 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: 160V | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Document Outline
- Table of Contents
- ispGDX160V/VA Data Sheet
- ispGDX160VA: DC Electrical Characteristics
- ispGDX160VA: AC Characteristics
- ispGDX160V: DC Electrical Characteristics
- ispGDX160V: AC Characteristics
- Signal Configuration: 272 BGA
- Signal Configuration: 208 fpBGA
- Pin Configuration: 208 PQFP
- Ordering Information
1
ispGDX
TM
160V/VA
In-System Programmable
3.3V Generic Digital Crosspoint
TM
Functional Block Diagram
Features
∑ IN-SYSTEM PROGRAMMABLE GENERIC DIGITAL
CROSSPOINT FAMILY
-- Advanced Architecture Addresses Programmable
PCB Interconnect, Bus Interface Integration and
Jumper/Switch Replacement
-- "Any Input to Any Output" Routing
-- Fixed HIGH or LOW Output Option for Jumper/DIP
Switch Emulation
-- Space-Saving PQFP and BGA Packaging
-- Dedicated IEEE 1149.1-Compliant Boundary Scan
Test
∑ HIGH PERFORMANCE E
2
CMOS
Æ
TECHNOLOGY
-- 3.3V Core Power Supply
-- 3.5ns Input-to-Output/3.5ns Clock-to-Output Delay*
-- 250MHz Maximum Clock Frequency*
-- TTL/3.3V/2.5V Compatible Input Thresholds and
Output Levels (Individually Programmable)*
-- Low-Power: 16.5mA Quiescent Icc*
-- 24mA I
OL
Drive with Programmable Slew Rate
Control Option
-- PCI Compatible Drive Capability*
-- Schmitt Trigger Inputs for Noise Immunity
-- Electrically Erasable and Reprogrammable
-- Non-Volatile E
2
CMOS Technology
∑ ispGDXVTM OFFERS THE FOLLOWING ADVANTAGES
-- 3.3V In-System Programmable Using Boundary Scan
Test Access Port (TAP)
-- Change Interconnects in Seconds
∑ FLEXIBLE ARCHITECTURE
-- Combinatorial/Latched/Registered Inputs or Outputs
-- Individual I/O Tri-state Control with Polarity Control
-- Dedicated Clock/Clock Enable Input Pins (four) or
Programmable Clocks/Clock Enables from I/O Pins
(40)
-- Single Level 4:1 Dynamic Path Selection (Tpd = 3.5ns)
-- Programmable Wide-MUX Cascade Feature
Supports up to 16:1 MUX
-- Programmable Pull-ups, Bus Hold Latch and Open
Drain on I/O Pins
-- Outputs Tri-state During Power-up ("Live Insertion"
Friendly)
∑ DESIGN SUPPORT THROUGH LATTICE'S ispGDX
DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE
-- MS Windows or NT / PC-Based or Sun O/S
-- Easy Text-Based Design Entry
-- Automatic Signal Routing
-- Program up to 100 ISP Devices Concurrently
-- Simulator Netlist Generation for Easy Board-Level
Simulation
* "VA" Version Only
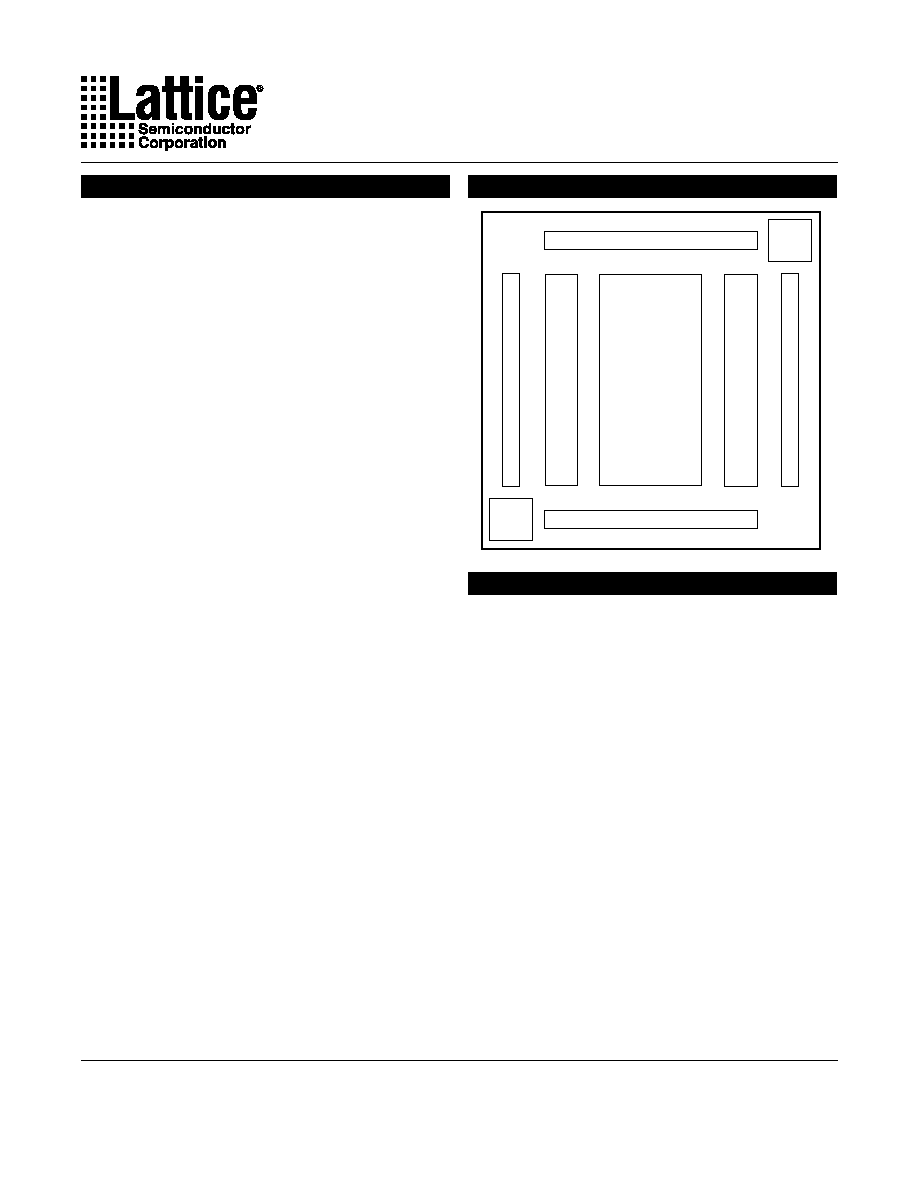
Global Routing
Pool
(GRP)
I/O
Cells
I/O Pins B
Boundary
Scan
Control
I/O
Cells
ISP
Control
I/O Pins
A
I/O Pins C
I/O Pins D
Description
The ispGDXV/VA architecture provides a family of fast,
flexible programmable devices to address a variety of
system-level digital signal routing and interface require-
ments including:
∑ Multi-Port Multiprocessor Interfaces
∑ Wide Data and Address Bus Multiplexing
(e.g. 16:1 High-Speed Bus MUX)
∑ Programmable Control Signal Routing
(e.g. Interrupts, DMAREQs, etc.)
∑ Board-Level PCB Signal Routing for Prototyping or
Programmable Bus Interfaces
The devices feature fast operation, with input-to-output
signal delays (Tpd) of 3.5ns and clock-to-output delays of
3.5ns.
The architecture of the devices consists of a series of
programmable I/O cells interconnected by a Global Rout-
ing Pool (GRP). All I/O pin inputs enter the GRP directly
or are registered or latched so they can be routed to the
required I/O outputs. I/O pin inputs are defined as four
sets (A,B,C,D) which have access to the four MUX inputs
gdx160va_04
Copyright © 2000 Lattice Semiconductor Corporation. All brand or product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. The specifications and information herein
are subject to change without notice.
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR CORP., 5555 Northeast Moore Ct., Hillsboro, Oregon 97124, U.S.A.
July 2000
Tel. (503) 268-8000; 1-800-LATTICE; FAX (503) 268-8556; http://www.latticesemi.com

2
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Description (Continued)
found in each I/O cell. Each output has individual, pro-
grammable I/O tri-state control (OE), output latch clock
(CLK), clock enable (CLKEN), and two multiplexer con-
trol (MUX0 and MUX1) inputs. Polarity for these signals
is programmable for each I/O cell. The MUX0 and MUX1
inputs control a fast 4:1 MUX, allowing dynamic selection
of up to four signal sources for a given output. A wider
16:1 MUX can be implemented with the MUX expander
feature of each I/O and a propagation delay increase of
2.0ns. OE, CLK, CLKEN, and MUX0 and MUX1 inputs
can be driven directly from selected sets of I/O pins.
Optional dedicated clock input pins give minimum clock-
to-output delays. CLK and CLKEN share the same set of
I/O pins. CLKEN disables the register clock when
CLKEN = 0.
Through in-system programming, connections between
I/O pins and architectural features (latched or registered
inputs or outputs, output enable control, etc.) can be
defined. In keeping with its data path application focus,
the ispGDXV devices contain no programmable logic
arrays. All input pins include Schmitt trigger buffers for
noise immunity. These connections are programmed
into the device using non-volatile E
2
CMOS technology.
Non-volatile technology means the device configuration
is saved even when the power is removed from the
device.
In addition, there are no pin-to-pin routing constraints for
1:1 or 1:n signal routing. That is,
any I/O pin configured
as an input can drive one or more I/O pins configured as
outputs.
The device pins also have the ability to set outputs to
fixed HIGH or LOW logic levels (Jumper or DIP Switch
mode). Device outputs are specified for 24mA sink and
12mA source current (at JEDEC LVTTL levels) and can
be tied together in parallel for greater drive. On the
ispGDXVA, each I/O pin is individually programmable for
3.3V or 2.5V output levels as described later. Program-
mable output slew rate control can be defined
independently for each I/O pin to reduce overall ground
bounce and switching noise.
All I/O pins are equipped with IEEE1149.1-compliant
Boundary Scan Test circuitry for enhanced testability. In
addition, in-system programming is supported through
the Test Access Port via a special set of private com-
mands.
The ispGDXV I/Os are designed to withstand "live inser-
tion" system environments. The I/O buffers are disabled
during power-up and power-down cycles. When design-
ing for "live insertion," absolute maximum rating conditions
for the Vcc and I/O pins must still be met.
Table 1. ispGDXV Family Members
ispGDXV/VA Device
ispGDX160V/VA
I/O Pins
160
I/O-OE Inputs*
40
I/O-CLK / CLKEN Inputs*
40
I/O-MUXsel1 Inputs*
40
I/O-MUXsel2 Inputs*
40
BSCAN Interface
4
RESET
1
Pin Count/Package
208-Pin PQFP
208-Ball fpBGA
272-Ball BGA
* The CLK/CLK_EN, OE, MUX0 and MUX1 terminals on each I/O cell can each be assigned to
25% of the I/Os.
** Global clock pins Y0, Y1, Y2 and Y3 are multiplexed with CLKEN0, CLKEN1, CLKEN2 and
CLKEN3 respectively in all devices.
TOE
1
Dedicated Clock Pins**
4
EPEN
1
80
20
20
20
20
4
1
100-Pin TQFP
1
2
1
240
60
60
60
60
4
1
388-Ball fpBGA
1
4
1
ispGDX80VA
ispGDX240VA

3
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Architecture
The ispGDXV/VA architecture is different from traditional
PLD architectures, in keeping with its unique application
focus. The block diagram is shown below. The program-
mable interconnect consists of a single Global Routing
Pool (GRP). Unlike ispLSI devices, there are no pro-
grammable logic arrays on the device. Control signals for
OEs, Clocks/Clock Enables and MUX Controls must
come from designated sets of I/O pins. The polarity of
these signals can be independently programmed in each
I/O cell.
Each I/O cell drives a unique pin. The OE control for each
I/O pin is independent and may be driven via the GRP by
one of the designated I/O pins (I/O-OE set). The I/O-OE
set consists of 25% of the total I/O pins. Boundary Scan
test is supported by dedicated registers at each I/O pin.
In-system programming is accomplished through the
standard Boundary Scan protocol.
The various I/O pin sets are also shown in the block
diagram below. The A, B, C, and D I/O pins are grouped
together with one group per side.
I/O Architecture
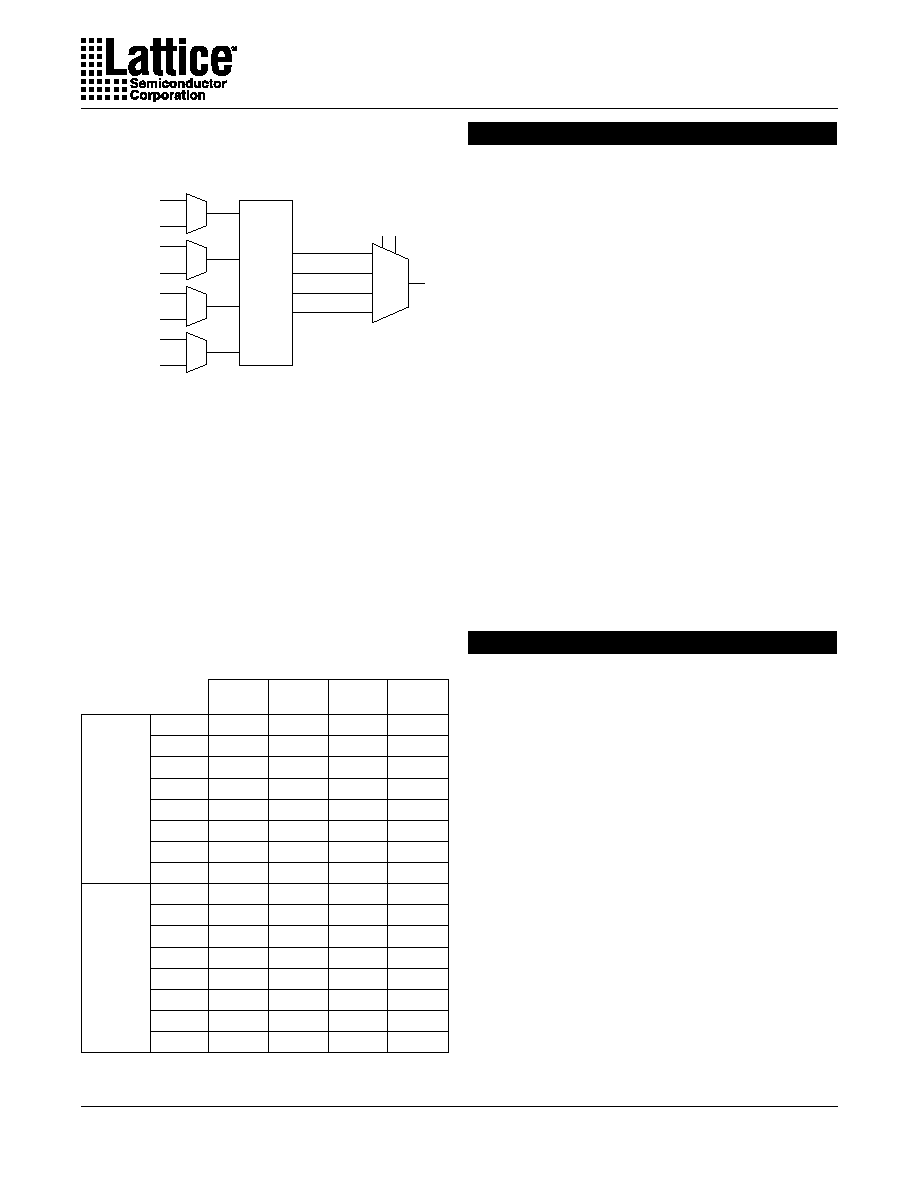
Each I/O cell contains a 4:1 dynamic MUX controlled by
two select lines as well as a 4x4 crossbar switch con-
trolled by software for increased routing flexiability (Figure
1). The four data inputs to the MUX (called M0, M1, M2,
and M3) come from I/O signals in the GRP and/or
adjacent I/O cells. Each MUX data input can access one
quarter of the total I/Os. For example, in a 160 I/O
ispGDXV, each data input can connect to one of 40 I/O
pins. MUX0 and MUX1 can be driven by designated I/O
pins called MUXsel1 and MUXsel2. Each MUXsel input
covers 25% of the total I/O pins (e.g. 40 out of 160). MUX0
and MUX1 can be driven from either MUXsel1 or MUXsel2.
Figure 1. ispGDXV/VA I/O Cell and GRP Detail (160 I/O Device)
I/OCell 0
I/O Cell 1
I/O Cell 78
I/O Cell 79
80 I/O Cells
Boundary
Scan Cell
Bypass Option
I/O Cell N
Register
or Latch
I/O
Pin
Prog.
Pull-up
(VCCIO)
Prog. Slew Rate
D
A
B
CLK
Reset
Q
4-to-1 MUX
160 Input GRP
Inputs Vertical
Outputs Horizontal
I/O Cell 159
I/O Cell 158
I/O Cell 81
M0
I/O Group A
I/O Group B
I/O Group C
I/O Group D
M1
4x4
Crossbar
Switch
M2
M3
MUX1
MUX0
Global
Reset
I/O Cell 80
∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑
∑
∑
∑
80 I/O Cells
ispGDXV/VA architecture enhancements over ispGDX (5V)
∑
∑
∑
∑
∑
∑
E
2
CMOS
Programmable
Interconnect
Logic "0" Logic "1"
160 I/O Inputs
C
R
Y0-Y3
Global
Clocks /
Clock_Enables
Prog.
Bus Hold
Latch
CLK_EN
From MUX Outputs
of 2 Adjacent I/O Cells
From MUX Outputs
of 2 Adjacent I/O Cells
To 2 Adjacent
I/O Cells above
To 2 Adjacent
I/O Cells below
Prog. Open Drain
2.5V/3.3V Output
∑
∑
∑
N+1
N+2
N-1
N-2

