
Two fully programmable serial 1/0
channels (DC TO 512K BAUD )
Tri-state TTL drive capabilities for
bi-directional data bus and control bus
on each channel
Loopback control for communications
link fault isolation for each UART
Line break generation and detection
for each UART
Complete status reporting capabilities
Generation and stripping of serial
asynchronous data control bits
(start ,stop parity )
Programmable baud rate generator
and modem control signals for each
channel
Fully prioritized independent interrupt
system controls for each channel
16byte FIFO buffers on both transmit
and receive of each channel to reduce
number of interrupts presented to the
CPU
Programmable FIFO threshold loves
of 1,4,8,or 14,bytes on each channel
Two modes of DMA signaling
available for transfer of data
characters to and from FIFO buffers
Fully bi-directional centronics
compatible parallel port direct printer
interface
Advanced CMOS low power
technology with single +5voit supply
68-pin PLCC package
1
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
Data Communications
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
Key Features
Dual Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
with 16-BYTE FIFO & Parallel Printer Port
Pin Configuration
.
.
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
SOUT1
DTR1*
RTS1*
DSR1*
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
TXRdy0*
VCC
RTS0*
DTR0*
SOUT0
DSR*D
INT2
SLIN*+
INIT*+
AFD*+
STB*+
VSS
PD0
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
PD5
PD6
PD7
INT0
BDO
VS
S
D
S
R
O
*
R
LS
D
0
*
RI
0
*
D
S
R
*
C
S
O
*
A
2
A
1
A
O
IO
W
*
I
O
R
*
C
SO
*
RE
SE
T
∑
VCC
SIN
0
T
XR
D
y
1
*
VS
S
R
xr
dy
0
*
RIS
D
1
*
VSS
RI
1
*
DS
R
1
*
CL
K
CS
O
)
V
SS
L
P
T
O
E
*
A
CK
PE
BU
SY
SL
CT
VC
C
ER
RO
R
*
STS
1
R
X
R
d
y
1
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
16C552
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
IMP

The low power COMS IMP16C522 is a single
device solution for serving two serial
input/output ports simultaneously and one fully
bi-directional parallel port for the IBM PC ATM
PS/2 and compatible systems. The parallel
port is full compatible to the Centronics printer
port and IBM serial parallel Adapter. Each
Universal Asynchronous Receiver and
transmitter (UART) is fully programmable.
Each UART in the IMP16C522 is capable of
buffering up to 16 bytes of data upon reception,
relieving the CPU of interrupt overhead.
Buffering of data also allows greater latency
time in interrupt servicing which is vital
in a multitasking environment, DMA signaling
between the internal FIFO buffers and host
CPU allows single or multiple character
transfers. Each UART has a maximum
recommended data rate of 256k with a clock
frequency of 80MHZ
The IMP16C552 is an enhanced dual channel
version of the IMP16C550A Universal
Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter
(UART) plus a bi-directional parallel data port
which fully support a Centronics compatible
printer interface
The two serial input/output Universal
Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter interface
simultaneously in microprocessor-based
system. Each UART performs parallel-to-serial
conversion on the output and serial-to parallel
conversion on the input. Two modes of
operation exits for each I/0 channel after
a hardware reset. Each UART is functionally
compatible to the IMP16C450(character
mode)and an alternate mode (FIFO
mode)which is only available on the IMP16C552
It can be activated through software relieving
the CPU of excessive overhead due to due to
interrupts. The complete status of each UART
can be read at any time from internal
registers. The parallel port allows information
received from the data base to be printed. The
parallel port together with the two serial ports,
provides IBM PC ATM and PS/2tm compatible
with a single device solution.
2
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
Description
General Description
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

FIGURE 2 -
IMP16C552 Block Diagram
UART 0
SELECT 1
CONTROL
LOGIC
RCVR BUFR
REGISTER
RCVR SHIFT
REGISTER
RECEIVER
FIFO
XMIT HOLD
REGISTER
XMIT SHIFT
REGISTER
SIN0
SOUT0
XMIT FIFO
MODEM
CONTROL
RTS0*
DTR0*
CTR0*
DSR0*
RLSD0*
RI0*
RCVR BUFR
REGISTER
RCVR SHIFT
REGISTER
RECEIVER
FIFO
XMIT HOLD
REGISTER
XMIT SHIFT
REGISTER
SIN1
SOUT1
XMIT FIFO
MODEM
CONTROL
RTS1*
DTR1*
CTS1*
DSR1*
RLSD1*
RI1*
PARALLEL
PORT
PD0-PD7
INIT*
AFD*
STB*
SLIN*
INIT2*
PARALLEL
PORT
SELECT
AND
CONTROL
LOGIC
ERR*
SLCT*
BUSY*
PE
ACK*
LPTOE*
INT0
TXRDY0*
RXRDY0*
DATA
BUS
BUFFER
D0-D7
SELECT
AND
CONTR
OL
LOGIC
A0
A1
A2
IOW*
IOR*
CLK
MR*
CS1*
CS2*
CS0*
UART 1
SELECT 2
CONTROL
LOGIC
INT1
TXRDY1*
RXRDY1*
3
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

Note: in the following descriptions a low represents a logic 0 and high represents a logic 1
Mnemonic Pin
type
Pin# description
CSO*,CS1*
CS2*
IOR*
IOW*
CLK
A2,A1,A0
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
32,3,38
37
36
4
33,34
35
Chip select pins: when CS0,CS1 and CS2 are low the chip is selected
this enable communication between the device and the CPU cs0 selects
serial channel 0,CS1* selects serial channel 1 and CS2* selects the
parallel port
Read strobe :when IOR* is low while the chip is selected the CPU can
write status information or data from the selected register of serial
channel 0, serial channel 1,or parallel port
Write strobe : when IOW* is low while the chip is selected the CPU can
write control words or data into the selected register of senal channel
0,serial channel 1,or parallel port
Clock: external clock input
Register Select pins :Address signals connected to these 3 input s
select a register for the CPU to read from or write to during data transfer
A table of registers for serial channel 0,1 parallel port and their
addresses is shown below .Note that the state of the Divisor latch
Access Bit (DLAB)of each channel ,affects the most significant bit of
the line control register of each channel affects the selection of certain
registers the DLAB must be set high by the system software to access
the baud generator Divisor Latches
REGISTER ADDRESSES
Serial channel 0 or1
DLAB A2 A1 A0 Register
0 0 0 0 Receiver buffer register(read)
0 0 0 0 Transmitter holding register(write)
0 0 0 1 Interrupt enable register
x 0 1 0 Interrupt Identification register(read)
x 0 1 0 FIFO control register(write)
x 0 1 1 line control register
x 1 0 0 MODEM control register
x 1 0 1 line status register
x 1 1 0 MODEM status register
x 1 1 1 Scratch pad register
1 0 0 0 Divisor latch register (least significant byte)
1 0 0 0 Divisor latch register (most significant byte)
Parallel port
x x 0 0 port data register
x x 0 1 port status (read only )
x x 1 0 port control register
x x 1 1 not allowed
4
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
Pin Description
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
Mnemonic Pin
type
Pin# description
RESET
SIN0 STS1
DSR0*,
DSR1*
DSR0*
DSR1*
RLSD0*
RISD1*
RI0* RI1*
VCC
VSS
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
39
41.62
28.13
31.5
29.8
30.6
23.40.64
2.7.27
43.54
Master reset: When this input is low it clears all the register(except the
Receiver Buffer, Transfer Holding and Divisor Latches) and the control
logic of the both channels and parallel port the states of various output
signals are affected by an active RESET input (refer to table 1) .this
input is buffered with a TTL-compatible schmitt trigger with 0.5v
hysteresis.
Serial inputs :Serial data input from the communication link such as
peripheral device , MODE or data set to the associated serial channel
Clear To Send: When low this pin indicates that the MODEM or data
set is ready to exchange data The CTS0(1)*.signal is a MODEM status
input whose conditions can be tested by the CPU reading bit4(CTS)of
the MODEM Status Register Bit4 is the complement of the CTS0(1)
signal Bit 0 (DCTS )of the MODEM status register indicates whether the
CTS(1)* input has changed state since the previous reading of the
modem status register CTS0(1)* has no the Transmitter
Note: whenever the CTS bit of the MODEM status register changes
state an interrupt is generated if the MODEM status interrupt is enabled
Data Set Ready :When low this pin indicates that modem or data set is
ready to establish the communication link with the UART the DSR0(1)
signal is a MODEM status input whose condition can be tested by the
CPU reading bit 5 (DSR)of the MODEM status register bit 5 is the
complement of the DSR0(1)* signal. bit 1 (DDSR) of the MODEM Status
Register Indicates whether the DSR0(1)* input has changed state since
the previous reading of the MODEM Status Register DSR0(1)* has no
the transmitter
Note: Whenever the DSR bit of the MODEM Status Register changes
state, an interrupt is generated if the MODEM status interrupt is enable
Receiver Line Signal Detect: When low ,this pin indicates that the data
canter has been detected by the MODEM or data set The RLSD0(1)*
signal is a MODEM status input whose condition can be tested by the
CPU reading bit 7(RLSD)of the MODEM Status Register Bit 7 is the
complement of the RLSD0(1)* signal. Bit 3 (DRLSD) of the MODEM
Status Register indicates whether the RLSD0(1)* input has changed
state since the previous reading of the MODEM Status Register
RLSD0(1)* has no effect on the receive
Note: whenever the RLSD bit of the MODE status register changes state
on interrupt is generated if the MODEM status interrupt is enable
Ring indicator : when low this pin indicates that a telephone ringing
signal has been received by the MODEM or data set The RI0(1)* signal
is a MODEM status input whose condition can be tested by the CPU
reading bit 6 (RI) of the MODEM Status Register Bit 6 is the
complement of the RI0(1) signal Bit2 (TERI) of MODEM Status
Register indicates whether the RI0(1) input signal has changed from a
low to a high state since the previous reading of the MODEM Status
Register.
Note: whenever the RI bit of the MODEM Status Register changes from
a low to a high state an interrupt is generated if the MODEM status
interrupt is enabled
+5V supply
Ground
5
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
Mnemonic Pin
type
Pin# Description
DTR0*
DTR1*
RTS0*
RTS1*
TXRdy0*
TXRDy1*
Rxrdy0*
RXRdy1
BDO
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
25,11
24,12
22,42
9,61
44
Data Terminal Ready :When low this informs the MODEM or data set
that the UART is ready to establish a communication link The
DTR0(1)* output signal can be set to an active low by programming bit 0
(DTR) of the MODEM Control Register to a 1.A Master reset operation
sets this inactive (high) state. Loop mode operation holds this signal in
its inactive state
Request To Send: When low this informs the MODEM or data set that
the UART is ready to exchange data. The RTS0(1)* output signal can be
set to an active low by programming bit 1 (RTS)of the MODEM Control
register to a 1.A Master Reset operation sets this signal to its inactive
(high) state . Loop operation holds this signal in its inactive state
Transmitter Ready pins: Transmitter DMA signalling is available through
this pin for each serial channel When operating in the FIFO mode one
of two types of DMA signaling can be selected via FCR3. When
operating as in the Character Mode, only DMA mode 0is allowed. Mode
0 supports single transfer multi-transfer DMA where multiple transfers
are made continuously until the XMIT FIFO has been filled
TXRDY mode 0:when in non FIFO mode (FCR3=1) or in the FIFO mode
(FCR0=1,FCR3=0) there are no characters in the XMIT FIFO or XMIT
holding register the TXRDY pin will be low active . once it is activated
the TXRDY0 TXRDY1.pin will go inactive after the first character is
loaded into the XMIT FIFO or holding register
TXRDY MODE 1:In the FIFO Mode (FCR0=1,FCR3=1)if there is at least
one untilled position in the XMIT FIFO, it will go low active. This pin will
become inactive when the XMIT FIFO is completely full
Receiver Ready pins: Receiver DMA signaling is available through this
pin when operating in the FIFO mode one of two types of DMA
signaling can be selected via FCR3. When operating as in the Character
Mode, only DMA mode O is allowed Mode 0supports single transfer
DMA where a transfer is made between CPU bus cycles Mode 1
supports multiple transfers DMA where multiple transfer are made
continuously until the RCVR FIFO has been emptied
RXRDY Mode 0: When in the FI FO Mode (FCR=0)or in the FIFO Mode
(FCR0=1.FCR3=0)there is at least 1 character in the RCVR FIFO or
RCVR holding register the RXRDY0*, RXRDY1* pin will go low active,
Once it is activated the RXRDY0*, RXRDY1* pin will go inactive when
there are no more characters in the FIFO or holding register
RXRDY MODE 1: in the FIFO mode (FCR0=1,FCR3=1 ) the trigger level
or the timeout has been reached, the RXRDY0*, RXRDY1* pin will go
low active. Once it is activated it will go inactive when there are no more
characters in the FIFO or holding register.
Bus Buffer Output :This goes high whenever the CPU is reading data or
status from either the serial channel or parallel port It can be used to
disable or control direction of a data bus transceiver between the CPU
and the device.
6
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

