 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: H.261 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
ITU-T
H.261
TELECOMMUNICATION
(03/93)
STANDARDIZATION SECTOR
OF ITU
{This document has included corrections to typographical errors listed in Annex
5 to COM 15R 16-E dated June 1994. - Sakae OKUBO}
LINE TRANSMISSION OF NON-TELEPHONE
SIGNALS
VIDEO CODEC FOR AUDIOVISUAL
SERVICES AT p
◊
64 kbit/s
ITU-T Recommendation H.261
(Previously "CCITT Recommendation")

FOREWORD
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is a permanent organ of the International Telecommunication
Union. The ITU-T is responsible for studying technical, operating and tariff questions and issuing Recommendations on them
with a view to standardizing telecommunications on a worldwide basis.
The World Telecommunication Standardization Conference (WTSC), which meets every four years, established the topics for
study by the ITU-T Study Groups which, in their turn, produce Recommendations on these topics.
ITU-T Recommendation H.261 was revised by the ITU-T Study Group XV (1988-1993) and was approved by the WTSC
(Helsinki, March 1-12, 1993).
___________________
NOTES
1
As a consequence of a reform process within the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the CCITT ceased
to exist as of 28 February 1993. In its place, the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) was created as of 1
March 1993. Similarly, in this reform process, the CCIR and the IFRB have been replaced by the Radiocommunication
Sector.
In order not to delay publication of this Recommendation, no change has been made in the text to references containing the
acronyms "CCITT, CCIR or IFRB" or their associated entities such as Plenary Assembly, Secretariat, etc. Future editions of
this Recommendation will contain the proper terminology related to the new ITU structure.
2
In this Recommendation, the expression "Administration" is used for conciseness to indicate both a
telecommunication administration and a recognized operating agency.
©
ITU 1994
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the ITU.

Recommendation H.261 (03/93)
i
CONTENTS
Recommendation H.261 (03/93)
Page
1
Scope ..............................................................................................................................................................
1
2
Brief specification ..........................................................................................................................................
1
2.1
Video input and output......................................................................................................................
2
2.2
Digital output and input ....................................................................................................................
2
2.3
Sampling frequency ..........................................................................................................................
2
2.4
Source coding algorithm ...................................................................................................................
2
2.5
Bit rate ..............................................................................................................................................
2
2.6
Symmetry of transmission.................................................................................................................
3
2.7
Error handling ...................................................................................................................................
3
2.8
Multipoint operation .........................................................................................................................
3
3
Source coder...................................................................................................................................................
3
3.1
Source format....................................................................................................................................
3
3.2
Video source coding algorithm .........................................................................................................
3
3.3
Coding control ..................................................................................................................................
6
3.4
Forced updating ................................................................................................................................
6
4
Video multiplex coder ....................................................................................................................................
7
4.1
Data structure ....................................................................................................................................
7
4.2
Video multiplex arrangement............................................................................................................
7
4.3
Multipoint considerations .................................................................................................................
18
5
Transmission coder.........................................................................................................................................
19
5.1
Bit rate ..............................................................................................................................................
19
5.2
Video data buffering .........................................................................................................................
19
5.3
Video coding delay ...........................................................................................................................
20
5.4
Forward error correction for coded video signal...............................................................................
20
Annex A ≠ Inverse transform accuracy specification...............................................................................................
21
Annex B ≠ Hypothetical reference decoder .............................................................................................................
22
Annex C ≠ Codec delay measurement method.........................................................................................................
23
Annex D ≠ Still image transmission.........................................................................................................................
24

