
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
1
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
SYNCHRONOUS
DRAM MODULE
MT18LSDT1672G ≠ 128MB,
MT18LSDT3272G ≠ 256MB,
MT18LSDT6472G ≠ 512MB
For the latest data sheet, please refer to the Micron
‚
Web
site:
www.micron.com/moduleds
Features
∑ JEDEC-standard 168-pin, dual in-line memory
module (DIMM)
∑ PC133- and PC100-compliant
∑ Registered inputs with one-clock delay
∑ Phase-lock loop (PLL) clock driver to reduce loading
∑ Utilizes 100 MHz and 133 MHz SDRAM
components
∑ ECC-optimized pinout
∑ Single +3.3V power supply
∑ Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive
edge of PLL clock
∑ Internal pipelined operation; column address can
be changed every clock cycle
∑ Internal SDRAM banks for hiding row access/precharge
∑ Programmable burst lengths: 1, 2, 4, 8, or full page
∑ Auto Precharge and Auto Refresh Modes
∑ Self Refresh Mode
∑ 128MB and 256MB: 64ms, 4,096-cycle refresh;
512MB: 64ms, 8,192-cycle refresh
∑ LVTTL-compatible inputs and outputs
∑ Serial Presence-Detect (SPD)
NOTE:
Registered mode adds one clock cycle to CL.
Figure 1: 168-Pin DIMM (MO-168)
NOTE:
1. The designators for component and PCB revision
are the last two characters of each part number.
Consult factory for current revision codes. Example:
MT18LSDT1672G-133B1
OPTIONS
MARKING
∑ Package
168-pin DIMM (gold)
G
∑ Frequency/CAS Latency
133 MHz/CL = 2
-13E
133 MHz/CL = 3
-133
100 MHz/CL = 2
-10E
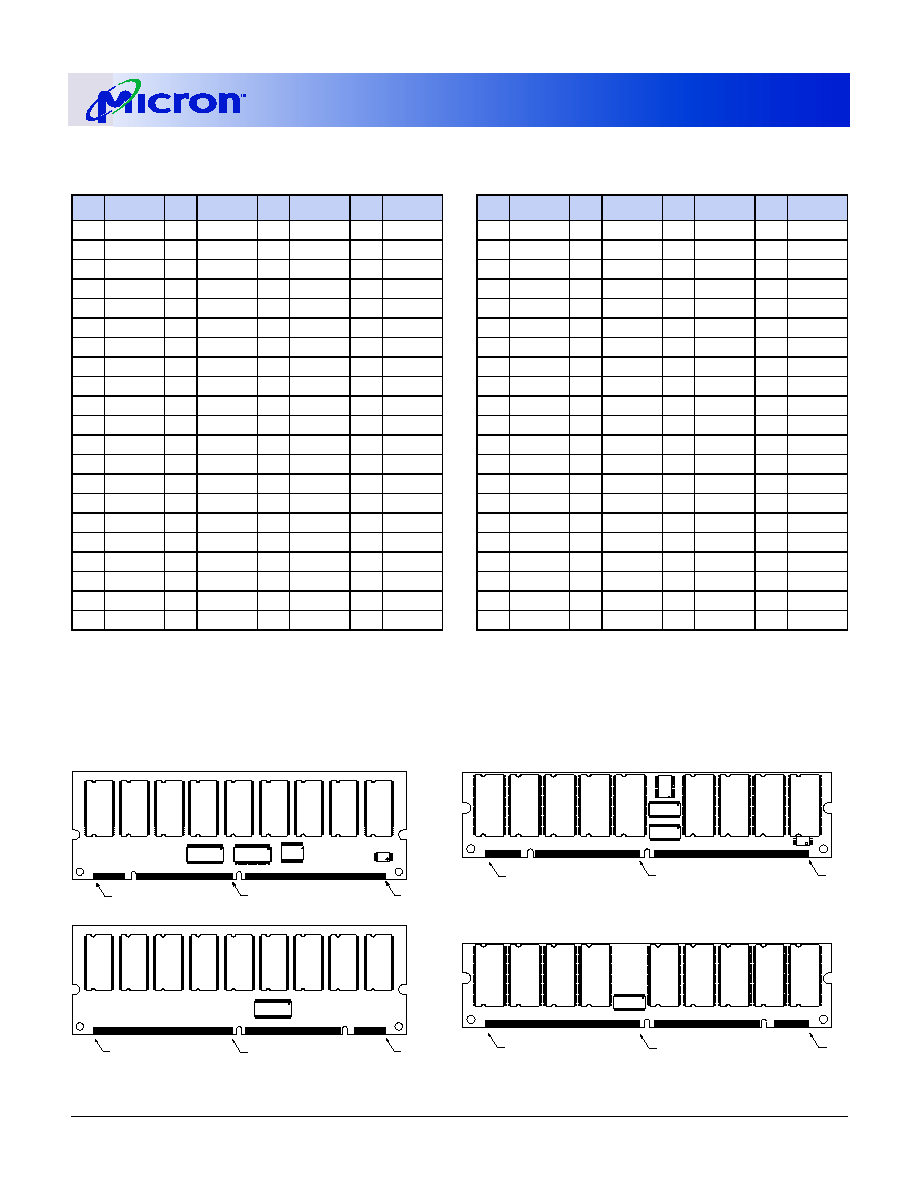
Table 1:
Address Table
PARAMETER
128MB
256MB
512MB
Refresh Count
4K
4K
8K
Device Config.