Mnemonic Pin
type
Pin# description
INT0.INT1
SOUT0
SOUT1
D0-D7
PD7-PD0
STB*+
AFD*+
INIT*+
SLIN*+
INT2
ERROR*
SLCT
BUSY
PE
ACK
OUT
OUT
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
1/0
0
1
1
1
1
1
45.50
26.10
14-21
46-53
55
56
57
58
59
63
65
66
67
68
Serial channel interrupts Tri-state @ output (enable by bits of MCR of
each serial channel )goes high whenever an interrupt is pending for the
associated serial channel These pins are tri-stated whenever associated
channel is in loopback mode. These pins are reset during a Master
Reset.
Serial Output pins: Composite serial data output to the communications
link (peripheral MODEM or data set )the SOUTO S0 SOUT1 signal is
set to the marking(logic 1)state upon a Master Reset operation
Data Bus D0--D7: Tri-StateÆ bus provides bi-directional
communications between the UART and the CPU Data control words
and status information are transferred via the D0-D7 Data bus
Parallel Port Data Bus: Bi-directional data port which provides parallel
input and output to the system. The eight lines are hold in a
high-impedance state when LPTOE is high
Line printer Strobe: Output line when active (low) provides the line
printer with a signal to latch the data currently on the parallel port data
bus
Line printer Auto Teed: Output line when active (low) provides signal for
the line printer to auto feed continuous form paper
Line Printer Initiallze : Output line to printer when active (low) signal
the line printer to begin an initialization routine
Line printer Select :Output line when active (low)selects the printer
Parallel Port Interrupt :Tri-StateÆ output (enable by bit 4 of the Printer
Control Register ) goes active on the positive transition of ACK*. This
interrupt is reset low upon a reset operation or after pending interrupts
are serviced
Line Printer Error :Input line from the line printer informs the parallel port
of an error by inputting an active low signal Set low by the printer upon a
deselect condition PE or other error condition
Line Printer Select :input from the line printer that goes high when the
line printer has been selected
Line Printer Busy :input from the line printer that goes high when the line
printer has an operation in progress
Paper Empty :input form the line printer goes high when the printer is
out of paper
Printer Acknowledge :input form line printer that goes low to confirm the
data transfer from the MS16C552 to the printer was successful. This
input control INT2 pin directly.
Line Printer Output Enable: When low this input signal enables the
parallel port data bus as output. When high the parallel port data bus
pins are hold in a high impedance state. For normal line printer
operation, this line may be permanently grounded.
7
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
LPTOE*
1
1
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
MASTER RESET
A low level input on RESET* pin reset both serial channels and parallel port and forces internal
register and output pins as shown in Table 1.
TABLE1-Reset Configuration of Registers and Output signal for serial channel
Register/signal
Reset control
Reset state
Interrupt Enable register
Interrupt Identification
Register
Line Control Register
Mode Control Register
Line Status Register
Mode Status Register
SOUT
INTRPT(RCVR ERRS)
INTRPT(RCVR DATA READY)
INTRPT(THRE)
RTS*
DTR*
RCVR FIFO
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset
MODEM Signal Inputs
Master Reset
Master Reset/Read LSR
Master Reset /Read RBR
Master Reset /Read II/write
THR
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset
All bits low-bits(4-7)are
Permanently low
Bit 0is forced high and
bits(1-3),6,7are Forced
low-bits 4and 5are
permanently Low
All bits low
All bits low-bits (5-7) are
permanently Low
All bits low-except nits
5.6which are high
Bits(0-3) low
Bits(4-7)follow input signals
High
Low
Low
Low
High
High
Undefined data
8
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
Operational Description
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
TABLE1-Reset Configuration of Register and Output Signal for each serial channel
(continued)
Register/signal
Reset control
Reset state
XMIT FIFO
FIFO CONTROL
RXRDY∞ ,TXRDY∞
Parallel port
Port data register
Port status register
Port control register
STB∞AFD∞INIT∞SLIN
INT2
Master Reset
Master Reset
Master Reset/internal
conditions
Master Reset
According to Status Pins
Master Reset
Master Reset
According to ACK* INPUT
when enable
Undefined data
All bits low-{(0-3),6,7forced
and 4,5 permanent}
High
All bits low
Undefined
All bits low except bits 5,6,7
which are high
All pins high except INIT*
which is low
Tri-StatedÆ
9
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
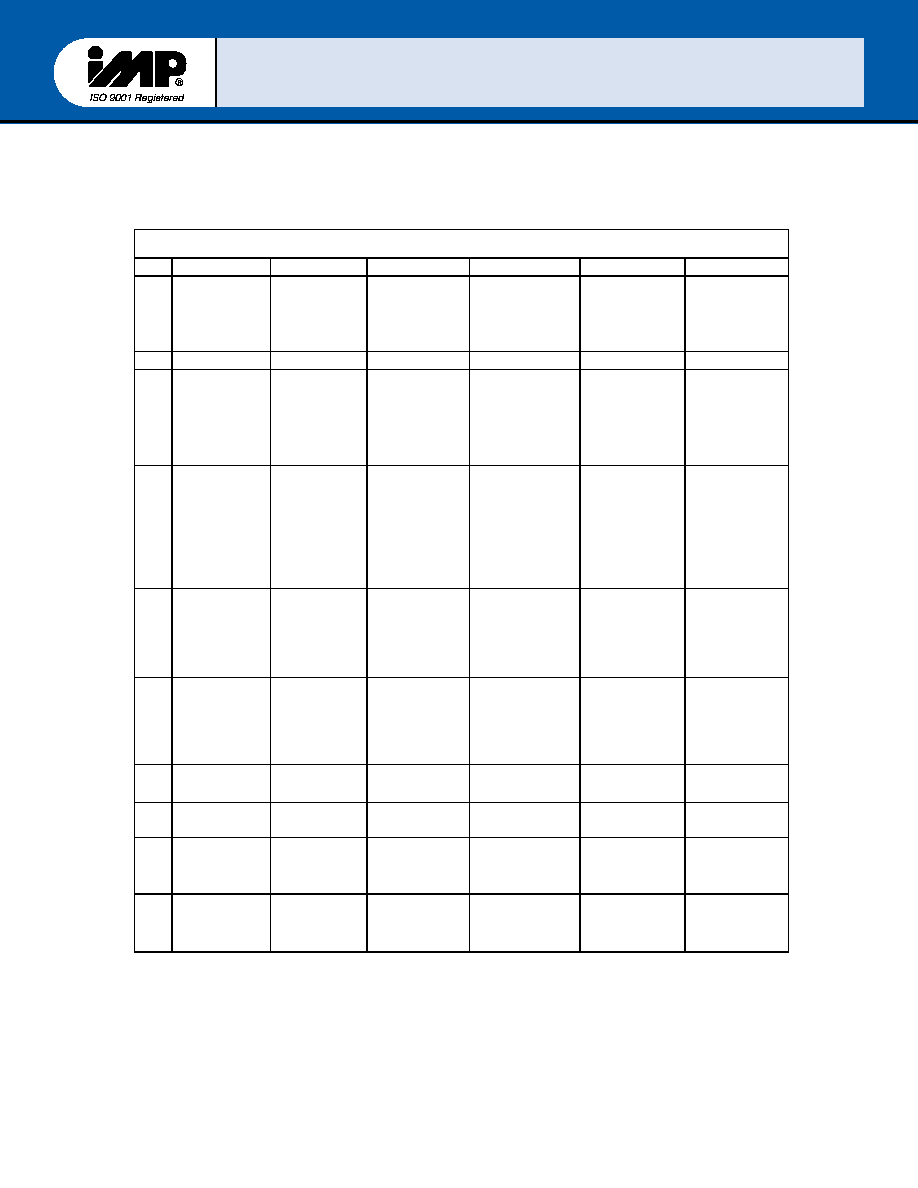
INTERALL REGISTER DESCRIPTION
The system programmer has access to any of the register as summerized in Table II
Table II Accessible
IMP16c552 Registers for each serial channel
Register address
0DLAB=0 0DLAB=0 1DLAB=0 2
2
3
Bit
no
Receiver
Buffer
Register
(Read only)
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Interrupt
Enable
Register
Interrupt
Identification
Register
(Read only)
FIFO control
Register
(Write only)
Line
Control
Register
RBR
THR
IER
IIR
FCR
LCR
0
Data Bit 0
Data Bit0
Enable
Receiver
Data register
Interrupt
(ERBF)
``0"if
Interrupt
Pending
FIFO
Enable
(FEWO)
Word Length
Select bit 0
(WLSO)
1
Data Bit 1
Data Bit 1
Enable
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Empty
Interrupt
(ETBEI)
Interrupt
ID bit 0
(IIDB0)
Receiver
FIFO
Reset
(RFR)
Word
length
Select bit 1
(WLS1)
2
Data Bit 2
Data Bit 2
Enable
Receiver
Line status
interrupt
(ERLS)
Interrupt
ID bit 1
(IIDB1)
Transmitter
FIFO
Reset
(TFR)
Number of
Stop Bits
(STB)
3
Data Bit3
Data Bit3
Enable
MODEM
Status
interrupt
(EDSSI)
Interrupt
ID bit 2
(IIDB2)
DMA
Mode
Select
(DMS)
Parity
Enable
(PEN)
4
Data Bit4
Data Bit4
0
0
Reserved
Even parity
Select (EPS)
5
Data Bit5
Data Bit5
0
0
Reserved
Stick parity
(STP)
6
Data Bit6
Data Bit6
0
FIFO
Enable(*)
(FE)
RCVR FIFO
Trigger
Level (LSB)
Set Break
Control
7
Data Bit7
Data Bit7
0
FIFO
Enable(*)
(FE)
RCVR FIFO
Trigger
Level (MSB)
Divisor Latch
Access bit
(DLAB)
10
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
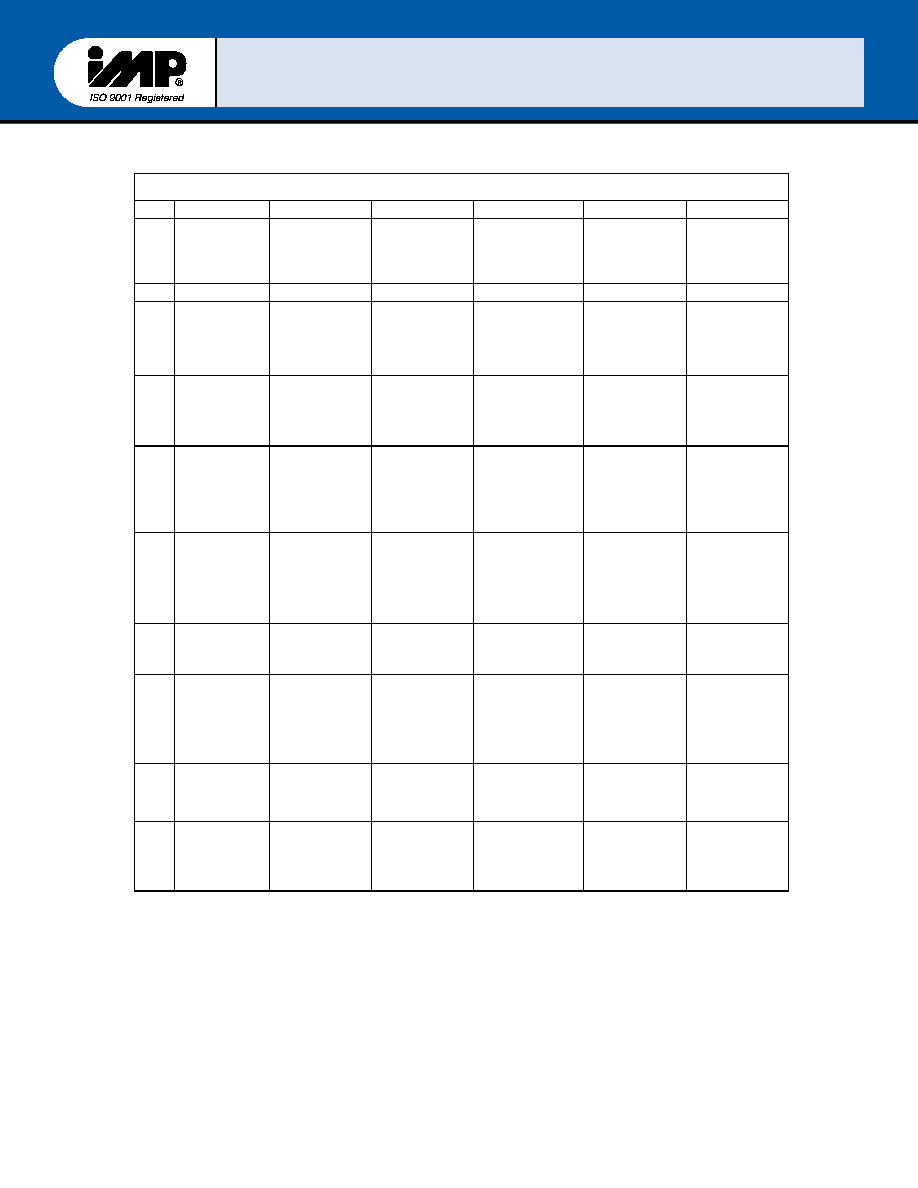
Table II Accessible
IM16c552 Registers for each serial channel
Register address
4
5
6
7
0DLAB=1 1DLAB=1
Bit
no
MODEM
Control
Register
Line status
Register
(read only)
MODEM
Status
Register
Scratch
Pad
Register
Divisor
Latch
(LSB)
Divisor
Latch
(MSB)
MCR
LSR
MSR
SCR
DLL
DLM
0 Data
Terminal
Read
(RTS)
Data
Ready
(DR)
Delta
Clear to
Send
(DCTS)
Bit 0
Bit 0
Bit 8
1 Request
to
send (RTS)
Overrun
Error
(OE)
Delta
Data set
Ready
(DDSR)
Bit 1
Bit 1
Bit 9
2
Cut 1
Parity
Error
(PE)
Trailing
Edge Ring
Indicator
(TERI)
Bit 2
Bit 2
Bit 10
3
Out 2
(INTE)
Framing
Error
(FE)
Delta
Receiver
Line
Detect
(DRLSD)
Bit 3
Bit 3
Bit 11
4 Loop
Break
Interrupt (BI)
Clear to
Send (CTS)
Bit 4
Bit 4
Bit 12
5 0
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Empty
(THRE)
Data Set
Ready
(DSR)
Bit 5
Bit 5
Bit 13
6 0
Transmitter
Empty
(TEMT)
Ring
Indicator
(RI)
Bit 6
Bit 6
Bit 14
7 0
Error
in
RCVR
FIFO(``)
(EIRF)
Receive
Line Signal
Detect
(RLSD)
Bit 7
Bit 7
Bit 15
(*) These bits are read 0 in Character Mode of IMP16C552
11
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
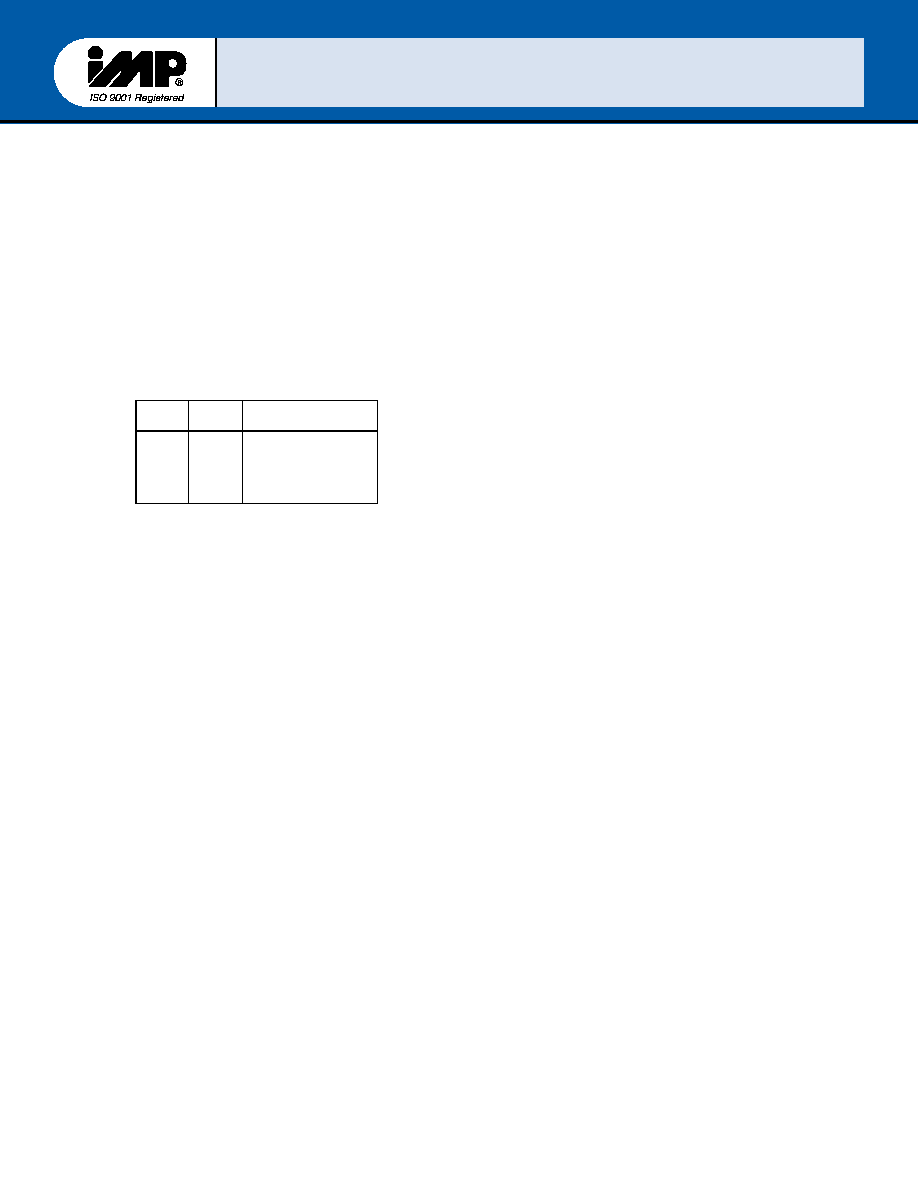
Line Control Register
The system programmer specifies the format
of the asynchronous data communications
exchange and sets the divisor latch access bit
via the line control register (LCR) the