4
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Flexible mapping of MUXsel
x
to MUX
x
allows the user to
change the MUX select assignment after the ispGDXV/
VA device has been soldered to the board. Figure 1
shows that the I/O cell can accept (by programming the
appropriate fuses) inputs from the MUX outputs of four
adjacent I/O cells, two above and two below. This en-
ables cascading of the MUXes to enable wider (up to
16:1) MUX implementations.
The I/O cell also includes a programmable flow-through
latch or register that can be placed in the input or output
path and bypassed for combinatorial outputs. As shown
in Figure 1, when the input control MUX of the register/
latch selects the "A" path, the register/latch gets its inputs
from the 4:1 MUX and drives the I/O output. When
selecting the "B" path, the register/latch is directly driven
by the I/O input while its output feeds the GRP. The
programmable polarity Clock to the latch or register can
be connected to any I/O in the I/O-CLK/CLKEN set (one-
quarter of total I/Os) or to one of the dedicated clock input
pins (Y
x
). The programmable polarity Clock Enable input
to the register can be programmed to connect to any of
the I/O-CLK/CLKEN input pin set or to the global clock
enable inputs (CLKEN
x
). Use of the dedicated clock
inputs gives minimum clock-to-output delays and mini-
mizes delay variation with fanout. Combinatorial output
mode may be implemented by a dedicated architecture
bit and bypass MUX. I/O cell output polarity can be
programmed as active high or active low.
MUX Expander Using Adjacent I/O Cells
The ispGDXV/VA allows adjacent I/O cell MUXes to be
cascaded to form wider input MUXes (up to 16 x 1)
without incurring an additional full Tpd penalty. However,
there are certain dependencies on the locality of the
adjacent MUXes when used along with direct MUX
inputs.
Adjacent I/O Cells
Expansion inputs MUXOUT[n-2], MUXOUT[n-1],
MUXOUT[n+1], and MUXOUT[n+2] are fuse-selectable
for each I/O cell MUX. These expansion inputs share the
same path as the standard A, B, C and D MUX inputs, and
allow adjacent I/O cell outputs to be directly connected
without passing through the global routing pool. The
relationship between the [N+i] adjacent cells and A, B, C
and D inputs will vary depending on where the I/O cell is
located on the physical die. The I/O cells can be grouped
into "normal" and "reflected" I/O cells or I/O "hemi-
spheres." These are defined as:
I/O MUX Operation
MUX1
MUX0
Data Input Selected
0
0
M0
0
1
M1
1
1
M2
1
0
M3
Device
Normal I/O Cells
Reflected I/O Cells
B9-B0, A19-A0,
D19-D10
B10-B19, C0-C19,
D0-D9
B19-B0, A39-A0,
D39-D20
B20-B39, C0-C39,
D0-D19
ispGDX80VA
ispGDX160V/VA
ispGDX240VA
B29-B0, A59-A0,
D59-D30
B30-B59, C0-C59,
D0-D29
Table 2 shows the relationship between adjacent I/O
cells as well as their relationship to direct MUX inputs.
Note that the MUX expansion is circular and that I/O cell
B20, for example, draws on I/Os B19 and B18, as well as
B21 and B22, even though they are in different hemi-
spheres of the physical die. Table 2 shows some typical
cases and all boundary cases. All other cells can be
extrapolated from the pattern shown in the table.
D20
D19
B19
B20
A0
A39
C39
C
0
D39
B0
D0
B39
I/O cell 0
I/O cell 159
I/O cell 79
I/O cell 80
I/O cell index increases in this direction
I/O cell index increases in this direction
Figure 2. I/O Hemisphere Configuration of
ispGDX160V/VA
Direct and Expander Input Routing
Table 2 also illustrates the routing of MUX direct inputs
that are accessible when using adjacent I/O cells as
inputs. Take I/O cell D23 as an example, which is also
shown in Figure 3.
5
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
B20
B21
B22
B23
D16
D17
D18
D19
D20
D21
D22
D23
B16
B17
B18
B19
B22
B23
B24
B25
D18
D19
D20
D21
D18
D19
D20
D21
B14
B15
B16
B17
B21
B22
B23
B24
D17
D18
D19
D20
D19
D20
D21
D22
B15
B16
B17
B18
B19
B20
B21
B22
D15
D16
D17
D18
D21
D22
D23
D24
B17
B18
B19
B20
B18
B19
B20
B21
D14
D15
D16
D17
D22
D23
D24
D25
B18
B19
B20
B21
Data D/
MUXOUT
Data C/
MUXOUT
Data B/
MUXOUT
Data A/
MUXOUT
Reflected
I/O Cells
Normal
I/O Cells
Table 2. Adjacent I/O Cells (Mapping of
ispGDX160V/VA)
It can be seen from Figure 3 that if the D21 adjacent I/O
cell is used, the I/O group "A" input is no longer available
as a direct MUX input.
The ispGDXV/VA can implement MUXes up to 16 bits
wide in a single level of logic, but care must be taken
when combining adjacent I/O cell outputs with direct
MUX inputs. Any particular combination of adjacent I/O
cells as MUX inputs will dictate what I/O groups (A, B, C
or D) can be routed to the remaining inputs. By properly
choosing the adjacent I/O cells, all of the MUX inputs can
be utilized.
S0
S1
4 x 4
Crossbar
Switch
.m0
.m1
.m2
.m3
D23
I/O Group A
D21 MUX Out
I/O Group B
D22 MUX Out
I/O Group C
D24 MUX Out
I/O Group D
D25 MUX Out
ispGDX160V/VA I/O Cell
Figure 3. Adjacent I/O Cells vs. Direct Input Path for
ispGDX160V/VA, I/O D23
Special Features
Slew Rate Control
All output buffers contain a programmable slew rate
control that provides software-selectable slew rate op-
tions.
Open Drain Control
All output buffers provide a programmable Open-Drain
option which allows the user to drive system level reset,
interrupt and enable/disable lines directly without the
need for an off-chip Open-Drain or Open-Collector buffer.
Wire-OR logic functions can be performed at the printed
circuit board level.
Pull-up Resistor
All pins have a programmable active pull-up. A typical
resistor value for the pull-up ranges from 50k
to 80k
.
Output Latch (Bus Hold)
All pins have a programmable circuit that weakly holds
the previously driven state when all drivers connected to
the pin (including the pin's output driver as well as any
other devices connected to the pin by external bus) are
tristated.
ispGDX160VA New Features
Unique to the ispGDX160VA are user-programmable
I/Os supporting either 3.3V or 2.5V output voltage level
options. The ispGDX160VA uses a VCCIO pin to provide
the 2.5V reference voltage when used. The ispGDX160VA
VCCIO pin occupies the same location as VCC on the
ispGDX160V, allowing drop-in replacement. The
ispGDX160VA offers improved performance by reducing
fanout delays and has PCI compatible drive capability.
Only the ispGDX160VA is available in the fastest (3.5ns)
Commercial speed grade and in -5,-7, and -9ns Industrial
grades in all packages.
The ispGDX160VA has a device ID different from the
ispGDX160V requiring that the latest Lattice download
software be used for programming and verification. Al-
though the ispGDX160VA and ispGDX160V are
functionally equivalent, they are not 100% JEDEC com-
patible. All design files must be recompiled targeting the
ispGDX160VA.

6
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
The ispGDXV/VA Family architecture has been devel-
oped to deliver an in-system programmable signal routing
solution with high speed and high flexibility. The devices
are targeted for three similar but distinct classes of end-
system applications:
Programmable, Random Signal
Interconnect (PRSI)
This class includes PCB-level programmable signal rout-
ing and may be used to provide arbitrary signal swapping
between chips. It opens up the possibilities of program-
mable system hardware. It is characterized by the need
to provide a large number of 1:1 pin connections which
are statically configured, i.e., the pin-to-pin paths do not
need to change dynamically in response to control in-
puts.
Programmable Data Path (PDP)
This application area includes system data path trans-
ceiver, MUX and latch functions. With today's 32- and
64-bit microprocessor buses, but standard data path glue
components still relegated primarily to eight bits, PCBs
are frequently crammed with a dozen or more data path
glue chips that use valuable real estate. Many of these
applications consist of "on-board" bus and memory inter-
faces that do not require the very high drive of standard
glue functions but can benefit from higher integration.
Therefore, there is a need for a flexible means to inte-
grate these on-board data path functions in an analogous
way to programmable logic's solution to control logic
integration. Lattice's CPLDs make an ideal control logic
complement to the ispGDXV/VA in-system program-
mable data path devices as shown below.
Data Path
Bus #1
Control
Inputs
(from P)
Address
Inputs
(from P)
Control
Outputs
System
Clock(s)
Data Path
Bus #2
Configuration
(Switch)
Outputs
ISP/JTAG
Interface
ispLSI/
ispMACH
Device
ispGDXV/VA
Device
Buffers / Registers
Decoders
Buffers / Registers
State Machines
Figure 4. ispGDXV/VA Complements Lattice CPLDs
Applications
Programmable Switch Replacement (PSR)
Includes solid-state replacement and integration of me-
chanical DIP Switch and jumper functions. Through
in-system programming, pins of the ispGDXV/VA de-
vices can be driven to HIGH or LOW logic levels to
emulate the traditional device outputs. PSR functions do
not require any input pin connections.
These applications actually require somewhat different
silicon features. PRSI functions require that the device
support arbitrary signal routing on-chip between any two
pins with no routing restrictions. The routing connections
are static (determined at programming time) and each
input-to-output path operates independently. As a result,
there is little need for dynamic signal controls (OE,
clocks, etc.). Because the ispGDXV/VA device will inter-
face with control logic outputs from other components
(such as ispLSI or ispMACH) on the board (which fre-
quently change late in the design process as control logic
is finalized), there must be no restrictions on pin-to-pin
signal routing for this type of application.
PDP functions, on the other hand, require the ability to
dynamically switch signal routing (MUXing) as well as
latch and tri-state output signals. As a result, the pro-
grammable interconnect is used to define
possible signal
routes that are then selected dynamically by control
signals from an external MPU or control logic. These
functions are usually formulated early in the conceptual
design of a product. The data path requirements are
driven by the microprocessor, bus and memory architec-
ture defined for the system. This part of the design is the
earliest portion of the system design frozen, and will not
usually change late in the design because the result
would be total system and PCB redesign. As a result, the
ability to accommodate
arbitrary any pin-to-any pin re-
routing is not a strong requirement as long as the designer
has the ability to define his functions with a reasonable
degree of freedom initially.
As a result, the ispGDXV/VA architecture has been
defined to support PSR and PRSI applications (including
bidirectional paths) with no restrictions, while PDP appli-
cations (using dynamic MUXing) are supported with a
minimal number of restrictions as described below. In this
way, speed and cost can be optimized and the devices
can still support the system designer's needs.
The following diagrams illustrate several ispGDXV/VA
applications.

7
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Figure 6. Data Bus Byte Swapper
Figure 7. Four-Port Memory Interface
Contr
ol Bus
Data Bus A
Data Bus B
OEA OEB
I/OA
D0-7
D8-15
D8-15
D0-7
I/OB
XCVR
OEA OEB
I/OA
I/OB
XCVR
OEA OEB
I/OA
I/OB
XCVR
OEA OEB
I/OA
I/OB
XCVR
Bus 4
Bus 3
Bus 2
Bus 1
Port #1
OE1
Memory
Port
OEM
SEL0
SEL1
To
Memory
Port #2
OE2
Port #3
OE3
Note: All OE and SEL lines driven by external arbiter logic (not shown).
Port #4
OE4
4-to-1
16-Bit MUX
Bidirectional
Figure 5. Address Demultiplex/Data Buffering
Contr
ol Bus
MUXed Ad
dress Data Bus
D
Q
CLK
OEA
OEB
I/OA
I/OB
Address
Buffered
Data
To Memory/
Peripherals
XCVR
Address
Latch
Applications (Continued)
Designing with the ispGDXV/VA
As mentioned earlier, this architecture satisfies the PRSI
class of applications without restrictions: any I/O pin as a
single input or bidirectional can drive any other I/O pin as
output.
For the case of PDP applications, the designer does have
to take into consideration the limitations on pins that can
be used as control (MUX0, MUX1, OE, CLK) or data
(MUXA-D) inputs. The restrictions on control inputs are
not likely to cause any major design issues because the
input possibilities span 25% of the total pins.
The MUXA-D input partitioning requires that designers
consciously assign pinouts so that MUX inputs are in the
appropriate, disjoint groups. For example, since the
MUXA group includes I/O0-39 (160 I/O device), it is not
possible to use I/O0 and I/O9 in the same MUX function.
As previously discussed, data path functions will be
assigned early in the design process and these restric-
tions are reasonable in order to optimize speed and cost.
User Electronic Signature
The ispGDXV/VA Family includes dedicated User Elec-
tronic Signature (UES) E
2
CMOS storage to allow users
to code design-specific information into the devices to
identify particular manufacturing dates, code revisions,
or the like. The UES information is accessible through
the boundary scan programming port via a specific com-
mand. This information can be read even when the
security cell is programmed.
Security
The ispGDXV/VA Family includes a security feature that
prevents reading the device program once set. Even
when set, it does not inhibit reading the UES or device ID
code. It can be erased only via a device bulk erase.

