Document Outline
- General Description
- Features
- Block Diagram
- Pin Assignment
- Functional Description
- Parallel & Serial Load Operation Diagram
- Pin Descriptions
- Pin Characteristics
- Parallel & Serial Mode Function Table
- Programmable VCO Frequency Function Table
- Programmable Output Divider Function Table
- Absolute Maximum Ratings
- Power Supply DC Characteristics
- LVCMOS DC Characteristics
- LVPECL DC Characteristics
- Input Frequency Characteristics
- Crystal Characteristics
- AC Characteristics
- Parameter Measurement Information
- 3.3V Output Load AC Test Circuit Diagram
- Output Skew Diagram
- Period Jitter Diagram
- Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter Diagram
- Output Rise/Fall Time Diagram
- odc & tPeriod Diagram
- Application Information
- Power Supply Filtering Techniques
- Power Supply Filtering Diagram
- Crystal Input & Oscillator Interface
- Crystal Interface Diagram
- Crystal Frequency Plot
- Series Capacitor Plot
- Termination for LVPECL Outputs
- LVPECL Output Termination Diagrams
- Layout Guideline
- Schematic of Recommended Layout
- Power & Grounding
- Clock Traces & Termination
- Crystal
- PCB Board Layout
- Power Considerations
- Power Dissipation
- Junction Temperature
- Thermal Resistance
- Calculations & Equations
- LVPECL Driver Circuit & Termination Diagram
- Reliability Information
- Transistor Count
- Package Outline
- Package Dimensions
- Ordering Information
- Revision History Sheet
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
1
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
G
ENERAL
D
ESCRIPTION
The ICS8430-01 is a general purpose, dual output
Crystal-to-3.3V Differential LVPECL High Fre-
quency Synthesizer and a member of the
HiPerClockSTM family of High Performance Clock
Solutions from ICS. The ICS8430-01 has a select-
able TEST_CLK or crystal inputs. The VCO operates at a fre-
quency range of 250MHz to 500MHz. The VCO frequency is
programmed in steps equal to the value of the input reference
or crystal frequency. The VCO and output frequency can be
programmed using the serial or parallel interfaces to the con-
figuration logic. Frequency steps as small as 1MHz can be
achieved using a 16MHz crystal or TEST_CLK.
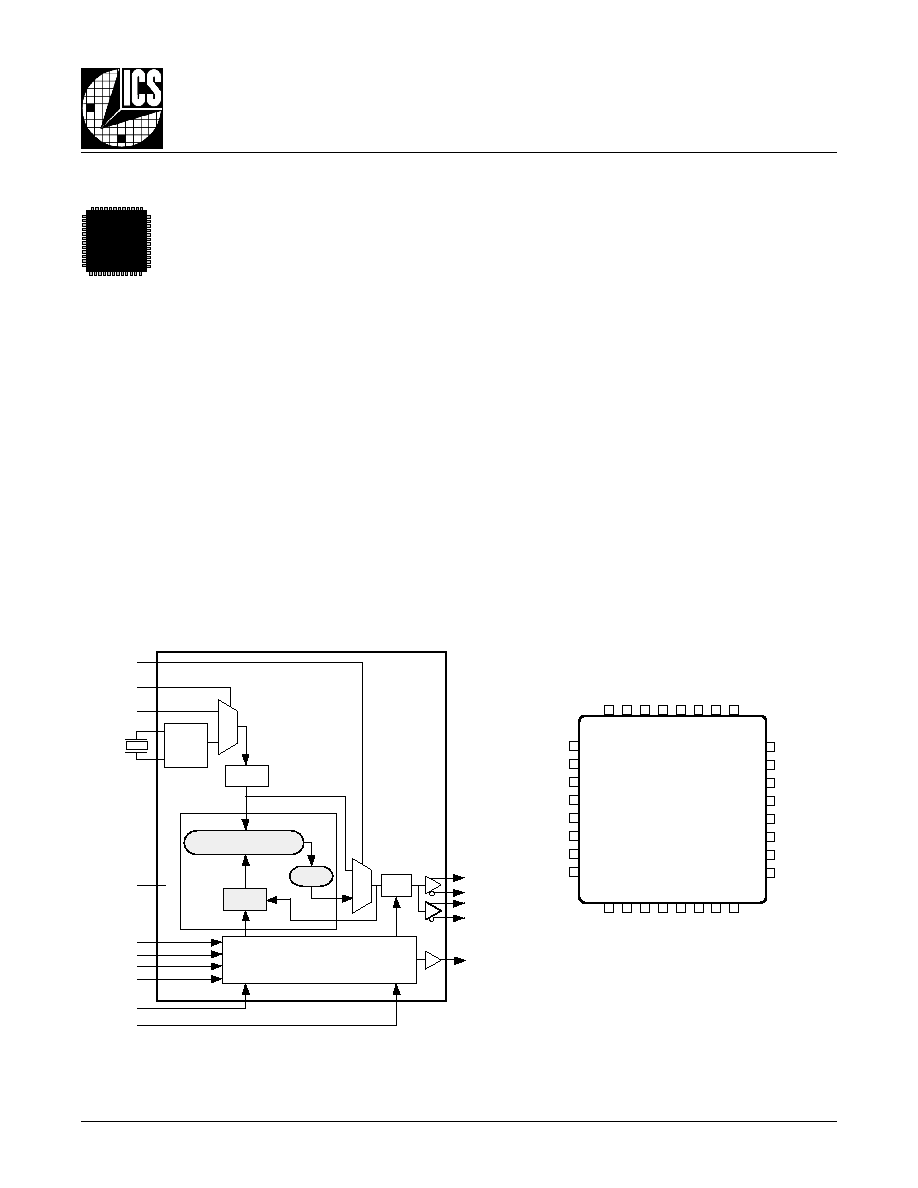
B
LOCK
D
IAGRAM
P
IN
A
SSIGNMENT
F
EATURES
�
Dual differential 3.3V LVPECL outputs
�
Selectable crystal oscillator interface or
LVCMOS TEST_CLK
�
Output frequency range: 20.83MHz to 500MHz
�
Crystal input frequency range: 14MHz to 27MHz
�
VCO range: 250MHz to 500MHz
�
Parallel or serial interface for programming counter
and output dividers
�
RMS period jitter: 6ps (maximum)
�
Cycle-to-cycle jitter: 30ps (maximum)
�
3.3V supply voltage
�
0�C to 70�C ambient operating temperature
�
Industrial temperature information available upon request
HiPerClockSTM
,&6
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
XTAL1
TEST_CLK
XTAL_SEL
V
CCA
S_LOAD
S_DATA
S_CLOCK
MR
M5
M6
M7
M8
N 0
N 1
N 2
V
EE
V
EE
nFOUT0
FOUT0
V
CCO
nFOUT1
FOUT1
V
CC
TEST
X
T
AL2
nP_LOAD
VCO_SEL
M0
M1
M2
M3
M4
32-Lead LQFP
7mm x 7mm x 1.4mm package body
Y Package
Top View
OSC
VCO_SEL
XTAL_SEL
TEST_CLK
XTAL1
XTAL2
S_LOAD
S_DATA
S_CLOCK
nP_LOAD
M0:M8
N0:N2
VCO
PLL
FOUT0
nFOUT0
FOUT1
nFOUT1
TEST
�
N
CONFIGURATION
INTERFACE
LOGIC
�
M
0
1
0
1
�
16
PHASE DETECTOR
ICS8430-01
MR
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
2
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
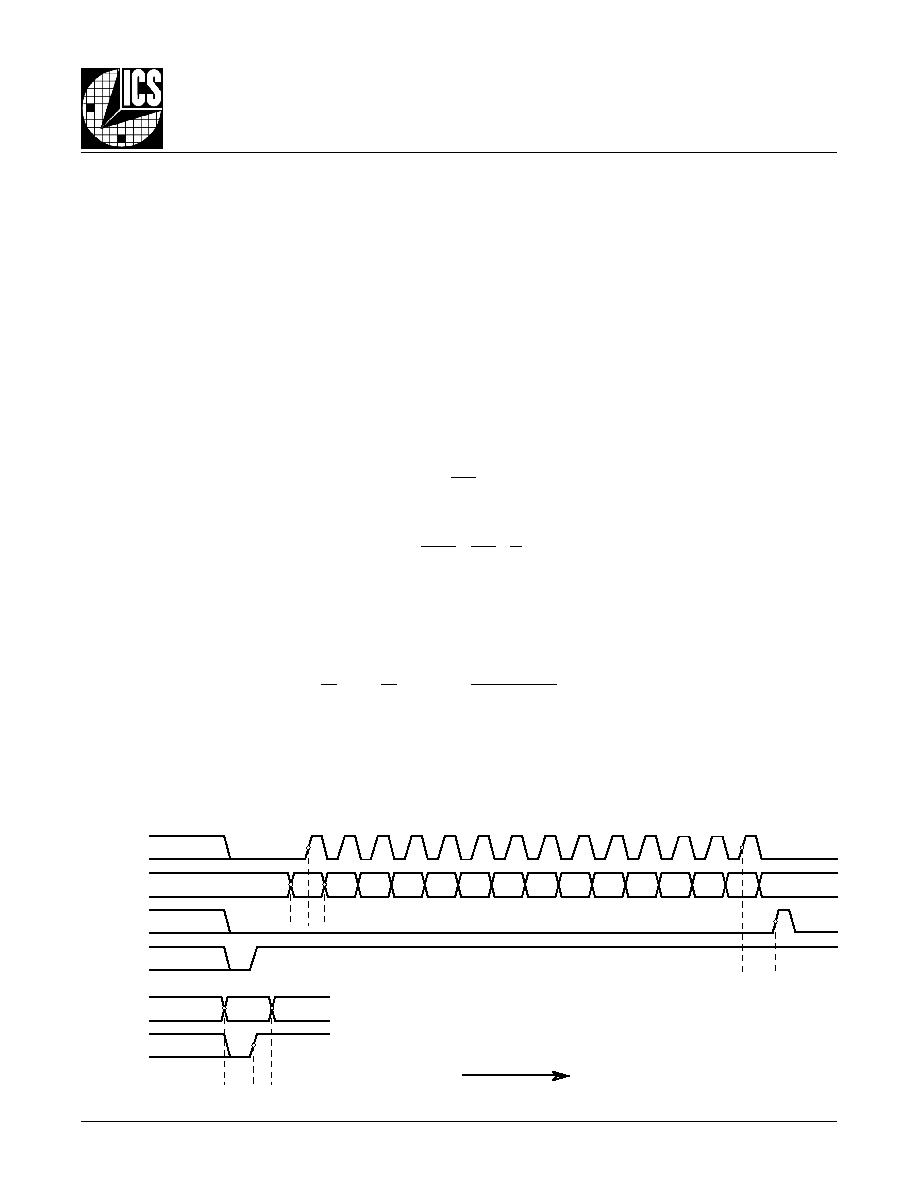
F
IGURE
1. P
ARALLEL
& S
ERIAL
L
OAD
O
PERATIONS
Time
S
ERIAL
L
OADING
P
ARALLEL
L
OADING
M, N
t
S
t
H
t
S
t
H
t
S
T1
T0
N2
N1
N0
M8
M7
M6
M5
M4
M3
M2
M1
M0
F
UNCTIONAL
D
ESCRIPTION
NOTE: The functional description that follows describes operation using a 16MHz crystal. Valid PLL loop divider values for
different crystal or input frequencies are defined in the Input Frequency Characteristics, Table 5, NOTE 1.
The ICS8430-01 features a fully integrated PLL and therefore requires no external components for setting the loop bandwidth.
A parallel-resonant, fundamental crystal is used as the input to the on-chip oscillator. The output of the oscillator is divided