programmer can also read the contents of the
line control register the read capability
simplifies system programming and eliminates
the need for separate storage in system
memory of the line characteristics
Bits 0 and1 : these two bit s specify the
number of bits each transmitted or serial
character the encoding of bits 0and 1 is as
follows:
Bit 1
Bit 0
Character length
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
5bits
6bits
7bits
8bits
Bit 2: this bit specifies the number of stop bits
transmitted and received in each serial
character if bit 2is a logic 0 0ne stop bit is
generated in the transmitted data if bit 2 is
logic 1 when a 5-bit word length is selected
via bits 0 and1 ,0ne and half stop bits are
generated if bit 2 is a logic 1 when either a
6-7- ,or 8-bit word length is selected .2 stop
bits are generated the receiver checks the fist
stop-bit only regardless of the number of stop
bits selected
Bit3:this bit is the parity enable bit when bits 3
is a logic 1 a parity bit is generated (transmit
data)or checked (receive data )between the
last data word bit and stop bit of the serial
data (the parity bit is used to produce an ever
or odd number of 1's when the data word bits
and the parity bit are summed
Bit 4:this bit is the even parity selects bit when
bit 3 is a logic 1 and bit 4 is a logic 0 an odd
number of logic 1 `s is transmitted or checked
in the data word bits and parity bit when bit 3
is a logic 1 and bit 4 is a logic 1 and even
number of logic 1s is transmitted or checked
in the data word bits and parity bit
Bit 5: this bit is the stick parity bit when bits 3
and 5 are logic 1 the parity bit is transmitted
and detected by the receiver in the opposite
state indicated by bit 4 is bit 5 is zero stick
parity is disabled
Bit 6:thus bit is the break control bit it causes
a break control condition to be transmitted to
the receiving UART when bit 6 set to a logic 1
the serial output (SOUT) is forced to the
spacing (logic0) state and remains there until
bit 6 is set to a logic 0 this bit acts only on
SOUT pin and has no effect on transmitted
logic this feature enable the CPU to alert a
terminal in a computer communications
system if the following sequence is followed
no erroneous characters will be transmission
because of break.
1 .Load an all 0s pad character in response to THRE
2. set break after the next THER
3. wait for the transmitted to be idle (TEMT=1) and clear
break when normal transmitted has to be restored
During the break the transmitted can be the
used as a character time to accurately
establish the break duration
Bit 7:this bit the divisor latch access bit (DLAB)
it must be set high (logic1)to access the
divisor latches of the baud rate generator
during a read or write operation it must be
set low (logic 0) to access the receiver buffer
the transmitter holding register or the interrupt
enable register
Programmable baud rate generator
The UART contains a programmable baud
generator that is capable of taking any clock
input from DC to 8 0 MHz and dividing it by
any divisor from 1 to 2
≠1 the output
frequency of the baud generator is 16 x the
baud rate two 8-bit latches store the divisor in
a 16-bit binary format. These Divisor Latches
must be loaded during initialization to ensure
proper operation of the Baud Rate Generator.
Upon loading either of the Divisor Latches, a
16-bit Baud counter is immediately loaded.
This prevents long counts on initial load.
Table III. IV and V illustrate the use of the
Baud Rate Generator with three different
driving frequencies. Table III references to a
1.8430 MHz clock, table IV to a 3.070 MHz
clock, and table V to a 8 MHz clock. For baud
rates of 38400 and below, the error obtained
is minimal. The accuracy of the desired baud
rate is dependent on the crystal frequency
chosen. Using a divisor of zero is not
recommended. In no case should the data
rate be greater than 512K baud.
12
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
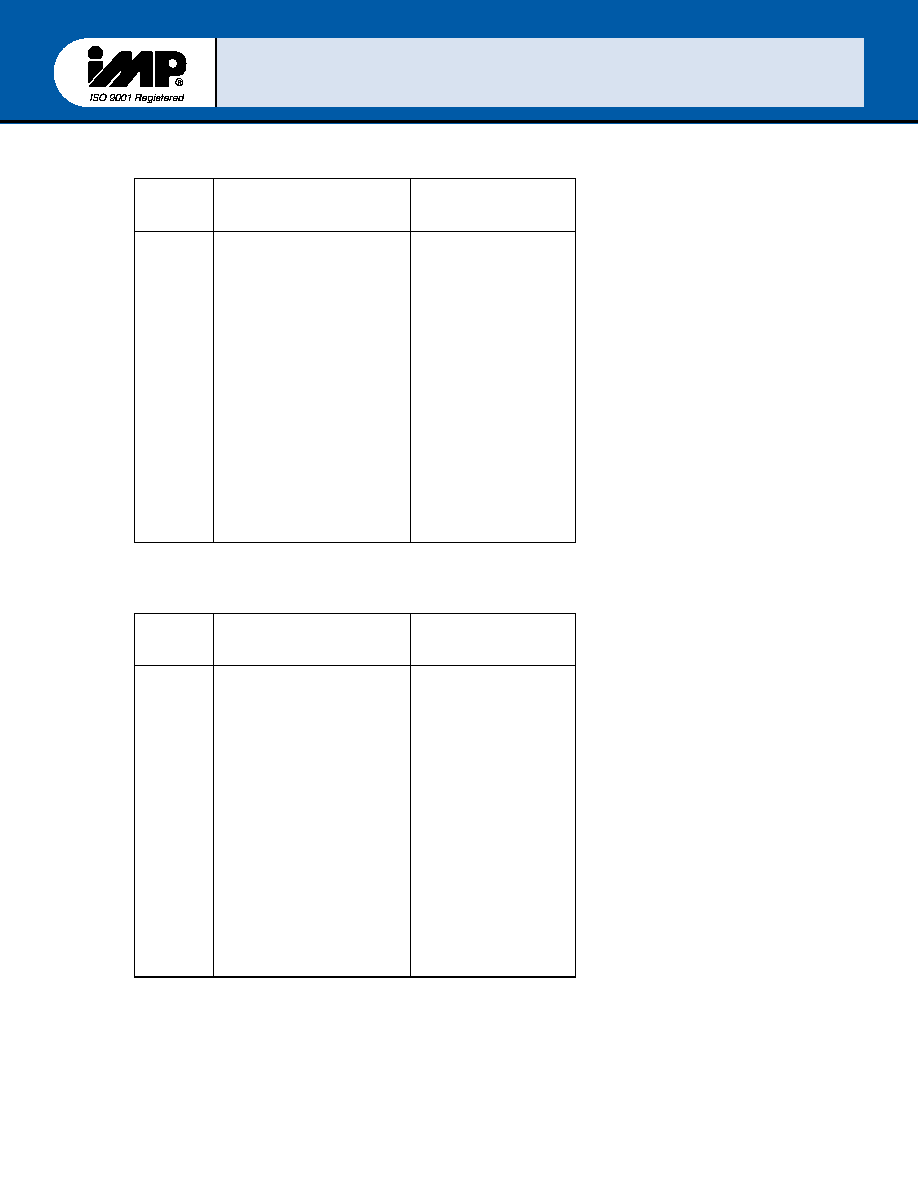
TABLE lll- Baud Rates Using 1.8432 MHz Clock
Desired
Baud
Rate
Divisor Used
to Generate
16x Clock
Percent Error
Difference Between
Desired and Actual
50
75
110
134.5
150
300
600
1200
1800
2000
2400
3600
4800
7200
9600
19200
38400
56000
2304
1536
1047
857
768
384
192
96
64
58
48
32
24
16
12
6
3
2
-
-
0.026
0.058
-
-
-
-
-
0.690
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
2.860
TABLE IV- Baud Rate using 3.072 MHz clock
Desired
Baud
Rate
Divisor Used
To Generate
16x clock
Percent Error
Difference Between
Desired and Actual
50
75
110
134.5
150
300
600
1200
1800
2000
2400
3600
4800
7200
9600
19200
38400
56000
3840
2560
1745
1428
1280
640
320
160
107
96
80
53
40
27
20
10
5
3
-
-
0.026
0.034
-
-
-
-
0.312
-
-
0.628
-
1.230
-
-
-
14.285
13
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
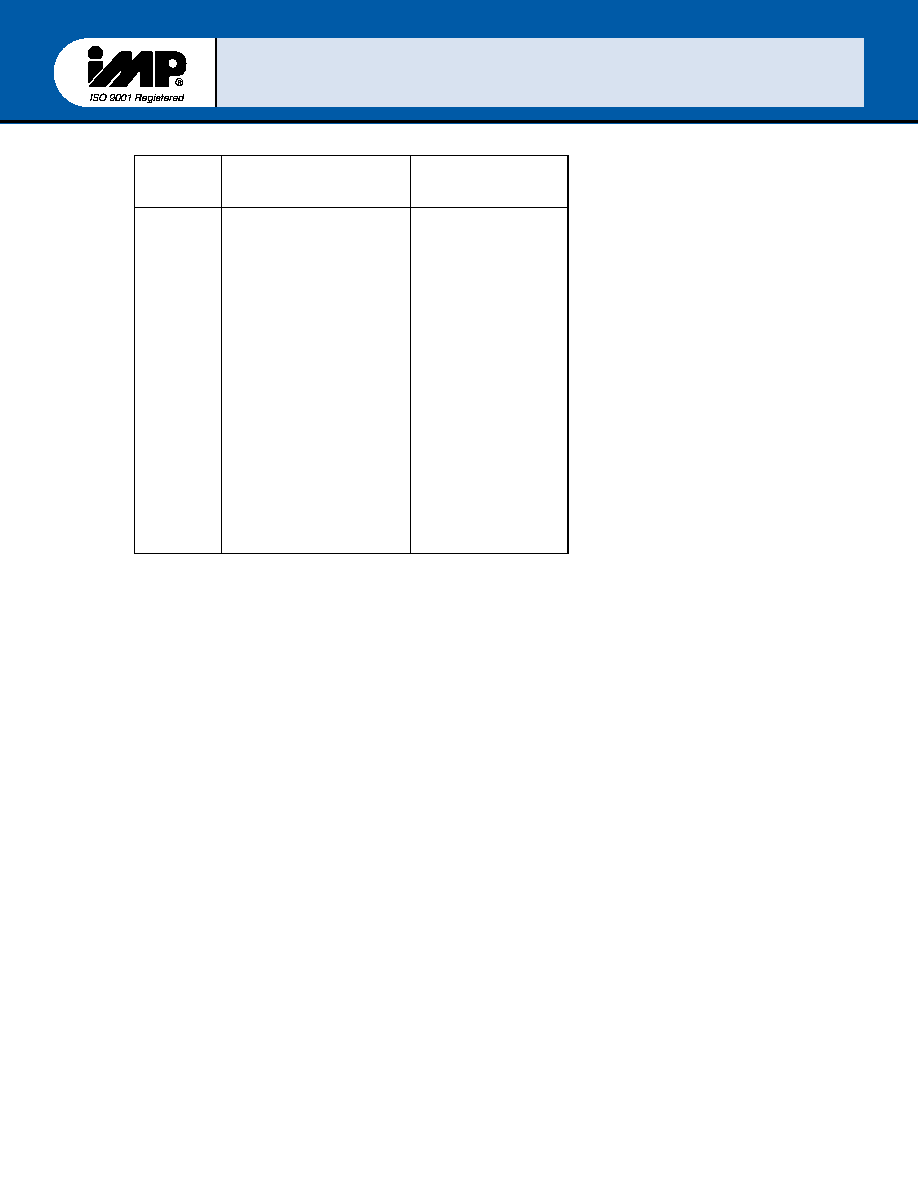
Table V- Baud Rate using 8.0 MHz Clock
Desired
Baud
Rate
Divisor Used
To Generate
16x clock
Percent Error
Difference Between
Desired and Actual
50
75
110
134.5
150
300
600
1200
1800
2000
2400
3600
4800
7200
9600
19200
38400
56000
128000
256000
10000
6667
4545
3717
3333
1667
833
417
277
250
208
139
104
69
52
26
13
9
4
2
-
0.005
0.010
0.013
0.010
0.020
0.040
0.080
0.080
≠
1.160
0.080
1.160
0.644
1.160
1.160
1.160
0.790
2.344
2.344
Line Status Register
This register provides status information to the
CPU concerning the data transfer. Table II
shows the contents of the Line Status Register.
Description of each bit follows:
Bit 0: This bit is the receiver Data Ready
(RDR) indicator. Bit 0 is set to a logic 1
whenever a complete incoming character has
been received and transferred into the
Receive Buffer Register of the FIFO. Bit 0 is
reset to a logic 0 by reading all of the data in
the Receive Buffer Register (for character
mode ) or the RCVR FIFO (for FIFO mode).
Bit 1: This bit is the Overrun Error (OE)
indicator. Bit 1 indicates that data in the
Receiver Buffer Register was not read by the
CPU before the next character was
transferred into the Receiver Buffer Register,
thereby destroying the previous character.
The OE indicator is set to a logic 1 upon
detection of an overrun condition and reset
whenever the CPU reads the contents of the
Line Status Register. If the FIFO mode data
continues to fill FIFO beyond the trigger level.
an overrun error will occur only after the FIFO
is full and the next character has been
completely received in the shift register. An
OE is indicated as soon as it happens . The
character in the shift register is overwritten,
but nothing will transferred to the FIFO.
Bit 2: This bit is the Parity Error (PE) indicator.
Bit 2 indicates that the received data character
does not have the correct even or odd parity,
as selected by the even-parity-select bit. The
PE is set to a logic 1 upon detection of a parity
error and is reset to a logic 0 whenever the
CPU reads the contents of the Line Status
Register. In the FIFO mode this error is
associated with the particular character in the
FIFO and revealed to the CPU when the
associated character is the top of the FIFO.
Bit 3: This bit is the Framing Error (FE)
indicator. Bit 3 indicates that the received
character did not have a valid Stop bit. Bit 3 is
set to a logic 1 whenever the Stop bit following
the last data bit or parity bit is detected as a
logic 0 bit (Spacing level). The FE indicator is
reset whenever the CPU reads the contents of
the Line Status Register. In the FIFO mode
14
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

