
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
1 - 3
I
FRMS
= 2x 300 A
I
FAVM
= 2x 165 A
V
RRM
= 800-1800 V
Symbol
Test Conditions
Characteristic Values
I
R
T
VJ
= T
VJM
; V
R
= V
RRM
20
mA
V
F
I
F
= 300 A; T
VJ
= 25
∞
C
1.3
V
V
T0
For power-loss calculations only
0.8
V
r
T
T
VJ
= T
VJM
1.3
m
W
Q
S
T
VJ
= 125
∞
C; I
F
= 300 A, -di/dt = 50 A/
m
s
550
m
C
I
RM
235
A
R
thJC
per diode; DC current
0.21
K/W
per module
other values
0.105
K/W
R
thJK
per diode; DC current
see Fig. 6/7
0.31
K/W
per module
0.155
K/W
d
S
Creepage distance on surface
12.7
mm
d
A
Strike distance through air
9.6
mm
a
Maximum allowable acceleration
50
m/s
2
Data according to IEC 60747 and refer to a single diode unless otherwise stated.
IXYS reserves the right to change limits, test conditions and dimensions
Dimensions in mm (1 mm = 0.0394")
V
RSM
V
RRM
Type
V
V
900
800
MDD 142-08N1
1300
1200
MDD 142-12N1
1500
1400
MDD 142-14N1
1700
1600
MDD 142-16N1
1900
1800
MDD 142-18N1
Symbol
Test Conditions
Maximum Ratings
I
FRMS
T
VJ
= T
VJM
300
A
I
FAVM
T
C
= 100
∞
C; 180
∞
sine
165
A
I
FSM
T
VJ
= 45
∞
C;
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine
4700
A
V
R
= 0
t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine
5000