by 16 prior to the phase detector. With a 16MHz crystal, this provides a 1MHz reference frequency. The VCO of the PLL
operates over a range of 250MHz to 500MHz. The output of the M divider is also applied to the phase detector.
The phase detector and the M divider force the VCO output frequency to be M times the reference frequency by adjusting
the VCO control voltage. Note that for some values of M (either too high or too low), the PLL will not achieve lock. The output of the
VCO is scaled by a divider prior to being sent to each of the LVPECL output buffers. The divider provides a 50% output duty cycle.
The programmable features of the ICS8430-01 support two input modes to program the M divider and N output divider.
The two input operational modes are parallel and serial.
Figure 1 shows the timing diagram for each mode. In parallel mode,
the nP_LOAD input is initially LOW. The data on inputs M0 through M8 and N0 through N2 is passed directly to the M divider
and N output divider. On the LOW-to-HIGH transition of the nP_LOAD input, the data is latched and the M divider remains
loaded until the next LOW transition on nP_LOAD or until a serial event occurs. As a result, the M and N bits can be hard-
wired to set the M divider and N output divider to a specific default state that will automatically occur during power-up. The
TEST output is LOW when operating in the parallel input mode. The relationship between the VCO frequency, the crystal
frequency and the M divider is defined as follows:
The M value and the required values of M0 through M8 are shown in Table 3B, Programmable VCO Frequency Function Table.
Valid M values for which the PLL will achieve lock for a 16MHz reference are defined as 250
M
500. The frequency out is
defined as follows:
Serial operation occurs when nP_LOAD is HIGH and S_LOAD is LOW. The shift register is loaded by sampling the S_DATA
bits with the rising edge of S_CLOCK. The contents of the shift register are loaded into the M divider and N output divider
when S_LOAD transitions from LOW-to-HIGH. The M divide and N output divide values are latched on the HIGH-to-LOW
transition of S_LOAD. If S_LOAD is held HIGH, data at the S_DATA input is passed directly to the M divider and N output
divider on each rising edge of S_CLOCK. The serial mode can be used to program the M and N bits and test bits T1 and T0.
The internal registers T0 and T1 determine the state of the TEST output as follows:
T1
T0
TEST Output
0
0
LOW
0
1
S_Data, Shift Register Input
1
0
Output of M divider
1
1
CMOS Fout
S_CLOCK
S_DATA
S_LOAD
nP_LOAD
M0:M8, N0:N2
nP_LOAD
16
M
fVCO =
fxtal x
N
fout =
fVCO
=
16
M
fxtal x
N

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
3
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
ABLE
1. P
IN
D
ESCRIPTIONS
r
e
b
m
u
N
e
m
a
N
e
p
y
T
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
D
0
3
,
9
2
,
8
2
2
,
1
,
2
3
,
1
3
2
M
,
1
M
,
0
M
6
M
,
5
M
,
4
M
,
3
M
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
n
o
i
t
i
s
n
a
r
t
H
G
I
H
-
o
t
-
W
O
L
n
o
d
e
h
c
t
a
l
a
t
a
D
.
s
t
u
p
n
i
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
t
u
p
n
i
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
f
o
4
,
3
8
M
,
7
M
t
u
p
n
I
p
u
ll
u
P
7
,
5
2
N
,
0
N
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
,
C
3
e
l
b
a
T
n
i
d
e
n
i
f
e
d
s
a
e
u
l
a
v
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
s
e
n
i
m
r
e
t
e
D
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
e
l
b
a
T
n
o
i
t
c
n
u
F
6
1
N
t
u
p
n
I
p
u
ll
u
P
6
1
,
8
V
E
E
r
e
w
o
P
.
s
n
i
p
y
l
p
p
u
s
e
v
i
t
a
g
e
N
9
T
S
E
T
t
u
p
t
u
O
t
u
p
t
u
O
.
n
o
i
t
a
r
e
p
o
f
o
e
d
o
m
l
a
i
r
e
s
e
h
t
n
i
E
V
I
T
C
A
s
i
h
c
i
h
w
t
u
p
t
u
o
t
s
e
T
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
e
d
o
m
l
e
ll
a
r
a
p
n
i
W
O
L
n
e
v
i
r
d
0
1
V
C
C
r
e
w
o
P
.
n
i
p
y
l
p
p
u
s
e
r
o
C
2
1
,
1
1
1
T
U
O
F
n
,
1
T
U
O
F
t
u
p
t
u
O
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
C
E
P
V
L
V
3
.
3
.
r
e
z
i
s
e
h
t
n
y
s
e
h
t
r
o
f
t
u
p
t
u
o
l
a
i
t
n
e
r
e
f
f
i
D
3
1
V
O
C
C
r
e
w
o
P
.
n
i
p
y
l
p
p
u
s
t
u
p
t
u
O
5
1
,
4
1
0
T
U
O
F
n
,
0
T
U
O
F
t
u
p
t
u
O
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
C
E
P
V
L
V
3
.
