 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: MIC4424CN | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
January 1999
1
MIC4423/4424/4425
MIC4423/4424/4425
Micrel
MIC4423/4424/4425
Dual 3A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver
Bipolar/CMOS/DMOS Process
Final Information
Features
∑
Reliable, low-power bipolar/CMOS/DMOS construction
∑
Latch-up protected to >500mA reverse current
∑
Logic input withstands swing to ≠5V
∑
High 3A-peak output current
∑
Wide 4.5V to 18V operating range
∑
Drives 1800pF capacitance in 25ns
∑
Short <40ns typical delay time
∑
Delay times consistent with in supply voltage change
∑
Matched rise and fall times
∑
TTL logic input independent of supply voltage
∑
Low equivalent 6pF input capacitance
∑
Low supply current
3.5mA with logic-1 input
350
µ
A with logic-0 input
∑
Low 3.5
typical output impedance
∑
Output voltage swings within 25mV of ground or V
S
.
∑
`426/7/8-, `1426/7/8-, `4426/7/8-compatible pinout
∑
Inverting, noninverting, and differential configurations
General Description
The MIC4423/4424/4425 family are highly reliable BiCMOS/
DMOS buffer/driver/MOSFET drivers. They are higher output
current versions of the MIC4426/4427/4428, which are
improved versions of the MIC426/427/428. All three families
are pin-compatible. The MIC4423/4424/4425 drivers are
capable of giving reliable service in more demanding electrical
environments than their predecessors. They will not latch
under any conditions within their power and voltage ratings.
They can survive up to 5V of noise spiking, of either polarity,
on the ground pin. They can accept, without either damage or
logic upset, up to half an amp of reverse current (either
polarity) forced back into their outputs.
The MIC4423/4424/4425 series drivers are easier to use,
more flexible in operation, and more forgiving than other
CMOS or bipolar drivers currently available. Their BiCMOS/
DMOS construction dissipates minimum power and provides
rail-to-rail voltage swings.
Primarily intended for driving power MOSFETs, the MIC4423/
4424/4425 drivers are suitable for driving other loads
(capacitive, resistive, or inductive) which require low-
impedance, high peak currents, and fast switching times.
Heavily loaded clock lines, coaxial cables, or piezoelectric
transducers are some examples. The only known limitation on
loading is that total power dissipated in the driver must be kept
within the maximum power dissipation limits of the package.
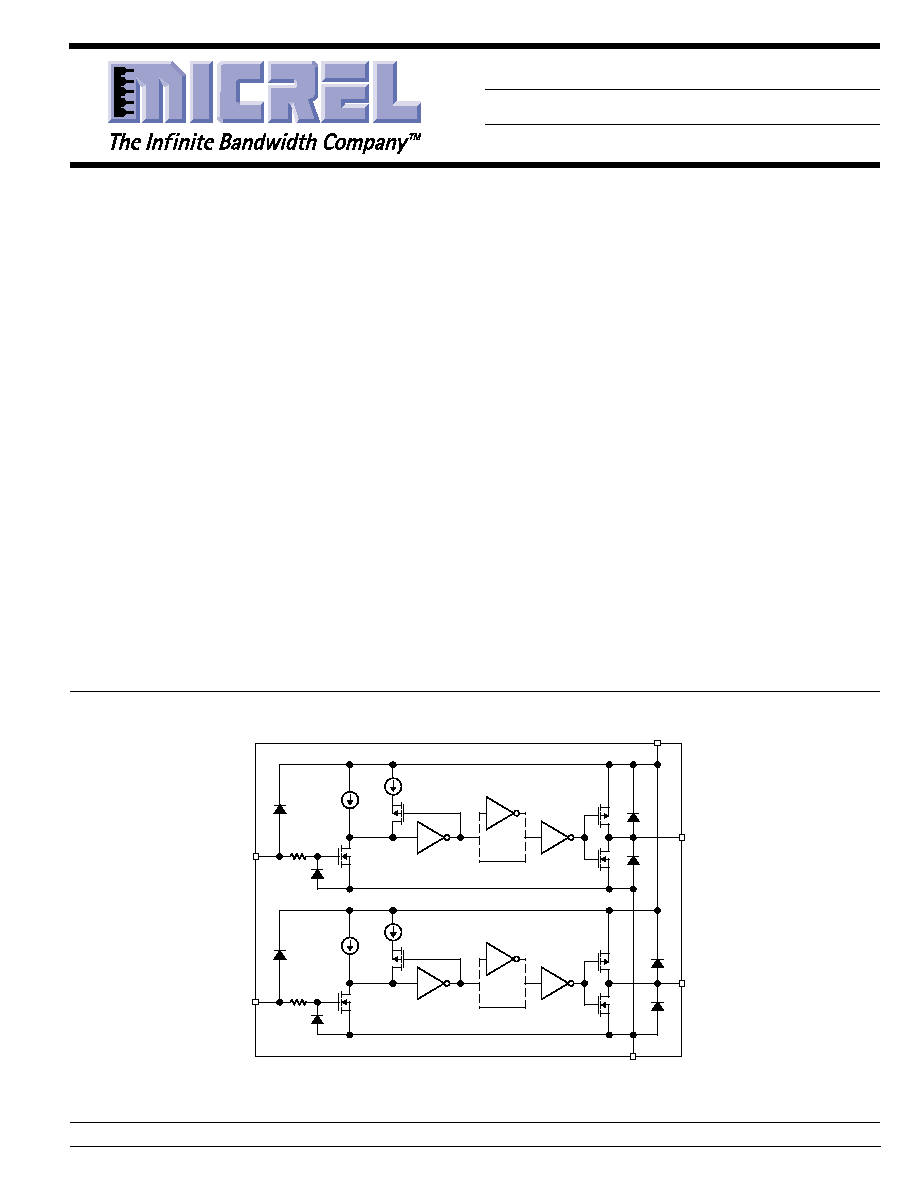
Functional Diagram
Integrated Component Count:
4 Resistors
4 Capacitors
52 Transistors
Ground Unused Inputs
INA
OUTA
INVERTING
NONINVERTING
0.1mA
0.6mA
2k
INB
OUTB
INVERTING
NONINVERTING
0.1mA
0.6mA
2k
V
S
GND