this error is associated with the particular
character in the FIFO it applies to. This error
is revealed to the CPU when its associated
character is at the top of the FIFO. The UART
will resynchronize after a Framing Error.
Bits 4: This bit is the Break Interrupt (BI)
indicator. Bit 4 is set to a logic 1 whenever the
received data input is held in the spacing
(logic 0 ) state for longer than a full word
transmission time (that is, the total time of
Start bit + data bits + Parity + Stop bits ). The
BI indicator is reset whenever the CPU reads
the contents of the Line Status Register. When
in FIFO mode, BI is associated to the
particular character in the FIFO, and this bit is
set when the associated character is at the
top of the FIFO. When a break occurs, only
one zero character is loaded into the FIFO.
The next character transferred is enable after
SIN goes to the marking state (logic 1 ) and
receives the next valid start bit.
Note: Bits 1 through 4 are the error conditions
that produce a Receiver Line Status interrupt
whenever any of the corresponding conditions
are detected and the interrupt enabled.
Bit 5: This is the Transmitter Holding
Register empty (THRE) indicator. Bit 5
indicates that the UART is ready to accept a
new character for transmission. In addition,
this bit causes the UART to issue an interrupt
to the CPU when the Transmit Holding
Register Empty Interrupt enable is set high.
The THRE bit is set to a logic 1 when a
character is transferred from the Transmitter
Holding Register into the Transmitter Shift
Register. The bit is reset to logic 0
concurrently with the loading of the
Transmitter Holding Register by the CPU. In
the FIFO mode, this bit will be set when XMIT
FIFO is empty, and cleared when as least one
character is written to XMIT FIFO.
Bit 6: This bit is the Transmitter Empty
(TEMT) indicator. Bit 6 is set to a logic 1
whenever the Transmitter Holding Register
(THR) and the Transmitter Shift Register
(TSR) are both empty. It is reset to a logic 0
whenever either the THR or the TSR contains
a data character. In the FIFO mode this bit is
set to 1 whenever the transmitter FIFO and
shift register are both empty.
Bit 7 : In the Character Mode, this bit
(LSR7) is a 0. In the FIFO mode it is set when
there is a least one parity error, framing error
or break indication in the FIFO. LSR7 is clear
when the CPU reads the LSR, if there are no
subsequent errors in the FIFO.
Note: The Line Status Register is intended
for read operations only. Writing to this
register is not recommended.
Interrupt Identification Register
In order to provide minimum software
overhead during data character transfers, the
UART prioritizes interrupts into four levels and
records these in the interrupt Identification
Register. The four levels of interrupt
conditions are as follows :Receiver Line
Status (priority 1), Received Data Ready
(priority 3 ) , and MODEM Status (priority 4).
Information indicating that a prioritized
interrupt is pending and source of that
interrupt is stored in the Interrupt Identification
Register (refer to Table VI). Register IIR.
When addressed during chip select time,
freezes the highest priority interrupt pending
and no other interrupts are acknowledged until
the particular interrupt is serviced by the CPU.
Its contents are indicated in Table VI and are
described below:
Bit 0: This bit can be used in a prioritized or
polled environment to indicate whether an
interrupt is pending when bit 0 is a logic 0 an
interrupt is pending and the IIR contents may
be used as a pointer to the appropriate
interrupts service routine when bit 0 is a logic
1 no interrupt is pending and polling (if
used)continues
Bit 1,2 : these two bits of IIR are used to
identity the highest priority interrupt pending
(see Table VI)
Bit3 : In the character mode this bit 0 in the
FIFO mode this bit is set along with bit 2 when
a timeout interrupt is pending
Bit 4,5: These two bits of the IIR are always
logic 0
15
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