3
.
r
e
z
i
s
e
h
t
n
y
s
e
h
t
r
o
f
t
u
p
t
u
o
l
a
i
t
n
e
r
e
f
f
i
D
7
1
R
M
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
s
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
l
a
n
r
e
t
n
i
e
h
t
,
H
G
I
H
c
i
g
o
l
n
e
h
W
.
t
e
s
e
R
r
e
t
s
a
M
h
g
i
H
e
v
i
t
c
A
e
h
t
d
n
a
w
o
l
o
g
o
t
x
T
U
O
F
s
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
u
r
t
e
h
t
g
n
i
s
u
a
c
t
e
s
e
r
e
r
a
l
a
n
r
e
t
n
i
e
h
t
,
W
O
L
c
i
g
o
l
n
e
h
W
.
h
g
i
h
o
g
o
t
x
T
U
O
F
n
s
t
u
p
t
u
o
d
e
t
r
e
v
n
i
t
o
n
s
e
o
d
R
M
f
o
n
o
i
t
r
e
s
s
A
.
d
e
l
b
a
n
e
e
r
a
s
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
h
t
d
n
a
s
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
s
e
u
l
a
v
T
d
n
a
,
N
,
M
d
e
d
a
o
l
t
c
e
f
f
a
8
1
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
s
e
h
t
o
t
n
i
t
u
p
n
i
A
T
A
D
_
S
t
a
t
n
e
s
e
r
p
a
t
a
d
l
a
i
r
e
s
n
i
s
k
c
o
l
C
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
f
o
e
g
d
e
g
n
i
s
i
r
e
h
t
n
o
9
1
A
T
A
D
_
S
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
e
g
d
e
g
n
i
s
i
r
e
h
t
n
o
d
e
l
p
m
a
s
a
t
a
D
.
t
u
p
n
i
l
a
i
r
e
s
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
S
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
f
o
0
2
D
A
O
L
_
S
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
.
s
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
e
h
t
o
t
n
i
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
s
m
o
r
f
a
t
a
d
f
o
n
o
i
t
i
s
n
a
r
t
s
l
o
r
t
n
o
C
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
1
2
V
A
C
C
r
e
w
o
P
.
n
i
p
y
l
p
p
u
s
g
o
l
a
n
A
2
2
L
E
S
_
L
A
T
X
t
u
p
n
I
p
u
ll
u
P
.
e
c
r
u
o
s
e
c
n
e
r
e
f
e
r
L
L
P
e
h
t
s
a
s
t
u
p
n
i
t
s
e
t
r
o
l
a
t
s
y
r
c
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
s
t
c
e
l
e
S
.
W
O
L
n
e
h
w
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
s
t
c
e
l
e
S
.
H
G
I
H
n
e
h
w
s
t
u
p
n
i
L
A
T
X
s
t
c
e
l
e
S
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
3
2
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
t
u
p
n
i
k
c
o
l
c
t
s
e
T
5
2
,
4
2
2
L
A
T
X
,
1
L
A
T
X
t
u
p
n
I
.
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
h
t
s
i
2
L
A
T
X
.
t
u
p
n
i
e
h
t
s
i
1
L
A
T
X
.
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
r
o
t
a
ll
i
c
s
o
l
a
t
s
y
r
C
6
2
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
t
u
p
n
I
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
s
i
0
M
:
8
M
t
a
t
n
e
s
e
r
p
a
t
a
d
n
e
h
w
s
e
n
i
m
r
e
t
e
D
.
t
u
p
n
i
d
a
o
l
l
e
ll
a
r
a
P
e
h
t
s
t
e
s
0
N
:
2
N
t
a
t
n
e
s
e
r
p
a
t
a
d
n
e
h
w
d
n
a
,
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
o
t
n
i
d
e
d
a
o
l
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
.
e
u
l
a
v
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
N
7
2
L
E
S
_
O
C
V
t
u
p
n
I
p
u
ll
u
P
.
e
d
o
m
s
s
a
p
y
b
r
o
L
L
P
n
i
s
i
r
e
z
i
s
e
h
t
n
y
s
r
e
h
t
e
h
w
s
e
n
i
m
r
e
t
e
D
.
s
l
e
v
e
l
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
i
L
T
T
V
L
/
S
O
M
C
V
L
:
E
T
O
N
p
u
ll
u
P
d
n
a
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
.
s
e
u
l
a
v
l
a
c
i
p
y
t
r
o
f
,
s
c
i
t
s
i
r
e
t
c
a
r
a
h
C
n
i
P
,
2
e
l
b
a
T
e
e
S
.
s
r
o
t
s
i
s
e
r
t
u
p
n
i
l
a
n
r
e
t
n
i
o
t
r
e
f
e
r
T
ABLE
2. P
IN
C
HARACTERISTICS
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
C
N
I
e
c
n
a
t
i
c
a
p
a
C
t
u
p
n
I
4
F
p
R
P
U
L
L
U
P
r
o
t
s
i
s
e
R
p
u
ll
u
P
t
u
p
n
I
1
5
K
R
N
W
O
D
L
L
U
P
r
o
t
s
i
s
e
R
n
w
o
d
ll
u
P
t
u
p
n
I
1
5
K

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
4
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
ABLE
3A. P
ARALLEL
AND
S
ERIAL
M
ODE
F
UNCTION
T
ABLE
s
t
u
p
n
I
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
R
M
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
M
N
D
A
O
L
_
S
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
A
T
A
D
_
S
H
X
X
X
X
X
X
.
W
O
L
s
t
u
p
t
u
o
s
e
c
r
o
F
.
t
e
s
e
R
L
L
a
t
a
D
a
t
a
D
X
X
X
M
e
h
t
o
t
y
l
t
c
e
r
i
d
d
e
s
s
a
p
s
t
u
p
n
i
N
d
n
a
M
n
o
a
t
a
D
.
W
O
L
d
e
c
r
o
f
t
u
p
t
u
o
T
S
E
T
.
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
N
d
n
a
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
L
a
t
a
D
a
t
a
D
L
X
X
d
e
d
a
o
l
s
n
i
a
m
e
r
d
n
a
s
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
u
p
n
i
o
t
n
i
d
e
h
c
t
a
l
s
i
a
t
a
D
.
s
r
u
c
c
o
t
n
e
v
e
l
a
i
r
e
s
a
li
t
n
u
r
o
n
o
i
t
i
s
n
a
r
t
W
O
L
t
x
e
n
li
t
n
u
L
H
X
X
L
a
t
a
D
n
o
a
t
a
d
h
t
i
w
d
e
d
a
o
l
s
i
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
S
.
e
d
o
m
t
u
p
n
i
l
a
i
r
e
S
.
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
f
o
e
g
d
e
g
n
i
s
i
r
h
c
a
e
n
o
A
T
A
D
_
S
L
H
X
X
L
a
t
a
D
e
h
t
o
t
d
e
s
s
a
p
e
r
a
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
s
e
h
t
f
o
s
t
n
e
t
n
o
C
.
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
N
d
n
a
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
L
H
X
X
L
a
t
a
D
.
d
e
h
c
t
a
l
e
r
a
s
e
u
l
a
v
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
N
d
n
a
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
L
H
X
X
L
X
X
.
s
r
e
t
s
i
g
e
r
t
f
i
h
s
t
c
e
f
f
a
t
o
n
o
d
t
u
p
n
i
l
a
i
r
e
s
r
o
l
e
ll
a
r
a
P
L
H
X
X
H
a
t
a
D
.
d
e
k
c
o
l
c
s
i
t
i
s
a
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
o
t
y
l
t
c
e
r
i
d
d
e
s
s
a
p
A
T
A
D
_
S
W
O
L
=
L
:
E
T
O
N
H
G
I
H
=
H
e
r
a
c
t
'
n
o
D
=
X
n
o
i
t
i
s
n
a
r
t
e
g
d
e
g
n
i
s
i
R
=
n
o
i
t
i
s
n
a
r
t
e
g
d
e
g
n
il
l
a
F
=
T
ABLE
3B. P
ROGRAMMABLE
VCO F
REQUENCY
F
UNCTION
T
ABLE
T
ABLE
3C. P
ROGRAMMABLE
O
UTPUT
D
IVIDER
F
UNCTION
T
ABLE
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
F
O
C
V
)
z
H
M
(
e
d
i
v
i
D
M
6
5
2
8
2
1
4
6
2
3
6
1
8
4
2
1
8
M
7
M
6
M
5
M
4
M
3
M
2
M
1
M
0
M
0
5
2
0
5
2
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
5
2
1
5
2
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
2
5
2
2
5
2
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
3
5
2
3
5
2
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
8
9
4
8
9
4
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
9
9
4
9
9
4
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
5
0
0
5
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
.
z
H
M
6
1
f
o
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
f
l
a
t
s
y
r
c
r
o
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
a
o
t
d
n
o
p
s
e
r
r
o
c
s
e
i
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
f
g
n
i
t
l
u
s
e
r
e
h
t
d
n
a
s
e
u
l
a
v
e
d
i
v
i
d
M
e
s
e
h
T
:
1
E
T
O
N
s
t
u
p
n
I
e
u
l
a
V
r
e
d
i
v
i
D
N
)
z
H
M
(
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
F
t
u
p
t
u
O
2
N
1
N
0
N
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
0
0
0
1
0
5
2
0
0
5
0
0
1
5
.