8
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
Absolute Maximum Ratings
1,2
Supply Voltage V
cc
................................. -0.5 to +5.4V
Input Voltage Applied ............................... -0.5 to +5.6V
Off-State Output Voltage Applied ............ -0.5 to +5.6V
Storage Temperature ................................ -65 to 150
∞
C
Case Temp. with Power Applied .............. -55 to 125
∞
C
Max. Junction Temp. (T
J
) with Power Applied ... 150
∞
C
1. Stresses above those listed under the "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. Functional
operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification
is not implied (while programming, follow the programming specifications).
2. Compliance with the Thermal Management section of the Lattice Semiconductor Data Book or CD-ROM is a requirement.
DC Recommended Operating Conditions
C
SYMBOL
Table 2-0006/gdx160va
C
PARAMETER
PACKAGE TYPE
Dedicated Clock Capacitance
8
UNITS
TYPICAL
TEST CONDITIONS
1
2
7
PQFP
BGA, fpBGA
PQFP
BGA, fpBGA
I/O Capacitance
pf
10
pf
pf
10
pf
V = 3.3V, V = 2.0V
V = 3.3V, V = 2.0V
CC
CC
Y
I/O
Capacitance (T
A
=25
o
C, f=1.0 MHz)
PARAMETER
MINIMUM
MAXIMUM
UNITS
Erase/Reprogram Cycles
10,000
--
Cycles
Erase/Reprogram Specifications
SYMBOL
Table 2-0005/gdx160va
V
CC
V
CCIO
PARAMETER
Supply Voltage
I/O Reference Voltage
Commercial
T
A
= 0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
MIN.
MAX.
UNITS
3.00
2.3
3.60
3.60
V
Industrial
T
A
= -40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
3.00
3.60
V
V

9
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
Switching Test Conditions
Input Pulse Levels
Input Rise and Fall Time
Input Timing Reference Levels
Output Timing Reference Levels
Output Load
GND to V
CCIO(MIN)
<
1.5ns 10% to 90%
V
CCIO(MIN)
/2
V
CCIO(MIN)
/2
See Figure 8
3-state levels are measured 0.5V from steady-state active level.
Output Load Conditions (See Figure 8)
TEST CONDITION
R1
3.3V
2.5V
R2
CL
A
35pF
D
35pF
B
35pF
35pF
Active High
Slow Slew
Active Low
C
5pF
5pF
156
156
156
144
144
144
R1
R2
153
153
153
134
134
134
Active Low to Z
at V +0.5V
OL
Active High to Z
at V -0.5V
OH
Table 2-0004A/gdx160va
DC Electrical Characteristics for 3.3V Range
1
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
Figure 8. Test Load
V
CCIO
R1
R2
CL
*
Device
Output
Test
Point
*
CL includes Test Fixture and Probe Capacitance.
0213D
V
OL
SYMBOL
1. I/O voltage configuration must be set to VCC.
Table 2-0007/gdx160va
V
OH
V
IH
V
IL
PARAMETER
Output Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
V
CC
=
V
CC (MIN)
I
OL
=
+100
µ
A
I
OL
=
+24mA
I
OH
=
-100
µ
A
I
OH
=
-12mA
V
CC
=
V
CC (MIN)
V
OH
V
OUT
or V
OUT
V
OL(MAX)
V
OH
V
OUT
or V
OUT
V
OL (MAX)
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNITS
≠
2.8
2.0
-0.3
≠
≠
≠
≠
0.2
≠
5.25
0.8
V
≠
≠
0.55
V
V
2.4
≠
≠
V
V
CCIO
I/O Reference Voltage
3.0
≠
≠
3.6
V
V
V

10
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
DC Electrical Characteristics for 2.5V Range
1
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
V
IH
SYMBOL
2.5V/gdx160va
V
OH
PARAMETER
Input High Voltage
Output High Voltage
V
OH(MIN)
V
OUT
or V
OUT
V
OL(MAX)
V
OH(MIN)
V
OUT
or V
OUT
V
OL(MAX)
V
CCIO=MIN
,
I
OH
=
-8mA
V
CCIO=MIN
,
I
OL
=
8mA
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNITS
1.7
1.8
≠
≠
5.25
≠
V
V
CCIO
V
IL
I/O Reference Voltage
Input Low Voltage
2.3
-0.3
≠
≠
≠
2.7
0.7
V
V
V
V
CCIO=MIN
,
I
OH
=
-100
µ
A
2.1
≠
≠
V
≠
≠
0.6
V
V
CCIO=MIN
,
I
OL
=
100
µ
A
≠
≠
0.2
V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage
1. I/O voltage configuration must be set to VCCIO.
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
SYMBOL
1. One output at a time for a maximum of one second. V
OUT
=
0.5V was selected to avoid test problems by
tester ground degradation. Characterized, but not 100% tested.
2. Typical values are at V
CC
=
3.3V and T
A
=
25
∞
C.
3. I
CC
/ MHz = (0.003 x I/O cell fanout) + 0.029.
e.g. An input driving four I/O cells at 40MHz results in a dynamic I
CC
of approximately ((0.003 x 4) + 0.029) x 40 = 1.64mA.
4. For a typical application with 50% of I/O pins used as inputs, 50% used as outputs or bi-directionals.
5. This parameter limits the total current sinking of I/O pins surrounding the nearest GND pin.
DC Char_gdx160va
I
PU
I
BHLS
PARAMETER
I/O Active Pullup Current
Bus Hold Low Sustaining Current
I
IH
I
IL
Input or I/O High Leakage Current
Input or I/O Low Leakage Current
0V
V
IN
V
IL (MAX)
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
2
MAX.
UNITS
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
-10
10
-200
50
µ
A
I
BHT
Bus Hold Trip Points
V
IL
≠
V
IH
V
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
40
≠
≠
µ
A
(V
CCIO
-0.2)
V
IN
V
CCIO
V
CCIO
V
IN
5.25V
0V
V
IN
V
IL (MAX)
I
OS
1
Output Short Circuit Current
≠
≠
-250
mA
V
CC
=
3.3V, V
OUT
=
0.5V, T
A
=
25
∞
C
I
CCQ
4
Quiescent Power Supply Current
≠
16.5
≠
mA
V
IL
=
0.5V, V
IH
=
V
CC
V
IN
=
V
IL (MAX)
I
BHHS
Bus Hold High Sustaining Current
-40
≠
≠
µ
A
V
IN
=
V
IH (MIN)
I
BHLO
Bus Hold Low Overdrive Current
≠
≠
550
µ
A
0V
V
IN
V
CCIO
I
CC
Dynamic Power Supply Current
per Input Switching
One input toggling at 50% duty cycle,
outputs open.
≠
See
Note 3
≠
mA/
MHz
I
CONT
5
Maximum Continuous I/O Pin Sink
Current Through Any GND Pin
≠
≠
≠
160
mA
I
BHHO
Bus Hold High Overdrive Current
≠
≠
-550
µ
A
0V
V
IN
V
CCIO

11
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
5.0
5.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
5.0
8.5
6.0
9.5
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
≠
≠
14.0
≠
5.0
0.5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Data Prop. Delay from Any I/O pin to Any I/O Pin (4:1 MUX)
Data Prop. Delay from MUXsel Inputs to Any Output (4:1 MUX)
Clock Frequency, Max. Toggle
Clock Frequency with External Feedback
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before I/O Clock
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Reg. Hold Time (Y
x
)
Input Latch or Reg. Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Output Latch or Reg. Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Reg. Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (I/O Clock)
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Reg. Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Output Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input to Output Enable
Input to Output Disable
Test OE Output Enable
Test OE Output Disable
Clock Pulse Duration, High
Clock Pulse Duration, Low
Register Reset Delay from RESET Low
Reset Pulse Width
Output Delay Adder for Output Timings Using Slow Slew Rate
Output Skew (tgco1 Across Chip)
External Timing Parameters
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
ns
ns
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
≠
≠
143
111
4.0
3.0
4.0
3.0
2.5
1.5
4.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
3.5
3.5
≠
10.0
≠
≠
A
A
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
A
A
A
A
B
C
B
C
≠
≠
≠
≠
D
A
t
pd
2
t
sel
2
f
max (Tog.)
f
max (Ext.)
t
su1
t
su2
t
su3
t
su4
t
suce1
t
suce2
t
suce3
t
h1
t
h2
t
h3
t
h4
t
hce1
t
hce2
t
hce3
t
gco1
2
t
gco2
2
t
co1
2
t
co2
2
t
en
2
t
dis
2
t
toeen
2
t
toedis
2
t
wh
t
wl
t
rst
t
rw
t
sl
t
sk
DESCRIPTION
PARAMETER
( )
1
tsu3+tgco1
UNITS
-5
MIN. MAX.
1. All timings measured with one output switching, fast output slew rate setting, except
t
sl
.
2. The delay parameters are measured with Vcc as I/O voltage reference. An additional 0.5ns delay is incurred when Vccio is
used as I/O voltage reference.
#
3.5
3.5
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
3.5
6.0
4.0
7.0
5.0
5.0
6.0
6.0
≠
≠
8.0
≠
3.5
0.5
≠
≠
250
166.7
3.0
2.5
2.5
2.0
2.5
1.5
3.0
0.0
0.5
0.0
1.0
0.0
1.0
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
2.0
2.0
≠
5.0
≠
≠
-3
MIN. MAX.
TEST
1
COND.

12
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
9.0
9.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
9.0
13.5
11.5
15.7
10.5
10.5
10.5
10.5
≠
≠
22.0
≠
9.0
1.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Data Prop. Delay from Any I/O pin to Any I/O Pin (4:1 MUX)
Data Prop. Delay from MUXsel Inputs to Any Output (4:1 MUX)
Clock Frequency, Max. Toggle
Clock Frequency with External Feedback
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before I/O Clock
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Reg. Hold Time (Y
x
)
Input Latch or Reg. Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Output Latch or Reg. Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Reg. Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (I/O Clock)
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Reg. Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Output Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input to Output Enable
Input to Output Disable
Test OE Output Enable
Test OE Output Disable
Clock Pulse Duration, High
Clock Pulse Duration, Low
Register Reset Delay from RESET Low
Reset Pulse Width
Output Delay Adder for Output Timings Using Slow Slew Rate
Output Skew (tgco1 Across Chip)
External Timing Parameters
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
ns
ns
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
≠
≠
83
62.5
7.0
6.0
7.0
6.0
4.0
3.0
8.5
0.0
3.0
0.0
3.0
0.0
3.0
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
6.0
6.0
≠
18.0
≠
≠
A
A
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
A
A
A
A
B
C
B
C
≠
≠
≠
≠
D
A
t
pd
2
t
sel
2
f
max (Tog.)
f
max (Ext.)
t
su1
t
su2
t
su3
t
su4
t
suce1
t
suce2
t
suce3
t
h1
t
h2
t
h3
t
h4
t
hce1
t
hce2
t
hce3
t
gco1
2
t
gco2
2
t
co1
2
t
co2
2
t
en
2
t
dis
2
t
toeen
2
t
toedis
2
t
wh
t
wl
t
rst
t
rw
t
sl
t
sk
DESCRIPTION
PARAMETER
( )
1
tsu3+tgco1
UNITS
-9
MIN. MAX.
1. All timings measured with one output switching, fast output slew rate setting, except
t
sl
.
2. The delay parameters are measured with Vcc as I/O voltage reference. An additional 0.5ns delay is incurred when Vccio is
used as I/O voltage reference.
#
-7
MIN. MAX.
TEST
1
COND.
≠
≠
100
80
5.5
4.5
5.5
4.5
3.5
2.5
6.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
5.0
5.0
≠
14.0
≠
≠
7.0
7.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
7.0
11.0
9.0
13.0
8.5
8.5
8.5
8.5
≠
≠
18.0
≠
7.0
0.5

13
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
External Timing Parameters (Continued)
1.0
0.0
0 4 10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.2
1.4
1.6
GRP Delay (ns)
I/O Cell Fanout
ispGDX160VA Maximum
GRP Delay vs. I/O Cell Fanout
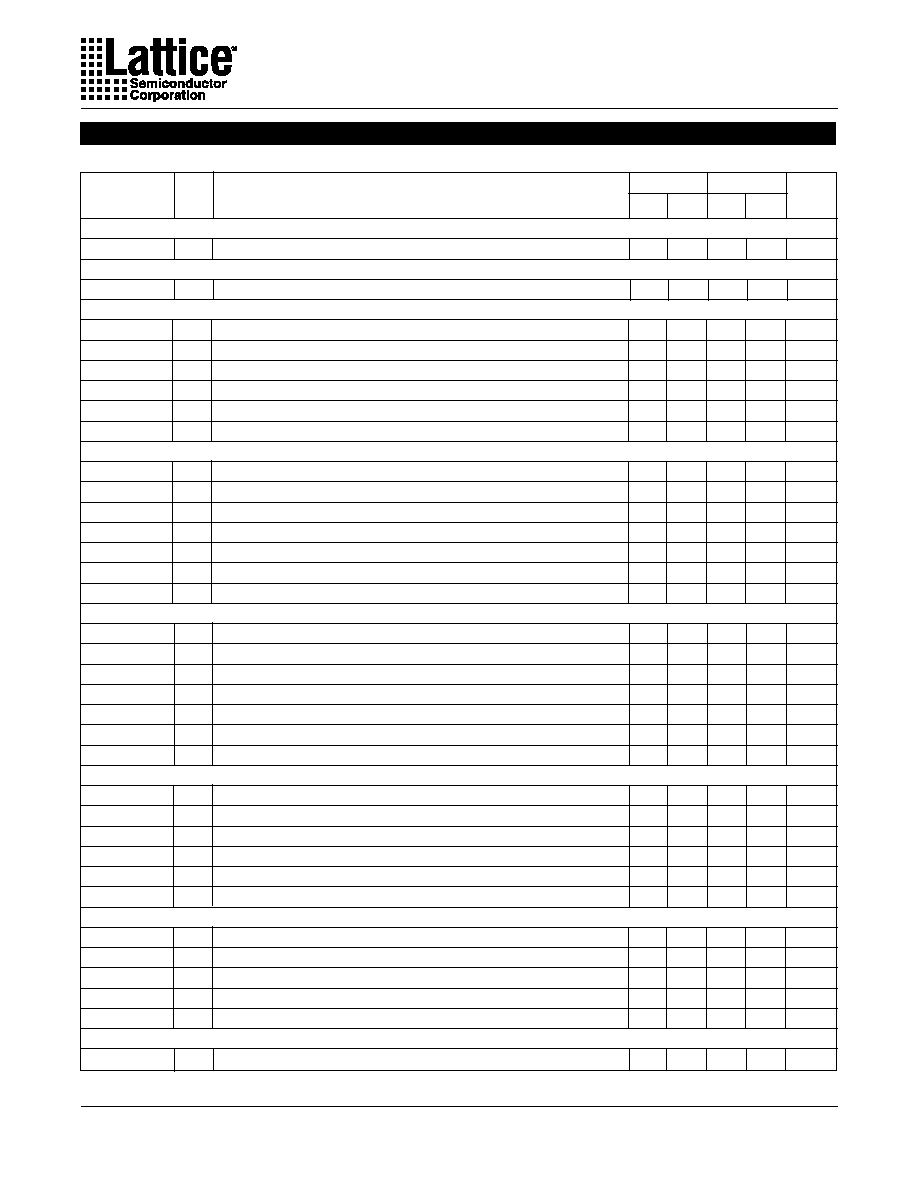
ispGDX160VA timings are specified with a GRP load
(fanout) of four I/O cells. The figure below shows the
GRP Delay with increased GRP loads. These deltas
apply to any signal path traversing the GRP (MUXA-D,
OE, CLK/CLKEN, MUXsel0-1). Global Clock signals
which do not use the GRP have no fanout delay adder.
14
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
-3
-5
PARAMETER #
DESCRIPTION
1
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. UNITS
Inputs
t
io
32
Input Buffer Delay
--
0.4
--
0.9
ns
GRP
t
grp
33
GRP Delay
--
1.1
--
1.1
ns
MUX
t
muxd
34
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Data Delay
--
1.0
--
1.5
ns
t
muxexp
35
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Expander Delay
--
1.5
--
2.0
ns
t
muxs
36
I/O Cell Data Select
--
1.0
--
1.5
ns
t
muxsio
37
I/O Cell Data Select (I/O Clock)
--
1.5
--
3.0
ns
t
muxsg
38
I/O Cell Data Select (Yx Clock)
--
1.5
--
2.0
ns
t
muxselexp
39
I/O Cell MUX Data Select Expander Delay
--
1.5
--
2.0
ns
Register
t
iolat
40
I/O Latch Delay
--
1.0
--
1.0
ns
t
iosu
41
I/O Register Setup Time Before Clock
--
0.8
--
2.0
ns
t
ioh
42
I/O Register Hold Time After Clock
--
1.7
--
1.5
ns
t
ioco
43
I/O Register Clock to Output Delay
--
1.2
--
0.5
ns
t
ior
44
I/O Reset to Output Delay
--
1.0
--
1.5
ns
t
cesu
45
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Clock
--
2.3
--
2.0
ns
t
ceh
46
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time After Clock
--
0.2
--
0.5
ns
Data Path
t
fdbk
47
I/O Register Feedback Delay
--
0.6
--
0.9
ns
t
iobp
48
I/O Register Bypass Delay
--
0.0
--
0.0
ns
t
ioob
49
I/O Register Output Buffer Delay
--
0.0
--
0.0
ns
t
muxcg
50
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (Yx Clock)
--
1.5
--
2.0
ns
t
muxcio
51
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (I/O Clock)
--
1.5
--
3.0
ns
t
iodg
52
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (Yx Clock)
--
3.5
--
4.0
ns
t
iodio
53
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (I/O Clock)
--
3.5
--
5.0
ns
Outputs
t
ob
54
Output Buffer Delay
--
1.0
--
1.5
ns
t
obs
55
Output Buffer Delay (Slow Slew Option)
--
4.5
--
6.5
ns
t
oeen
56
I/O Cell OE to Output Enable
--
3.5
--
4.0
ns
t
oedis
57
I/O Cell OE to Output Disable
--
3.5
--
4.0
ns
t
goe
58
GRP Output Enable and Disable Delay
--
0.0
--
0.0
ns
t
toe
59
Test OE Enable and Disable Delay
--
2.5
--
2.0
ns
Clocks
t
ioclk
60
I/O Clock Delay
--
0.3
--
2.0
ns
t
gclk
61
Global Clock Delay
--
1.3
--
2.0
ns
t
gclkeng
62
Global Clock Enable (Yx Clock)
--
1.5
--
2.5
ns
t
gclkenio
63
Global Clock Enable (I/O Clock)
--
1.0
--
3.5
ns
t
ioclkeng
64
I/O Clock Enable (Yx Clock)
--
0.5
--
2.5
ns
Global Reset
t
gr
65
Global Reset to I/O Register Latch
--
6.0
--
11.0
ns
Internal Timing Parameters
1
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
1. Internal Timing Parameters are not tested and are for reference only.
2. Refer to the Timing Model in this data sheet for further details.