A
T
VJ
= T
VJM
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine
4100
A
V
R
= 0
t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine
4300
A
Ú
i
2
dt
T
VJ
= 45
∞
C
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine
110 000
A
2
s
V
R
= 0
t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine
104 000
A
2
s
T
VJ
= T
VJM
t = 10 ms (50 Hz), sine
84 000
A
2
s
V
R
= 0
t = 8.3 ms (60 Hz), sine
77 000
A
2
s
T
VJ
-40...+150
∞
C
T
VJM
150
∞
C
T
stg
-40...+125
∞
C
V
ISOL
50/60 Hz, RMS
t = 1 min
3000
V~
I
ISOL
£
1 mA
t = 1 s
3600
V~
M
d
Mounting torque (M6)
2.25-2.75/20-25 Nm/lb.in.
Terminal connection torque (M6)
4.5-5.5/40-48 Nm/lb.in.
Weight
Typical including screws
120
g
Features
q
International standard package
q
Direct copper bonded Al
2
O
3
-ceramic
base plate
q
Planar passivated chips
q
Isolation voltage 3600 V~
q
UL registered, E 72873
Applications
q
Supplies for DC power equipment
q
DC supply for PWM inverter
q
Field supply for DC motors
q
Battery DC power supplies
Advantages
q
Space and weight savings
q
Simple mounting
q
Improved temperature and power
cycling
q
Reduced protection circuits
MDD 142
High Power
Diode Modules
3
1
2
3
1
2
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