TABLE VI- interrupt Control Functions
Interrupt Identification Interrupt Set Reset Functions
Register
Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit
0
Priority
level
Interrupt
type
Interrupt source
Interrupt reset
control
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
.--
Highest
second
Second
Third
Fourth
None
Receiver
Line Status
Received
Data
Available
Character
Timeout
Identification
(`')
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Empty
MODEM
Status
None
Overrun error
or party error
or framing
or break interrupt
Receiver Data
Available
or Trigger Level
Reached
No characters
have been input to
or removed from
the RCVR FIFO
during the Last 4
character times,
and there is at
least one
character in it
during this time.
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Empty
Clear to send or
Data Set ready or
Ring Indicator or
Received Line
Signal Detect
.---
Reading the
Line Status
Register
Reading the
Receiver Buffer
Register or the
FIFO Drops below
the Trigger Level
Reading the
Receiver Buffer
Register
Reading the IIR
Register (if source
of interrupt) or
Writing into the
Transmitter
Holding Register
Reading the
MODEM status
Register
(*) This interrupt type is not available in character mode of IMP6C552.
16
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

FIGURE 3 ≠ Interrupt Control logic for channel 0 and 1
Bit 6, 7: These two bits, when set, indicate
that the device is in FIFO Mode, i.e. when
FCRO=1.
Interrupt Enable Register
This 8-bit register enables the four interrupt
sources of the DUART to separately activate
the chip Interrupt (INTRPT) output signal.
Each interrupt can individually activate the
interrupt (INTRPT) output signal. Its contents
are indicated in Table 3-2 and are described
below by resetting bits 0 through 3 of the
interrupt Enable Register (IER). Similarly,
setting bits of the IER register to a logic 1
enables the selected interrupt (s). Disabling
an interrupt prevents it from being indicated as
active in the IIR and from activating the
INTRPT output signal. All other system
functions operated in their normal manner,
including the setting of the Line Status and
MODE Status Registers.
Bit 0: This bit enables the Received Data
Available Interrupt (and timeout interrupt in
the FIFO mode) when set to logic 1.
Bit 1: This bit enables the Transmitter
Holding Register Empty Interrupt when set to
logic 1.
Bit 2: This bit enables the Receiver Line
Status Interrupt when set to logic 1.
Bit 3: This bit enables the MODEM Status
Interrupt when set to logic 1.
Bit 4-7: These four bits are always logic 0.
Scratch Pad Register
This 8-bit Read/Write Register does not
control the UART in anyway. It is intended as
a scratch pad register to be used by the
programmer to hold general purpose data
temporarily.
FIFO Control Register
This write only register is located at the same
address as the IIR (read only). This register
is used to enable FIFO Mode, clear FIFO's,
set the RCVR FIFO trigger levels, and select
the mode of DMA signaling.
Bit 0: Writing a 1 to this bit enables both the
XMIT and RCVR FIFO's. When changing from
FIFO Mode to Character Mode and vice versa,
data is not automatically cleared from the
FIFO's. This bit must be a 1 when writing to
other FCR bits or they will not be
programmed.
Bit 1: Writing a 1 to FCR1 will reset its
counters to 0, and then self clear this bit to 0.
The shift register is not cleared.
Bit 2: Functions the same as bit 1, except
for XMIT FIFO counters.
Bit 3: If FCR0=1, setting FCR# to a 1 will
cause the RXRDY and TXRDY pins to change
from mode 0 to mode 1 (see description of
RXRDY and TXRDY pins).
INT0/1
RCVR line Status Interrupt 0/1
RCVR Data Status Interrupt 0/1
RCVR Timout Status Interrupt 0/1
THRE Interrupt 0/1
MODEM status interrupt 0/1
LOOPBACK enable(MCR0/1 bit
4)
Internal OUTPUT2(MCR0/1 bit 3)
17
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
Bit 4, 5: FCR 4 and FCR5 are reserved for
future use.
Bit 6,7: FCR6 and FCR7 are used to set the
trigger level for the RCVR FIFO interrupt as
follows:
7
6
RCVR FIFO Trigger
Level (In bytes)
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
01
04
08
14
MODEM Control Register
This 8-bit register controls the interface with
the MODEM or data set (or a peripheral
device emulating a MODEM ). The contents of
the MODEM Control Register are indicated in
Table II and are described below:
Bit 0: This bit controls the Data Terminal
Ready (DTR*) output. When bit 0 is set to a
logic 1, DTR* output is forced to a logic 0.
When bit 0 is reset to a logic 0, DTR* output is
forced to a logic 1.
Note: the DTR* output of the UART may be
applied to an EIA inverting line driver (such
as DS1488) to obtain the proper polarity input
at the succeeding MODEM or data set.
Bit 1: This bit controls the Request to Send
(RTS*) output. Bit 1 affects the RTS* output in
a manner identical to that bit 0 affects output
DTR*.
Bit 2: This bit controls the internal OUTPUT 1
signal, which is an auxiliary user-designated
output. Bit 2 affects the OIUTPUT 1 in a
manner identical to bit 0 affects output DTR*.
Internal OUTPUT1 signal is not connected the
external pin.
Bit 3: This bit controls the internal OUTPUT2
signal, which is an auxiliary user-designated
output. Bit 3 affects the OUT2* output in a
manner identical to bit not connected to the
external pin. When set, this bit enables INT2
pin internally.
Bit 4: This bit provides a local loopback
feature for diagnostic testing of the UART.
When bit 4 is set to logic 1, the following occur.
The transmitter Serial Output (SOUT) is set to
a logic 1 (high) state: the receiver Serial
Input (SIN) is disconnected; the output of the
Transmitter Shift Register is "looped back" into
the Receiver Shift Register input: the four
MODEM Control inputs (CTS*, DSR*. RLSD*
and RI*) are disconnected. And the MODEM
Control output pins (RST*, DTR*) are forced
to their inactive state (high). In the diagnostic
mode, data that is transmitted is immediately
received. This feature allows the processor to
verify the transmit-and receive-data paths of
the UART.
In the diagnostic mode, the receiver and
transmitter interrupts are full operational. Their
sources are external to the part. The MODEM
control Interrupts are also operational, but the
sources of interrupts are now the lower four
bits of the MODEM Control Register instead of
the four MODEM control inputs. The interrupts
are still controlled by the Interrupt Enable
Register.
Bit 5-7: These bits are permanently set to
logic 0.
MODEM STATUS Register
This 8-bit register provides the current state of
the control lines from the MODEM or data set
(or a peripheral device emulating a modem) to
the CPU. In addition to this current-state
information, four bits of the MODEM Status
Register provide change information. These
bits are set to a logic 1 whenever a control
input from the MODEM changes state. They
are reset to logic 0 whenever the CPU reads
the MODEM Status Register.
The contents of the MODEM Status Register
are indicated in Table II and described below:
Bit 0: This bit is the Delta Clear to Send
(DCTS) indicator. Bit 0 when set to logic 1,
indicates that the CTS* input to the chip has
changed state since the last time it was read
by the CPU.
Bit 1: This bit is the Delta Data Set Ready
(DDSR) indicator, Bit 1 when set to logic 1,
indicates that the DSR input to the chip has
18
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

changed state since the last time it was read
by the CPU.
Bit 2: This bit is the Trailing Edge of Rin
Indicator (TREI) detector. Bit 2 indicates that
the RI input to the chip has changed from a
low to high state since the last time it was
read by the CPU.
Bit 3: This bit is the Delta Received Line
Signal Detector (DRLSD) indicator. Bit 3
when set to logic 1, indicates that the RLSD
input to the chip has changed state since the
last time it was read by the CPU.
Note: Whenever bit 0, 1, 2, or 3 is set to logic
1, a MODEM Status Interrupt is generated, if
bit 3 (EDSSI) of the interrupt enable register is
set.
Bit 4: This bit is the complement of the Clear
to Send (CTS*) input. This bit is equivalent
to bit RTS of the MODEM control register, if bit
4 of the MCR is set to 1 (loop mode).
Bit 5: This bit is the complement of the Data
Set Ready (DSR)* input. This bit is
equivalent to bit DTR of the MODEM control
register, if bit 4 of the MCR is set to 1(loop
mode).
Bit 6: This bit is the complement of the Ring
Indicator (RI)* input. This bit is equivalent to
bit OUT1 of the MODEM control register, if bit
4 the MCR is set to 1 (loop mode).
Bit 7: This bit is the complement of the
Received Line Signal Detect (RLSD) input.
This bit equivalent to bit OUT2 of the MODEM
control register, if bit 4 of the MCR is set to 1
(loop mode).
FIFO Interrupt Mode Operation
When the RCVR FIFO and receiver interrupts
are enabled, (FCR0=1, IER0=1) RCVR
interrupts will occur as follows:
A. The receive data available interrupt will
be issued to the CPU when the FIFO
has reached its programmed trigger
level; it will be cleared as soon as the
FIFO drops below its programmed
trigger level.
B. The IIR receive data available indication
also occurs when the FIFO trigger level
is reached, and like the interrupt, it is
cleared when the FIFO drops below the
trigger level.
C. The receiver line status interrupt
(IIR=06), as before, has higher priority
than the received data available (IIR=04)
interrupt.
D. The data ready bit (LSR bit 0) is set as
soon as a character is transferred from
the shift register to the RCVR FIFO. It
is reset when the FIFO is empty.
When RCVR FIFO and receiver interrupts are
enabled, RCVR FIFO timeout interrupts will
occur as follows:
A. A FIFO timeout interrupt will occur, if the
following conditions exists:
-at least one character is in the RCVR
FIFO.
-the most recent serial character received
was longer than 4 continuous
character times ago (if 2 stop bits are
programmed the second one is included
in this time delay ).
-the most recent CPU read of the FIFO
was longer than 4 continuous character
times ago.
This will cause a maximum character received
to interrupt issued delay of 160 ms at 300
BAUD with a 12 bit character.
B. character times are calculated by using
the RCLK input for a clock signal (this
makes the delay proportional to the baud
rate).
C. When a timeout interrupt has occurred, it
is cleared and the timer is reset when the
CPU reads one character form the RCVR
FIFO.
D. When a timeout interrupt has not
occurred the ` timeout timer is reset after
a new character is received or after the
19
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

CPU reads the RCVR FIFO.
When the XMIT FIFO and transmitter
interrupts are enabled (FCR0=1, IER1=1),
XMIT interrupts will occur as follows:
A. The transmitter holding register interrupt
(02) occurs when the XMIT FIFO is empty;
it is cleared as soon as the transmitter
holding register is written to (1 to 16
characters may be written to this XMIT
FIFO while servicing this interrupt) or the
IIR is read.
B. The transmitter FIFO empty indications
will be delayed 1 character time minus
the last stop bit time whenever the
following occurs: THRE=1 and there have
not been at least tow bytes at the same
time in the transmit FIFO, since the last
THRE=1, The first transmitter interrupt
after changing FCR0 will be immediate, if
it is enabled.
Character timeout and RCVR FIFO trigger
level interrupts have the same priority as the
current received data available interrupt; XMIT
FIFO empty has the same priority as the
current transmitter holding register empty
interrupt.
FIFO Polled Mode Operation
With FCR0=1 RESETTING IER1, IER2,
IERR3 or all to zero puts the UART in the
RCVR and XMITTER are controlled
separately either one or both can be in the
polled mode of operation.
In this mode the users program will check
RCVR and XMITTED status via the LSR. As
stated previously:
LSR0 will be set as long as there is one byte
in the RCVR FIFO.
LSR1 to LSR4 will specify which error(s) has
occurred. Character error status is handled
the same way as when in the interrupt mode,
the IIR is not affected since IER2=0.
LSR5 will indicate when the XMIT FIFO is
empty.
LSR6 will indicate that both the XMIT FIFO
and shift register are empty.
LSR7 will indicate whether there are any
errors in the RCVR FIFO.
There is no trigger level reached or timeout
condition indicated in the FIFO Polled Mode.
However, the RCVR and XMIT FIFO's are still
fully capable of holding characters.
20
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

The parallel port supports Centronics type printers. When CS2* is low, the parallel port is selected allowing access to all
parallel port data, control and status registers.
PARALLEL PORT REGISTER ADDRESSES
Cs2* A1 A0 IOR* LOW* Operation
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
Read Port Data Register
Read Port Status Register
Read Port Control Register
Invalid Operation
Write Port Data Register
Invalid Operation
Write Port Control Register
Invalid Operation
ACCESSIBLE PARALLEL PORT REGISTERS
Bit
No
.
Port
Data
Register
Port
Status
Register
(Read
only)
Port
Control
Registe
r
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Data Bit 0
Data Bit 1
Data Bit 2
Data Bit 3
Data Bit 4
Data Bit 5
Data Bit 6
Data Bit 7
1
1
1
ERRORS*
SLCTS
PES
ACKS*
BUSYS*
STBE
AFDE
INITE*
SLINE
INTE
1
1
1
Register Description
Port Data Register
This 8-bit data register can be modified by the
CPU to write data to the parallel port.
Bits 0-7: Data bits
Port Status Register
This register is a read only register reporting
the state of status input pins ERROR*, SLCT,
PE, ACK*, and BUSY.
Bits 0:2: these bits are always read as 1.
Bits 3: Reports status of ERROR* pin.
Bits 4: Reports status of SLCT pin.
Bits 5: Reports status of PE pin.
Bits 6: Reports status of ACK*.
Bits 7: Reports inverted status of BUSY pin.
Port Control Register
This register controls output pins STB*,
AFD*, INIT*, SLIN*, INT2, When read, it
reports the status of the control pins.
Bits 0: This bit, when written 1/0, force STB*
pin low/high.
Bits 1: This bit, when written 1/0, force AFD*
pin low/high.
Bits 2: This bit, when written 1/0, force INIT*
pin low/high.
Bits 3: This bit, when written 1/0, force SLIN*
pin low/high.
Bits 4: This bit, when written 1/0, enables /
disables INT2 pin.
Bits 5-7: Always read as 1.
21
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
Parallel Port Description
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