16 Meg x 4
32 Meg x 4
64 Meg x 4
Device Banks
4 (BA0, BA1) 4 (BA0, BA1) 4 (BA0, BA1)
Row Addressing 4K(A0≠A11)
4K (A0≠A11)
8K (A0-A12)
Column Addr.
1K (A0≠A9) 2K (A0≠A9,A11) 2K (A0-A9,A11)
Module Ranks
1 (S0,S2)
1 (S0,S2)
1 (S0,S2)
Table 2:
Timing Parameters
MODULE
MARKING
CLOCK
FREQUENCY
ACCESS TIME
SETUP
TIME
HOLD
TIME
CL = 2
CL = 3
-13E
133 MHz
5.4ns
≠
1.5
0.8
-133
133 MHz
≠
5.4ns
1.5
0.8
-10E
100 MHz
9ns
7.5ns
2ns
1ns
Table 3:
Part Numbers
PART NUMBER
CONFIG
SYSTEM
BUS SPEED
MT18LSDT1672G-13E__
16 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT1672G-133__
16 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT1672G-10E__
16 Meg x 72
100 MHz
MT18LSDT3272G-133__
32 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT3272G-13E__
32 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT3272G-10E__
32 Meg x 72
100 MHz
MT18LSDT6472G-133__
64 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT6472G-13E__
64 Meg x 72
133 MHz
MT18LSDT6472G-10E__
64 Meg x 72
100 MHz
U1
U2
U3
U4
U5
U12
U11
U10
U6
U7
U8
U9
U14
Standard PCB
Low Profile PCB
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
2
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
NOTE:
Pin 126 is NC for 128MB and 256MB modules, A12 for 512MB module.
Figure 2: Pin Locations (168-Pin DIMM)
Table 4:
Pin Assignment
(168-Pin DIMM Front)
PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL
1
V
SS
22
CB1
43
V
SS
64
V
SS
2
DQ0
23
V
SS
44
NC
65
DQ21
3
DQ1
24
NC
45
S2#
66
DQ22
4
DQ2
25
NC
46
DQMB2
67
DQ23
5
DQ3
26
V
DD
47
DQMB3
68
V
SS
6
V
DD
27
WE#
48
NC
69
DQ24
7
DQ4
28
DQMB0
49
V
DD
70
DQ25
8
DQ5
29
DQMB1
50
NC
71
DQ26
9
DQ6
30
S0#
51
NC
72
DQ27
10
DQ7
31
NC
52
CB2
73
V
DD
11
DQ8
32
V
SS
53
CB3
74
DQ28
12
V
SS
33
A0
54
V
SS
75
DQ29
13
DQ9
34
A2
55
DQ16
76
DQ30
14
DQ10
35
A4
56
DQ17
77
DQ31
15
DQ11
36
A6
57
DQ18
78
V
SS
16
DQ12
37
A8
58
DQ19
79
DNU
17
DQ13
38
A10
59
V
DD
80
NC
18
V
DD
39
BA1
60
DQ20
81
NC
19
DQ14
40
V
DD
61
NC
82
SDA
20
DQ15
41
V
DD
62
NC
83
SCL
21
CB0
42
CKO
63
CKE1
84
V
DD
Table 5:
Pin Assignment (168-Pin
DIMM Back)
PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL PIN SYMBOL
85
V
SS
106
CB5
127
V
SS
148
V
SS
86
DQ32
107
V
SS
128
CKE0
149
DQ53
87
DQ33
108
NC
129
S3#
150
DQ54
88
DQ34
109
NC
130 DQMB6
151
DQ55
89
DQ35
110
V
DD
131 DQMB7 152
V
SS
90
V
DD
111
CAS#
132
NC
153
DQ56
91
DQ36
112 DQMB4 133
V
DD
154
DQ57
92
DQ37
113 DQMB5 134
NC
155
DQ58
93
DQ38
114
S1#
135
NC
156
DQ59
94
DQ39
115
RAS#
136
CB6
157
V
DD
95
DQ40
116
V
SS
137
CB7
158
DQ60
96
V
SS
117
A1
138
V
SS
159
DQ61
97
DQ41
118
A3
139
DQ48
160
DQ62
98
DQ42
119
A5
140
DQ49
161
DQ63
99
DQ43
120
A7
141
DQ50
162
V
SS
100
DQ44
121
A9
142
DQ51
163
DNU
101
DQ45
122
BA0
143
V
DD
164
NC
102
V
DD
123
A11
144
DQ52
165
SA0
103
DQ46
124
V
DD
145
NC
166
SA1
104
DQ47
125
DNU
146
NC
167
SA2
105
CB4
126
NC/
A12
147
REGE
168
V
DD
U15
U16
U17
U18
U19
U20
U24
U21
U22
U23
Back View
PIN 168
PIN 124
PIN 85
U1
U2
U3
U4
U5
U12
U11
U10
U6
U7
U8
U9
U14
U15
U16
U17
U18
U24
U19
U20
U21
U22
U23
Front View
Front View
Back View
PIN 1
PIN 40
PIN 84
PIN 168
PIN 124
PIN 85
Front View
PIN 1
PIN 40
PIN 84
U1
U10
U11
U12
U2
U4
U3
U5
U6
U7
U8
U9
U14

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
3
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Table 6:
Pin Descriptions
Pin numbers are listed in module pinout order; see pin assignment tables on page 2 for more information
PIN NUMBERS
SYMBOL
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
27, 111, 115
WE#, CAS#, RAS#
Input
Command Inputs: WE#, CAS#, and RAS# (along with S0#, S2#)
define the command being entered.
