deactivates first
/D must come before a
and
or a
and
combination. The user has to guarantee this.
ACC
ACC
EXT
EXT
DF
DW
DH
RD DS
CS
RD DS
CS
WR
W
CS
WR
W
CS
A
CS
RD
CS
WR
Timing Characteristics
V
= 5.0 � 10%, V
= 0 V, V
= 0 V, and T = - 40 to +85�C
DD
BAT
SS
A
Parameter
Chip select duration, write cycle
Write pulse duration
Time between two transfers
RAM access time
1)
Data valid to Hi-impedance
2)
Write data settle time
3)
Data hold time
4)
Advance write time
PF response delay
Rise time (all inputs)
Fall time (all inputs)
CS delay after /D
A
5)
CS
A
delay to /D
t
CS
t
WR
t
W
t
ACC
t
DF
t
DW
t
DH
t
ADW
t
PF
t
R
t
F
t
A/Ds
t
A/Dt
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Table 5
50
50
100
10
50
10
10
5
10
60
40
100
200
200
50
30
C
= 50 pF
LOAD
Symbol
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Typical V
Current vs. Temperature
DD
Fig. 3
7
6
5
4
I
[�A]
DD
T [�C]
A
3
2
1
0
-50
-25
0
V
= 5.5 V, V
= 3 V
DD
BAT
V
= 4 V, V
= 0 V
DD
BAT
V
= 3 V, V
= 0 V
DD
BAT
25
50
75
100
Switch-over Electrical Characteristics
ON resistance of V
to V
DD
OUT
ON resistance of V
to V
BAT
OUT
V
voltage over V
for switching
DD
BAT
V
voltage under V
for switching
DD
BAT
V
rising edge switching delay to
DD
PFO and V
OUT
V
falling edge switching delay to
DD
PFO and V
OUT
T = - 40 to 85 C, inputs to V
, outputs not connected, unless otherwise specified
A
DD
0
R
VDD
R
BAT
V
SVDD
V
SBAT
T
RDD
T
FDD
3.00
2.98
4
24
3.21
3.08
14
8
8
40
3.45
3.18
100
60
W
W
V
V
�s
�s
V
= 3V, V
= 0 V, I
=100mA
DD
BAT
OUT
V
= 0V, V
= 3V, I
= 20mA
DD
BAT
OUT
V
= 3V, V
open
BAT
OUT
V
= 3V, V
open
BAT
OUT
V
= 3V, V
rise from 2.8 V to 3.5V
BAT
DD
V
= 3V, V
falling from 3.5 V to 2.8 V
BAT
DD
Parameter
Symbol
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Test Conditions
Table 4
V3025
R

4
Typical Frequency on IRQ
DF
F
0
ppm
T [ C]
A
0
Address 10 hex = 00 hex
250
200
150
100
50
0
-50
-30
-10
10
30
50
70
90
Fig. 5
Typical V
Current vs. Temperature
BAT
Fig.4
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
I
[�A]
BA
T
T [ C]
A
0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
-50
V
= 0 V
DD
-25
0
V
= 4 V
BAT
V
= 3 V
BAT
V
= 2 V
BAT
25
50
75
100
Module Characteristic
Fig. 6
= the ratio of the change in frequency to the nominal value
expressed in ppm (It can be thought of as the frequency
deviation at any temperature.)
= the temperature of interest in C
= the turnover temperature (25 �5 C)
o
O
To determine the clock error (accuracy) at a given temperature, add
the frequency tolerance at 25 C to the value obtained from the
formula above.
O
[ppm]
F
r
equency
ratio
[
ppm]
-100
-200
-300
-400
T - 100
O
T - 50
O
Temperature [ C]
O
T [ C]
O
T
O
T +50
O
T +100
O
DF
F
0
DF/F
O
T
T
O
min.
max.
DF
F
0
ppm
C
O
2
= - 0.038
(T - T ) �10%
O
2
V3025
R

5
Fig. 9a
t
CS
t
ACC
t
W
t
A/Dt
t
R
t
A/Ds
t
F
DATA VALID
t
DF
CS
A/D
RD DS
/
DATA
Read Timing for Intel (
and
pulse) and Motorola (
or
pin tied to
, and R/ )
RD
WR
DS
RD
CS
W
Timing Waveforms
Typical V
Switch Resistance vs. Temperature
DD
-50
-25
25
50
75
100
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
V =2 V
DD
V =3 V
DD
V =5 V
DD
V =4 V
DD
R[
]
DD
V
=0 V
BAT
T [ C]
A
0
Fig. 7
Typical Battery Switch Resistance vs. Temperature
35
-50
-25
25
50
75
100
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
V
=2 V
BAT
V
=3 V
BAT
V
=4 V
BAT
R[
]
BA
T
V =0 V
DD
T [ C]
A
0
Fig. 8
V3025
R




