 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: ML4872 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

July 2000
ML4872
High Current Boost Regulator with Shutdown
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ML4872 is a continuous conduction boost regulator
designed for DC to DC conversion in multiple cell battery
powered systems. Continuous conduction allows the
regulator to maximize output current for a given inductor.
The maximum switching frequency can exceed 200kHz,
allowing the use of small, low cost inductors. The ML4872
is capable of start-up with input voltages as low as 1.8V
and is available in 5V and 3.3V output versions with an
output voltage accuracy of ±3%.
An integrated synchronous rectifier eliminates the need
for an external Schottky diode and provides a lower
forward voltage drop, resulting in higher conversion
efficiency. In addition, low quiescent battery current and
variable frequency operation result in high efficiency
even at light loads. The ML4872 requires only one
inductor and two capacitors to build a very small
regulator circuit capable of achieving conversion
efficiencies approaching 90%.
The SHDN input allows the user to stop the regulator from
switching and powers down the control circuitry.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
FEATURES
s
Guaranteed full load start-up and operation at
1.8V Input
s
Continuous conduction mode for high output current
s
Very low supply current (20µA output referenced) for
micropower operation
s
Pulse frequency modulation and internal synchronous
rectification for high efficiency
s
Maximum switching frequency > 200kHz
s
Minimum external components
s
Low ON resistance internal switching FETs
s
5V and 3.3V output versions
VL2
5
VOUT
6
+
≠
VIN
2
SHDN
4
1.25V
START-UP
3
GND
VL1
1
SYNCHRONOUS
RECTIFIER
CONTROL
BOOST
CONTROL
+
≠
+
≠
8
PWR GND
FEATURING
Extended Commercial Temperature Range
-20∞C to 70∞C
for Portable Handheld Equipment
2
ML4872
PIN CONFIGURATION
PIN DESCRIPTION
ML4872
8-Pin SOIC (S08)
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
VL1
VIN
GND
SHDN
PWR GND
NC
VL2
VOUT
TOP VIEW
PIN
NAME
FUNCTION
1
V
L1
Boost inductor connection
2
V
IN
Battery input voltage
3
GND
Ground
4
SHDN
Pulling this pin to V
IN
causes the
regulator to stop switching, and
powers down the control circuitry
PIN
NAME
FUNCTION
5
V
OUT
Boost regulator output
6
V
L2
Boost inductor connection
7
NC
No connection
8
PWR GND
Return for the NMOS output transistor

3
ML4872
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Absolute maximum ratings are those values beyond which
the device could be permanently damaged. Absolute
maximum ratings are stress ratings only and functional
device operation is not implied.
V
OUT
.......................................................................... 7V
Voltage on any other pin ..... GND ≠ 0.3V to V
OUT
+ 0.3V
Peak Switch Current (I
PEAK
) ......................................... 2A
Average Switch Current (I
AVG
) ..................................... 1A
Junction Temperature .............................................. 150∫C
Storage Temperature Range ...................... ≠65∫C to 150∫C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 10 sec) ...................... 260∫C
Thermal Resistance (
q
JA
) .................................... 160∫C/W
OPERATING CONDITIONS
Temperature Range
ML4872CS-X .............................................. 0∫C to 70∫C
ML4872ES-X ........................................... ≠20∫C to 70∫C
V
IN
Operating Range
ML4872CS-X ................................ 1.8V to V
OUT
≠ 0.2V
ML4872ES-X ................................ 2.0V to V
OUT
≠ 0.2V
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Unless otherwise specified, V
IN
= Operating Voltage Range, T
A
= Operating Temperature Range (Note 1).
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
SUPPLY
I
IN
V
IN
Current
V
IN
= V
OUT
≠ 0.2V
2
5
µA
I
OUT(Q)
V
OUT
Quiescent Current
SHDN = 0V
25
35
µA
SHDN = V
IN
15
22
µA
I
L(Q)
V
L
Quiescent Current
1
µA
PFM REGULATOR
I
L
Peak Current
1.2
1.4
1.7
A
V
OUT
Output Voltage
I
L(PEAK)
= 0
-3 Suffix
3.30
3.35
3.40
V
-5 Suffix
4.95
5.05
5.15
V
Load Regulation
See Figure 1, -3 Suffix
3.20
3.25
3.40
V
V
IN
= 2.4V, I
OUT
= 400mA
See Figure 1, -5 Suffix
4.85
4.95
5.15
V
V
IN
= 2.4V, I
OUT
= 220mA
SHUTDOWN
Input Bias Current
≠100
100
nA
Shutdown Threshold
V
SHDN
= high to low
0.4
0.6
1.1
V
Note 1: Limits are guaranteed by 100% testing, sampling, or correlation with worst case test conditions.