42, 79, 125, 163
CK0-CK3
Input
Clock: CK0 is distributed through an on-board PLL to all
devices. CK1-CK3 are terminated.
128
CKE0
Input
Clock Enable: CKE0 activates (HIGH) and deactivates (LOW)
the CK0 signal. Deactivating the clock provides POWER-
DOWN and SELF REFRESH operation (all device banks idle) or
CLOCK SUSPEND operation (burst access in progress). CKE0 is
synchronous except after the device enters power-down and
self refresh modes, where CKE0 becomes asynchronous until
after exiting the same mode. The input buffers, including
CK0, are disabled during power-down and self refresh
modes, providing low standby power.
30, 45
S0#, S2#
Input
Chip Select: S0#, S2# enable (registered LOW) and disable
(registered HIGH) the command decoder. All commands are
masked when S0#, S2# are registered HIGH. S0#, S2# are
considered part of the command code.
28-29, 46-47, 112-113, 130-
131
DQMB0- DQMB7
Input
Input/Output Mask: DQMB is an input mask signal for write
accesses and an output enable signal for read accesses. Input
data is masked when DQMB is sampled HIGH during a WRITE
cycle. The output buffers are placed in a High-Z state (two-
clock latency) when DQMB is sampled HIGH during a READ
cycle.
39, 122
BA0, BA1
Input
Bank Address: BA0 and BA1 define to which device bank the
ACTIVE, READ, WRITE or PRECHARGE command is being
applied.
33≠38, 117≠121, 123,
126
(512MB)
A0-A11
(128MB/ 256MB)
A
0-A12
(512MB)
Input
Address Inputs: A0-A11 (128MB/256MB) or A0-A12 (512MB)
are sampled during the ACTIVE command (device row-
address A0-A11/12) and READ/WRITE command (device
column-address A0-A9 (128MB) or A0- A9/A11 (256MB/
512MB), with A10 defining auto precharge) to select one
location out of the memory array in the respective device
bank. A10 is sampled during a PRECHARGE command to
determine if both device banks are to precharged (A10
HIGH). The address inputs also provide the op-code during a
LOAD MODE REGISTER command.
81
WP
Input
Write Protect: Serial presence-detect hardware write protect.
83
SCL
Input
Serial Clock for Presence-Detect: SCL is used to synchronize
the presence-detect data transfer to and from the module.
165-167
SA0-SA2
Input
Presence-Detect Address Inputs: These pins are used to
configure the presence-detect device.
147
REGE
Input
Register Enable.
2-5, 7-11, 13-17, 19-20, 55-
58, 60, 65-67, 69-72, 74-77,
86-89, 91-95, 97-101, 103-
104, 139-142, 144, 149-151,
153-156, 158-161
DQ0-DQ63
Input/
Output
Data I/Os: Data bus.
21-22, 52-53, 105-106,
136-137
CB0-CB7
Input/
Output
Check Bits.

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
4
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
82
SDA
Input/
Output\
Serial Presence-Detect Data: SDA is a bidirectional pin used to
transfer addresses and data into and data out of the
presence-detect portion of the module.
6, 18, 26, 40-41, 49, 59, 73,
84, 90, 102, 110, 124, 133,
143, 157, 168
V
DD
Supply
Power Supply: +3.3V ±0.3V.
1, 12, 23, 32, 43, 54, 64, 68,
78, 85, 96, 107, 116, 127,
138, 148, 152, 162
V
SS
Supply
Ground.