Micrel, Inc. ∑ 1849 Fortune Drive ∑ San Jose, CA 95131 ∑ USA ∑ tel + 1 (408) 944-0800 ∑ fax + 1 (408) 944-0970 ∑ http://www.micrel.com

MIC4423/4424/4425
Micrel
MIC4423/4424/4425
2
January 1999
Ordering Information
Part Number
Temperature Range
Package
Configuration
MIC4423CWM
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
16-Pin Wide SOIC
Dual Inverting
MIC4423BWM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
MIC4423BM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
8-Pin SOIC
Dual Inverting
MIC4423CN
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
8-Pin Plastic DIP
Dual Inverting
MIC4423BN
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
MIC4424CWM
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
16-Pin Wide SOIC
Dual Non-Inverting
MIC4424BWM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
MIC4424BM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
8-Pin SOIC
Dual Non-Inverting
MIC4424CN
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
8-Pin Plastic DIP
Dual Non-Inverting
MIC4424BN
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
MIC4425CWM
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
16-Pin Wide SOIC
Inverting + Non Inverting
MIC4425BWM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
MIC4425BM
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
8-Pin SOIC
Inverting + Non Inverting
MIC4425CN
0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
8-Pin Plastic DIP
Inverting + Non Inverting
MIC4425BN
≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
Pin Configuration
8
NC
2
INA
OUTA
14
3
NC
VS
13
4
GND
VS
12
5
GND
OUTB
11
6
NC
OUTB
10
7
INB
NC
9
1
NC
OUTA
15
NC
16
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
NC
INA
GND
INB
NC
OUTA
VS
OUTB
8-pin DIP (N)
8-pin SOIC (M)
16-lead Wide SOIC (WM)
A
B
7 OUTA
5 OUTB
INA 2
INB 4
MIC4423xN/M
MIC4424xN/M
MIC4425xN/M
A
B
7 OUTA
5 OUTB
INA 2
INB 4
A
B
7 OUTA
5 OUTB
INA 2
INB 4
A
B
14 OUTA
15 OUTA
10 OUTB
11 OUTB
INA 2
INB 7
MIC4423xWM
A
B
14 OUTA
15 OUTA
10 OUTB
11 OUTB
INA 2
INB 7
MIC4424xWM
A
B
14 OUTA
15 OUTA
10 OUTB
11 OUTB
INA 2
INB 7
MIC4425xWM
WM Package Note:
Duplicate GND, VS,
OUTA
, and OUTB pins
must be externally
connected together.
Driver Configuration
Pin Description
Pin Number
Pin Number
Pin Name
Pin Function
DIP, SOIC
Wide SOIC
2 / 4
2 / 7
INA/B
Control Input
3
4, 5
GND
Ground: Duplicate pins must be externally connected together.
6
12, 13
V
S
Supply Input: Duplicate pins must be externally connected together.
7 / 5
14, 15 / 10, 11
OUTA/B
Output: Duplicate pins must be externally connected together.
1, 8
1, 3, 6, 8, 9, 16
NC
not connected

January 1999
3
MIC4423/4424/4425
MIC4423/4424/4425
Micrel
MIC4423/4424/4425 Electrical Characteristics
(Note 5)
4.5V
V
S
18V; T
A
= 25
∞
C, bold values indicate ≠40
∞
C
T
A
+85
∞
C; unless noted.