1
6
6
.
6
6
1
3
3
.
3
3
3
0
1
0
2
5
2
1
0
5
2
0
1
1
3
3
3
.
3
8
6
6
.
6
6
1
1
0
0
4
5
.
2
6
5
2
1
1
0
1
6
6
6
.
1
4
3
3
.
3
8
1
1
0
8
5
2
.
1
3
5
.
2
6
1
1
1
2
1
3
8
.
0
2
6
6
.
1
4

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
5
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
ABLE
4A. P
OWER
S
UPPLY
DC C
HARACTERISTICS
,
V
CC
= V
CCA
= V
CCO
= 3.3V�5%, T
A
= 0�C
TO
70�C
T
ABLE
4B. LVCMOS / LVTTL DC C
HARACTERISTICS
,
V
CC
= V
CCA
= V
CCO
= 3.3V�5%, T
A
= 0�C
TO
70�C
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
V
H
I
t
u
p
n
I
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
h
g
i
H
,
R
M
,
2
N
:
0
N
,
8
M
:
0
M
,
A
T
A
D
_
S
,
D
A
O
L
_
S
,
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
,
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
L
E
S
_
L
A
T
X
,
L
E
S
_
O
C
V
2
V
C
C
3
.
0
+
V
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
2
V
C
C
3
.
0
+
V
V
L
I
t
u
p
n
I
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
w
o
L
,
R
M
,
2
N
:
0
N
,
8
M
:
0
M
,
A
T
A
D
_
S
,
D
A
O
L
_
S
,
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
,
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
L
E
S
_
L
A
T
X
,
L
E
S
_
O
C
V
3
.
0
-
8
.
0
V
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
3
.
0
-
3
.
1
V
I
H
I
t
u
p
n
I
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
h
g
i
H
,
R
M
,
1
N
,
0
N
,
8
M
-
6
M
,
4
M
-
0
M
,
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
,
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
,
D
A
O
L
_
S
,
A
T
A
D
_
S
V
C
C
V
=
N
I
V
5
6
4
.
3
=
0
5
1
A
�
L
E
S
_
O
C
V
,
L
E
S
_
L
A
T
X
,
5
M
V
C
C
V
=
N
I
V
5
6
4
.
3
=
5
A
�
I
L
I
t
u
p
n
I
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
w
o
L
,
R
M
,
1
N
,
0
N
,
8
M
-
6
M
,
4
M
-
0
M
,
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
,
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
,
D
A
O
L
_
S
,
A
T
A
D
_
S
V
C
C
,
V
5
6
4
.
3
=
V
N
I
V
0
=
5
-
A
�
L
E
S
_
O
C
V
,
L
E
S
_
L
A
T
X
,
5
M
V
C
C
,
V
5
6
4
.
3
=
V
N
I
V
0
=
0
5
1
-
A
�
V
H
O
t
u
p
t
u
O
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
h
g
i
H
1
E
T
O
N
;
T
S
E
T
6
.
2
V
V
L
O
t
u
p
t
u
O
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
w
o
L
1
E
T
O
N
;
T
S
E
T
5
.
0
V
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
V
C
C
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
y
l
p
p
u
S
e
r
o
C
5
3
1
.
3
3
.
3
5
6
4
.
3
V
V
A
C
C
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
y
l
p
p
u
S
g
o
l
a
n
A
5
3
1
.
3
3
.
3
5
6
4
.
3
V
V
O
C
C
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
y
l
p
p
u
S
t
u
p
t
u
O
5
3
1
.
3
3
.
3
5
6
4
.
3
V
I
E
E
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
r
e
w
o
P
0
4
1
A
m
I
A
C
C
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
g
o
l
a
n
A
5
1
A
m
NOTE 1: Outputs terminated with 50
to V
CCO
/2.
A
BSOLUTE
M
AXIMUM
R
ATINGS
Supply Voltage, V
CC
4.6V
Inputs, V
I
-0.5V to V
CC
+ 0.5 V
Outputs, V
O
-0.5V to V
CCO
+ 0.5V
Package Thermal Impedance,
JA
47.9�C/W (0 lfpm)
Storage Temperature, T
STG
-65�C to 150�C
NOTE: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute
Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the
device. These ratings are stress specifications only. Functional
operation of product at these conditions or any conditions be-
yond those listed in the
DC Characteristics or AC Character-
istics is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect product reliability.

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
6
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
ABLE
5. I
NPUT
F
REQUENCY
C
HARACTERISTICS
,
V
CC
= V
CCA
= V
CCO
= 3.3V�5%, T
A
= 0�C
TO
70�C
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
f
N
I
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
F
t
u
p
n
I
1
E
T
O
N
;
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
4
1
7
2
z
H
M
1
E
T
O
N
;
2
L
A
T
X
,
1
L
A
T
X
4
1
7
2
z
H
M
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
0
5
z
H
M
n
i
h
t
i
w
e
t
a
r
e
p
o
o
t
O
C
V
e
h
t
r
o
f
t
e
s
e
b
t
s
u
m
e
u
l
a
v
M
e
h
t
,
e
g
n
a
r
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
f
K
L
C
_
T
S
E
T
d
n
a
l
a
t
s
y
r
c
t
u
p
n
i
e
h
t
r
o
F
:
1
E
T
O
N
6
8
2
e
r
a
M
f
o
s
e
u
l
a
v
d
il
a
v
,
z
H
M
4
1
f
o
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
f
t
u
p
n
i
m
u
m
i
n
i
m
e
h
t
g
n
i
s
U
.
e
g
n
a
r
z
H
M
0
0
5
o
t
z
H
M
0
5
2
e
h
t
M
.
1
1
5
9
4
1
e
r
a
M
f
o
s
e
u
l
a
v
d
il
a
v
,
z
H
M
7
2
f
o
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
f
t
u
p
n
i
m
u
m
i
x
a
m
e
h
t
g
n
i
s
U
M
.
6
9
2
T
ABLE
6. C
RYSTAL
C
HARACTERISTICS
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
n
o
i
t
a
ll
i
c
s
O
f
o
e
d
o
M
l
a
t
n
e
m
a
d
n
u
F
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
F
4
1
7
2
z
H
M
)
R
S
E
(
e
c
n
a
t
s
i
s
e
R
s
e
i
r
e
S
t
n
e
l
a
v
i
u
q
E
0
7
e
c
n
a
t
i
c
a
p
a
C
t
n
u
h
S
7
F
p
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
F
T
U
O
y
c
n
e
u
q
e
r
F
t
u
p
t
u
O
3
8
.
0
2
0
0
5
z
H
M
t
)
c
c
(
t
ij
3
,
1
E
T
O
N
;
r
e
t
t
i
J
e
l
c
y
C
-
o
t
-
e
l
c
y
C
N
5
.
1
0
3
s
p
5
.
1
=
N
0
0
1
s
p
t
)
r
e
p
(
t
ij
1
E
T
O
N
;
S
M
R
,
r
e
t
t
i
J
d
o
i
r
e
P
N
5
.
1
6
s
p
5
.