AC, DC TIMING SPECIFICATION
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Temperature Under Bias 0
0
c to +70
0
c
Storage or Output Voltage ≠65
0
c to +
150
0
c
All Input or Output Voltages
With Respect to VSS -0. 5 V to + 7. 0
V
Power Dissipation 500 mw
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are
required. contact Modular for availability and
specifications. Note: Maximum rating
indicate limits beyond which permanent
damage may occur. Continuous operation at
these limits is not intended and should be
limited to those conditions specified under DC
electrical characteristics.
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TA=0
0
C to + 70
0
c, Vcc=+5V±5%, Vss=0V, unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter
Conditions
Min
Max Units
VILX
VIHX
VIL
VIH
VOL
VOH
ICC(AV)
IIL
ICL
LOZ
VILMR
VIHMR
Clock Input Low Voltage
Clock Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
Input High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Avg. Power Supply
Current(Vcc)
Input Leakage
Clock Leakage
Tri-StateÆ Leakage
MR Schmitt VIL
MR Schmitt VIH
IOL = 4.0 mA on D0-D7
= 12 mA on PD0-PD7
=10 mA on INT*, AFD*,
STB*, SLIN*(note1)
= 2mA on all other
OUTPUTS
IOH = -1. 0 mA (note 1)
= -2.0 mA on PD0-PD7
=-0.2 mA on INT*, AFD*
STB*, SLIN*
= -0.2mA on all other
OUTPUTS
Vcc =5. 25V, f=4MHz
No Loads on outputs
SIN, DSR, DCD
All other inputs =0. 8V
Vcc=5. 25V, Vss=0V
All other pins floating
VOUT = 0v, 5. 25v
VCC=5. 25V, VSS=0V
VOUT =0V, 5. 25V
1) chip deselected
2) WRITE mode, chip selected
-0. 5V
2. 0
-0. 5V
2. 0
2. 4
2. 0
0.8
Vcc
0.8
Vcc
0.4
10
±10
±10
±10
0. 8
V
V
V
V
V
V
mA
µA
µA
µA
V
V
22
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
CAPACITANCE
TA=25
0
C, VCC=VSS=0V
Symbol Parameter
Conditions
Min Typ Max Units
CXIN
CXOUT
CIN
COUT
Clock Input
Capacitance
Clock Output
Capacitance
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
Fc =1 MHz
Unmeasured pins
Returned to VSS
15
20
6
10
20
30
10
20
pF
pF
pF
pF
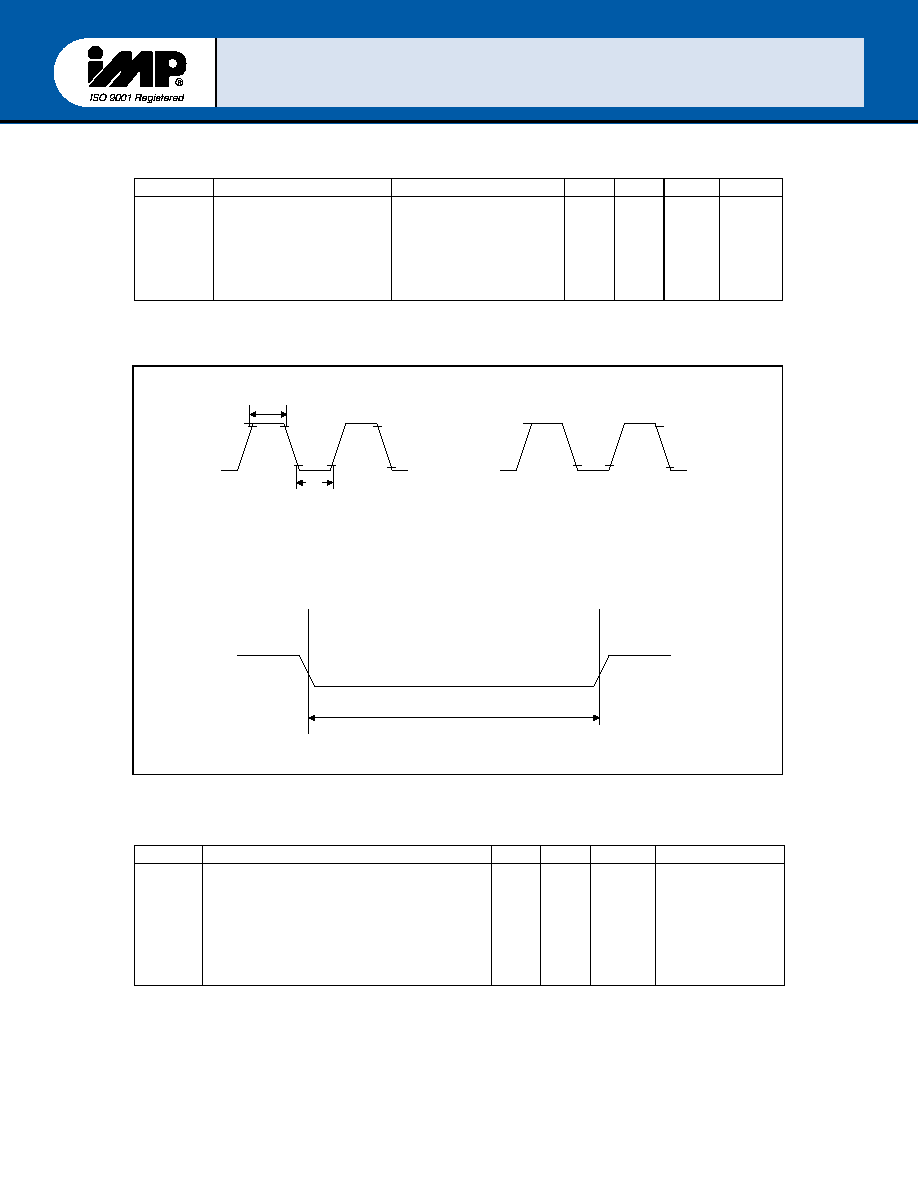
FIGURE 4 ≠ Clock and Reset Timing
Symbol Parameter
Min Max Units Test
Conditions
txh
txl
tMR
Duration of External
Clock High Pulse
Duration of External
Clock Low Pulse
Master Reset Pulse Width
55
55
5. 0
nsec
nsec
nsec
External Clock
(8. 0 MHz Max)
1TTL Load
(8. 0 MHz Max)
1TTL Load
External Clock Input(8.0 MHz Max.)
t
XH
2.4V
0.4V
t
XL
2.0V
0.8V
2.4V
Note:1
0.4V
AC Test Points
2.0V
0.8V
Note:2
t
MR
Reset Timing
Note 1 : Input drive levels are 0.4v (low) and 2.4 (high) for AC tests.
Note 2 : Output compare levels are 0.8v (low) and 2.0v (high) for AC lests.
MR
23
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
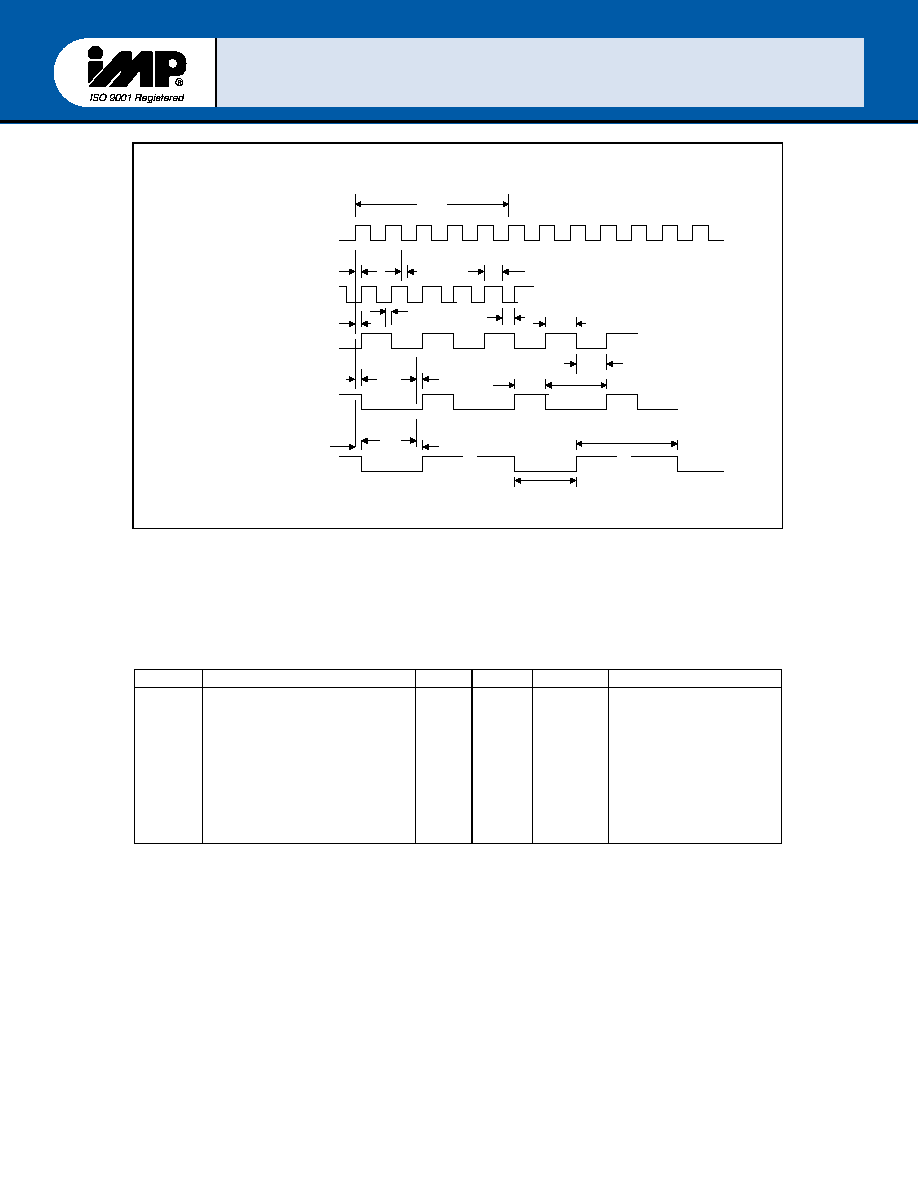
FIGURE 5 ≠ Baud Rate General Timing
Symbol Parameter
Min Max Units
Test
Conditions
N
tBLD
tBLD
tLW
tHW
Baud Rate Divisor
Baud Output Negative
Edge Delay
Baud Output Posisitve
Edge Delay
Baud Output Low Time
Baud Output High Time
1
75
100
(2
16
-1)
125
125
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
100pF Load
100pF Load
100pF Load
(fx=8. 0 MHz+2)
100pF Load
(fx=8. 0 MHz+2)
s
ss
ss
N
t
BLD
t
HW
t
LW
t
HW
t
BLD
t
BHD
t
BHD
t
BLD
t
BHD
t
HW
t
LW
t
BLD
t
BHD
t
LW
t
HW
=
(n-2)XTAL1 CYCLES
t
LW
=
2XTAL1 CYCLES
XTAL1
BAUDOUT*
(divide by 1)
BAUDOUT*
(divide by 2)
BAUDOUT*
(divide by 3)
BAUDOUT*
(divide by N,N>3)
24
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
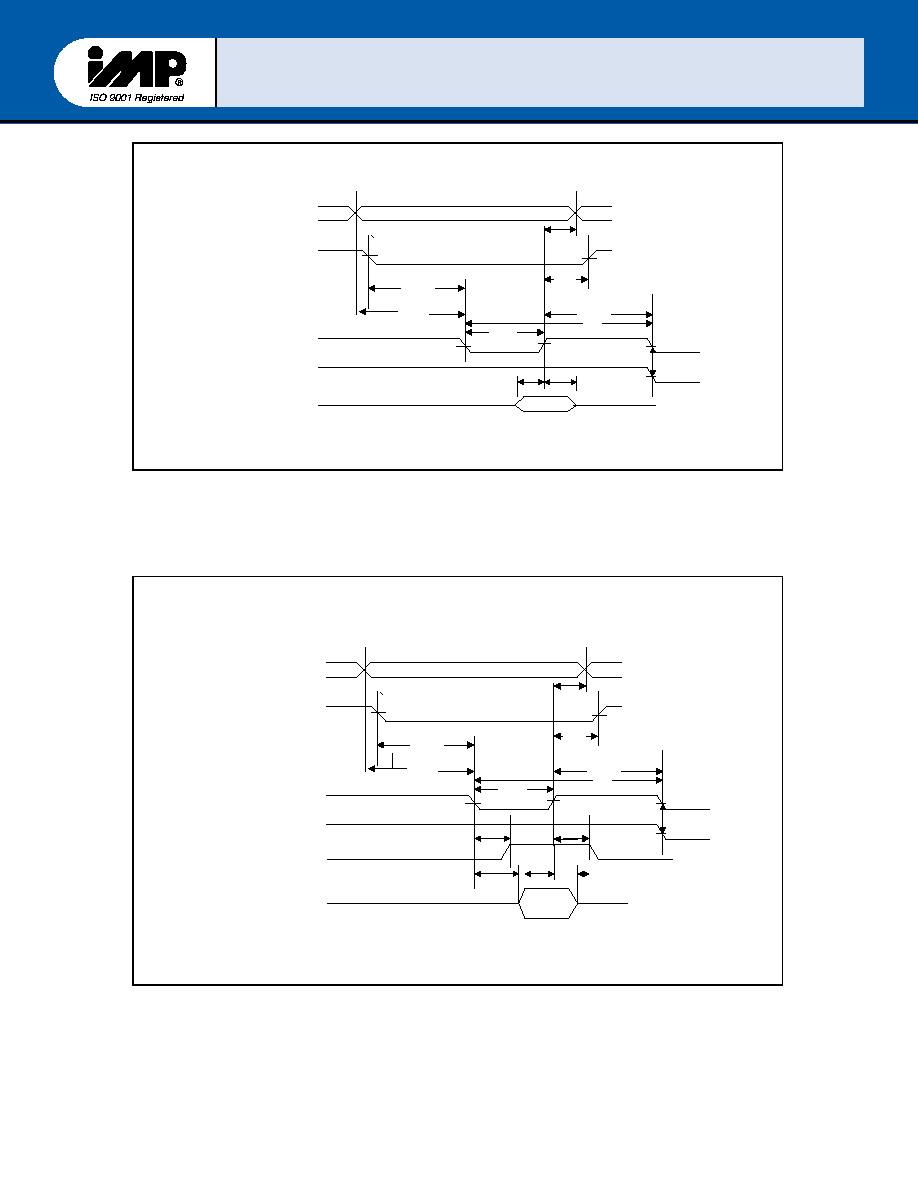
FIGURE 6 ≠ Write cycle Timing
FIGURE 7- Read Cycle Timing
VALID DATA
t
DH
tDD
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
t
WC
WC
t
DOW
ACTIVE
t
DOC
t
DOC
t
ACW
t
ACW
VALID
A0,A1,A2
CS0*(CS1*)
IOW*
IOR*
DATA
D0-D7
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
t
RC
RC
t
DIW
ACTIVE
t
DIC
t
DIC
t
ACR
t
ACR
VALID
A0,A1,A2
CS0*(CS1*)
IOR*
IOW*
BD0
t
DD
t
DD
VALID
DATA
t
HZ
t
DDD
DATA
D0-D7
25
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