24, 25, 26, 31, 44, 48, 50, 51,
61, 62, 63, 80, 108, 109, 114,
126 (128/256MB),129, 132,
134, 135, 145, 146, 164
NC
≠
Not Connected: These pins are not connected on these
modules.
Table 6:
Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin numbers are listed in module pinout order; see pin assignment tables on page 2 for more information
PIN NUMBERS
SYMBOL
TYPE
DESCRIPTION

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
5
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Figure 3: Functional Block Diagram
A0
SA0
SPD
SCL
SDA
A1
SA1
A2
SA2
RS0#
V
DD
V
SS
SDRAMs
SDRAMs
12pF
CK1-CK3
PLL
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
SDRAM x 2
REGISTER x 3
CK0
12pF
RDQMB4
DQM CS#
U1
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
RDQMB0
DQM CS#
U23
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ32
DQ33
DQ34
DQ35
DQM CS#
U2
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQM CS#
U22
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ36
DQ37
DQ38
DQ39
RDQMB5
DQM CS#
U3
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
RDQMB1
DQM CS#
U21
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ40
DQ41
DQ41
DQ43
DQM CS#
U4
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
DQM CS#
U20
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ44
DQ45
DQ46
DQ47
DQM CS#
U5
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
CB0
CB1
CB2
CB3
DQM
CS#
U19
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
CB4
CB5
CB6
CB7
RS2#
RDQMB6
DQM CS#
U6
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ16
DQ17
DQ18
DQ19
RDQMB2
DQM CS#
U18
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ48
DQ49
DQ50
DQ51
DQM CS#
U7
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ20
DQ21
DQ22
DQ23
DQM CS#
U17
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ52
DQ53
DQ54
DQ55
RDQMB7
DQM CS#
U8
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ24
DQ25
DQ26
DQ27
RDQMB3
DQM CS#
U16
U10, U11, U24
U13
U14
U12
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ56
DQ57
DQ58
DQ59
DQM CS#
U9
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ28
DQ29
DQ30
DQ31
DQM CS#
U15
U15
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ60
DQ61
DQ62
DQ63
RAS#
CAS#
CKE0
WE#
(128MB/256MB) ≠ A0-A11
(512MB) ≠ A0-A12
BA0
BA1
S0#, S2#
DQMB0 - DQMB7
PLL CLK
RRAS#: SDRAMs
RCAS#: SDRAMs
RCKE0: SDRAMs
RWE#: SDRAMs
RA0-RA11: SDRAMs
RA0-RA12: SDRAMs
RBA0: SDRAMs
RBA1: SDRAMs
RS0#, RS2#
RDQMB0 - RDQMB7
R
E
G
I
S
T
E
R
S
V
DD
REGE
10K
WP
NOTE:
1.
All resistor values are 10 ohms unless otherwise specified.
2. Per industry standard, Micron uses various component speed grades as referenced
in the Module Part Numbering Guide at
www.micron.com/numberguide
.
SDRAMS = MT48LC16M4A2TG for 128MB
SDRAMS = MT48LC32M4A2TG for 256MB
SDRAMS = MT48LC64M4A2TG for 512MB

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
6
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
General Description
The MT18LSDT1672G, MT18LSDT3272G, and
MT18LSDT6472G are high-speed CMOS, dynamic ran-
dom-access, 128MB, 256MB, and 512MB memory
modules organized in a x72 (ECC) configuration.
These modules use internally configured quad-bank
SDRAM devices, with a synchronous interface (all sig-
nals are registered on the positive edge of clock signal
CK0).
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM modules are
burst oriented; accesses start at a selected location and
continue for a programmed number of locations in a
programmed sequence. Accesses begin with the regis-
tration of an ACTIVE command, which is then fol-
lowed by a READ or WRITE command. The address
bits registered coincident with the ACTIVE command
are used to select the device bank and row to be
accessed (BA0, BA1 select the device bank, A0-A11
select the device row for the 128MB and 256MB mod-
ules; A0-A12 select the device row for the 512MB mod-
ule). The address bits registered coincident with the
READ or WRITE command are used to select the start-
ing device column location for the burst access.
These modules provide for programmable read or
write burst lengths of 1, 2, 4, or 8 locations, or full page,
with a burst terminate option. An auto precharge
function may be enabled to provide a self-timed
device row precharge that is initiated at the end of the
burst sequence.
These modules use an internal pipelined architec-
ture. Precharging one device bank while accessing one
of the other three device banks will hide the PRE-
CHARGE cycles and provide seamless, high-speed,
random-access operation.
These modules are designed to operate in 3.3V, low-
power memory systems. An auto refresh mode is pro-
vided, along with a power-saving, power-down mode.
All inputs and outputs are LVTTL-compatible.