1
=
N
5
2
s
p
t
)
o
(
k
s
3
,
2
E
T
O
N
;
w
e
k
S
t
u
p
t
u
O
5
1
s
p
t
R
e
m
i
T
e
s
i
R
t
u
p
t
u
O
%
0
8
o
t
%
0
2
0
0
2
0
0
7
s
p
t
F
e
m
i
T
ll
a
F
t
u
p
t
u
O
%
0
8
o
t
%
0
2
0
0
2
0
0
7
s
p
t
S
e
m
i
T
p
u
t
e
S
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
o
t
N
,
M
5
s
n
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
o
t
A
T
A
D
_
S
5
s
n
D
A
O
L
_
S
o
t
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
5
s
n
t
H
e
m
i
T
d
l
o
H
D
A
O
L
_
P
n
o
t
N
,
M
5
s
n
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
o
t
A
T
A
D
_
S
5
s
n
D
A
O
L
_
S
o
t
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
5
s
n
c
d
o
e
l
c
y
C
y
t
u
D
t
u
p
t
u
O
s
e
d
i
v
i
d
N
n
e
v
E
8
4
2
5
%
s
e
d
i
v
i
d
N
d
d
O
5
4
5
5
t
K
C
O
L
e
m
i
T
k
c
o
L
L
L
P
1
s
m
.
n
o
i
t
c
e
s
n
o
i
t
a
m
r
o
f
n
I
t
n
e
m
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
e
e
S
.
s
t
u
p
n
i
L
A
T
X
g
n
i
s
u
e
c
n
a
m
r
o
f
r
e
p
r
e
t
t
i
J
:
1
E
T
O
N
.
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
d
a
o
l
l
a
u
q
e
h
t
i
w
d
n
a
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
y
l
p
p
u
s
e
m
a
s
e
h
t
t
a
s
t
u
p
t
u
o
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
w
e
k
s
s
a
d
e
n
i
f
e
D
:
2
E
T
O
N
.
s
t
n
i
o
p
s
s
o
r
c
l
a
i
t
n
e
r
e
f
f
i
d
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
h
t
t
a
d
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
.
5
6
d
r
a
d
n
a
t
S
C
E
D
E
J
h
t
i
w
e
c
n
a
d
r
o
c
c
a
n
i
d
e
n
i
f
e
d
s
i
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
p
s
i
h
T
:
3
E
T
O
N
T
ABLE
7. AC C
HARACTERISTICS
, V
CC
= V
CCA
= V
CCO
= 3.3V�5%, T
A
= 0�C
TO
70�C
T
ABLE
4C. LVPECL DC C
HARACTERISTICS
,
V
CC
= V
CCA
= V
CCO
= 3.3V�5%, T
A
= 0�C
TO
70�C
l
o
b
m
y
S
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
C
t
s
e
T
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
s
t
i
n
U
V
H
O
1
E
T
O
N
;
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
h
g
i
H
t
u
p
t
u
O
V
O
C
C
4
.
1
-
V
O
C
C
0
.
1
-
V
V
L
O
1
E
T
O
N
;
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
w
o
L
t
u
p
t
u
O
V
O
C
C
0
.
2
-
V
O
C
C
7
.
1
-
V
V
G
N
I
W
S
g
n
i
w
S
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
t
u
p
t
u
O
k
a
e
P
-
o
t
-
k
a
e
P
6
.
0
5
9
.
0
V
0
5
h
t
i
w
d
e
t
a
n
i
m
r
e
t
s
t
u
p
t
u
O
:
1
E
T
O
N
V
o
t
O
C
C
,
n
o
i
t
c
e
s
"
n
o
i
t
a
m
r
o
f
n
I
t
n
e
m
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
"
e
e
S
.
V
2
-
.
e
r
u
g
i
f
"
t
i
u
c
r
i
C
t
s
e
T
d
a
o
L
t
u
p
t
u
O
V
3
.
3
"

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
7
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
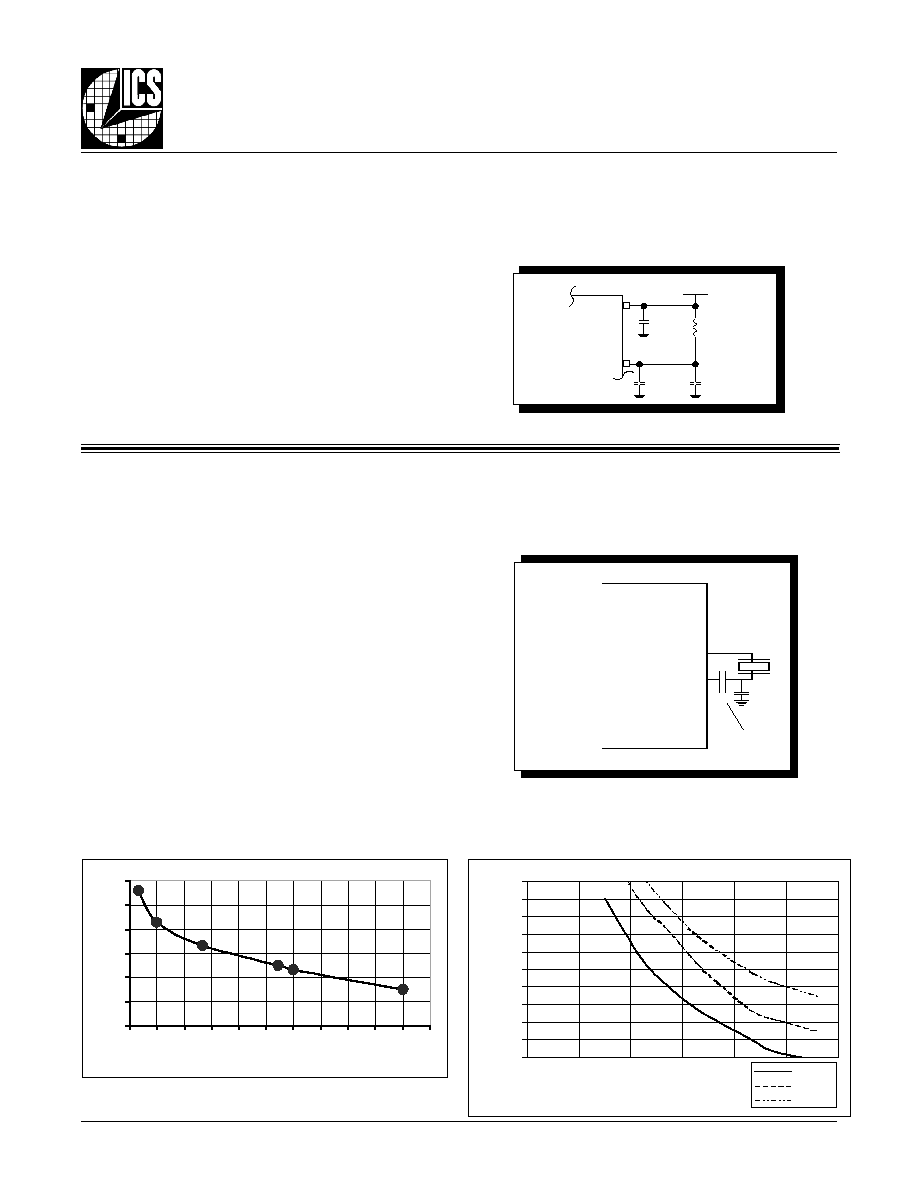
P
ARAMETER
M
EASUREMENT
I
NFORMATION
P
ERIOD
J
ITTER
O
UTPUT
S
KEW
3.3V O
UTPUT
L
OAD
AC T
EST
C
IRCUIT
SCOPE
Qx
nQx
LVPECL
V
CC
, V
CCA
, V
CCO
= 2V
C
YCLE
-
TO
-C
YCLE
J
ITTER
t
jit(cc) =
t
cycle n �
t
cycle n+1
1000 Cycles
t
cycle n
t
cycle n+1
O
UTPUT
R
ISE
/F
ALL
T
IME
V
OH
V
REF
V
OL
Mean Period
(First edge after trigger)
Reference Point
(Trigger Edge)
1
contains 68.26% of all measurements
2
contains 95.4% of all measurements
3
contains 99.73% of all measurements
4
contains 99.99366% of all measurements
6
contains (100-1.973x10
-7
)% of all measurements
Histogram
odc & t
P
ERIOD
V
EE
= -1.3V � 0.165V
tsk(o)
nFOUTx
FOUTx
nFOUTy
FOUTy
nFOUTx
FOUTx
Clock Outputs
20%
80%
80%
20%
t
R
t
F
V
SW I N G
Pulse Width
t
PERIOD
t
PW
t
PERIOD
odc =
FOUTx
nFOUTx
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
8
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
The ICS8430-01 features an internal oscillator that uses an
external quartz crystal as the source of its reference frequency.