Symbol Parameter
Min Max Units Test
conditions
TDIW
RC
tDD
tDDD
tHZ
tDOW
WC
tDS
tDH
tDIC
tDOC
tACR
tACW
tWC
tRC
IOR* Strobe Width
Read Cycle(tDIC + tDIW + tRC)
IOR* to Driver Enable/Disable Delay
Delay from IOR* to Data
IOR* to floating Data Delay
IOW* Strobe Width
Write Cycle (tDOC + tDOW + tWC)
Data Setup Time
Data Hold Time
IOR* delay from chip Select or Address
IOW* delay from chip Select or Address
Address and Chip Select Hold time from
IOR*
Address and Chip Select Hold time from
IOW*
Write Cycle Delay
Read Cycle Delay
50
105
0
0
50
110
15
15
25
25
2
2
60
50
60
40
100
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nsec
nesc
nesc
nesc
nesc
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
@100pF Load
@100pF Load
@100pF Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
1 TTL Load
26
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
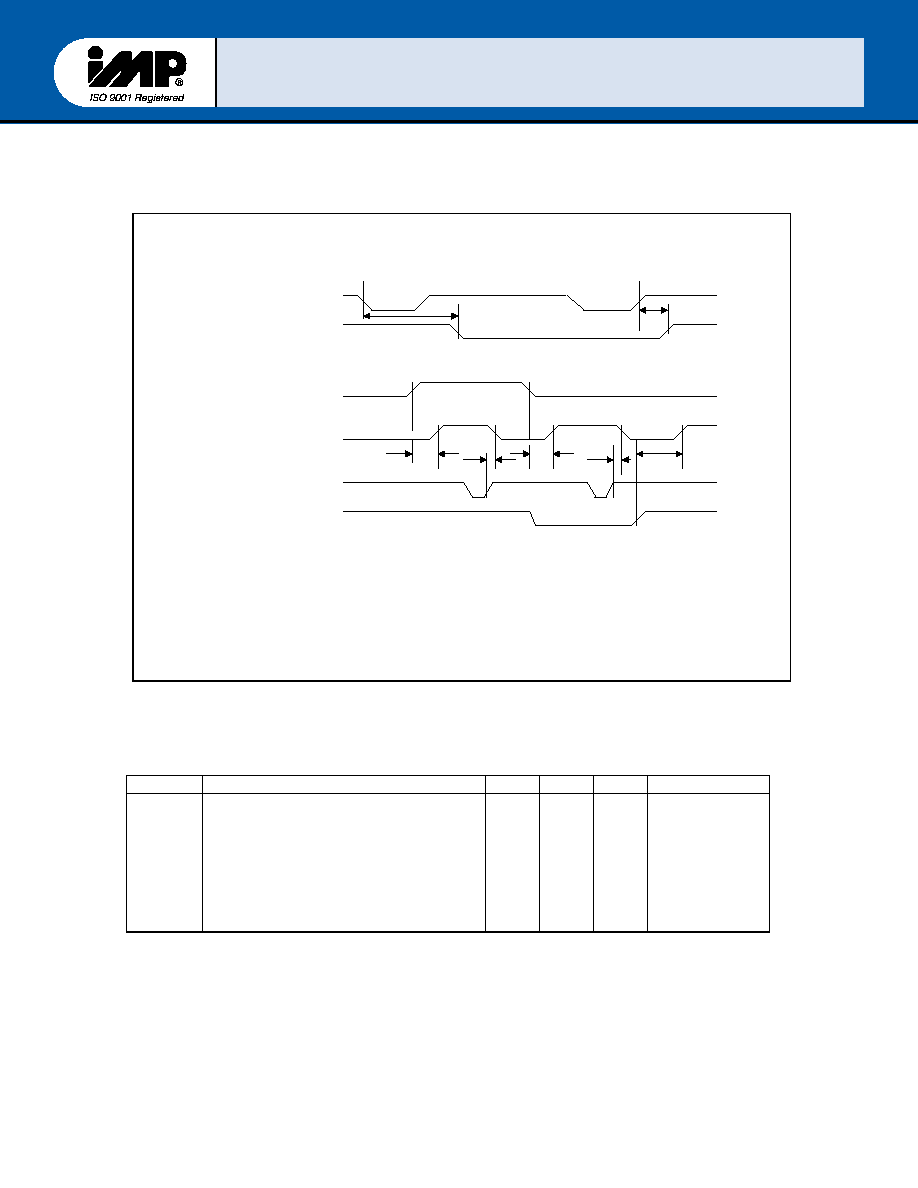
FIGURE 8 ≠ Modem Control Timing
Symbol Parameter
Min Max Units Test
Conditions
tMDO
tSIM
tRIM
Delay from IOW* (WR MCR)
Delay to Set Interrupt
From MODEM Input
Delay to Reset Interrupt
From IOR* (RD MSR)
200
200
30
nsec
nsec
nsec
100pF Load
100pF Load
100pF Load
t
SIM
t
RIM
t
SIM
t
RIM
t
SIM
t
MDO
t
MDO
IOW*(1)
(write MCR)
RIS*,DTR*
CTS*,DSR*,RLSD*
INT0
IOR*(2)
(read MSR)
RI*
NOTES:
(1)See Write cycle Timing
(2)See Read cycle Timing
27
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
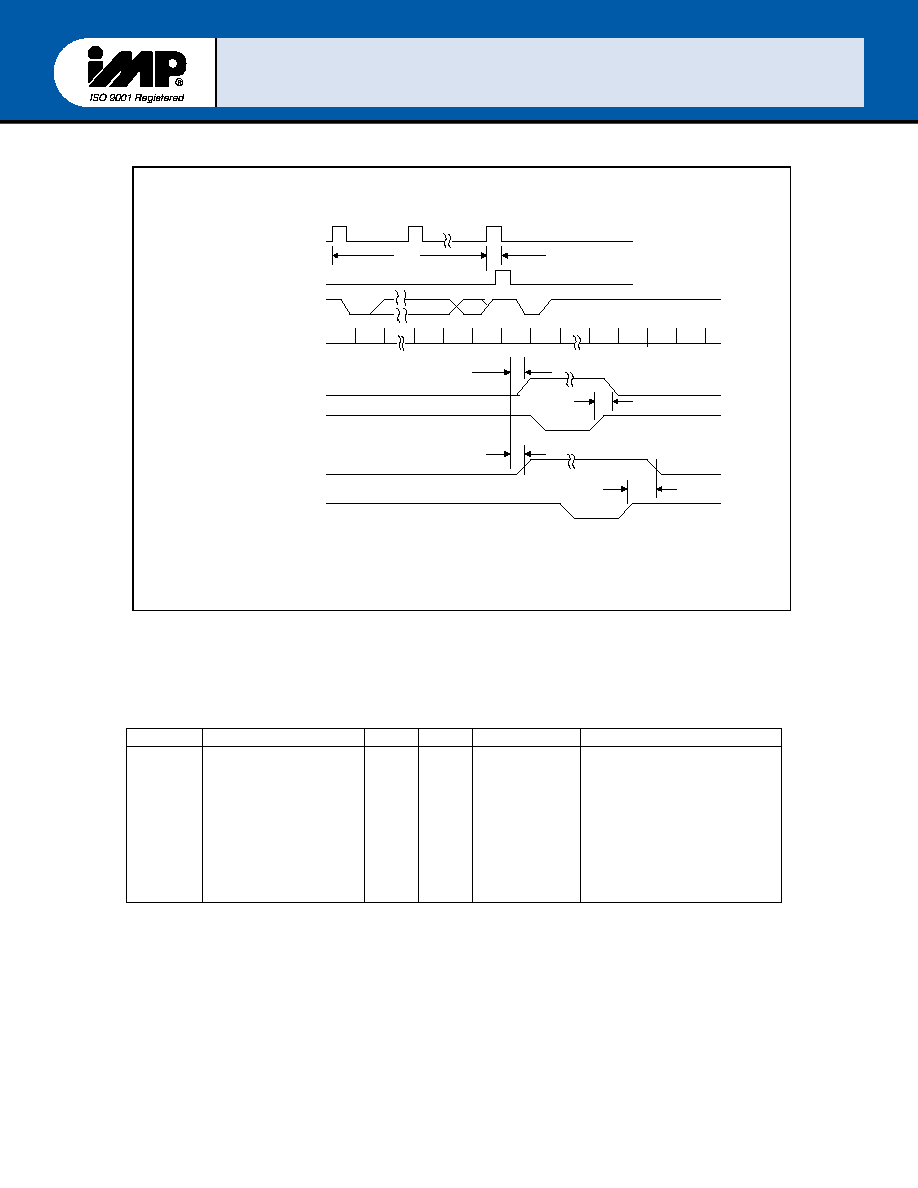
FIGURE 9 ≠ Receiver Timing
Symbol
Parameter Min
Max
Units
Test
Conditions
tSCD
tSINT
TrinT
Delay from RCLK
To Sample Time
Delay from
Stop to Set Interrupt
Delay From IOR*
(RD RBR or RD LSR)
Reset Interrupt
2
1(*)
32
µsec
RCLK Cycles
nsec
100pF Load
(*) When receiving the first byte in FIFO mode tSINT will be delayed 3 RCLK cycles, except for a
timeout interrupt where tSINT will be delayed 8 RCLK cycles.
8 CLKS
t
SCD
START
DATA BITS(5-8)
PARITY
STOP
START
t
SINT
t
RINT
ACTIVE
t
RINT
ACTIVE
RCLK
SAMPLE CLK
SIN0
SAMPLE CLK
RDR
INTERRUPT
IOR*(1)
(read RBR)
LSI
INTERRUPT
IOW*(1)
(read LSR)
Note:
(1)See Read Cycle timing
t
SINT
28
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
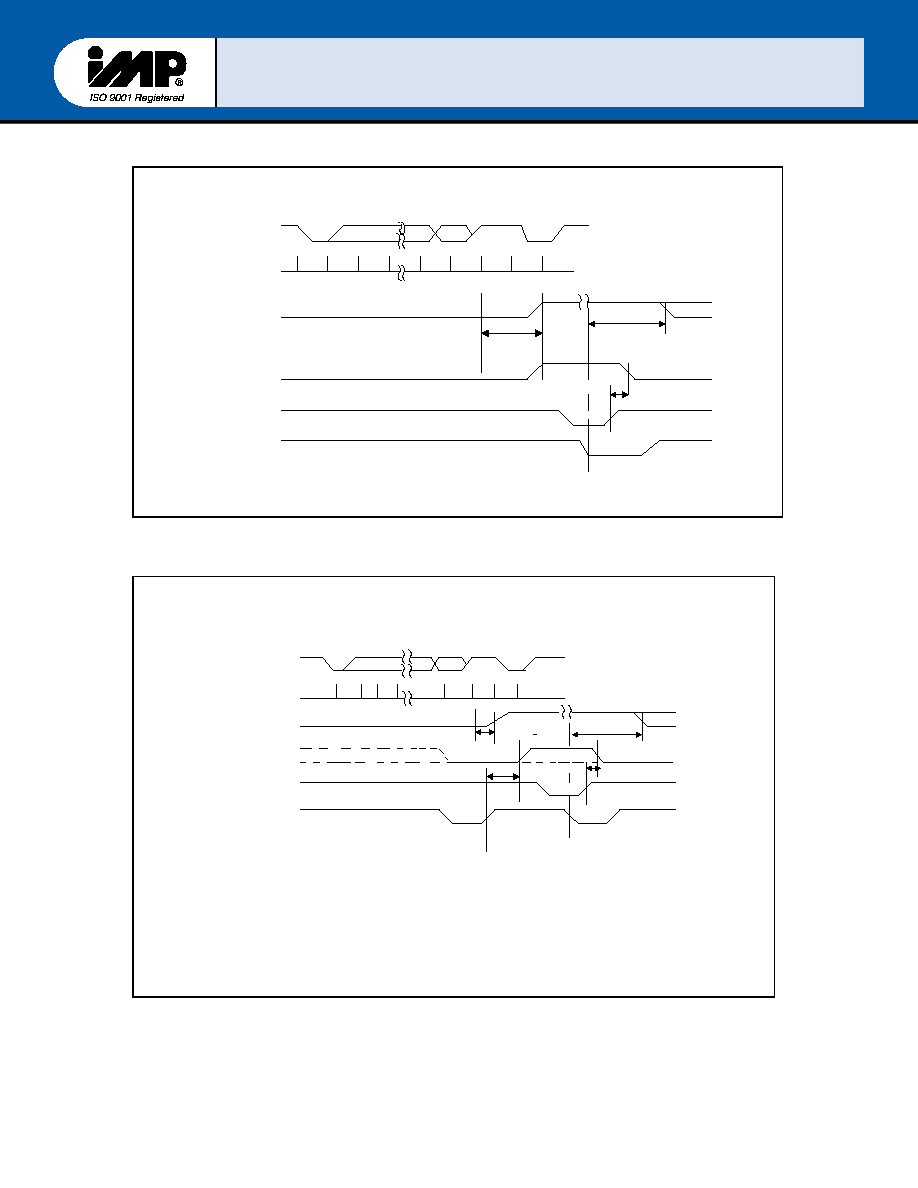
FIGURE 10 ≠ RCVR FIFO Timing for First Byte
FIGURE 11 ≠ RCVR FIFO Timing after First Byte(RDR already set)
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
t
RINT
t
SINT
t
RINT
FIFO below
trigger level
FIFO at or above trigger level
START
STOP
PARITY
DATA(5-8)
SIN
SAMPLE CLK
TRIGGER LEVEL
INTERRUPT
(FCR6,7=0,0)
LSI INTERRUPT
IOR*
(read LSR)
IOW*
(read RBR)
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
previous
byte read
from FIFO
ACTIVE
t
RINT
t
RINT
FIFO below
trigger levle
FIFO at or above trigger
level
t
SINT
t
SINT
top byte of FIFO
STOP START
PARITY
SERIAL IN
(SIN)
SAMPLE CLK
FIFO TRIGGER
LEVLINTERRUPT
OR TIMEOUT
LSI INTERRUPT
IOR*
(read LSR)
IOW*
(read RBR)
DATA(5-8)
29
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552
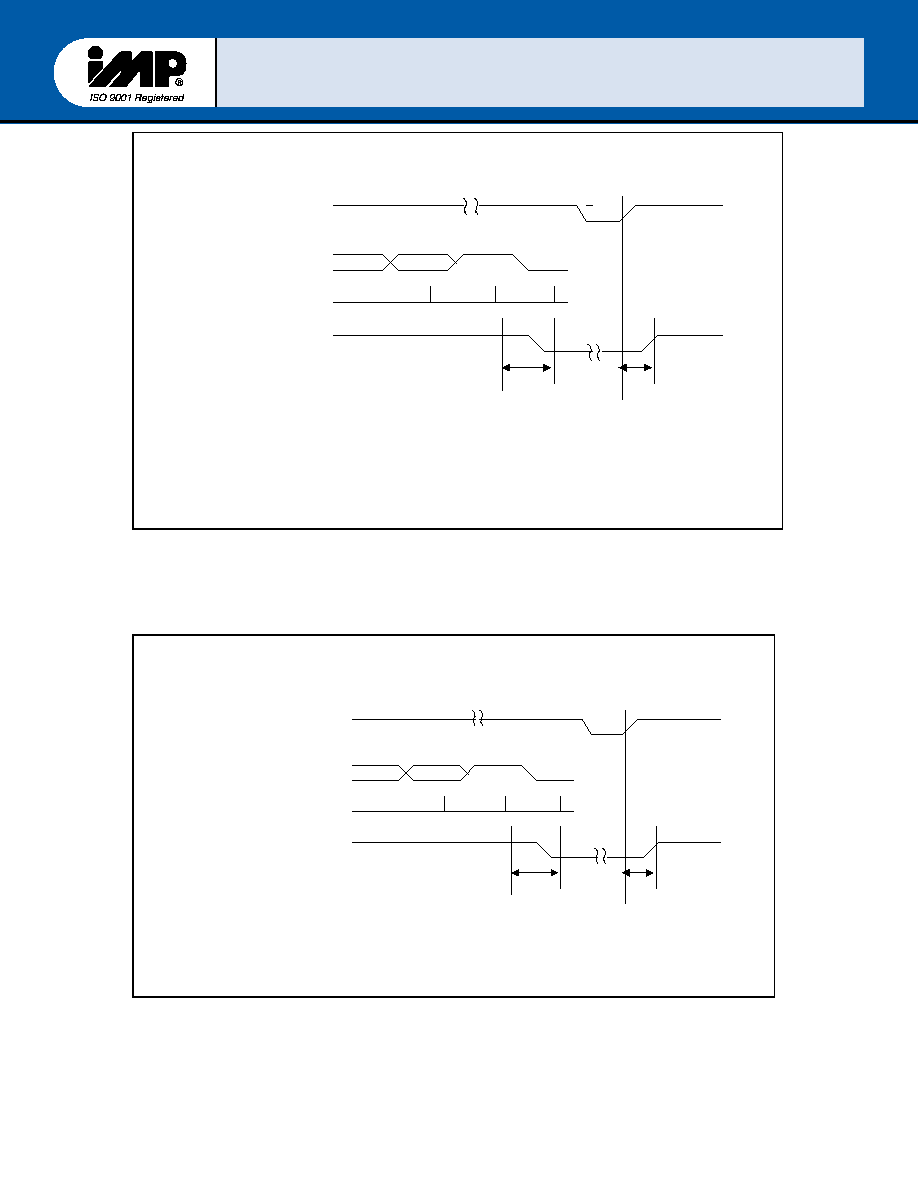
FIGURE 12 ≠ Receiver DMA Timing (FCR0=0 or FCR0=1 and FCR3=0)
Mode 0
FIGURE 13 ≠ Receiver DMA Timing (FCR0=1 and FCR3=1)
Mode 1
t
SINT
t
RINT
ACTIVE
Note1
STOP
PARITY
IOR*
(read RBR)
SIN0
(first byte)
SAMPLE CLK
RXRDY*
Note 1
FCR0=1:Reading of last byte from FIFO
FCR0=0:Reading RBR
t
SINT
ACTIVE
Note1
STOP
PARITY
t
RINT
IOR*
(read RBR)
SIN0
(first byte that reaches
trigger level)
SAMPLE CLK
RXRDY*
Note 1
Reading of last byte from FIFO
30
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