4
ML4872
Figure 1. Application Test Circuit
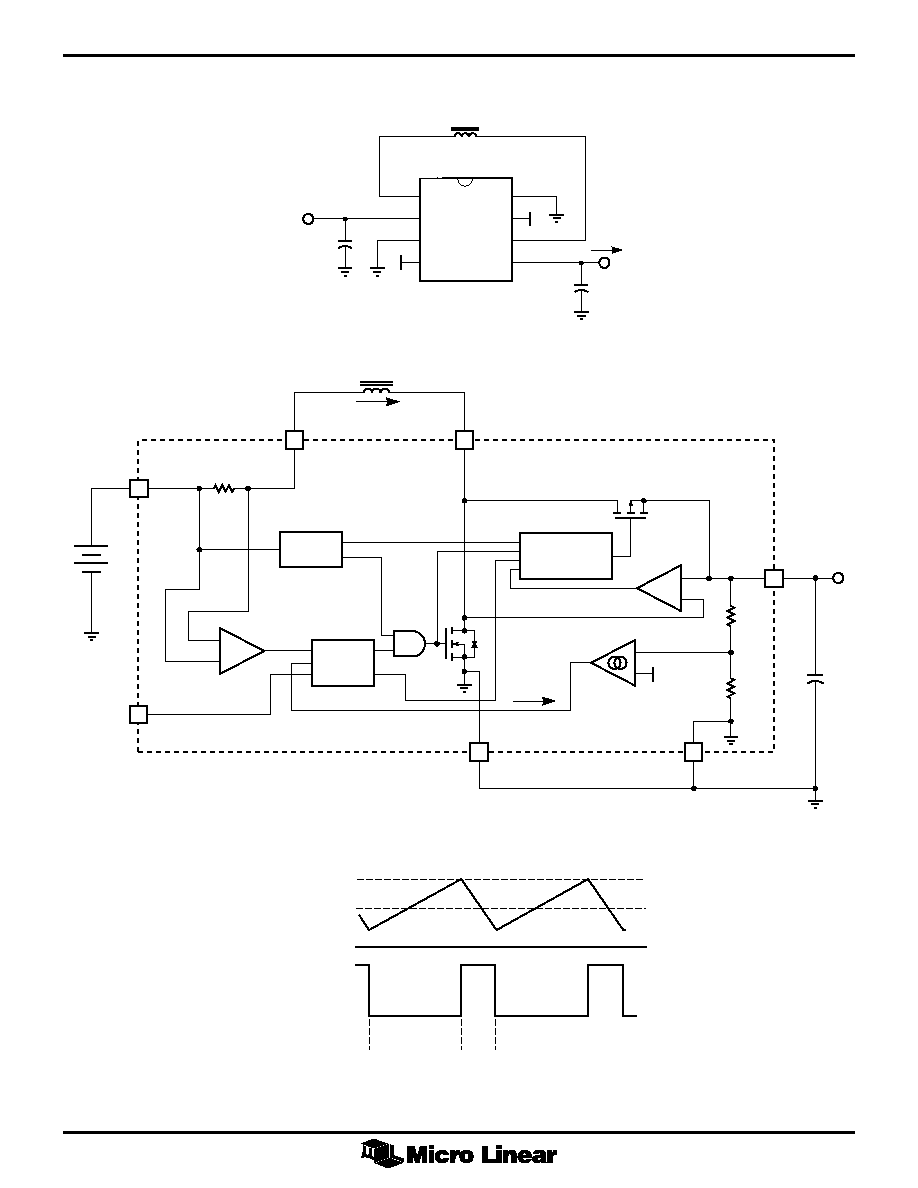
Figure 2. PFM Regulator Block Diagram
Figure 3. Inductor Current and Voltage Waveforms
ML4870
IOUT
200µF
100µF
VIN
20µH
(Sumida CD75)
VL1
VIN
GND
SHDN
PWR GND
NC
VL2
VOUT
Q1 ON
Q2 OFF
Q1 OFF
Q2 ON
IL
VL2
IL(MAX)
ISET
VOUT
0
0
VL2
5
VOUT
6
+
≠
VIN
IL
2
2.4V
START-UP
3
GND
VL1
1
SYNCHRONOUS
RECTIFIER
CONTROL
BOOST
CONTROL
+
≠
+
≠
8
PWR GND
A1
A2
A3
Q1
Q2
VOUT
RSENSE
ISET
SHDN
4

5
ML4872
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The ML4872 combines a unique form of current mode
control with a synchronous rectifier to create a boost
converter that can deliver high currents while maintaining
high efficiency. Current mode control allows the use of a
very small, high frequency inductor and output capacitor.