SDRAM modules offer substantial advances in
DRAM operating performance, including the ability to
synchronously burst data at a high data rate with auto-
matic device column-address generation, the ability to
interleave between device banks in order to hide pre-
charge time, and the capability to randomly change
device column addresses on each clock cycle during a
burst access. For more information regarding SDRAM
operation, refer to the 64Mb, 128Mb, and 256Mb
SDRAM data sheets.
PLL and Register Operation
These modules can be operated in either registered
mode (REGE pin HIGH), where the control/address
input signals are latched in the register on one rising
clock edge and sent to the SDRAM devices on the fol-
lowing rising clock edge (data access is delayed by one
clock), or in buffered mode (REGE pin LOW) where the
input signals pass through the register/buffer to the
SDRAM devices on the same clock. A phase-lock loop
(PLL) on the modules is used to redrive the clock sig-
nals to the SDRAM devices to minimize system clock
loading (CK0 is connected to the PLL, and CK1, CK2,
and CK3 are terminated).
Serial Presence-Detect Operation
These modules incorporate serial presence-detect
(SPD). The SPD function is implemented using a
2,048-bit EEPROM. This nonvolatile storage device
contains 256 bytes. The first 128 bytes can be pro-
grammed by Micron to identify the module type and
various SDRAM organizations and timing parameters.
The remaining 128 bytes of storage are available for
use by the customer. System READ/WRITE operations
between the master (system logic) and the slave
EEPROM device (DIMM) occur via a standard I
2
C bus
using the DIMM's SCL (clock) and SDA (data) signals,
together with SA (2:0), which provide eight unique
DIMM/EEPROM addresses. Write protect (WP) is tied
to ground on the module, permanently disabling hard-
ware write protect.
SDRAM Component Description
In general, the 64Mb, 128Mb, and 256Mb SDRAM
memory devices used for these modules are quad-
bank DRAMs, that operate at 3.3V and include a syn-
chronous interface (all signals are registered on the
positive edge of the clock signal, CK). The four banks
of a x4, 64Mb device are each configured as 4,096 bit-
rows, by 1,024 bit-columns, by 4 input/output bits. The
four banks of a x4, 128Mb device are each configured
as 4,096 bit-rows, by 2,048 bit-columns, by 4 input/
output bits. The four banks of a x4, 256MB device are
configured as 8,192 bit-rows, by 2,048 bit columns, by 4
input/output bits.
Module Functional Description
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst ori-
ented; accesses start at a selected location and con-
tinue for a programmed number of locations in a
programmed sequence. Accesses begin with the regis-
tration of an ACTIVE command, which is then fol-
lowed by a READ or WRITE command. The address
bits registered coincident with the ACTIVE command
are used to select the device bank and row to be
accessed BA0 and BA1 select the device bank, A0-A11
(for 128MB and 256MB module), or A0-A12 (for 512MB
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
7
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
module), select the device row. The address bits A0-A9
(for 64MB) or A0-A9, A11 (for the 256MB and 512MB
module), registered coincident with the READ or
WRITE command are used to select the starting device
column location for the burst access.
Prior to normal operation, the SDRAM must be ini-
tialized. The following sections provide detailed infor-
mation covering device initialization, register
definition, command descriptions and device opera-
tion.
Initialization
SDRAMs must be powered up and initialized in a
predefined manner. Operational procedures other
than those specified may result in undefined opera-
tion. Once power is applied to Vdd and VddQ (simulta-
neously) and the clock is stable (stable clock is defined
as a signal cycling within timing constraints specified
for the clock pin), the SDRAM requires a 100µs delay
prior to issuing any command other than a COM-
MAND INHIBIT or NOP. Starting at some point during
this 100µs period and continuing at least through the
end of this period, Command Inhibit or NOP com-
mands should be applied.
Once the 100µs delay has been satisfied with at least
one Command Inhibit or NOP command having been
applied, a PRECHARGE command should be applied.
All device banks must then be precharged, thereby
placing the device in the all device banks idle state.
Once in the idle state, two AUTO refresh cycles must
be performed. After the AUTO refresh cycles are com-
plete, the SDRAM is ready for mode register program-
ming. Because the mode register will power up in an
unknown state, it should be loaded prior to applying
any operational command.
Mode Register Definition
The mode register is used to define the specific
mode of operation of the SDRAM. This definition
includes the selection of a burst length, a burst type, a
CAS latency, an operating mode and a write burst
mode, as shown in Mode Register Definition Diagram.
The mode register is programmed via the LOAD
MODE REGISTER command and will retain the stored
information until it is programmed again or the device
loses power.
Mode register bits M0-M2 specify the burst length,
M3 specifies the type of burst (sequential or inter-
leaved), M4-M6 specify the CAS latency, M7 and M8
specify the operating mode, M9 specifies the write
burst mode, and M10 and M11 are reserved for future
use. For the 512MB module, address A12 (M12) is
undefined but should be driven LOW during loading of
the mode register.