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Input
V
IH
Logic 1 Input Voltage
2.4
V
V
IL
Logic 0 Input Voltage
0.8
V
I
IN
Input Current
0V
V
IN
V
S
≠1
1
µ
A
≠10
10
µ
A
Output
V
OH
High Output Voltage
V
S
≠0.025
V
V
OL
Low Output Voltage
0.025
V
R
O
Output Resistance HI State
I
OUT
= 10mA, V
S
= 18V
2.8
5
V
IN
= 0.8V, I
OUT
= 10mA, V
S
= 18V
3.7
8
Output Resistance LO State
I
OUT
= 10mA, V
S
= 18V
3.5
5
V
IN
= 2.4V, I
OUT
= 10mA, V
S
= 18V
4.3
8
I
PK
Peak Output Current
3
A
I
Latch-Up Protection
>500
mA
Withstand Reverse Current
Switching Time (Note 4)
t
R
Rise Time
test Figure 1, C
L
= 1800pF
23
35
ns
28
60
ns
t
F
Fall Time
test Figure 1, C
L
= 1800pF
25
35
ns
32
60
ns
t
D1
Delay Tlme
test Ffigure 1, C
L
= 1800pF
33
75
ns
32
100
ns
t
D2
Delay Time
test Figure 1, C
L
= 1800pF
38
75
ns
38
100
ns
Power Supply
I
S
Power Supply Current
V
IN
= 3.0V (both inputs)
1.5
2.5
mA
2
3.5
mA
I
S
Power Supply Current
V
IN
= 0.0V (both inputs)
0.15
0.25
mA
0.2
0.3
mA
Note 1.
Exceeding the absolute maximum rating may damage the device.
Note 2.
The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating rating.
Note 3.
Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precautions recommended. ESD tested to human body model, 1.5k in series with 100pF.
Note 4.
Switching times guaranteed by design.
Note 5.
Specification for packaged product only.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(Note 1)
Supply Voltage ........................................................... +22V
Input Voltage ................................. V
S
+ 0.3V to GND ≠ 5V
Junction Temperature .............................................. 150
∞
C
Storage Temperature Range .................... ≠65
∞
C to 150
∞
C
Lead Temperature (10 sec.) ..................................... 300
∞
C
ESD Susceptability, Note 3 ...................................... 1000V
Operating Ratings
(Note 2)
Supply Voltage (V
S
) .................................... +4.5V to +18V
Temperature Range
C Version .................................................. 0
∞
C to +70
∞
C
B Version ............................................... ≠40
∞
C to +85
∞
C
Package Thermal Resistance
DIP
JA
............................................................. 130
∞
C/W
DIP
JC
............................................................... 42
∞
C/W
Wide-SOIC
JA
................................................. 120
∞
C/W
Wide-SOIC
JC
................................................... 75
∞
C/W
SOIC
JA
.......................................................... 120
∞
C/W
SOIC
JC
............................................................ 75
∞
C/W
MIC4423/4424/4425
Micrel
MIC4423/4424/4425