Synchronous rectification replaces the conventional
external Schottky diode with an on-chip PMOS FET to
reduce losses and eliminate an external component. Also
included on-chip are an NMOS switch and current sense
resistor, further reducing the number of external
components, which makes the ML4872 very easy to use.
REGULATOR OPERATION
The ML4872 is a variable frequency, current mode
switching regulator. Its unique control scheme converts
efficiently over more than three decades of load current.
A block diagram of the boost converter is shown in Figure
2.
Error amp A3 converts deviations in the desired output
voltage to a small current, I
SET
. The inductor current is
measured through a 50m
W resistor which is amplified by
A1. The boost control block matches the average inductor
current to a multiple of the I
SET
current by switching Q1
on and off. The peak inductor current is limited by the
controller to about 1.5A.
At light loads, I
SET
will momentarily reach zero after an
inductor discharge cycle , causing Q1 to stop switching.
Depending on the load, this idle time can extend to
tenths of seconds. While the circuit is not switching, only
20µA of supply current is drawn from the output. This
allows the part to remain efficient even when the load
current drops below 200µA.
Amplifier A2 and the PMOS transistor Q2 work together
to form a low drop diode. When transistor Q1 turns off,
the current flowing in the inductor causes pin 6 to go
high. As the voltage on V
L2
rises above V
OUT
, amplifier
A2 allows the PMOS transistor Q2 to turn on. In
discontinuous operation, (where I
L
always returns to zero),
A2 uses the resistive drop across the PMOS switch Q2 to
sense zero inductor current and turns the PMOS switch
off. In continuous operation, the PMOS turn off is
independent of A2, and is determined by the boost control
circuitry.
Typical inductor current and voltage waveforms are
shown in Figure 3.
SHUTDOWN
The SHDN pin should be held low for normal operation.
Raising the shutdown voltage above the threshold level
will disable the synchronous rectifier and force I
SET
to
zero. This prevents switching from occurring, and the
output voltage becomes V
IN
≠ V
DIODE
.
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
OUTPUT CURRENT CAPABILITY
The maximum current available at the output of the
regulator is related to the maximum inductor current by
the ratio of the input to output voltage and the full load
efficiency. The maximum inductor current is
approximately 1.25A and the full load efficiency may be
as low as 70%. The maximum output current can be
determined by using the typical performance curves
shown in Figures 4 and 5, or by calculation using the
following equation:
I
V
V
A
OUT MAX
IN MIN
OUT
(
)
(
)
.
.
=
125
0 7
(1)
INDUCTOR SELECTION
The ML4872 is able to operate over a wide range of
inductor values. A value of 10µH is a good choice, but
any value between 5µH and 33µH is acceptable. As the
inductor value is changed the control circuitry will
automatically adjust to keep the inductor current under
control. Choosing an inductance value of less than 10µH
will reduce the component's footprint, but the efficiency
and maximum output current may drop.
It is important to use an inductor that is rated to handle
1.5A peak currents without saturating. Also look for an
inductor with low winding resistance. A good rule of
thumb is to allow 5 to 10m
W of resistance for each µH of
inductance.
The final selection of the inductor will be based on trade-
offs between size, cost and efficiency. Inductor tolerance,
core and copper loss will vary with the type of inductor
selected and should be evaluated with a ML4872 under
worst case conditions to determine its suitability.