15
Specifications
ispGDX160VA
-7
-9
PARAMETER #
DESCRIPTION
1
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. UNITS
Inputs
t
io
32
Input Buffer Delay
--
1.4
--
1.9
ns
GRP
t
grp
33
GRP Delay
--
1.1
--
1.1
ns
MUX
t
muxd
34
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Data Delay
--
2.0
--
2.5
ns
t
muxexp
35
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Expander Delay
--
2.5
--
3.0
ns
t
muxs
36
I/O Cell Data Select
--
2.0
--
2.5
ns
t
muxsio
37
I/O Cell Data Select (I/O Clock)
--
4.5
--
6.0
ns
t
muxsg
38
I/O Cell Data Select (Yx Clock)
--
2.5
--
3.0
ns
t
muxselexp
39
I/O Cell MUX Data Select Expander Delay
--
2.5
--
3.0
ns
Register
t
iolat
40
I/O Latch Delay
--
1.0
--
1.0
ns
t
iosu
41
I/O Register Setup Time Before Clock
--
3.2
--
4.4
ns
t
ioh
42
I/O Register Hold Time After Clock
--
2.3
--
2.6
ns
t
ioco
43
I/O Register Clock to Output Delay
--
0.5
--
0.5
ns
t
ior
44
I/O Reset to Output Delay
--
1.5
--
1.5
ns
t
cesu
45
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Clock
--
2.5
--
2.0
ns
t
ceh
46
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time After Clock
--
1.0
--
2.0
ns
Data Path
t
fdbk
47
I/O Register Feedback Delay
--
1.2
--
1.3
ns
t
iobp
48
I/O Register Bypass Delay
--
0.3
--
0.6
ns
t
ioob
49
I/O Register Output Buffer Delay
--
0.6
--
0.7
ns
t
muxcg
50
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (Yx Clock)
--
2.5
--
3.0
ns
t
muxcio
51
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (I/O Clock)
--
4.5
--
6.0
ns
t
iodg
52
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (Yx Clock)
--
5.0
--
6.0
ns
t
iodio
53
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (I/O Clock)
--
7.0
--
9.0
ns
Outputs
t
ob
54
Output Buffer Delay
--
2.2
--
2.9
ns
t
obs
55
Output Buffer Delay (Slow Slew Option)
--
9.2
--
11.9
ns
t
oeen
56
I/O Cell OE to Output Enable
--
6.0
--
7.5
ns
t
oedis
57
I/O Cell OE to Output Disable
--
6.0
--
7.5
ns
t
goe
58
GRP Output Enable and Disable Delay
--
0.0
--
0.0
ns
t
toe
59
Test OE Enable and Disable Delay
--
2.5
--
3.0
ns
Clocks
t
ioclk
60
I/O Clock Delay
--
3.2
--
4.4
ns
t
gclk
61
Global Clock Delay
--
2.7
--
3.4
ns
t
gclkeng
62
Global Clock Enable (Yx Clock)
--
3.7
--
5.4
ns
t
gclkenio
63
Global Clock Enable (I/O Clock)
--
5.7
--
8.4
ns
t
ioclkeng
64
I/O Clock Enable (Yx Clock)
--
4.2
--
6.4
ns
Global Reset
t
gr
65
Global Reset to I/O Register Latch
--
13.7
--
16.4
ns
Internal Timing Parameters
1
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
1. Internal Timing Parameters are not tested and are for reference only.
2. Refer to the Timing Model in this data sheet for further details.

16
Specifications
ispGDX160V
Absolute Maximum Ratings
1,2
Supply Voltage V
cc
................................. -0.5 to +5.4V
Input Voltage Applied ............................... -0.5 to +5.6V
Off-State Output Voltage Applied ............ -0.5 to +5.6V
Storage Temperature ................................ -65 to 150
∞
C
Case Temp. with Power Applied .............. -55 to 125
∞
C
Max. Junction Temp. (T
J
) with Power Applied ... 150
∞
C
1. Stresses above those listed under the "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. Functional
operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification
is not implied (while programming, follow the programming specifications).
2. Compliance with the Thermal Management section of the Lattice Semiconductor Data Book or CD-ROM is a requirement.
DC Recommended Operating Conditions
C
SYMBOL
Table 2 - 0006
C
PARAMETER
Dedicated Clock Capacitance
10
UNITS
TYPICAL
TEST CONDITIONS
1
2
8
I/O Capacitance
pf
pf
V = 3.3V, V = 2.0V
V = 3.3V, V = 2.0V
CC
CC
Y
I/O
Capacitance (T
A
=25
o
C, f=1.0 MHz)
T
A
= 0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
T
A
= -40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
SYMBOL
Table 2-0005/gdxv
V
CC
V
IH
1
V
IL
1
PARAMETER
Supply Voltage
Input High Voltage
1. Typical 100mV of input hysteresis.
Input Low Voltage
MIN.
MAX.
UNITS
3.0
3.0
2.0
-0.3
3.6
3.6
5.25
0.8
V
V
V
V
Commercial
Industrial
PARAMETER
MINIMUM
MAXIMUM
UNITS
Erase/Reprogram Cycles
10,000
--
Cycles
Erase/Reprogram Specifications

17
Specifications
ispGDX160V
Output Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Input or I/O Low Leakage Current
Input or I/O High Leakage Current
I/O Active Pull-Up Current
Bus Hold Low Sustaining Current
Bus Hold High Sustaining Current
Bus Hold Low Overdrive Current
Bus Hold High Overdrive Current
Bus Hold Trip Points
Output Short Circuit Current
Quiescent Power Supply Current
Dynamic Power Supply Current
per Input Switching
Maximum Continuous I/O Pin Sink
Current Through Any GND Pin
I
OL
=24 mA
I
OH
=-12 mA
0V
V
IN
V
IL
(Max.)
V
CC
V
IN
5.25V
0V
V
IN
V
IL
V
IN
= V
IL
(Max.)
V
IN
= V
IH
(Min.)
0V
V
IN
V
CC
0V
V
IN
V
CC
V
CC
= 3.3V, V
OUT
= 0.5V, T
A
= 25∞C
V
IL
= 0.5V, V
IH
= V
CC
One input toggling @ 50% duty cycle,
outputs open.
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
70
≠
≠
2.4
≠
≠
≠
50
-50
≠
≠
V
IL
≠
≠
≠
≠
0.55
≠
-10
10
-150
≠
≠
550
-550
V
IH
-250
≠
≠
96
Switching Test Conditions
DC Electrical Characteristics
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
V
V
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
V
mA
mA
mA/MHz
mA
V
OL
V
OH
I
IL
I
IH
I
IL-PU
I
BHLS
I
BHHS
I
BHLO
I
BHHO
I
BHT
I
OS
1
I
CCQ
4
I
CC
1. One output at a time for a maximum duration of one second. V
OUT
= 0.5V was selected to avoid test problems by tester ground
degradation. Characterized but not 100% tested.
2. Typical values are at V
CC
= 3.3V and T
A
= 25
o
C.
3. I
CC
/ MHz = (0.01 x I/O cell fanout) + 0.04
e.g. An input driving four I/O cells at 40 MHz results in a dynamic I
CC
of approximately ((0.01 x 4) + 0.04) x 40 = 3.2 mA.
4. For a typical application with 50% of I/O pins used as inputs, 50% used as outputs or bidirectionals.
5. This parameter limits the total current sinking of I/O pins surrounding the nearest GND pin.
SYMBOL
MIN.
MAX.
TYP.
2
PARAMETER
CONDITION
UNITS
Input Pulse Levels
GND to 3.0V
Input Rise and Fall Time
1.5ns 10% to 90%
Input Timing Reference Levels
1.5V
Output Timing Reference Levels
1.5V
Output Load
See figure at right
3-state levels are measured 0.5V from steady-state
active level.
+ 3.3V
R1
R2
CL
*
Device
Output
Test
Point
*
CL includes Test Fixture and Probe Capacitance.
See
Note 3
I
CONT
5
Output Load Conditions
TEST CONDITION
R1
R2
CL
A
153
134
35pF
B
134
35pF
153
35pF
Active High
Slow Slew
Active Low
C
D
153
5pF
35pF
134
5pF
Active Low to Z
at V +0.5V
OL
Active High to Z
at V -0.5V
OH
Table 2-0004A

18
Specifications
ispGDX160V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Data Prop. Delay from Any I/O pin to Any I/O pin (4:1 MUX)
Data Prop. Delay from MUXsel Inputs to Any Output (4:1 MUX)
Clock Frequency, Max. Toggle
Clock Frequency with External Feedback
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before Y
x
Output Latch or Register Setup Time Before I/O Clock
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Global Clock Enable Setup Time Before I/O Clock
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Y
x
Input Latch or Register Hold Time (Y
x
)
Input Latch or Register Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Output Latch or Register Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Register Hold Time (I/O Clock)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Global Clock Enable Hold Time (I/O Clock)
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time (Y
x
)
Output Latch or Register Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from Y
x
) to Output Delay
Output Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input Latch or Register Clock (from I/O pin) to Output Delay
Input to Output Enable
Input to Output Disable
Test OE Output Enable
Test OE Output Disable
Clock Pulse Duration, High
Clock Pulse Duration, Low
Register Reset Delay from RESET Low
Reset Pulse Width
Output Delay Adder for Output Timings Using Slow Slew Rate
Output Skew (tgco1 Across Chip)
External Timing Parameters
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
ns
ns
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
≠
≠
143
110
4.0
3.0
4.0
3.0
2.5
1.5
4.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
3.5
3.5
≠
10.0
≠
≠
5.0
6.5
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
5.0
8.5
6.0
9.5
6.0
6.0
9.0
9.0
≠
≠
14.0
≠
8.0
0.5
≠
≠
100
80.0
5.5
4.5
5.5
4.5
3.5
2.5
6.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
2.5
0.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
5.0
5.0
≠
14.0
≠
≠
7.0
9.0
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
7.0
11.0
9.0
13.0
8.5
8.5
12.0
12.0
≠
≠
18.0
≠
12.0
0.5
A
A
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
A
A
A
A
B
C
B
C
≠
≠
≠
≠
D
A
t
pd
t
sel
f
max (Tog.)
f
max (Ext.)
t
su1
t
su2
t
su3
t
su4
t
suce1
t
suce2
t
suce3
t
h1
t
h2
t
h3
t
h4
t
hce1
t
hce2
t
hce3
t
gco1
t
gco2
t
co1
t
co2
t
en
t
dis
t
toeen
t
toedis
t
wh
t
wl
t
rst
t
rw
t
sl
t
sk
DESCRIPTION
PARAMETER
TEST
1
COND.
( )
1
tsu3+tgco1
UNITS
-5
MIN. MAX.
-7
MIN. MAX.
1. All timings measured with one output switching, fast output slew rate setting, except
t
sl
.
#

19
Specifications
ispGDX160V
External Timing Parameters (Continued)
2
8
0
10
4
20
30
40
50
60
70
I/O Cell Fanout
GRP Delay (ns)
6
10
4
ispGDX160V Maximum
GRP Delay vs. I/O Cell Fanout
ispGDX160V timings are specified with a GRP load
(fanout) of four I/O cells. The figure below shows the
GRP Delay with increased GRP loads. These deltas
apply to any signal path traversing the GRP (MUXA-D,
OE, CLK/CLKEN, MUXsel0-1). Global Clock signals
which do not use the GRP have no fanout delay adder.