A 16MHz crystal divided by 16 before being sent to the phase
detector provides the reference frequency. The oscillator is a
series resonant, multi-vibrator type design. This design provides
better stability and eliminates the need for large on chip capacitors.
Though a series resonant crystal is preferred, a parallel resonant
crystal can be used. A parallel resonant mode crystal used in a
series resonant circuit will exhibit a frequency of oscillation a few
hundred ppm lower than specified. A few hundred ppm translates
to KHz inaccuracy. In general computing applications this level
of inaccuracy is irrelevant. If better ppm accuracy is required, an
external capacitor can be added to a parallel resonant crystal in
series to pin 24.
Figure 3A shows how to interface with a crystal.
Figures 3A, 3B, and 3C show various crystal parameters which
are recommended only as guidelines.
Figure 3A shows how to
interface a capacitor with a parallel resonant crystal.
Figure 3B
shows the capacitor value needed for the optimum ppm perfor-
F
IGURE
3B. Recommended tuning capacitance for various
parallel resonant crystals.
F
IGURE
3C. Recommended tuning capacitance for various
parallel resonant crystals.
14.318
15.000
16.667
24.000
19.440
20.000
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Crystal Frequency (MHz)
S
e
r
i
es
C
apac
itor
, C
1
(
p
F
)
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Series Capacitor, C1 (pF)
F
r
equency A
ccur
a
cy (
ppm
)
19.44MHz
16MHz
15.00MHz
C
RYSTAL
I
NPUT
AND
O
SCILLATOR
I
NTERFACE
A
PPLICATION
I
NFORMATION
F
IGURE
3A. C
RYSTAL
I
NTERFACE
Optional
XTAL2
(Pin 25, LQFP)
XTAL1
(Pin 24, LQFP)
ICS8430-01
mance over various parallel resonant crystals.
Figure 3C shows
the recommended tuning capacitance for various parallel reso-
nant crystals.
As in any high speed analog circuitry, the power supply pins
are vulnerable to random noise. The ICS8430-01 provides
separate power supplies to isolate any high switching
noise from the outputs to the internal PLL. V
CC
, V
CCA
and V
CCO
should be individually connected to the power supply
plane through vias, and bypass capacitors should be
used for each pin. To achieve optimum jitter performance,
power supply isolation is required.
Figure 2 illustrates how
a 10
resistor along with a 10
�
F and a .01
�
F bypass
capacitor should be connected to each V
CCA
pin.
F
IGURE
2. P
OWER
S
UPPLY
F
ILTERING
10
V
CCA
10
�
F
.01
�
F
3.3V
.01
�
F
V
CC
P
OWER
S
UPPLY
F
ILTERING
T
ECHNIQUES
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
9
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
The schematic of the ICS8430-01 layout example used in
this layout guideline is shown in
Figure 5A. The ICS8430-01
recommended PCB board layout for this example is shown in
Figure 5B. This layout example is used as a general guideline.
L
AYOUT
G
UIDELINE
F
IGURE
5A. S
CHEMATIC
OF
R
ECOMMENDED
L
AYOUT
XTAL_SEL
S_DATA
C11
0.1u
R3
50
IN+
C14
0.1u
Termination A
R7
10
R2
84
IN+
R2
50
TEST
MR
R3
125
TL1
Zo = 50 Ohm
Termination B
(Not shown in
the layout)
S_CLOCK
FO
U
T
N
C15
0.1u
FO
U
T
R1
50
VC
C
REF_IN
IN-
VCC
IN-
VC
C
R4
84
X1
TL2
Zo = 50 Ohm
R1
125
U1
8430-01
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
M5
M6
M7
M8
N0
N1
N2
VEE
TEST
VC
C
FO
U
T
1
nFO
U
T1
V
CCO
FO
U
T
0
nFO
U
T0
VEE
MR
S_CLOCK
S_DATA
S_LOAD
VCCA
nXTAL_SEL
TEST_CLK
XTAL1
M4
M3
M2
M1
M0
VC
O
_
SEL
nP_LO
AD
XTAL2
C16
10u
S_LOAD
VCC0
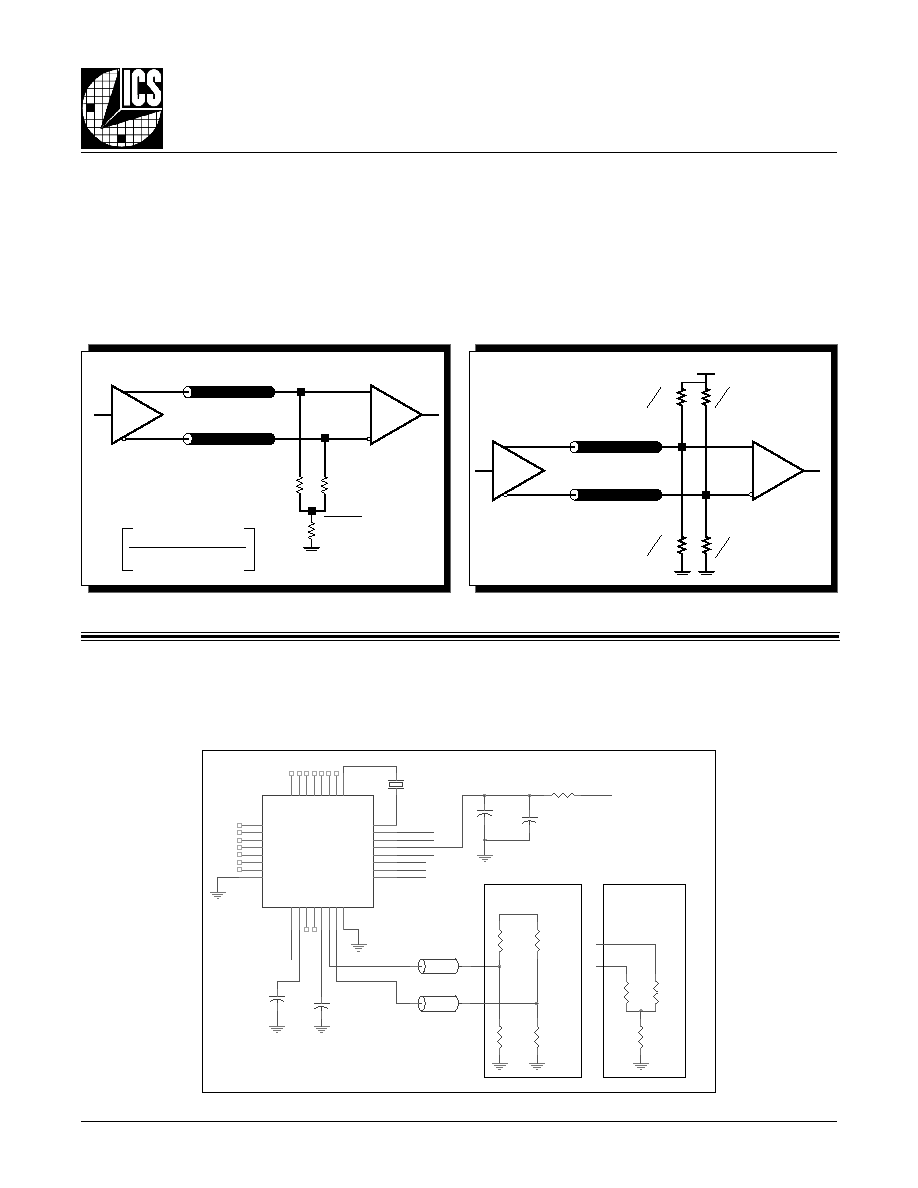
The clock layout topology shown below is a typical termina-
tion for LVPECL outputs. The two different layouts mentioned
are recommended only as guidelines.
FOUT and nFOUT are low impedance follower outputs that
generate ECL/LVPECL compatible outputs. Therefore, terminat-
ing resistors (DC current path to ground) or current sources
must be used for functionality. These outputs are designed to
F
IGURE
4B. LVPECL O
UTPUT
T
ERMINATION
3.3V
F
OUT
F
IN
5
2 Z
o
Z
o
5
2
Z
o
3
2
Z
o
3
2
Z
o
= 50
Z
o
= 50
F
IGURE
4A. LVPECL O
UTPUT
T
ERMINATION
RTT =
1
(V
OH
+ V
OL
/ V
CC
�2) �2
Z
o
50
50
RTT
V
CC
- 2V
F
IN
F
OUT
drive 50
transmission lines. Matched impedance techniques
should be used to maximize operating frequency and minimize
signal distortion.