Several manufacturers supply standard inductance values
in surface mount packages:
Coilcraft
(847) 639-6400
Coiltronics
(561) 241-7876
Dale
(605) 665-9301
Sumida
(847) 956-0666

6
ML4872
OUTPUT CAPACITOR
The output capacitor filters the pulses of current from the
switching regulator. Since the switching frequency will
vary with inductance, the minimum output capacitance
required to reduce the output ripple to an acceptable
level will be a function of the inductor used. Therefore, to
maintain an output voltage with less than 100mV of ripple
at full load current, use the following equation:
C
L
V
OUT
OUT
=
44
(2)
The output capacitor's Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
and Equivalent Series Inductance (ESL), also contribute to
the ripple. Just after the NMOS transistor, Q1, turns off,
the current in the output capacitor ramps quickly to
between 0.5A and 1.5A. This fast change in current
through the capacitor's ESL causes a high frequency (5ns)
spike to appear on the output. After the ESL spike settles,
the output still has a ripple component equal to the
inductor discharge current times the ESR. To minimize
these effects, choose an output capacitor with less than
10nH of ESL and 100m
W of ESR.
Suitable tantalum capacitors can be obtained from the
following vendors:
AVX
(207) 282-5111
Kemet
(846) 963-6300
Sprague
(207) 324-4140
Figure 5. Efficiency vs. I
OUT
Using the Circuit of Figure 8
Figure 4. I
OUT
vs. VIN Using the Circuit of Figure 8
Figure 6. No Load Input Current vs. V
IN
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
(Continued)
1000
800
600
400
200
0
I OUT
(mA)
VIN (V)
1.0
2.0
3.0
5.0
4.0
VOUT = 3.3V
VOUT = 5V
90
80
70
60
EFFICIENCY (%)
IOUT (mA)
1
10
100
1000
VOUT = 3.3V
VOUT = 5V
VIN = 2.4V
90
60
30
0
I IN
(µA)
VIN (V)
1.0
2.0
3.0
5.0
4.0
VOUT = 3.3V
VOUT = 5V

7
ML4872
INPUT CAPACITOR
Due to the high input current drawn at startup and
possibly during operation, it is recommended to decouple
the input with a capacitor with a value of 47µF to 100µF.
This filtering prevents the input ripple from affecting the
ML4872 control circuitry, and also improves the
efficiency by reducing the I squared R losses during the
charge cycle of the inductor. Again, a low ESR capacitor
(such as tantalum) is recommended.
It is also recommended that low source impedance
batteries be used. Otherwise, the voltage drop across the
source impedance during high input current situations will
cause the ML4872 to fail to start-up or to operate
unreliably. In general, for two cell applications the source
impedance should be less than 200m
W, which means that
small alkaline cells should be avoided.
LAYOUT
Good layout practices will ensure the proper operation of
the ML4872. Some layout guidelines follow:
∑ Use adequate ground and power traces or planes
∑ Keep components as close as possible to the ML4872
∑ Use short trace lengths from the inductor to the V
L1
and
V
L2
pins and from the output capacitor to the V
OUT
pin
∑ Use a single point ground for the ML4872 ground pin,
and the input and output capacitors
∑ Separate the ground for the converter circuitry from the
ground of the load circuitry and connect at a single
point
A sample layout is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Sample PC Board Layout
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
(Continued)
DESIGN EXAMPLE
In order to design a boost converter using the ML4872, it
is necessary to define a few parameters. For this example,
assume that V
IN
= 3.0V to 3.6V, V
OUT
= 5.0V, and
I
OUT(MAX)
= 500mA.
First, it must be determined whether the ML4871 is
capable of delivering the output current. This is done
using Equation 1:
I
V
V
A
A
OUT MAX
(
)
.
.
.
.
.
=
=
125
30
50
0 7
0 53
Next, select an inductor. As previously mentioned, the
recommended inductance is 10µH. Make sure that the
peak current rating of the inductor is at least 1.5A, and
that the DC resistance of the inductor is in the range of 50
to 100m
W.
Finally, the value of the output capacitor is determined
using Equation 2:
C
H
V
F
OUT
=
=
44 10
5 0
88
m
m
.