20
Specifications
ispGDX160V
-5
-7
PARAMETER #
DESCRIPTION
1
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. UNITS
Inputs
t
io
32
Input Buffer Delay
--
0.9
--
1.4
ns
GRP
t
grp
33
GRP Delay
--
1.1
--
1.1
ns
MUX
t
muxd
34
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Data Delay
--
1.5
--
2.0
ns
t
muxexp
35
I/O Cell MUX A/B/C/D Expander Delay
--
2.0
--
2.5
ns
t
muxs
36
I/O Cell Data Select
--
3.0
--
4.0
ns
t
muxsio
37
I/O Cell Data Select (I/O Clk)
--
4.5
--
6.5
ns
t
muxsg
38
I/O Cell Data Select (Yx Clk)
--
3.5
--
4.5
ns
t
muxselexp
39
I/O Cell MUX Data Select Expander Delay
--
3.5
--
4.5
ns
Register
t
iolat
40
I/O Latch Delay
--
1.0
--
1.0
ns
t
iosu
41
I/O Register Setup Time Before Clock
--
2.0
--
3.2
ns
t
ioh
42
I/O Register Hold Time After Clock
--
1.5
--
2.3
ns
t
ioco
43
I/O Register Clock to Output Delay
--
0.5
--
0.5
ns
t
ior
44
I/O Reset to Output Delay
--
1.5
--
1.5
ns
t
cesu
45
I/O Clock Enable Setup Time Before Clock
--
2.0
--
2.5
ns
t
ceh
46
I/O Clock Enable Hold Time After Clock
--
0.5
--
1.0
ns
Data Path
t
fdbk
47
I/O Register Feedback Delay
--
0.9
--
1.2
ns
t
iobp
48
I/O Register Bypass Delay
--
0.0
--
0.3
ns
t
ioob
49
I/O Register Output Buffer Delay
--
0.0
--
0.6
ns
t
muxcg
50
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (Yx Clk)
--
2.0
--
2.5
ns
t
muxcio
51
I/O Register A/B/C/D Data Input MUX Delay (I/O Clk)
--
3.0
--
4.5
ns
t
iodg
52
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (Yx Clk)
--
4.0
--
5.0
ns
t
iodio
53
I/O Register I/O MUX Delay (I/O Clk)
--
5.0
--
7.0
ns
Outputs
t
ob
54
Output Buffer Delay
--
1.5
--
2.2
ns
t
obs
55
Output Buffer Delay (Slow Slew Option)
--
9.5
--
14.2
ns
t
oeen
56
I/O Cell OE to Output Enable
--
4.0
--
6.0
ns
t
oedis
57
I/O Cell OE to Output Disable
--
4.0
--
6.0
ns
t
goe
58
GRP Output Enable and Disable Delay
--
0.0
--
0.0
ns
t
toe
59
Test OE Enable and Disable Delay
--
5.0
--
6.0
ns
Clocks
t
ioclk
60
I/O Clock Delay
--
2.0
--
3.2
ns
t
gclk
61
Global Clock Delay
--
2.0
--
2.7
ns
t
gclkeng
62
Global Clock Enable (Yx Clk)
--
2.5
--
3.7
ns
t
gclkenio
63
Global Clock Enable (I/O Clk)
--
3.5
--
5.7
ns
t
ioclkeng
64
I/O Clock Enable (Yx Clk)
--
2.5
--
4.2
ns
Global Reset
t
gr
65
Global Reset to I/O Register Latch
--
11.0
--
13.7
ns
Internal Timing Parameters
1
Over Recommended Operating Conditions
1. Internal Timing Parameters are not tested and are for reference only.
2. Refer to the Timing Model in this data sheet for further details.

21
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Switching Waveforms
Clock Width
CLK
(I/O INPUT)
t
wl
t
wh
COMBINATORIAL
I/O OUTPUT
VALID INPUT
DATA (I/O INPUT)
t
pd
t
sel
VALID INPUT
MUXSEL (I/O INPUT)
Combinatorial Output
COMBINATORIAL
I/O OUTPUT
OE (I/O INPUT)
t
en
t
dis
I/O Output Enable/Disable
Registered Output
Reset
REGISTERED
I/O OUTPUT
t
rst
RESET
t
rw
I/O Pin
RESET
TOE
Y0,1,2,3
Y0,1,2,3, Enable
tgclk #61
tgclkeng #62
tgclkenio #63
MUX0
MUX1
tgrp #33
MUX Expander Input
GRP
A
B
C
D
OE
tgoe #58
tmuxexp #35
tmuxselexp #39
tiobp #48
CLK
CLKEN
MUX Expander Output
tioob #49
tmuxd #34
tmuxs #36
tmuxio #37
tmuxg #38
tmuxcg #50
tmuxcio #51
tiod #52, #53
tgr #65
0902/gdx160v/va
tio #32
tfdbk #47
tioclk #60
tioclkeg #64
tiolat #40
tiosu #41
tioh #42
tioco #43
tior #44
tcesu #45
tceh #46
tob #54
tobs #55
toeen #56
toedis #57
ttoe #59
CLK
CLKEN
D
Q
DATA
(I/O INPUT)
REGISTERED
I/O OUTPUT
CLK
CLKEN
VALID INPUT
t
t
h
t
suce
t
ceh
t
co
1/
f
max
(external fdbk)
t
gco
su
ispGDXV Timing Model

22
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
ispGDX Development System
Lattice's ispGDX Development System Interface
The ispGDX Development System supports ispGDX
design using a simple language syntax and an easy-to-
use Graphical User Interface (GUI) called Design
Manager. From creation to In-System Programming, the
ispGDX system is an easy-to-use, self-contained design
tool delivered on CD-ROM media.
Features
∑ Easy-to-use Text Entry System
∑ ispGDX Design Compiler
- Design Rule Checker
- I/O Connectivity Checker
- Automatic Compiler Function
∑ Industry Standard JEDEC File for Programming
∑ Min / Max Timing Report
∑ Interfaces To Popular Timing Simulators
∑ User Electronic Signature (UES) Support
∑ Detailed Log and Report Files For Easy Design Debug
∑ On-Line Help
∑ Windows
Æ
3.1x, Windows 95, Windows 98 and Win-
dows NT
Æ
Compatible Graphical User Interface
∑ SUN O/S, Command Line Driven version available
PC Version
With the ispGDX GUI for the PC, command line entry is
not required. The tools run under Microsoft Windows 3.1,
Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows NT. When the
ispGDX software is invoked, the Design Manager and an
accompanying message window are displayed. The
Design Manager consists of the Menu Bar, Tool Bar,
Status Bar and the work area. The figure below shows
these elements of the ispGDX GUI.
The Menu Bar displays topics related to functions used in
the design process. Access the various drop-down menus
and submenus by using the mouse or "hot" keys. The
menu items available in the ispGDX system are FILE,
EDIT, DEVICE, INVOKE, INTERFACES, VIEW, WIN-
DOW and HELP.
The Tool Bar is a quick and easy way to perform many of
the functions found in the menus with a single click of the
mouse. File, Edit, Undo, Redo, Find, Print Download and
Compiler are just some of the Icons found in the ispGDX
Tool Bar. For instance, the Compiler Icon performs the
same function as the Invoke => Compiler menu com-
mands, including design analysis and rule checking and
the fitting operation.
The Status Bar displays action prompts and the line and
column numbers reflect the location of the cursor within
the message window or the work area.
Workstation Version
The ispGDX software is also available for use under the
Sun O/S 4.1.x or Solaris 2.4 or 2.5. The Sun version of the
ispGDX software is invoked from the command line
under the UNIX operating system. A GUI is not supported
in this environment.
In the UNIX environment, the ispGDX Design File (GDF)
must be created using a text editor. Once the GDF has
been created, invoke the ispGDX workstation software
from the UNIX command line. The following is an ex-
ample of how to invoke ispGDX software.
Usage:
ispGDX
[-i input_file]
[-of[edif|orcad|viewlogic|verilog|vhdl]]
[-p part name]
[-r par_file]
Where:
-i input_file
ispGDX design file
-of [edif | orcad | viewlogic |
Output format
verilog | vhdl]
-p part_name
ispGDX part number
-r par_file
Read parameters from
parameter file

23
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
The GDF File
The GDF file is a simple text description of the design
function, device and pin parameters. The file has four
parts: device selection, set and constant statements, a
pin section and a connection section. A sample file looks
like this:
// 32-Bit Data 3 to 1 Mux
DESIGN
datamux;
PART ispGDX160V-7Q208;
PARAM SECURITY ON;
PARAM OPENDRAIN ON;
//
USE OPEN DRAIN
//
OPTION
PARAM PULL HOLD;
// USE BUS HOLD
//
LATCH OPTION
SET
BUS_A
[dataA31..dataA0];
SET
BUS_B
[dataB31..dataB0];
SET
BUS_C
[dataC31..dataC0];
SET
BUS_D
[dataD31..dataD0];
INPUT
BUS_A
{A31..A0};
INPUT
BUS_B
{B31..B0};
INPUT
BUS_C
{C31..C0};
OUTPUT BUS_D
{D31..D0};
INPUT [oe]
{B37};
INPUT [clk] {B36};
INPUT [sel1]
{B38};
INPUT [sel0]
{B39};
BEGIN
BUS_D.m0 = BUS_A;
BUS_D.m1 = BUS_B;
BUS_D.m2 = BUS_C;
BUS_D.m3 = VCC;
// Default all
// outputs to VCC
BUS_D.s1 = sel1;
BUS_D.s0 = sel0;
BUS_D.oe = oe;
BUS_D.clk = clk;
END
This example shows a simple, but complete, 32-bit 3:1
MUX design. Once completed, the compiler takes over.
Powerful Syntax
Lattice's ispGDX Design System uses simple, but power-
ful, syntax to easily define a design. The !(bang) operator
controls pin polarity and can be used in both the pin and
connection sections of the design definition. Dot exten-
sions define data inputs, select controls for the 4:1
multiplexor, and control inputs of sequential elements
and tri-state buffers. Dot extensions are .M# (MUX Input),
.S# (MUX Select), and control functions, such as .CLK,
.EN, .OE and .A (shown in adjacent table). Pin Attributes
are assigned in the pin section of the GDF as well.
SLOWSLEW selects the slow slew rate for an output
buffer. The Pull parameter can be used to select the
internal pull-up or bus hold latch. OPEN drain can be
used to select open drain operation. The COMB attribute
distinguishes the structure for bidirectional pins. If COMB
is used, the input register, or latch, of an output buffer will
be applied to bidirectional pins.
Please consult the ispGDX Development System Manual
for full details.
Type
Dot Ext.
Description
MUX
Input
MUX
Selection
Control
MUX
Output
.M0
MUXA Data input to 4:1 MUX
.M1
MUXB Data input to 4:1 MUX
MUX0 Selection input to 4:1 MUX
MUX1 Selection input to 4:1 MUX
.M2
MUXC Data Input to 4:1 MUX
.M3
.S0
.S1
MUXD Data input to 4:1 MUX
.CLK
Clock for a register
.CE
Clock enable for register clock
.A
Adjacent MUX output of an I/O cell
.EN
Latch enable for a latch signal
.OE
Output enable for 3-state output
or bidirectional signal
ispGDXV Dot Ext
ispGDX GDF File Dot Extensions
ispGDX Development System (Continued)

24
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
The ispGDX Design System Compiler
After the GDF file is created, the compiler checks the
syntax and provides helpful hints and the location of any
syntax errors. The compiler performs design rule checks,
such as, clock and enable designations, the use of input/
output/BIDI usage, and the proper use of attributes. I/O
connectivity is also checked to ensure polarity, MUX
selection controls, and connections are properly made.
Compilation is completed automatically and report and
programming files are saved.
Reports Generated
When the ispGDX system compiles a design and gener-
ates the specified netlists, the following output files are
created:
Report Files:
.log
Compiler History
.rpt
Compiler Report
.mfr
Maximum Frequency Timing Report
.tsu
Set-up and Hold Timing Report
.tco
Clock to Out Timing Report
.tpt
Timing Report
Simulation File:
.sim
Post-Route Simulation With LAC Format
Netlists:
.edo
EDIF Output
.vlo
Verilog Output
.ifo
OrCAD Output
.vho
VHDL non-VITAL with Maximum Delays Output
.vhn
VHDL non-VITAL with Maximum Delays Output
.vto
VHDL VITAL Output
Download:
.jed
JEDEC Device Programming File
Third-Party Timing Simulation
The ispGDX Design System will generate simulation
netlists as specified by a user. The simulation netlist
formats available are: EDIF, Verilog (OVI compliant),
VHDL (VITAL compliant), Viewlogic, and OrCAD.
For In-System Programming, Lattice's ispGDX devices
may be programmed, alone or in a chain with up to 100
other Lattice ISP devices, using Lattice's ISP Daisy
Chain Download software. This powerful Windows-based
tool can be launched from the Tool Bar or by Invoking the
Download option from the drop down menu within the
ispGDX Design System. ISP Daisy Chain Download
version 7.1 or above supports the ispGDX Family de-
vices.
ispGDX Development System (Continued)

25
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Figure 9. ispJTAG Device Programming Interface
In-System Programmability
All necessary programming of the ispGDXV/VA is done
via four TTL level logic interface signals. These four
signals are fed into the on-chip programming circuitry
where a state machine controls the programming.
On-chip programming can be accomplished using an
IEEE 1149.1 boundary scan protocol. The IEEE 1149.1-
compliant interface signals are Test Data In (TDI), Test
Data Out (TDO), Test Clock (TCK) and Test Mode Select
(TMS) control. The EPEN pin is also used to enable or
disable the JTAG port.
The embedded controller port enable pin (EPEN) is used
to enable the JTAG tap controller and in that regard has
similar functionality to a TRST pin. When the pin is driven
high, the JTAG TAP controller is enabled. This is also true
when the pin is left unconnected, in which case the pin is
pulled high by the permanent internal pullup. This allows
ISP programming and BSCAN testing to take place as
specified by the Instruction Table.
When the pin is driven low, the JTAG TAP controller is
driven to a reset state asynchronously. It stays there
while the pin is held low. After pulling the pin high the
JTAG controller becomes active. The intent of this fea-
ture is to allow the JTAG interface to be directly controlled
by the data bus of an embedded controller (hence the
name Embedded Port Enable). The EPEN signal is used
as a "device select" to prevent spurious programming
and/or testing from occuring due to random bit patterns
on the data bus. Figure 9 illustrates the block diagram for
the ispJTAG interface.
ispGDX
160V/VA
Device
TDO
TDI
TMS
TCK
EPEN
ispJTAG
Programming
Interface
ispLSI
Device
ispMACH
Device
ispGDX
160V/VA
Device
ispGDX
160V/VA
Device

26
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Boundary Scan
The ispGDXV/VA devices provide IEEE1149.1a test
capability and ISP programming through a standard
Boundary Scan Test Access Port (TAP) interface.
The boundary scan circuitry on the ispGDXV/VA Family
operates independently of the programmed pattern. This
allows customers using boundary scan test to have full
test capability with only a single BSDL file.
The ispGDXV/VA devices are identified by the 32-bit
JTAG IDCODE register. The device ID assignments are
listed in Table 4.
Table 3. I/O Shift Register Order
Figure 10. Boundary Scan Register Circuit for I/O Pins
Normal
Function
OE
EXTEST
Update DR
SCANOUT
(to next cell)
Clock DR
SCANIN
(from previous
cell
Shift DR
Normal
Function
TOE
D
Q
D
Q
D
Q
D
Q
D
Q
I/O Pin
Reset
BSCAN
Registers
BSCAN
Latches
HIGHZ
0
1
0
1
PROG_MODE
EXTEST
I/O Shift Reg Order/ispGDXVA
ispGDX160V/VA
TDI, TOE, Y2, Y3,
RESET
, Y1, Y0, I/O B20 .. B39, I/O C0 .. C39, I/O D0 .. D19, I/O B19 .. B0,
I/O A39.. A0, I/O D39 .. D20, TDO
I/O SHIFT REGISTER ORDER
DEVICE
Table 4. ispGDX160V/VA Device ID Codes
ID Code/GDX160V/VA
ispGDX160V
0000, 0000, 0011, 0101, 0011, 0000, 0100, 0011
ispGDX160VA
0001, 0000, 0011, 0101, 0011, 0000, 0100, 0011
32-BIT BOUNDARY SCAN ID CODE
DEVICE