The mode register must be loaded when all device
banks are idle, and the controller must wait the speci-
fied time before initiating the subsequent operation.
Violating either of these requirements will result in
unspecified operation.
Figure 4: Mode Register Definition
Diagram
Reserved*
Reserved*
M2
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
M1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
M0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
M3 = 0
1
2
4
8
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Full Page
M3 = 1
1
2
4
8
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Operating Mode
Standard Operation
All other states reserved
0
-
0
-
Defined
-
0
1
Burst Type
Sequential
Interleaved
CAS Latency
Reserved
2
3
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
M6
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
M4
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
M5
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
Burst Length
Burst Length
CAS Latency
BT
A9
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A8
A2
A1
A0
Mode Register (Mx)
Address Bus
9
7
6
5
4
3
8
2
1
0
M3
M6-M0
M8
M7
Op Mode
A10
A11
10
11
12
WB
0
1
Write Burst Mode
Programmed Burst Length
Single Location Access
M9
*Should program
M12, M11, M10 = "0, 0, 0"
to ensure compatibility
with future devices.
A12
Burst Length
CAS Latency
BT
A9
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A8
A2
A1
A0
Mode Register (Mx)
Address Bus
9
7
6
5
4
3
8
2
1
0
Op Mode
A10
A11
10
11
Reserved* WB
*Should program
M11, M10 = "0, 0"
to ensure compatibility
with future devices.
512MB Module
128MB and 256MB Modules

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
8
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Burst Length
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst ori-
ented, with the burst length being programmable, as
shown in Mode Register Definition Diagram. The burst
length determines the maximum number of column
locations that can be accessed for a given READ or
WRITE command. Burst lengths of 1, 2, 4, or 8 loca-
tions are available for both the sequential and the
interleaved burst types, and a full-page burst is avail-
able for the sequential type. The full-page burst is used
in conjunction with the BURST TERMINATE com-
mand to generate arbitrary burst lengths.
Reserved states should not be used, as unknown
operation or incompatibility with future versions may
result.
When a READ or WRITE command is issued, a block
of columns equal to the burst length is effectively
selected. All accesses for that burst take place within
this block, meaning that the burst will wrap within the
block if a boundary is reached, as shown in the Burst
Definition Table. The block is uniquely selected by A1-
A9 (64MB) or A1-A9, A11 (128MB/256MB) when the
burst length is set to two; A2-A9 or A2-A9, A11 when
the burst length is set to four; and by A3-A9 or A3-A9,
A11 when the burst length is set to eight. The remain-
ing (least significant) address bit(s) is (are) used to
select the starting location within the block. Full-page
bursts wrap within the page if the boundary is reached,
as shown in the Burst Definition Table.
Burst Type
Accesses within a given burst may be programmed
to be either sequential or interleaved; this is referred to
as the burst type and is selected via bit M3.
The ordering of accesses within a burst is deter-
mined by the burst length, the burst type and the start-
ing column address, as shown in the Burst Definition
Table.
CAS Latency
The CAS latency is the delay, in clock cycles,
between the registration of a READ command and the
availability of the first piece of output data. The latency
can be set to two or three clocks.
M
NOTE:
1. For full-page accesses: y = 1,024 (128MB); y= 2,048
(256MB and512MB).
2. For a burst length of two, A1≠A9 (128MB) or A1≠
A9/A11(256MB and512MB) select the block of two
burst; A0 selects the starting column within the
block.
3. For a burst length of four, A2≠A9 or A2≠A9/A11
select the block of four burst; A0≠A1 select the
starting column within the block.
4. For a burst length of eight, A3≠A9 or A3≠A9/A11
select the block of eight burst; A0≠A2 select the
starting column within the block.
5. For a full-page burst, the full row is selected and
A0≠A9 or A0≠A9/A11 select the starting column.
6. Whenever a boundary of the block is reached
within a given sequence above, the following
access wraps within the block.
7. For a burst length of one, A0≠A9 or A0≠A9/A11
select the unique column to be accessed, and Mode
Register bit M3 is ignored.
Table 7:
Burst Definition Table
BURST
LENGTH
STARTING
COLUMN
ADDRESS
ORDER OF ACCESSES
WITHIN A BURST
TYPE =
SEQUENTIAL
TYPE =
INTERLEAVED
2
A0
0
0-1
0-1
1
1-0
1-0
4
A1 A0
0
0
0-1-2-3
0-1-2-3
0
1
1-2-3-0
1-0-3-2
1
0
2-3-0-1
2-3-0-1
1
1
3-0-1-2
3-2-1-0
8
A2 A1 A0
0
0
0
0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7
0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7
0
0
1
1-2-3-4-5-6-7-0
1-0-3-2-5-4-7-6
0
1
0
2-3-4-5-6-7-0-1
2-3-0-1-6-7-4-5
0
1
1
3-4-5-6-7-0-1-2
3-2-1-0-7-6-5-4
1
0
0
4-5-6-7-0-1-2-3
4-5-6-7-0-1-2-3
1
0
1
5-6-7-0-1-2-3-4
5-4-7-6-1-0-3-2
1
1
0
6-7-0-1-2-3-4-5
6-7-4-5-2-3-0-1
1
1
1
7-0-1-2-3-4-5-6
7-6-5-4-3-2-1-0
Full
Page
(y)
n = A0-A9, or
n =A0-A9/A11
(location 0-y)
Cn, Cn+1, Cn+2,
Cn+3, Cn+4...,
...Cn-1, Cn...