4
January 1999
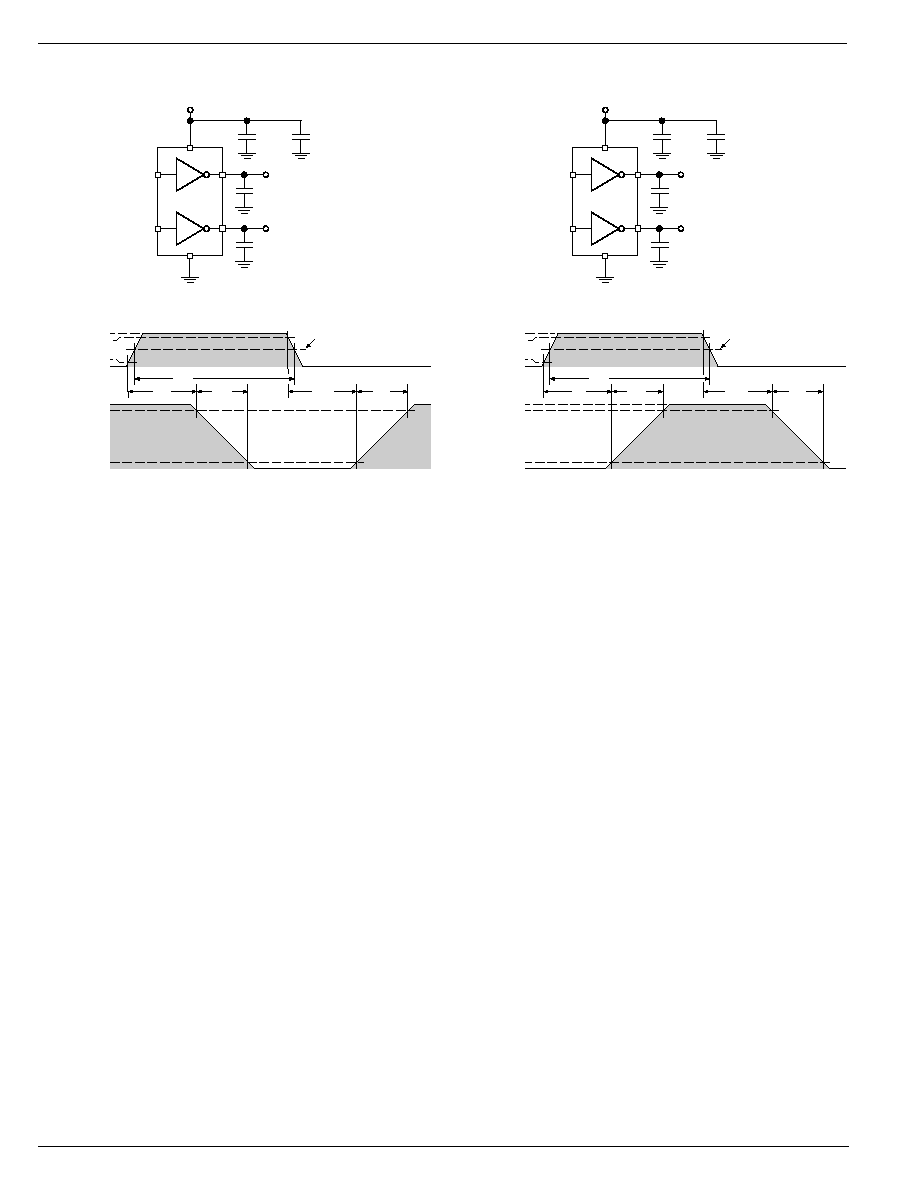
Figure 1a. Inverting Driver Switching Time
Test Circuit
A
B
INA
INB
MIC4423
OUTA
1800pF
V
S
= 18V
0.1µF
4.7µF
OUTB
1800pF
A
B
INA
INB
MIC4424
OUTA
1800pF
V
S
= 18V
0.1µF
4.7µF
OUTB
1800pF
t
D1
90%
10%
t
F
10%
0V
5V
t
D2
t
R
V
S
OUTPUT
INPUT
90%
0V
t
PW
0.5µs
2.5V
t
PW
90%
10%
t
R
10%
0V
5V
t
F
V
S
OUTPUT
INPUT
90%
0V
t
PW
0.5µs
t
D1
t
D2
t
PW
2.5V
Figure 1b. Noninverting Driver Switching Time

January 1999
5
MIC4423/4424/4425
MIC4423/4424/4425
Micrel
Typical Characteristic Curves
0
20
40
60
80
100
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
T
RISE
(ns)
V
SUPPLY
(V)
Rise Time vs.
Supply Voltage
4700pF
2200pF
1800pF
1000pF
470pF
3300pF
0
20
40
60
80
100
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
T
FALL
(ns)
V
SUPPLY
(V)
Fall Time vs.
Supply Voltage
1000pF
1800pF
2200pF
3300pF
4700pF
470pF
0
20
40
60
80
100
100
1000
10000
T
RISE
(ns)
C
LOAD
(pF)
Rise Time
vs. Capacitive Load
5V
12V
18V
0
20
40
60
80
100
100
1000
10000
T
FALL
(ns)
C
LOAD
(pF)
Fall Time vs.
Capacitive Load
5V
18V
12V
0
10
20
30
40
-75
-30
15
60
105
150
TIME (ns)
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (∞C)
Rise and Fall Time
vs. Temperature
T
R
T
F
V
S
= 18V
C
LOAD
= 1800pF
0
10
20
30
40
50
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
T (ns)
INPUT (V)
Propagation Delay vs.
Input Amplitude
V
S
= 18V
C
LOAD
= 1800pF
T
D1
T
D2
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
100
1000
10000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
C
LOAD
(pF)
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load
V
SUPPLY
= 18V
20kHz
100kHz
500kHz
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
10
100
1000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Supply Current
vs. Frequency
V
SUPPLY
= 18V
1000pF
3300pF
10000pF
100pF
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
100
1000
10000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
C
LOAD
(pF)
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load
V
SUPPLY
= 12V
20kHz
100kHz
500kHz
2MHz
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
10
100
1000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Supply Current
vs. Frequency
V
SUPPLY
= 12V
10000pF
1000pF
100pF
3300pF
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
100
1000
10000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
C
LOAD
(pF)
Supply Current vs.
Capacitive Load
V
SUPPLY
= 5V
100kHz
500kHz
2MHz
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
10
100
1000
I
SUPPLY
(mA)
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Supply Current
vs. Frequency
V
SUPPLY
= 5V
1000pF
2200pF
10000pF
100pF
4700pF