2 - 3
MDD 142
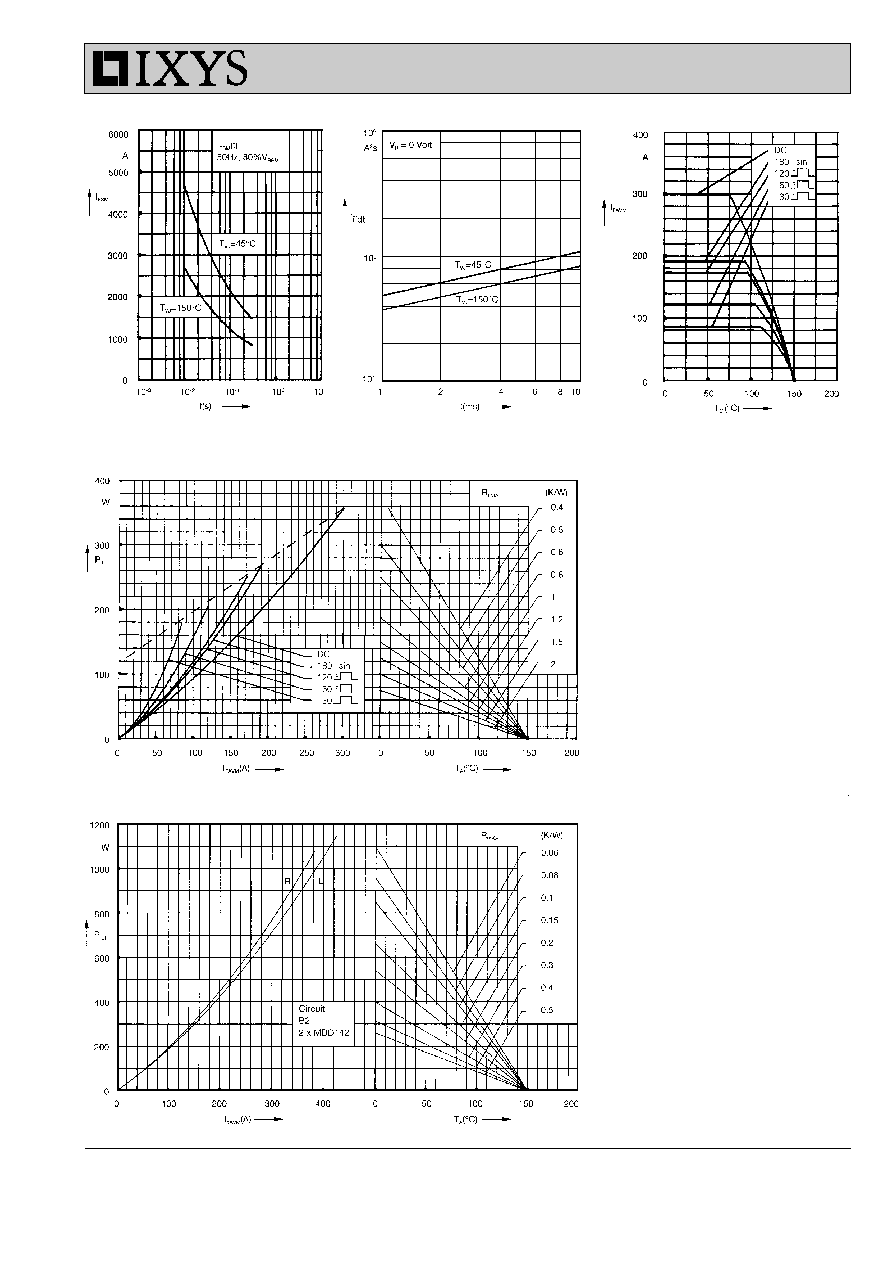
Fig. 1 Surge overload current
I
FSM
: Crest value, t: duration
Fig. 2
Ú
i
2
dt versus time (1-10 ms)
Fig. 2a Maximum forward current
at case temperature
Fig. 3
Power dissipation versus
forward current and ambient
temperature (per diode)
Fig. 4 Single phase rectifier bridge:
Power dissipation versus direct
output current and ambient
temperature
R = resistive load
L = inductive load
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
3 - 3
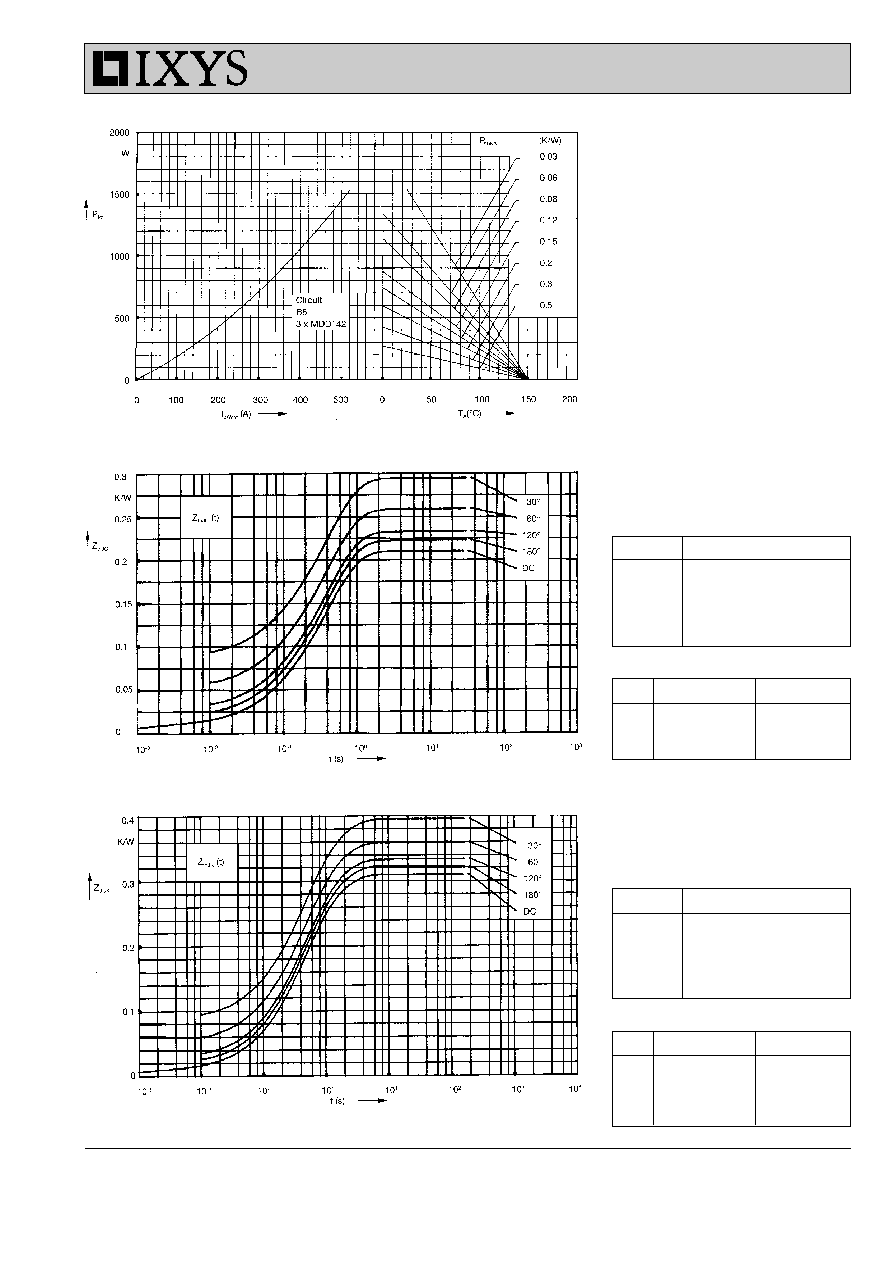
Fig. 5 Three phase rectifier bridge:
Power dissipation versus direct
output current and ambient
temperature
Fig. 6 Transient thermal impedance
junction to case (per diode)
Fig. 7 Transient thermal impedance
junction to
heatsink
(per diode)
R
thJK
for various conduction angles d:
d
R
thJK
(K/W)
DC
0.31
180
∞
0.323
120
∞
0.333
60
∞
0.360
30
∞
0.395
Constants for Z
thJK
calculation:
i
R
thi
(K/W)
t
i
(s)
1
0.0087
0.001
2
0.0163
0.065
3
0.185
0.4
4
0.1
1.29
MDD 142
R
thJC
for various conduction angles d:
d
R
thJC
(K/W)
DC
0.210
180
∞
0.223
120
∞
0.233
60
∞
0.260
30
∞
0.295
Constants for Z
thJC
calculation:
i
R
thi
(K/W)
t
i
(s)
1
0.0087
0.001
2
0.0163
0.065
3
0.185
0.4