27
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
The ispJTAG programming is accomplished by execut-
ing Lattice private instructions under the Boundary Scan
State Machine.
Details of the programming sequence are transparent to
the user and are handled by Lattice ISP Daisy Chain
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
Update-IR
Exit2-IR
Pause-IR
Exit1-IR
Shift-IR
Capture-IR
Select-IR-Scan
Update-DR
Exit2-DR
Pause-DR
Exit1-DR
Shift-DR
Capture-DR
Select-DR-Scan
Run-Test/Idle
Test-Logic-Reset
Figure 12. Boundary Scan State Machine
Figure 11. Boundary Scan Register Circuit for Input-Only Pins
Downlowad (ispDCDTM), ispCODE `C' routines or any
third-party programmers. Contact Lattice Technical Sup-
port to obtain more detailed programming information.
SCANOUT
(to next cell)
Clock DR
SCANIN
(from previous
cell
Shift DR
D
Q
Input Pin
Boundary Scan (Continued)

28
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Units
t
btcp
TCK [BSCAN test] clock pulse width
100
≠
ns
t
btch
TCK [BSCAN test] pulse width high
50
≠
ns
tbtcl
TCK [BSCAN test] pulse width low
50
≠
ns
tbtsu
TCK [BSCAN test] setup time
20
≠
ns
tbth
TCK [BSCAN test] hold time
25
≠
ns
trf
TCK [BSCAN test] rise and fall time
50
≠
mV/ns
tbtco
TAP controller falling edge of clock to valid output
≠
25
ns
tbtoz
TAP controller falling edge of clock to data output disable
≠
25
ns
tbtvo
TAP controller falling edge of clock to data output enable
≠
25
ns
tbtcpsu
BSCAN test Capture register setup time
20
≠
ns
tbtcph
BSCAN test Capture register hold time
25
≠
ns
tbtuco
BSCAN test Update reg, falling edge of clock to valid output
≠
50
ns
tbtuoz
BSCAN test Update reg, falling edge of clock to output disable
≠
50
ns
tbtuov
BSCAN test Update reg, falling edge of clock to output enable
≠
50
ns
Figure 13. Boundary Scan Waveforms and Timing Specifications
TMS
TDI
TCK
TDO
Data to be
captured
Data to be
driven out
Valid Data
Valid Data
Valid Data
Valid Data
Data Captured
btsu
T
bth
T
btcl
T
btch
T
btcp
T
btvo
T
btco
T
btoz
T
btcsu
T
btch
T
btuov
T
btuco
T
btuoz
T
Boundary Scan (Continued)

29
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
I/O
Input/Output Pins ≠ These are the general purpose bidirectional data pins. When used as outputs,
each may be independently latched, registered or tristated. They can also each assume one other
control function (OE, CLK/CLKEN, and MUXsel as described in the text).
TOE
Test Output Enable Pin ≠ This pin tristates all I/P pins when a logic low is driven.
RESET
Active LOW Input Pin ≠ Resets all I/O register outputs when LOW.
Yx/CLKENx
Input Pins ≠These can be either Global Clocks or Clock Enables.
EPEN
Input Pin ≠ JTAG TAP Controller Enable Pin. When high, JTAG operation is enabled. When low,
JTAG TAP controller is driven to reset.
TDI
Input Pin ≠ Serial data input during ISP programming or Boundary Scan mode.
TCK
Input Pin ≠ Serial data clock during ISP programming or Boundary Scan mode.
TMS
Input Pin ≠ Control input during ISP programming or Boundary Scan mode.
TDO
Output Pin ≠ Serial data output during ISP programming or Boundary Scan mode.
GND
Ground (GND)
VCC
Vcc ≠ Supply voltage (3.3V).
VCCIO
2
Input ≠ This pin is used if optional 2.5V output is to be used. Every I/O can independently select either
3.3V or the optional voltage as its output level. If the optional output voltage is not required, this pin
must be connected to the VCC supply. Programmable pull-up resistors and bus-hold latches only draw
current from this supply.
NC
1
No Connect.
Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Description
1. NC pins are not to be connected to any active signals, VCC or GND.
2. "VA" version only.

30
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Signal Locations: ispGDX160V/VA
Signal
208-Pin PQFP
208-Ball fpBGA
272-Ball BGA
TOE
178
D9
A12
RESET
185
A8
D10
Y0/CLKEN0
75
N8
V10
Y1/CLKEN1
76
R8
Y10
Y2/CLKEN2
180
B9
C11
Y3/CLKEN3
181
C9
A11
EPEN
183
A9
B10
TDI
81
P9
Y12
TCK
80
T9
U11
TMS
79
T8
V11
TDO
78
P8
W11
GND
6, 15, 25, 35, 44, 54, 63,
D4, D13, G7, G8, G9,
A1, D4, D8, D13, D17, H4, H17, J9, J10, J11, J12,
77, 91, 100, 110, 119, 129,
G10, H7, H8, H9, H10,
K9, K10, K11, K12, L9, L10, L11, L12, M9, M10,
139, 148, 159, 168, 182,
J7, J8, J9, J10, K7, K8,
M11, M12, N4, N17, U4, U8, U13, U17
195, 204
K9, K10, N4, N13
VCC
1, 17, 33, 49, 65, 89, 105,
E13
1
, F4, F13, L4, L13,
C18
1
, D6, D11, D15, F4, F17, K4, L17, R4, R17, U6,
121, 137, 153, 156
1
, 170,
M4, M13, N5, N11, N12 U10, U15
184, 193
D5, D6, D12, E4
VCCIO
156
1
E13
1
C18
1
NC
73, 74, 179
A10, P7, T7
A2, A6, A7, A10, A15, A19, A20, B1, B2, B4, B11,
B14, B18, B19, B20, C2, C3, C10, D2, D3, D16, E2,
E17, E19, H1, H3, H18, H20, K20, L1, N1, N3, N18
N20, T2, T4, T19, U5, U18, U19, V3, V14, V18, V19,
W1, W2, W3, W7, W10, W14, W19, W20, Y1, Y2, Y6,
Y9, Y11, Y18, Y20
1. VCC on ispGDX160V, VCCIO on ispGDX160VA.

31
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
I/O Locations: ispGDX160V/VA (Ordered by I/O Signal Name and 208-Pin PQFP Location)
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
VCC
I/O A0
CLK/CLKEN
2
B2
E4
I/O A1
OE
3
B1
C1
I/O A2
MUXsel1
4
C2
D1
I/O A3
MUXsel2
5
A1
E3
GND
I/O A4
CLK/CLKEN
7
C1
E1
I/O A5
OE
8
D3
F3
I/O A6
MUXsel1
9
D2
G4
I/O A7
MUXsel2
10
D1
F2
I/O A8
CLK/CLKEN
11
E3
F1
I/O A9
OE
12
E2
G3
I/O A10
MUXsel1
13
E1
G2
I/O A11
MUXsel2
14
F3
G1
GND
I/O A12
CLK/CLKEN
16
F2
H2
VCC
I/O A13
OE
18
F1
J4
I/O A14
MUXsel1
19
G4
J3
I/O A15
MUXsel2
20
G2
J2
I/O A16
CLK/CLKEN
21
G3
J1
I/O A17
OE
22
G1
K2
I/O A18
MUXsel1
23
H4
K3
I/O A19
MUXsel2
24
H2
K1
GND
I/O A20
CLK/CLKEN
26
H3
L2
I/O A21
OE
27
H1
L3
I/O A22
MUXsel1
28
J1
L4
I/O A23
MUXsel2
29
J3
M1
I/O A24
CLK/CLKEN
30
J2
M2
I/O A25
OE
31
J4
M3
I/O A26
MUXsel1
32
K1
M4
VCC
I/O A27
MUXsel2
34
K3
N2
GND
I/O A28
CLK/CLKEN
36
K2
P1
I/O A29
OE
37
K4
P2
I/O A30
MUXsel1
38
L1
R1
I/O A31
MUXsel2
39
L2
P3
I/O A32
CLK/CLKEN
40
L3
R2
I/O A33
OE
41
M1
T1
I/O A34
MUXsel1
42
M2
P4
I/O A35
MUXsel2
43
M3
R3
GND
I/O A36
CLK/CLKEN
45
N1
U1
I/O A37
OE
46
N2
T3
I/O A38
MUXsel1
47
N3
U2
I/O A39
MUXsel2
48
P1
V1
VCC
I/O B0
CLK/CLKEN
50
P2
U3
I/O B1
OE
51
R1
V2
I/O B2
MUXsel1
52
R2
W4
I/O B3
MUXsel2
53
T1
V4
GND
I/O B4
CLK/CLKEN
55
P3
Y3
I/O B5
OE
56
T2
Y4
I/O B6
MUXsel1
57
R3
V5
I/O B7
MUXsel2
58
P4
W5
I/O B8
CLK/CLKEN
59
T3
Y5
I/O B9
OE
60
R4
V6
I/O B10
MUXsel1
61
T4
U7
I/O B11
MUXsel2
62
P5
W6
GND
I/O B12
CLK/CLKEN
64
R5
V7
VCC
I/O B13
OE
66
N6
Y7
I/O B14
MUXsel1
67
T5
V8
I/O B15
MUXsel2
68
R6
W8
I/O B16
CLK/CLKEN
69
P6
Y8
I/O B17
OE
70
T6
U9
I/O B18
MUXsel1
71
N7
V9
I/O B19
MUXsel2
72
R7
W9
GND
I/O B20
CLK/CLKEN
82
R9
W12
I/O B21
OE
83
N9
V12
I/O B22
MUXsel1
84
T10
U12
I/O B23
MUXsel2
85
P10
Y13
I/O B24
CLK/CLKEN
86
R10
W13
I/O B25
OE
87
N10
V13
I/O B26
MUXsel1
88
T11
Y14
VCC
I/O B27
MUXsel2
90
P11
Y15
GND
I/O B28
CLK/CLKEN
92
R11
W15
I/O B29
OE
93
T12
Y16
I/O B30
MUXsel1
94
P12
U14
I/O B31
MUXsel2
95
R12
V15
I/O B32
CLK/CLKEN
96
T13
W16
I/O B33
OE
97
R13
Y17
I/O B34
MUXsel1
98
T14
V16
I/O B35
MUXsel2
99
P13
W17
GND
I/O B36
CLK/CLKEN
101
R14
U16
I/O B37
OE
102
T15
V17
I/O B38
MUXsel1
103
T16
W18
I/O B39
MUXsel2
104
R15
Y19
VCC
I/O C0
CLK/CLKEN
106
P14
T17
I/O C1
OE
107
P15
V20
I/O C2
MUXsel1
108
R16
U20
I/O C3
MUXsel2
109
N14
T18
GND
I/O C4
CLK/CLKEN
111
P16
T20
I/O C5
OE
112
N15
R18
I/O C6
MUXsel1
113
N16
P17
I/O C7
MUXsel2
114
M14
R19
I/O C8
CLK
115
M15
R20
I/O C9
OE
116
M16
P18
I/O C10
MUXsel1
117
L15
P19
I/O C11
MUXsel2
118
L14
P20
GND
I/O C12
CLK/CLKEN
120
L16
N19
VCC
I/O C13
OE
122
K13
M17
I/O C14
MUXsel1
123
K15
M18
I/O C15
MUXsel2
124
K14
M19
I/O C16
CLK/CLKEN
125
K16
M20
I/O C17
OE
126
J13
L19
I/O C18
MUXsel1
127
J15
L18
I/O C19
MUXsel2
128
J14
L20
GND
I/O C20
CLK/CLKEN
130
J16
K19
I/O C21
OE
131
H14
K18
I/O C22
MUXsel1
132
H16
K17
I/O C23
MUXsel2
133
H15
J20
I/O C24
CLK/CLKEN
134
H13
J19
I/O C25
OE
135
G16
J18
I/O C26
MUXsel1
136
G14
J17
VCC
I/O C27
MUXsel2
138
G15
H19
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
GND
I/O C28
CLK/CLKEN
140
G13
G20
I/O C29
OE
141
F16
G19
I/O C30
MUXsel1
142
F14
F20
I/O C31
MUXsel2
143
F15
G18
I/O C32
CLK/CLKEN
144
E16
F19
I/O C33
OE
145
E14
E20
I/O C34
MUXsel1
146
E15
G17
I/O C35
MUXsel2
147
D16
F18
GND
I/O C36
CLK/CLKEN
149
C16
D20
I/O C37
OE
150
D15
E18
I/O C38
MUXsel1
151
D14
D19
I/O C39
MUXsel2
152
C15
C20
VCC
I/O D0
CLK/CLKEN
154
B16
D18
I/O D1
OE
155
A16
C19
VCC/VCCIO
1
I/O D2
MUXsel1
157
B15
B17
I/O D3
MUXsel2
158
A15
C17
GND
I/O D4
CLK/CLKEN
160
C14
A18
I/O D5
OE
161
B14
A17
I/O D6
MUXsel1
162
A14
C16
I/O D7
MUXsel2
163
C13
B16
I/O D8
CLK/CLKEN
164
B13
A16
I/O D9
OE
165
A13
C15
I/O D10
MUXsel1
166
C12
D14
I/O D11
MUXsel2
167
B12
B15
GND
I/O D12
CLK/CLKEN
169
D11
C14
VCC
I/O D13
OE
171
A12
A14
I/O D14
MUXsel1
172
C11
C13
I/O D15
MUXsel2
173
B11
B13
I/O D16
CLK/CLKEN
174
D10
A13
I/O D17
OE
175
A11
D12
I/O D18
MUXsel1
176
B10
C12
I/O D19
MUXsel2
177
C10
B12
GND
VCC
I/O D20
CLK/CLKEN
186
C8
A9
I/O D21
OE
187
B8
B9
I/O D22
MUXsel1
188
D8
C9
I/O D23
MUXsel2
189
A7
D9
I/O D24
CLK/CLKEN
190
C7
A8
I/O D25
OE
191
B7
B8
I/O D26
MUXsel1
192
D7
C8
VCC
I/O D27
MUXsel2
194
A6
B7
GND
I/O D28
CLK/CLKEN
196
C6
C7
I/O D29
OE
197
B6
B6
I/O D30
MUXsel1
198
A5
A5
I/O D31
MUXsel2
199
C5
D7
I/O D32
CLK/CLKEN
200
B5
C6
I/O D33
OE
201
A4
B5
I/O D34
MUXsel1
202
B4
A4
I/O D35
MUXsel2
203
C4
C5
GND
I/O D36
CLK/CLKEN
205
A3
A3
I/O D37
OE
206
C3
D5
I/O D38
MUXsel1
207
B3
C4
I/O D39
MUXsel2
208
A2
B3
NOTE: VCC and GND Pads Shown for Reference,
1
VCC in ispGDX160V