Figures 4A and 4B show two different layouts
which are recommended only as guidelines. Other suitable clock
layouts may exist and it would be recommended that the board
designers simulate to guarantee compatibility across all printed
circuit and clock component process variations.
T
ERMINATION
FOR
LVPECL O
UTPUTS
Z
o
= 50
Z
o
= 50
The layout in the actual system will depend on the selected
component types, the density of the components, the density
of the traces, and the stack up of the P.C. board.

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
10
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
The following component footprints are used in this layout
example: All the resistors and capacitors are size 0603.
P
OWER
AND
G
ROUNDING
Place the decoupling capacitors C14 and C15 as close as pos-
sible to the power pins. If space allows, placing the decoupling
capacitor at the component side is preferred. This can reduce
unwanted inductance between the decoupling capacitor and the
power pin generated by the via.
Maximize the pad size of the power (ground) at the decoupling
capacitor. Maximize the number of vias between power (ground)
and the pads. This can reduce the inductance between the power
(ground) plane and the component power (ground) pins.
If V
CCA
shares the same power supply with V
CC
, insert the RC
filter R7, C11, and C16 in between. Place this RC filter as close
to the V
CCA
pin as possible.
C
LOCK
T
RACES
AND
T
ERMINATION
The component placements, locations and orientations should be
arranged to achieve the best clock signal quality. Poor clock signal
quality can degrade the system performance or cause system fail-
ure. In the synchronous high-speed digital system, the clock signal
is less tolerable to poor signal quality than other signals. Any ring-
ing on the rising or falling edge or excessive ring back can cause
system failure. The trace shape and the trace delay might be re-
stricted by the available space on the board and the component
location. While routing the traces, the clock signal traces should be
routed first and should be locked prior to routing other signal traces.
� The traces with 50
transmission lines TL1 and TL2 at
FOUT and nFOUT should have equal delay and run ad-
jacent to each other. Avoid sharp angles on the clock trace.
Sharp angle turns cause the characteristic impedance to
change on the transmission lines.
� Keep the clock trace on the same layer. Whenever pos-
sible, avoid any vias on the clock traces. Any via on the
trace can affect the trace characteristic impedance and
hence degrade signal quality.
� To prevent cross talk, avoid routing other signal traces in
parallel with the clock traces. If running parallel traces is
unavoidable, allow more space between the clock trace
and the other signal trace.
� Make sure no other signal trace is routed between the
clock trace pair.
The matching termination resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4 should
be located as close to the receiver input pins as possible. Other
termination schemes can also be used but are not shown in
this example.
C
RYSTAL
The crystal X1 should be located as close as possible to the pins
24 (XTAL1) and 25 (XTAL2). The trace length between the X1
and U1 should be kept to a minimum to avoid unwanted parasitic
inductance and capacitance. Other signal traces should not be
routed near the crystal traces.
F
IGURE
5B. PCB B
OARD
L
AYOUT
FOR
ICS8430-01
TL1, TL2 are 50 Ohm traces and
equal length
C15
C16
VCC
TL
1
R4
VIA
R7
R1
GND
U1
TL1
R3
X1
Close to the input
pins of the
receiver
C14
PIN 1
T
L1N
VCCA
TL1N
R2
C11

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
11
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
P
OWER
C
ONSIDERATIONS
This section provides information on power dissipation and junction temperature for the ICS8430-01.
Equations and example calculations are also provided.
1. Power Dissipation.
The total power dissipation for the ICS8430-01 is the sum of the core power plus the power dissipated in the load(s).
The following is the power dissipation for V
CC
= 3.3V + 5% = 3.465V, which gives worst case results.
NOTE: Please refer to Section 3 for details on calculating power dissipated in the load.
�
Power (core)
MAX
= V
CC_MAX
* I
EE_MAX
= 3.465V * 140mA = 485.1mW
�
Power (outputs)
MAX
= 30.2mW/Loaded Output pair
If all outputs are loaded, the total power is 2 * 30.2mW = 60.4mW
Total Power
_MAX
(3.465V, with all outputs switching) = 485.1mW + 60.4mW = 545.5mW
2. Junction Temperature.
Junction temperature, Tj, is the temperature at the junction of the bond wire and bond pad and directly affects the reliability of the
device. The maximum recommended junction temperature for HiPerClockS
TM
devices is 125�C.
The equation for Tj is as follows: Tj =
JA
* Pd_total + T
A
Tj = Junction Temperature
JA
= Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance
Pd_total = Total Device Power Dissipation (example calculation is in section 1 above)
T
A
= Ambient Temperature
In order to calculate junction temperature, the appropriate junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
JA
must be used. Assuming a
moderate air flow of 200 linear feet per minute and a multi-layer board, the appropriate value is 42.1�C/W per Table 8 below.
Therefore, Tj for an ambient temperature of 70�C with all outputs switching is:
70�C + 0.546W * 42.1�C/W = 93�C. This is well below the limit of 125�C
This calculation is only an example. Tj will obviously vary depending on the number of loaded outputs, supply voltage, air flow,
and the type of board (single layer or multi-layer).
q
JA
by Velocity (Linear Feet per Minute)
0
200
500
Single-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards
67.8�C/W
55.9�C/W
50.1�C/W
Multi-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards
47.9�C/W
42.1�C/W
39.4�C/W
NOTE: Most modern PCB designs use multi-layered boards. The data in the second row pertains to most designs.
T
ABLE
8. T
HERMAL
R
ESISTANCE
q
JA
FOR
32-
PIN
LQFP, F
ORCED
C
ONVECTION
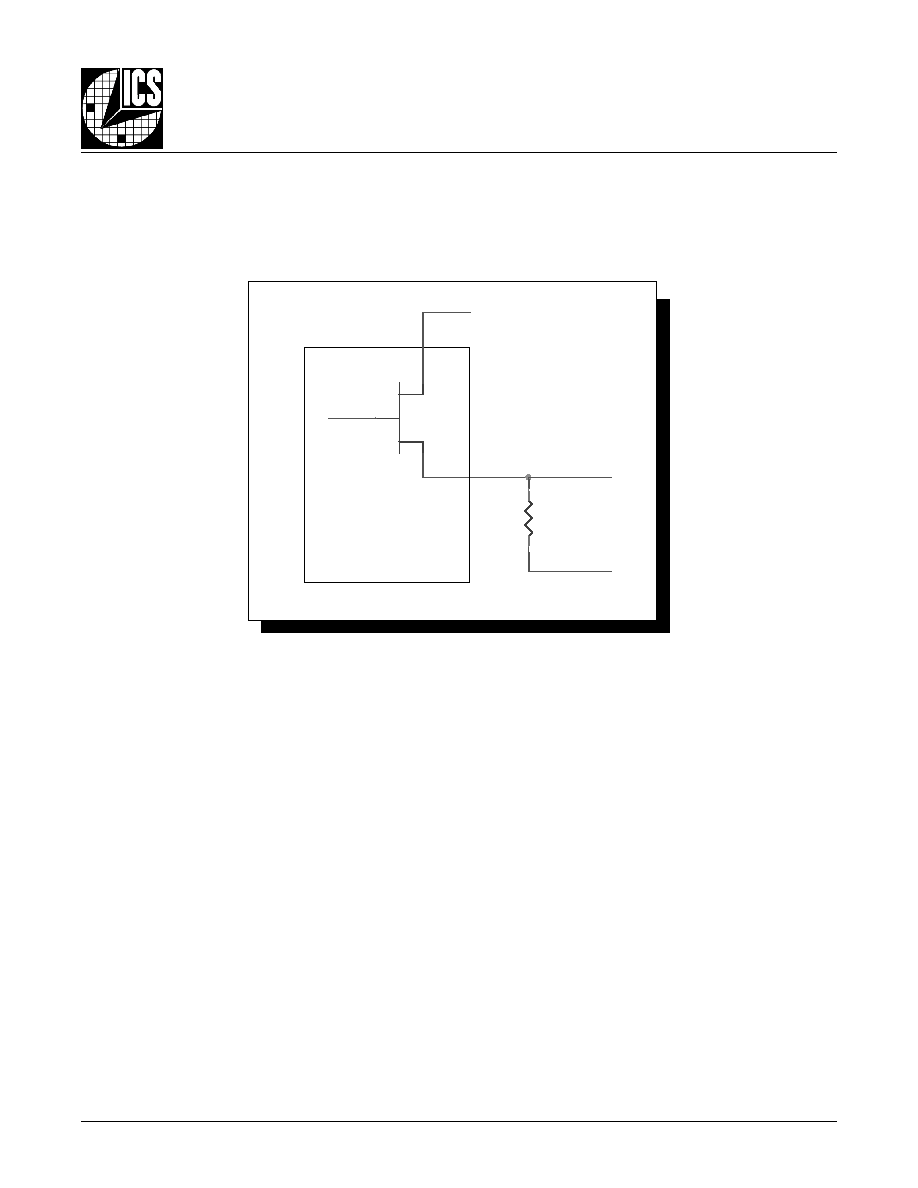
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
12
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
3. Calculations and Equations.
The purpose of this section is to derive the power dissipated into the load.