FIGURE 14 ≠ Transmitter Timing
Symbol Parameter
Min Max Units
Test
Conditions
tHR
tIR
tIRS
tSI
tSTI
tSXA
tWXI
Delay from IOW* (WR THR)
to Reset Interrupt
Delay from IOR* (RD IIR) to Reset
Interrupt(THRE)
Delay from Initial INTRPT reset to
transmit Start
Delay from Initial Write to Interrupt
Delay from Stop to Interrupt(THRE)
Delay from Start to TXREY Active
Delay from Write to TXRDY Inactive
0
16
8
0
0
50
250
12
32
8
8
60
nsec
nsec
BAUDOUT
Cycles
BAUDOUT
Cycles
BAUDOUT
Cycles
(note 1)
BAUDOUT
Cycles
nsec
100pF Load
100pF Load
(note 1)
(note 1)
100pF Load
100pF Load
SERIAL OUT
(SOUT)
THRE INTERRUPT
IOW*(1)
(write THR)
IOR*(2)
(read IIR)
NOTES:
(1)See Write Cycle Timing
(2)See Read Cycle Timing
START DATA(5-8)
PARITY
STOP
tIRS
tHR
tSI
tHR
tSTI
START
tIR
31
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

FIGURE 15-Transmitter Ready Timing in DMA
(FCR0=0 or FCR0=1 and FCR3=0)
Mode 0
FIGURE 16-Transmitter Ready Timing in DMA
(FCR0=0 or FCR0=1 and FCR3=0)
Mode 1
DATA
BYTE#16
PARITY
STOP
START
FIFO full
FIFO not full
tWXI
tSXA
FIFO not full
IOW*
(write THR)
SOUT0
TXRDY*
DATA
BYTE#1
PARITY
STOP
START
not empty
empty
tWXI
tSXA
empty
IOW*
(write THR)
SOUT0
TXRDY*
32
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

FIGURE 17- Parallel Port Timing
9
8
17
1
6
2
3
4
10
7
5
Write Data
12
Read Data
13
14
15
13
16
ADDRESS
11
CS2*
LPTOE*
A0,A1
D0-D7
IOW*
IOR*
PD0-PD7
SLIN*,INIT*
AFD*,STB*
IOW*
IOR*
D0-D7
ACK*
INT2
RESET*
PD0-PD7
SLIN*,INIT*
AFD*,STB*
33
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

Symbo
l
Parameter Min
Max
Units
Test
Conditions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
CS2* low to IOR*, IOW* low
Address valid to IOR*, IOW* low
Data setup to IOW* high
Data hold to IOW* high
IOW* high to PD0-PD7
IOW* high to INIT*, AFD*, SLIN*, STB*
IOW*, IOR* high to CE* low
Pulse width IOW* low
Address hold after IOW*, IOR* high
CS2* hold after IOW* IOR* high
IOW* IOR* hold after CS2* high
IOR* low to data valid
IOR* high to D7-D0. Hi-Z
ACK* to INT2
IOW* high to INT2 Hi-Z
RST* low to D7-D0, SLIN*, STB* INIT*,
AFD*
LPTOE* low to PD0-PD7 Delay
LPTOE* high to PD0-PD7Hi-Z
30
30
30
30
0
100
20
0
10
100
100
125
100
50
60
65
50
100
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number
Package Operating Temperature
IMP16C552-CJ68 68 pin PLCC 0 +70
IMP16C552-IJ68 68 pin PLCC -40 +85
34
408-432-9100/www.impweb.com © 2002 IMP, Inc.
IMP16C552
IMP16C552

