32
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
I/O A3
MUXsel2
5
A1
E3
I/O D39
MUXsel2
208
A2
B3
I/O D36
CLK/CLKEN
205
A3
A3
I/O D33
OE
201
A4
B5
I/O D30
MUXsel1
198
A5
A5
I/O D27
MUXsel2
194
A6
B7
I/O D23
MUXsel2
189
A7
D9
I/O D17
OE
175
A11
D12
I/O D13
OE
171
A12
A14
I/O D9
OE
165
A13
C15
I/O D6
MUXsel1
162
A14
C16
I/O D3
MUXsel2
158
A15
C17
I/O D1
OE
155
A16
C19
I/O A1
OE
3
B1
C1
I/O A0
CLK/CLKEN
2
B2
E4
I/O D38
MUXsel1
207
B3
C4
I/O D34
MUXsel1
202
B4
A4
I/O D32
CLK/CLKEN
200
B5
C6
I/O D29
OE
197
B6
B6
I/O D25
OE
191
B7
B8
I/O D21
OE
187
B8
B9
I/O D18
MUXsel1
176
B10
C12
I/O D15
MUXsel2
173
B11
B13
I/O D11
MUXsel2
167
B12
B15
I/O D8
CLK/CLKEN
164
B13
A16
I/O D5
OE
161
B14
A17
I/O D2
MUXsel1
157
B15
B17
I/O D0
CLK/CLKEN
154
B16
D18
I/O A4
CLK/CLKEN
7
C1
E1
I/O A2
MUXsel1
4
C2
D1
I/O D37
OE
206
C3
D5
I/O D35
MUXsel2
203
C4
C5
I/O D31
MUXsel2
199
C5
D7
I/O D28
CLK/CLKEN
196
C6
C7
I/O D24
CLK/CLKEN
190
C7
A8
I/O D20
CLK/CLKEN
186
C8
A9
I/O D19
MUXsel2
177
C10
B12
I/O D14
MUXsel1
172
C11
C13
I/O D10
MUXsel1
166
C12
D14
I/O D7
MUXsel2
163
C13
B16
I/O D4
CLK/CLKEN
160
C14
A18
I/O C39
MUXsel2
152
C15
C20
I/O C36
CLK/CLKEN
149
C16
D20
I/O A7
MUXsel2
10
D1
F2
I/O A6
MUXsel1
9
D2
G4
I/O A5
OE
8
D3
F3
I/O D26
MUXsel1
192
D7
C8
I/O D22
MUXsel1
188
D8
C9
I/O D16
CLK/CLKEN
174
D10
A13
I/O D12
CLK/CLKEN
169
D11
C14
I/O C38
MUXsel1
151
D14
D19
I/O C37
OE
150
D15
E18
I/O C35
MUXsel2
147
D16
F18
I/O A10
MUXsel1
13
E1
G2
I/O A9
OE
12
E2
G3
I/O A8
CLK/CLK_EN
11
E3
F1
I/O C33
OE
145
E14
E20
I/O C34
MUXsel1
146
E15
G17
I/O C32
CLK/CLKEN
144
E16
F19
I/O A13
OE
18
F1
J4
I/O A12
CLK/CLKEN
16
F2
H2
I/O A11
MUXsel2
14
F3
G1
I/O C30
MUXsel1
142
F14
F20
I/O C31
MUXsel2
143
F15
G18
I/O C29
OE
141
F16
G19
I/O A17
OE
22
G1
K2
I/O A15
MUXsel2
20
G2
J2
I/O A16
CLK/CLKEN
21
G3
J1
I/O A14
MUXsel1
19
G4
J3
I/O C28
CLK/CLKEN
140
G13
G20
I/O C26
MUXsel1
136
G14
J17
I/O C27
MUXsel2
138
G15
H19
I/O C25
OE
135
G16
J18
I/O A21
OE
27
H1
L3
I/O A19
MUXsel2
24
H2
K1
I/O A20
CLK/CLKEN
26
H3
L2
I/O A18
MUXsel1
23
H4
K3
I/O C24
CLK/CLKEN
134
H13
J19
I/O C21
OE
131
H14
K18
I/O C23
MUXsel2
133
H15
J20
I/O C22
MUXsel1
132
H16
K17
I/O A22
MUXsel1
28
J1
L4
I/O A24
CLK/CLKEN
30
J2
M2
I/O A23
MUXsel2
29
J3
M1
I/O A25
OE
31
J4
M3
I/O C17
OE
126
J13
L19
I/O C19
MUXsel2
128
J14
L20
I/O C18
MUXsel1
127
J15
L18
I/O C20
CLK/CLKEN
130
J16
K19
I/O A26
MUXsel1
32
K1
M4
I/O A28
CLK/CLKEN
36
K2
P1
I/O A27
MUXsel2
34
K3
N2
I/O A29
OE
37
K4
P2
I/O C13
OE
122
K13
M17
I/O C15
MUXsel2
124
K14
M19
I/O C14
MUXsel1
123
K15
M18
I/O C16
CLK/CLKEN
125
K16
M20
I/O A30
MUXsel1
38
L1
R1
I/O A31
MUXsel2
39
L2
P3
I/O A32
CLK/CLKEN
40
L3
R2
I/O C11
MUXsel2
118
L14
P20
I/O C10
MUXsel1
117
L15
P19
I/O C12
CLK/CLKEN
120
L16
N19
I/O A33
OE
41
M1
T1
I/O A34
MUXsel1
42
M2
P4
I/O A35
MUXsel2
43
M3
R3
I/O C7
MUXsel2
114
M14
R19
I/O Locations: ispGDX160V/VA (Ordered by 208-Ball BGA Location)
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O C8
CLK
115
M15
R20
I/O C9
OE
116
M16
P18
I/O A36
CLK/CLKEN
45
N1
U1
I/O A37
OE
46
N2
T3
I/O A38
MUXsel1
47
N3
U2
I/O B13
OE
66
N6
Y7
I/O B18
MUXsel1
71
N7
V9
I/O B21
OE
83
N9
V12
I/O B25
OE
87
N10
V13
I/O C3
MUXsel2
109
N14
T18
I/O C5
OE
112
N15
R18
I/O C6
MUXsel1
113
N16
P17
I/O A39
MUXsel2
48
P1
V1
I/O B0
CLK/CLKEN
50
P2
U3
I/O B4
CLK/CLKEN
55
P3
Y3
I/O B7
MUXsel2
58
P4
W5
I/O B11
MUXsel2
62
P5
W6
I/O B16
CLK/CLKEN
69
P6
Y8
I/O B23
MUXsel2
85
P10
Y13
I/O B27
MUXsel2
90
P11
Y15
I/O B30
MUXsel1
94
P12
U14
I/O B35
MUXsel2
99
P13
W17
I/O C0
CLK/CLKEN
106
P14
T17
I/O C1
OE
107
P15
V20
I/O C4
CLK/CLKEN
111
P16
T20
I/O B1
OE
51
R1
V2
I/O B2
MUXsel1
52
R2
W4
I/O B6
MUXsel1
57
R3
V5
I/O B9
OE
60
R4
V6
I/O B12
CLK/CLKEN
64
R5
V7
I/O B15
MUXsel2
68
R6
W8
I/O B19
MUXsel2
72
R7
W9
I/O B20
CLK/CLKEN
82
R9
W12
I/O B24
CLK/CLKEN
86
R10
W13
I/O B28
CLK/CLKEN
92
R11
W15
I/O B31
MUXsel2
95
R12
V15
I/O B33
OE
97
R13
Y17
I/O B36
CLK/CLKEN
101
R14
U16
I/O B39
MUXsel2
104
R15
Y19
I/O C2
MUXsel1
108
R16
U20
I/O B3
MUXsel2
53
T1
V4
I/O B5
OE
56
T2
Y4
I/O B8
CLK/CLKEN
59
T3
Y5
I/O B10
MUXsel1
61
T4
U7
I/O B14
MUXsel1
67
T5
V8
I/O B17
OE
70
T6
U9
I/O B22
MUXsel1
84
T10
U12
I/O B26
MUXsel1
88
T11
Y14
I/O B29
OE
93
T12
Y16
I/O B32
CLK/CLKEN
96
T13
W16
I/O B34
MUXsel1
98
T14
V16
I/O B37
OE
102
T15
V17
I/O B38
MUXsel1
103
T16
W18

33
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
I/O C32
CLK/CLKEN
144
E16
F19
I/O C30
MUXsel1
142
F14
F20
I/O A11
MUXsel2
14
F3
G1
I/O A10
MUXsel1
13
E1
G2
I/O A9
OE
12
E2
G3
I/O A6
MUXsel1
9
D2
G4
I/O C34
MUXsel1
146
E15
G17
I/O C31
MUXsel2
143
F15
G18
I/O C29
OE
141
F16
G19
I/O C28
CLK/CLKEN
140
G13
G20
I/O A12
CLK/CLKEN
16
F2
H2
I/O C27
MUXsel2
138
G15
H19
I/O A16
CLK/CLKEN
21
G3
J1
I/O A15
MUXsel2
20
G2
J2
I/O A14
MUXsel1
19
G4
J3
I/O A13
OE
18
F1
J4
I/O C26
MUXsel1
136
G14
J17
I/O C25
OE
135
G16
J18
I/O C24
CLK/CLKEN
134
H13
J19
I/O C23
MUXsel2
133
H15
J20
I/O A19
MUXsel2
24
H2
K1
I/O A17
OE
22
G1
K2
I/O A18
MUXsel1
23
H4
K3
I/O C22
MUXsel1
132
H16
K17
I/O C21
OE
131
H14
K18
I/O C20
CLK/CLKEN
130
J16
K19
I/O A20
CLK/CLKEN
26
H3
L2
I/O A21
OE
27
H1
L3
I/O A22
MUXsel1
28
J1
L4
I/O C18
MUXsel1
127
J15
L18
I/O C17
OE
126
J13
L19
I/O C19
MUXsel2
128
J14
L20
I/O A23
MUXsel2
29
J3
M1
I/O A24
CLK/CLKEN
30
J2
M2
I/O A25
OE
31
J4
M3
I/O A26
MUXsel1
32
K1
M4
I/O C13
OE
122
K13
M17
I/O C14
MUXsel1
123
K15
M18
I/O C15
MUXsel2
124
K14
M19
I/O C16
CLK/CLKEN
125
K16
M20
I/O A27
MUXsel2
34
K3
N2
I/O C12
CLK/CLKEN
120
L16
N19
I/O A28
CLK/CLKEN
36
K2
P1
I/O A29
OE
37
K4
P2
I/O A31
MUXsel2
39
L2
P3
I/O A34
MUXsel1
42
M2
P4
I/O C6
MUXsel1
113
N16
P17
I/O C9
OE
116
M16
P18
I/O C10
MUXsel1
117
L15
P19
I/O C11
MUXsel2
118
L14
P20
I/O A30
MUXsel1
38
L1
R1
I/O A32
CLK/CLKEN
40
L3
R2
I/O A35
MUXsel2
43
M3
R3
I/O D36
CLK/CLKEN
205
A3
A3
I/O D34
MUXsel1
202
B4
A4
I/O D30
MUXsel1
198
A5
A5
I/O D24
CLK/CLKEN
190
C7
A8
I/O D20
CLK/CLKEN
186
C8
A9
I/O D16
CLK/CLKEN
174
D10
A13
I/O D13
OE
171
A12
A14
I/O D8
CLK/CLKEN
164
B13
A16
I/O D5
OE
161
B14
A17
I/O D4
CLK/CLKEN
160
C14
A18
I/O D39
MUXsel2
208
A2
B3
I/O D33
OE
201
A4
B5
I/O D29
OE
197
B6
B6
I/O D27
MUXsel2
194
A6
B7
I/O D25
OE
191
B7
B8
I/O D21
OE
187
B8
B9
I/O D19
MUXsel2
177
C10
B12
I/O D15
MUXsel2
173
B11
B13
I/O D11
MUXsel2
167
B12
B15
I/O D7
MUXsel2
163
C13
B16
I/O D2
MUXsel1
157
B15
B17
I/O A1
OE
3
B1
C1
I/O D38
MUXsel1
207
B3
C4
I/O D35
MUXsel2
203
C4
C5
I/O D32
CLK/CLKEN
200
B5
C6
I/O D28
CLK/CLKEN
196
C6
C7
I/O D26
MUXsel1
192
D7
C8
I/O D22
MUXsel1
188
D8
C9
I/O D18
MUXsel1
176
B10
C12
I/O D14
MUXsel1
172
C11
C13
I/O D12
CLK/CLKEN
169
D11
C14
I/O D9
OE
165
A13
C15
I/O D6
MUXsel1
162
A14
C16
I/O D3
MUXsel2
158
A15
C17
I/O D1
OE
155
A16
C19
I/O C39
MUXsel2
152
C15
C20
I/O A2
MUXsel1
4
C2
D1
I/O D37
OE
206
C3
D5
I/O D31
MUXsel2
199
C5
D7
I/O D23
MUXsel2
189
A7
D9
I/O D17
OE
175
A11
D12
I/O D10
MUXsel1
166
C12
D14
I/O D0
CLK/CLKEN
154
B16
D18
I/O C38
MUXsel1
151
D14
D19
I/O C36
CLK/CLKEN
149
C16
D20
I/O A4
CLK/CLK_EN
7
C1
E1
I/O A3
MUXsel2
5
A1
E3
I/O A0
CLK/CLKEN
2
B2
E4
I/O C37
OE
150
D15
E18
I/O C33
OE
145
E14
E20
I/O A8
CLK/CLKEN
11
E3
F1
I/O A7
MUXsel2
10
D1
F2
I/O A5
OE
8
D3
F3
I/O C35
MUXsel2
147
D16
F18
I/O Locations: ispGDX160V/VA (Ordered by 272-Ball BGA Location)
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O
Control
208
208
272
Signal
Signal
PQFP fpBGA BGA
I/O C5
OE
112
N15
R18
I/O C7
MUXsel2
114
M14
R19
I/O C8
CLK
115
M15
R20
I/O A33
OE
41
M1
T1
I/O A37
OE
46
N2
T3
I/O C0
CLK/CLKEN
106
P14
T17
I/O C3
MUXsel2
109
N14
T18
I/O C4
CLK/CLKEN
111
P16
T20
I/O A36
CLK/CLKEN
45
N1
U1
I/O A38
MUXsel1
47
N3
U2
I/O B0
CLK/CLKEN
50
P2
U3
I/O B10
MUXsel1
61
T4
U7
I/O B17
OE
70
T6
U9
I/O B22
MUXsel1
84
T10
U12
I/O B30
MUXsel1
94
P12
U14
I/O B36
CLK/CLKEN
101
R14
U16
I/O C2
MUXsel1
108
R16
U20
I/O A39
MUXsel2
48
P1
V1
I/O B1
OE
51
R1
V2
I/O B3
MUXsel2
53
T1
V4
I/O B6
MUXsel1
57
R3
V5
I/O B9
OE
60
R4
V6
I/O B12
CLK/CLKEN
64
R5
V7
I/O B14
MUXsel1
67
T5
V8
I/O B18
MUXsel1
71
N7
V9
I/O B21
OE
83
N9
V12
I/O B25
OE
87
N10
V13
I/O B31
MUXsel2
95
R12
V15
I/O B34
MUXsel1
98
T14
V16
I/O B37
OE
102
T15
V17
I/O C1
OE
107
P15
V20
I/O B2
MUXsel1
52
R2
W4
I/O B7
MUXsel2
58
P4
W5
I/O B11
MUXsel2
62
P5
W6
I/O B15
MUXsel2
68
R6
W8
I/O B19
MUXsel2
72
R7
W9
I/O B20
CLK/CLKEN
82
R9
W12
I/O B24
CLK/CLKEN
86
R10
W13
I/O B28
CLK/CLKEN
92
R11
W15
I/O B32
CLK/CLKEN
96
T13
W16
I/O B35
MUXsel2
99
P13
W17
I/O B38
MUXsel1
103
T16
W18
I/O B4
CLK/CLKEN
55
P3
Y3
I/O B5
OE
56
T2
Y4
I/O B8
CLK/CLKEN
59
T3
Y5
I/O B13
OE
66
N6
Y7
I/O B16
CLK/CLKEN
69
P6
Y8
I/O B23
MUXsel2
85
P10
Y13
I/O B26
MUXsel1
88
T11
Y14
I/O B27
MUXsel2
90
P11
Y15
I/O B29
OE
93
T12
Y16
I/O B33
OE
97
R13
Y17
I/O B39
MUXsel2
104
R15
Y19