The closest standard value would be a 100µF capacitor
with an ESR rating of 100m
W. If such a low ESR value
cannot be found, two 47µF capacitors in parallel could
also be used.
The complete circuit is shown in Figure 8. As mentioned
previously, the use of an input supply bypass capacitor is
highly recommended.
Figure 8. Typical Application Circuit
ML4872
VOUT
100µF
100µF
VIN
10µH
(Sumida CD75)
VL1
VIN
GND
SHDN
PWR GND
NC
VL2
VOUT

8
ML4872
I
OUT(MAX)
(mA)
V
IN
(V)
V
OUT
= 3.3V
V
OUT
= 5.0V
1.8
386.2
286.2
2.0
451.9
332.1
2.2
521.5
379.1
2.4
585.9
430.0
2.6
651.0
479.0
2.8
716.5
525.4
3.0
782.0
571.8
3.2
618.5
3.4
665.0
3.6
711.7
3.8
758.7
4.0
805.3
4.2
851.9
4.4
899.0
4.6
946.1
4.8
992.7
I
OUT
(mA)
EFFICIENCY PERCENTAGE
V
IN
= 2.4V, V
OUT
= 3.3V
1.0
82.0
2.0
84.4
5.0
87.0
10.0
87.6
20.0
87.9
50.0
88.3
100.0
88.6
200.0
88.2
586.0
65.1
V
IN
= 2.4V, V
OUT
= 5.0V
1.0
84.4
2.0
87.0
5.0
87.7
10.0
88.4
20.0
88.9
50.0
89.1
100.0
88.9
200.0
87.5
485.0
71.6
Table 1. Typical I
OUT
and Efficiency vs. V
IN
9
ML4872
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART NUMBER
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
TEMPERATURE RANGE
PACKAGE
ML4872CS-3
3.3V
0∫C to 70∫C
8-Pin SOIC (S08)
ML4872CS-5
5.0V
0∫C to 70∫C
8-Pin SOIC (S08)
ML4872ES-3
3.3V
≠20∫C to 70∫C
8-Pin SOIC (S08)
ML4872ES-5
5.0V
≠20∫C to 70∫C
8-Pin SOIC (S08)
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
inches (millimeters)
DS4872-01
SEATING PLANE
0.148 - 0.158
(3.76 - 4.01)
PIN 1 ID
0.228 - 0.244
(5.79 - 6.20)
0.189 - 0.199
(4.80 - 5.06)
0.012 - 0.020
(0.30 - 0.51)
0.050 BSC
(1.27 BSC)
0.015 - 0.035
(0.38 - 0.89)
0.059 - 0.069
(1.49 - 1.75)
0.004 - 0.010
(0.10 - 0.26)
0.055 - 0.061
(1.40 - 1.55)
8
0.006 - 0.010
(0.15 - 0.26)
0∫ - 8∫
1
0.017 - 0.027
(0.43 - 0.69)
(4 PLACES)
Package: S08
8-Pin SOIC
2092 Concourse Drive
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: (408) 433-5200
Fax: (408) 432-0295
http://www.microlinear.com
© Micro Linear 1998.
is a registered trademark of Micro Linear Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Products described herein may be covered by one or more of the following U.S. patents: 4,897,611; 4,964,026; 5,027,116; 5,281,862; 5,283,483; 5,418,502;
5,508,570; 5,510,727; 5,523,940; 5,546,017; 5,559,470; 5,565,761; 5,592,128; 5,594,376; 5,652,479; 5,661,427; 5,663,874; 5,672,959; 5,689,167; 5,714,897;
5,717,798; 5,742,151; 5,754,012; 5,757,174; 5,767,653. Japan: 2,598,946; 2,619,299; 2,704,176. Other patents are pending.
Micro Linear reserves the right to make changes to any product herein to improve reliability, function or design. Micro Linear does not assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product described herein, neither does it convey any license under its patent right nor the rights of others. The circuits
contained in this data sheet are offered as possible applications only. Micro Linear makes no warranties or representations as to whether the illustrated circuits
infringe any intellectual property rights of others, and will accept no responsibility or liability for use of any application herein. The customer is urged to consult
with appropriate legal counsel before deciding on a particular application.