LVPECL output driver circuit and termination are shown in
Figure 6.
T
o calculate worst case power dissipation into the load, use the following equations which assume a 50
load, and a termination
voltage of V
CCO
- 2V.
�
For logic high, V
OUT
= V
OH_MAX
= V
CCO_MAX
� 1.0V
(V
CCO_MAX
- V
OH_MAX
) = 1.0V
�
For logic low, V
OUT
= V
OL_MAX
= V
CCO_MAX
� 1.7V
(V
CCO_MAX
- V
OL_MAX
) = 1.7V
Pd_H is power dissipation when the output drives high.
Pd_L is the power dissipation when the output drives low.
Pd_H = [(V
OH_MAX
� (V
CCO_MAX
- 2V))/R
L
] * (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OH_MAX
) = [(2V - (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OH_MAX
))/R
L
] * (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OH_MAX
) =
[(2V - 1V)/50
] * 1V = 20.0mW
Pd_L = [(V
OL_MAX
� (V
CCO_MAX
- 2V))/R
L
] * (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OL_MAX
) = [(2V - (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OL_MAX
))/R
L
] * (V
CCO_MAX
- V
OL_MAX
) =
[(2V - 1.7V)/50
] * 1.7V = 10.2mW
Total Power Dissipation per output pair = Pd_H + Pd_L = 30.2mW
F
IGURE
6. LVPECL D
RIVER
C
IRCUIT
AND
T
ERMINATION
Q1
V
OUT
V
CCO
R L
50
V
CCO
- 2V

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
13
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
R
ELIABILITY
I
NFORMATION
T
RANSISTOR
C
OUNT
The transistor count for ICS8430-01 is: 4270
T
ABLE
9.
JA
VS
. A
IR
F
LOW
T
ABLE
q
JA
by Velocity (Linear Feet per Minute)
0
200
500
Single-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards
67.8�C/W
55.9�C/W
50.1�C/W
Multi-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards
47.9�C/W
42.1�C/W
39.4�C/W
NOTE: Most modern PCB designs use multi-layered boards. The data in the second row pertains to most designs.
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
14
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
P
ACKAGE
O
UTLINE
- Y S
UFFIX
T
ABLE
10. P
ACKAGE
D
IMENSIONS
Reference Document: JEDEC Publication 95, MS-026
N
O
I
T
A
I
R
A
V
C
E
D
E
J
S
R
E
T
E
M
I
L
L
I
M
N
I
S
N
O
I
S
N
E
M
I
D
L
L
A
L
O
B
M
Y
S
A
B
B
M
U
M
I
N
I
M
L
A
N
I
M
O
N
M
U
M
I
X
A
M
N
2
3
A
-
-
-
-
0
6
.
1
1
A
5
0
.
0
-
-
5
1
.
0
2
A
5
3
.
1
0
4
.
1
5
4
.
1
b
0
3
.
0
7
3
.
0
5
4
.
0
c
9
0
.
0
-
-
0
2
.
0
D
C
I
S
A
B
0
0
.
9
1
D
C
I
S
A
B
0
0
.
7
2
D
.
f
e
R
0
6
.
5
E
C
I
S
A
B
0
0
.
9
1
E
C
I
S
A
B
0
0
.
7
2
E
.
f
e
R
0
6
.
5
e
C
I
S
A
B
0
8
.
0
L
5
4
.
0
0
6
.
0
5
7
.
0
q
0
�
-
-
7
�
c
c
c
-
-
-
-
0
1
.
0

8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
15
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
ABLE
11. O
RDERING
I
NFORMATION
While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Circuit Systems, Incorporated (ICS) assumes no responsibility for either its use
or for infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would result from its use. No other circuits, patents, or licenses are implied. This product is intended for use
in normal commercial applications. Any other applications such as those requiring extended temperature range, high reliability, or other extraordinary environmental requirements are
not recommended without additional processing by ICS. ICS reserves the right to change any circuitry or specifications without notice. ICS does not authorize or warrant any ICS
product for use in life support devices or critical medical instruments.
r
e
b
m
u
N
r
e
d
r
O
/
t
r
a
P
g
n
i
k
r
a
M
e
g
a
k
c
a
P
t
n
u
o
C
e
r
u
t
a
r
e
p
m
e
T
1
0
-
Y
D
0
3
4
8
S
C
I
1
0
-
Y
D
0
3
4
8
S
C
I
P
F
Q
L
d
a
e
L
2
3
y
a
r
t
r
e
p
0
5
2
C
�
0
7
o
t
C
�
0
T
1
0
-
Y
D
0
3
4
8
S
C
I
1
0
-
Y
D
0
3
4
8
S
C
I
l
e
e
R
d
n
a
e
p
a
T
n
o
P
F
Q
L
d
a
e
L
2
3
0
0
0
1
C
�
0
7
o
t
C
�
0
8430DY-01
www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html
REV. A FEBRUARY 7, 2003
16
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
ICS8430-01
500MH
Z
, C
RYSTAL
-
TO
-3.3V D
IFFERENTIAL
LVPECL F
REQUENCY
S
YNTHESIZER
T
E
E
H
S
Y
R
O
T
S
I
H
N
O
I
S
I
V
E
R
v
e
R
e
l
b
a
T
e
g
a
P
e
g
n
a
h
C
f
o
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
D
e
t
a
D
A
1
T
A
4
T
2
3
5
7
.
m
a
r
g
a
i
d
s
n
o
i
t
a
r
e
p
O
d
a
o
L
l
a
i
r
e
S
&
l
e
ll
a
r
a
P
,
1
e
r
u
g
i
F
d
e
t
a
d
p
U
V
d
n
a
l
a
t
s
y
r
c
,
R
M
d
e
t
a
d
p
u
-
e
l
b
a
T
s
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
D
n
i
P
C
C
.
s
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
d
V
d
e
t
c
e
r
r
o
c
-
s
c
i
t
s
i
r
e
t
c
a
r
a
h
C
C
D
y
l
p
p
u
S
r
e
w
o
P
C
C
d
a
e
r
o
t
r
e
t
e
m
a
r
a
P
.
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
y
l
p
p
u
S
e
v
i
t
s
o
P
m
o
r
f
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
y
l
p
p
u
S
e
r
o
C
V
d
e
t
c
e
r
r
o
c
-
m
a
r
g
a
i
d
t
i
u
c
r
i
C
t
s
e
T
d
a
o
L
t
u
p
t
u
O
V
3
.
3
E
E
d
a
e
r
o
t
n
o
i
t
a
u
q
e
V
E
E
.
V
5
3
1
.
0
�
.
.
.
f
o
d
a
e
t
s
n
i
V
5
6
1
.
0
�
V
3
.
1
-
=
.
t
a
m
r
o
f
t
e
e
h
s
a
t
a
d
d
e
t
a
d
p
U
2
0
/
9
1
/
2
1
A
1
T
2
3
d
a
o
L
l
a
i
r
e
S
&
l
e
ll
a
r
a
P
,
1
e
r
u
g
i
F
n
i
s
l
e
b
a
l
A
T
A
D
_
S
d
n
a
K
C
O
L
C
_
S
d
e
t
c
e
r
r
o
C
s
n
o
i
t
a
r
e
p
O
.
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
d
R
M
d
e
s
i
v
e
r
-
e
l
b
a
T
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
D
n
i
P
3
0
/
7
/
2