34
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Signal Configuration: ispGDX160V/VA
ispGDX160V/VA 272-Ball BGA Signal Diagram
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
A
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
D4
I/O
D5
I/O
D8
NC
1
I/O
D13
I/O
D16
TOE
Y3/
CLKEN3
NC
1
I/O
D20
I/O
D24
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
D30
I/O
D34
I/O
D36
NC
1
GND
A
B
NC
1
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
D2
I/O
D7
I/O
D11
NC
1
I/O
D15
I/O
D19
EPEN
NC
1
I/O
D21
I/O
D25
I/O
D27
I/O
D29
I/O
D33
NC
1
I/O
D39
NC
1
NC
1
B
C
I/O
C39
I/O
D1
VCCIO
VCC
2
I/O
D3
I/O
D6
I/O
D9
I/O
D12
I/O
D14
I/O
D18
Y2/
CLKEN2
NC
1
I/O
D22
I/O
D26
I/O
D28
I/O
D32
I/O
D35
I/O
D38
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
A1
C
D
I/O
C36
I/O
C38
I/O
D0
GND NC
1
VCC
I/O
D10
GND
I/O
D17
VCC
RESET
I/O
D23
GND
I/O
D31
VCC
I/O
D37
GND NC
1
NC
1
I/O
A2
D
E
I/O
C33
NC
1
I/O
C37
NC
1
I/O
A0
I/O
A3
NC
1
I/O
A4
E
F
I/O
C30
I/O
C32
I/O
C35
VCC
VCC
I/O
A5
I/O
A7
I/O
A8
F
G
I/O
C28
I/O
C29
I/O
C31
I/O
C34
I/O
A6
I/O
A9
I/O
A10
I/O
A11
G
H
NC
1
I/O
C27
NC
1
GND
GND NC
1
I/O
A12
NC
1
H
J
I/O
C23
I/O
C24
I/O
C25
I/O
C26
GND GND GND GND
I/O
A13
I/O
A14
I/O
A15
I/O
A16
J
K
NC
1
I/O
C20
I/O
C21
I/O
C22
GND GND GND GND
VCC
I/O
A18
I/O
A17
I/O
A19
K
L
I/O
C19
I/O
C17
I/O
C18
VCC
GND GND GND GND
I/O
A22
I/O
A21
I/O
A20
NC
1
L
M
I/O
C16
I/O
C15
I/O
C14
I/O
C13
GND GND GND GND
I/O
A26
I/O
A25
I/O
A24
I/O
A23
M
N
NC
1
I/O
C12
NC
1
GND
GND NC
1
I/O
A27
NC
1
N
P
I/O
C11
I/O
C10
I/O
C9
I/O
C6
I/O
A34
I/O
A31
I/O
A29
I/O
A28
P
R
I/O
C8
I/O
C7
I/O
C5
VCC
VCC
I/O
A35
I/O
A32
I/O
A30
R
T
I/O
C4
NC
1
I/O
C3
I/O
C0
NC
1
I/O
A37
NC
1
I/O
A33
T
U
I/O
C2
NC
1
NC
1
GND
I/O
B36
VCC
I/O
B30
GND
I/O
B22 TCK
VCC
I/O
B17
GND
I/O
B10
VCC NC
1
GND
I/O
B0
I/O
A38
I/O
A36
U
V
I/O
C1
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
B37
I/O
B34
I/O
B31
NC
1
I/O
B25
I/O
B21 TMS
Y0/
CLKEN0
I/O
B18
I/O
B14
I/O
B12
I/O
B9
I/O
B6
I/O
B3
NC
1
I/O
B1
I/O
A39
V
W
NC
1
NC
1
I/O
B38
I/O
B35
I/O
B32
I/O
B28
NC
1
I/O
B24
I/O
B20 TDO
NC
1
I/O
B19
I/O
B15
NC
1
I/O
B11
I/O
B7
I/O
B2
NC
1
NC
1
NC
1
W
Y
NC
1
I/O
B39
NC
1
I/O
B33
I/O
B29
I/O
B27
I/O
B26
I/O
B23
TDI
NC
1
Y1/
CLKEN1
NC
1
I/O
B16
I/O
B13
NC
1
I/O
B8
I/O
B5
I/O
B4
NC
1
NC
1
Y
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
1. NCs are not to be connected to any active signals, Vcc or GND.
2. VCCIO on ispGDX160VA. VCC on ispGDX160V.
ispGDX160V/VA
Bottom View

35
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Signal Configuration: ispGDX160V/VA
ispGDX160V/VA 208-Ball fpBGA Signal Diagram
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
I/O
D1
I/O
D3
I/O
D6
I/O
D9
I/O
D13
I/O
D17
NC
1
EPEN RESET
I/O
D23
I/O
D27
I/O
D30
I/O
D33
I/O
D36
I/O
D39
I/O
A3
A
B
A
I/O
D0
I/O
D2
I/O
D5
I/O
D8
I/O
D11
I/O
D15
I/O
D18
Y2/
CLKEN2
I/O
D21
I/O
D25
I/O
D29
I/O
D32
I/O
D34
I/O
D38
I/O
A0
I/O
A1
B
C
I/O
C36
I/O
C39
I/O
D4
I/O
D7
I/O
D10
I/O
D14
I/O
D19
Y3/
CLKEN3
I/O
D20
I/O
D24
I/O
D28
I/O
D31
I/O
D35
I/O
D37
I/O
A2
I/O
A4
C
D
I/O
C35
I/O
C37
I/O
C38
GND
VCC
I/O
D12
I/O
D16
TOE
I/O
D22
I/O
D26
VCC
VCC
GND
I/O
A5
I/O
A6
I/O
A7
D
E
I/O
C32
I/O
C34
I/O
C33
VCCIO/
VCC
2
VCC
I/O
A8
I/O
A9
I/O
A10
E
F
I/O
C29
I/O
C31
I/O
C30
VCC
VCC
I/O
A11
I/O
A12
I/O
A13
F
G
I/O
C25
I/O
C27
I/O
C26
I/O
C28
GND
GND
GND
GND
I/O
A14
I/O
A16
I/O
A15
I/O
A17
G
H
I/O
C22
I/O
C23
I/O
C21
I/O
C24
GND
GND
GND
GND
I/O
A18
I/O
A20
I/O
A19
I/O
A21
H
J
I/O
C20
I/O
C18
I/O
C19
I/O
C17
GND
GND
GND
GND
I/O
A25
I/O
A23
I/O
A24
I/O
A22
J
K
I/O
C16
I/O
C14
I/O
C15
I/O
C13
GND
GND
GND
GND
I/O
A29
I/O
A27
I/O
A28
I/O
A26
K
L
I/O
C12
I/O
C10
I/O
C11
VCC
VCC
I/O
A32
I/O
A31
I/O
A30
L
M
I/O
C9
I/O
C8
I/O
C7
VCC
VCC
I/O
A35
I/O
A34
I/O
A33
M
N
I/O
C6
I/O
C5
I/O
C3
GND
VCC
VCC
I/O
B25
I/O
B21
Y0/
CLKEN0
I/O
B18
I/O
B13
VCC
GND
I/O
A38
I/O
A37
I/O
A36
N
P
I/O
C4
I/O
C1
I/O
C0
I/O
B35
I/O
B30
I/O
B27
I/O
B23
TDI
TDO
NC
1
I/O
B16
I/O
B11
I/O
B7
I/O
B4
I/O
B0
I/O
A39
P
R
I/O
C2
I/O
B39
I/O
B36
I/O
B33
I/O
B31
I/O
B28
I/O
B24
I/O
B20
Y1/
CLKEN1
I/O
B19
I/O
B15
I/O
B12
I/O
B9
I/O
B6
I/O
B2
I/O
B1
R
T
I/O
B38
I/O
B37
I/O
B34
I/O
B32
I/O
B29
I/O
B26
I/O
B22
TCK
TMS
NC
1
I/O
B17
I/O
B14
I/O
B10
I/O
B8
I/O
B5
I/O
B3
T
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
1. NCs are not to be connected to any active signals, Vcc or GND.
2. VCCIO on ispGDX160VA. VCC on ispGDX160V.
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
ispGDX160V/VA
Bottom View

36
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Pin Configuration: ispGDX160V/VA
ispGDX160V/VA 208-Pin PQFP Pinout Diagram
1. No Connect Pins (NC) are not to be connected to any active signal, Vcc or GND.
2. VCCIO on ispGDX160VA. VCC on ispGDX160V.
ispGDX160V/VA
Top View
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
208
207
206
205
204
203
202
201
200
199
198
197
196
195
194
193
192
191
190
189
188
187
186
185
184
183
182
181
180
179
178
177
176
175
174
173
172
171
170
169
168
167
166
165
164
163
162
161
160
159
158
157
VCC
I/O A 0
I/O A 1
I/O A 2
I/O A 3
GND
I/O A 4
I/O A 5
I/O A 6
I/O A 7
I/O A 8
I/O A 9
I/O A 10
I/O A 11
GND
I/O A 12
VCC
I/O A 13
I/O A 14
I/O A 15
I/O A 16
I/O A 17
I/O A 18
I/O A 19
GND
I/O A 20
I/O A 21
I/O A 22
I/O A 23
I/O A 24
I/O A 25
I/O A 26
VCC
I/O A 27
GND
I/O A 28
I/O A 29
I/O A 30
I/O A 31
I/O A 32
I/O A 33
I/O A 34
I/O A 35
GND
I/O A 36
I/O A 37
I/O A 38
I/O A 39
VCC
I/O B 0
I/O B 1
I/O B 2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
--
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
--
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
VCCIO/VCC
2
I/O D1
I/O D 0
VCC
I/O C 39
I/O C 38
I/O C 37
I/O C 36
GND
I/O C 35
I/O C 34
I/O C 33
I/O C 32
I/O C 31
I/O C 30
I/O C 29
I/O C 28
GND
I/O C 27
VCC
I/O C 26
I/O C 25
I/O C 24
I/O C 23
I/O C 22
I/O C 21
I/O C 20
GND
I/O C 19
I/O C 18
I/O C 17
I/O C 16
I/O C 15
I/O C 14
I/O C 13
VCC
I/O C 12
GND
I/O C 11
I/O C 10
I/O C 9
I/O C 8
I/O C 7
I/O C 6
I/O C 5
I/O C 4
GND
I/O C 3
I/O C 2
I/O C 1
I/O C 0
VCC
Data
Control
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
--
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
--
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
--
CLK/CLKEN
OE
MUXsel1
MUXsel2
Data
Control
I/O B 3
GND
I/O B 4
I/O B 5
I/O B 6
I/O B 7
I/O B 8
I/O B 9
I/O B 10
I/O B 11
GND
I/O B 12
VCC
I/O B 13
I/O B 14
I/O B 15
I/O B 16
I/O B 17
I/O B 18
I/O B 19
1
NC
1
NC
CLK_EN0/Y0
CLK_EN1/Y1
GND
TDO
TMS
TCK
TDI
I/O B 20
I/O B 21
I/O B 22
I/O B 23
I/O B 24
I/O B 25
I/O B 26
VCC
I/O B 27
GND
I/O B 28
I/O B 29
I/O B 30
I/O B 31
I/O B 32
I/O B 33
I/O B 34
I/O B 35
GND
I/O B 36
I/O B 37
I/O B 38
I/O B 39
--
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
--
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
--
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
Data
Control
I/O D 39
I/O D 38
I/O D 37
I/O D 36
GND
I/O D 35
I/O D 34
I/O D 33
I/O D 32
I/O D 31
I/O D 30
I/O D 29
I/O D 28
GND
I/O D 27
VCC
I/O D 26
I/O D 25
I/O D 24
I/O D 23
I/O D 22
I/O D 21
I/O D 20
RESET
VCC
EPEN
GND
Y3/CLK_EN3
Y2/CLK_EN2
NC
1
TOE
I/O D 19
I/O D 18
I/O D 17
I/O D 16
I/O D 15
I/O D 14
I/O D 13
VCC
I/O D 12
GND
I/O D 11
I/O D 10
I/O D 9
I/O D 8
I/O D 7
I/O D 6
I/O D 5
I/O D 4
GND
I/O D 3
I/O D 2
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
--
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
--
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
OE
CLK/CLKEN
--
MUXsel2
MUXsel1
Data
Control

37
Specifications
ispGDX160V/VA
Part Number Description
Ordering Information
Device Number
160V
160VA
Grade
Blank = Commercial
I = Industrial
ispGDX
XXXXX
X XXXX X
Speed
3 = 3.5ns Tpd
5 = 5ns Tpd
7 = 7ns Tpd
9 = 9ns Tpd
Package
Q208 = 208-Pin PQFP
B208 = 208-Ball fpBGA
B272 = 272-Ball BGA
-
Device Family
0212/ispGDXVA
Table 2-0041A/ispGDXV/A
208-Pin PQFP
208-Ball fpBGA
5
7
ispGDX160VA-5Q208
208-Ball fpBGA
5
ispGDX160VA-5B208
ispGDXVA
272-Ball BGA
5
ispGDX160VA-5B272
208-Pin PQFP
3.5
ispGDX160VA-3Q208
208-Ball fpBGA
3.5
ispGDX160VA-3B208
272-Ball BGA
3.5
ispGDX160VA-3B272
208-Pin PQFP
7
ispGDX160VA-7Q208
ispGDX160VA-7B208
272-Ball BGA
7
ispGDX160VA-7B272
208-Pin PQFP
208-Ball fpBGA
5
7
ispGDX160V-5Q208
208-Ball fpBGA
5
ispGDX160V-5B208
ispGDXV*
272-Ball BGA
5
ispGDX160V-5B272
208-Pin PQFP
7
ispGDX160V-7Q208
ispGDX160V-7B208
272-Ball BGA
7
ispGDX160V-7B272
FAMILY
ORDERING NUMBER
PACKAGE
tpd (ns)
COMMERCIAL
Table 2-0041C/ispGDXV
208-Pin PQFP
208-Ball fpBGA
5
7
ispGDX160VA-5Q208I
208-Ball fpBGA
5
ispGDX160VA-5B208I
ispGDXVA
ispGDXV*
272-Ball BGA
5
ispGDX160VA-5B272I
208-Pin PQFP
7
ispGDX160VA-7Q208I
208-Pin PQFP
7
ispGDX160V-7Q208I
ispGDX160VA-7B208I
272-Ball BGA
7
ispGDX160VA-7B272I
208-Ball fpBGA
9
208-Pin PQFP
9
ispGDX160VA-9Q208I
ispGDX160VA-9B208I
272-Ball BGA
9
ispGDX160VA-9B272I
FAMILY
ORDERING NUMBER
PACKAGE
tpd (ns)
INDUSTRIAL
*Use ispGDX160VA for new designs.
Note: The ispGDX160VA devices are dual-marked with both Commercial and Industrial grades. The Industrial speed grade is slower,
e.g. ispGDX160VA-3B208-5I.




