Notsupported
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
9
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
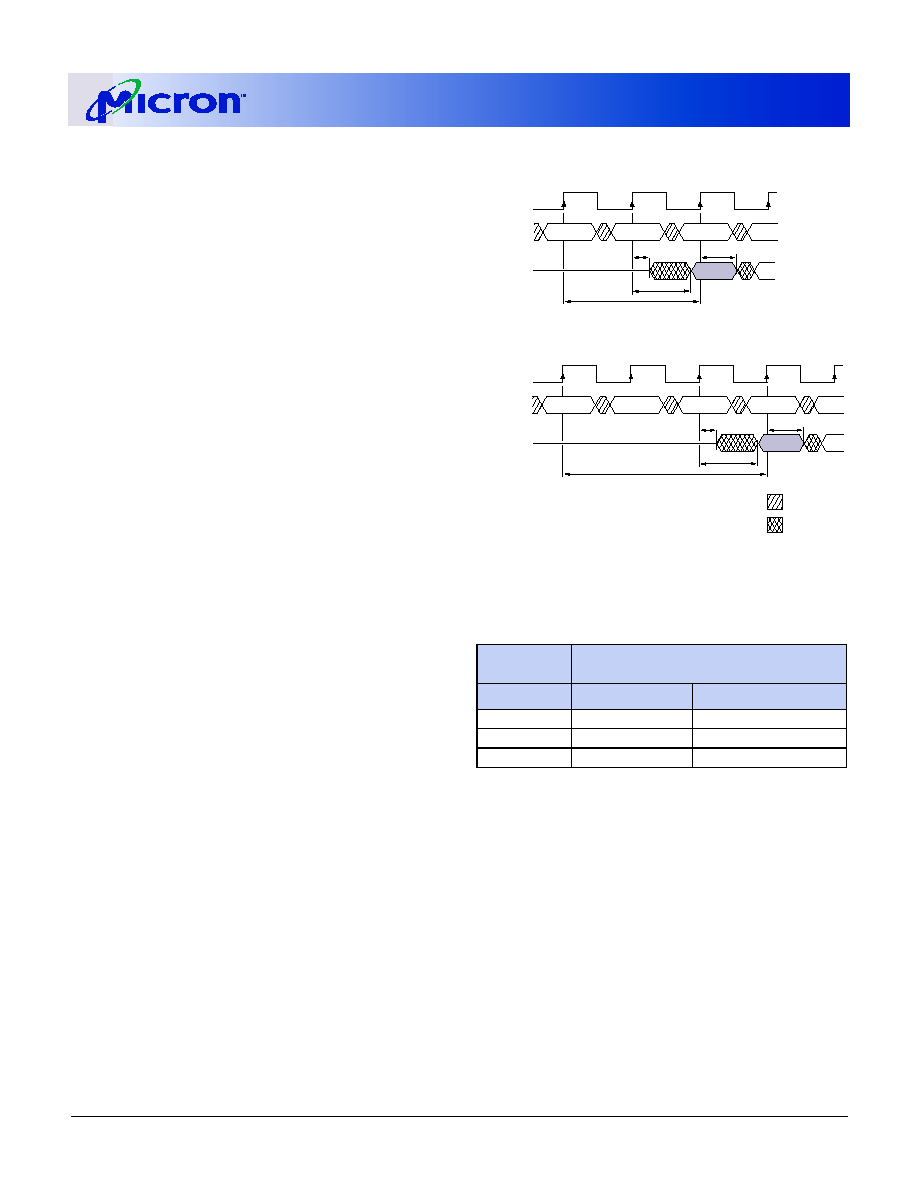
If a READ command is registered at clock edge n,
and the latency is m clocks, the data will be available
by clock edge n + m. The DQs will start driving as a
result of the clock edge one cycle earlier (n + m - 1),
and provided that the relevant access times are met,
the data will be valid by clock edge n + m. For example,
assuming that the clock cycle time is such that all rele-
vant access times are met, if a read command is regis-
tered at T0 and the latency is programmed to two
clocks, the DQs will start driving after T1 and the data
will be valid by T2, as shown in the CAS Latency Dia-
gram. The CAS Latency Table indicate the operating
frequencies at which each CAS latency setting can be
used.