Recommendation H.261 (03/93)
1
Recommendation H.261
Recommendation H.261 (03/93)
VIDEO CODEC FOR AUDIOVISUAL SERVICES AT p X 64 kbit/s
(Geneva, 1990; revised at Helsinki, 1993)
The CCITT,
considering
(a)
that there is significant customer demand for videophone, videoconference and other audiovisual services;
(b)
that circuits to meet this demand can be provided by digital transmission using the B, H
0
rates or their multiples up
to the primary rate or H
11
/H
12
rates;
(c)
that ISDNs are likely to be available in some countries that provide a switched transmission service at the B, H
0
or
H
11
/H
12
rate;
(d)
that the existence of different digital hierarchies and different television standards in different parts of the world
complicates the problems of specifying coding and transmission standards for international connections;
(e)
that a number of audiovisual services are likely to appear using basic and primary rate ISDN accesses and that some
means of intercommunication among these terminals should be possible;
(f)
that the video codec provides an essential element of the infrastructure for audiovisual services which allows such
intercommunication in the framework of Recommendation H.200;
(g)
that Recommendation H.120 for videoconferencing using primary digital group transmission was the first in an
evolving series of Recommendations,
appreciating
that advances have been made in research and development of video coding and bit rate reduction techniques which lead to
the use of lower bit rates down to 64 kbit/s so that this may be considered as the second in the evolving series of
Recommendations,
and noting
that it is the basic objective of the CCITT to recommend unique solutions for international connections,
recommends
that in addition to those codecs complying to Recommendation H.120, codecs having signal processing and transmission
coding characteristics described below should be used for international audiovisual services.
NOTES
1
Codecs of this type are also suitable for some television services where full broadcast quality is not required.
2
Equipment for transcoding from and to codecs according to Recommendation H.120 is under study.
1
Scope
This Recommendation describes the video coding and decoding methods for the moving picture component of audiovisual
services at the rates of p
◊
64 kbit/s, where p is in the range 1 to 30.
2
Brief specification
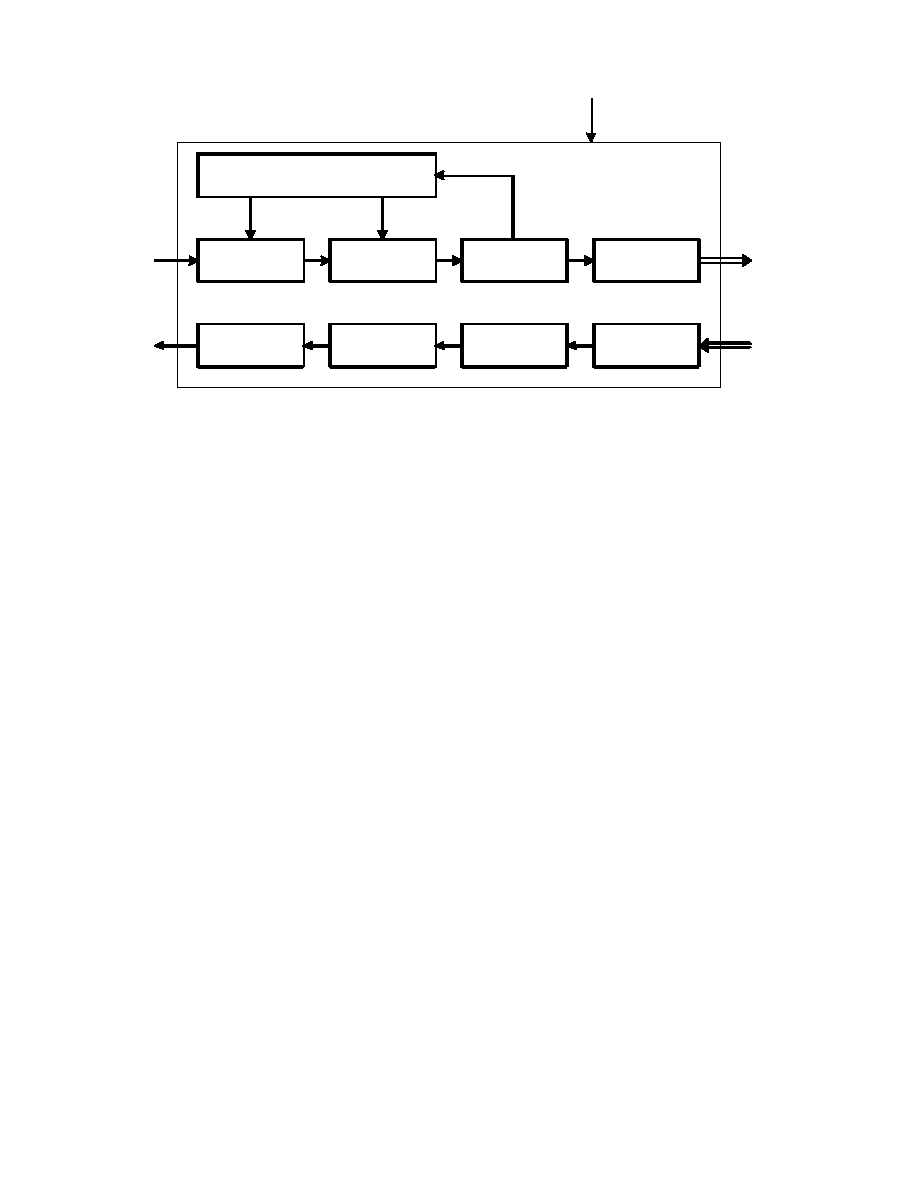
An outline block diagram of the codec is given in Figure 1.
2
Recommendation H.261 (03/93)
T 1 5 0 2 4 3 0 - 9 0 / d 0 1
C o d i n g c o n t r o l
S o u r c e
c o d e r
S o u r c e
d e c o d e r
V i d e o m u l t i p l e x
c o d e r
V i d e o m u l t i p l e x
d e c o d e r
T r a n s m i s s i o n
b u f f e r
R e c e i v i n g
b u f f e r
T r a n s m i s s i o n
c o d e r
C o d e d
b i t s t r e a m
V i d e o
s i g n a l
a ) V i d e o c o d e r
b ) V i d e o d e c o d e r
E x t e r n a l c o n t r o l
R e c e i v i n g
d e c o d e r
F I G U R E 1 / H . 2 6 1
O u t l i n e b l o c k d i a g r a m o f t h e v i d e o c o d e c
FIGURE 1/H.261...[D01] = 9 CM
2.1
Video input and output
To permit a single Recommendation to cover use in and between regions using 625- and 525-line television standards, the
source coder operates on pictures based on a common intermediate format (CIF). The standards of the input and output
television signals, which may, for example, be composite or component, analogue or digital and the methods of performing
any necessary conversion to and from the source coding format are not subject to Recommendation.
2.2
Digital output and input
The video coder provides a self-contained digital bit stream which may be combined with other multi-facility signals (for
example as defined in Recommendation H.221). The video decoder performs the reverse process.
2.3
Sampling frequency
Pictures are sampled at an integer multiple of the video line rate. This sampling clock and the digital network clock are
asynchronous.
2.4
Source coding algorithm
A hybrid of inter-picture prediction to utilize temporal redundancy and transform coding of the remaining signal to reduce
spatial redundancy is adopted. The decoder has motion compensation capability, allowing optional incorporation of this
technique in the coder.
2.5
Bit rate
This Recommendation is primarily intended for use at video bit rates between approximately 40 kbit/s and 2 Mbit/s.
2.6
Symmetry of transmission
The codec may be used for bidirectional or unidirectional visual communication.