Reserved states should not be used as unknown
operation or incompatibility with future versions may
result.
Operating Mode
The normal operating mode is selected by setting
M7 and M8 to zero; the other combinations of values
for M7 and M8 are reserved for future use and/or test
modes. The programmed burst length applies to both
read and write bursts.
Test modes and reserved states should not be used
because unknown operation or incompatibility with
future versions may result.
Write Burst Mode
When M9 = 0, the burst length programmed via
M0-M2 applies to both read and write bursts; when
M9 = 1, the programmed burst length applies to
read bursts, but write accesses are single-location
(nonburst) accesses.
Figure 5: CAS Latency Diagram
Table 8:
CAS Latency Table
Registered mode will add one clock cycle to CAS Latency
(CL) listed
ALLOWABLE OPERATING
FREQUENCY (MHZ)
SPEED
CL = 2
CL = 3
-13E
£ 133
£ 143
-133
£ 100
£ 133
-10E
£ 100
NA
CLK
DQ
T2
T1
T3
T0
CAS Latency = 3
LZ
D
OUT
tOH
t
COMMAND
NOP
READ
tAC
NOP
T4
NOP
DON'T CARE
UNDEFINED
CLK
DQ
T2
T1
T3
T0
CAS Latency = 2
LZ
D
OUT
tOH
t
COMMAND
NOP
READ
tAC
NOP

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
10
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Commands
The Truth Table provides a quick reference of avail-
able commands. This is followed by a written descrip-
tion of each command. For a more detailed
description of commands and operations refer to the
64Mb, 128Mb, or 256Mb SDRAM component
datasheets.
NOTE:
1. CKE is HIGH for all commands shown except Self Refresh.
2. A0≠A11 (128MB and 256MB), A0≠A12 (512MB) define the op-code written to the Mode Register, and should be
driven low.
3. A0≠A11 (128MB and 256MB), A0≠A12 (512MB) provide device row address. BA0, BA1 determine which device bank is
made active.
4. A0≠A9 provide device column address for 128MB module; A0≠A9/A11 for 256MB and 512MB modules; A10 HIGH
enables the auto precharge feature (nonpersistent), while A10 LOW disables the auto precharge feature; BA0, BA1
determine which device bank is being read from or written to.
5. A10 LOW: BA0, BA1 determine which device bank is being precharged. A10 HIGH: both device banks are precharged
and BA0, BA1 are "Don't Care."
6. This command is Auto Refresh if CKE is HIGH, Self Refresh if CKE is LOW.
7. Internal refresh counter controls row addressing; all inputs and I/Os are "Don't Care" except for CKE.
8. Activates or deactivates the DQs during WRITEs (zero-clock delay) and READs (two-clock delay).
Table 9:
Truth Table ≠ SDRAM Commands and DQMB Operation
Note: 1; notes appear below table)
NAME (FUNCTION)
CS#
RAS# CAS# WE#
DQMB
ADDR
DQS
NOTES
COMMAND INHIBIT (NOP)
H
X
X
X
X
X
X
NO OPERATION (NOP)
L
H
H
H
X
X
X
ACTIVE (Select bank and activate row)
L
L
H
H
X
Bank/Row
X
3
READ (Select bank and column, and start READ burst)
L
H
L
H
L/H
8
Bank/Col
X
4
WRITE (Select bank and column, and start WRITE burst)
L
H
L
L
L/H
8
Bank/Col
Valid
4
BURST TERMINATE
L
H
H
L
X
X
Active
PRECHARGE (Deactivate row in bank or banks)
L
L
H
L
X
Code
X
5
AUTO REFRESH or
SELF REFRESH (Enter self refresh mode)
L
L
L
H
X
X
X
6, 7
LOAD MODE REGISTER
L
L
L
L
X
Op-Code
X
2
Write Enable/Output Enable
≠
≠
≠
≠
L
≠
Active
8
Write Inhibit/Output High-Z
≠
≠
≠
≠
H
≠
High-Z
8

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
11
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses greater than those listed may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only,
and functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the opera-
tional sections of this specification is not implied.
Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect reliability.
Voltage on V
DD
Supply
Relative to V
SS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -1V to +4.6V
Voltage on Inputs, NC or I/O Pins
Relative to Vss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -1V to +4.6V
Operating Temperature
T
A
(ambient) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0∞C to +70∞C
Storage Temperature (plastic) . . . . . . -55∞C to +150∞C
Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18W
Table 10: DC Electrical Characteristics and Operating Conditions
Notes: 1, 5, 6; notes appear on page 15; 0
∞C £ T
A
£ +70∞C
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
MIN
MAX
UNITS
NOTES
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
V
DD
, V
DD
Q
3
3.6
V
INPUT HIGH VOLTAGE: Logic 1; All inputs
V
IH
2
V
DD
+ 0.3
V
22
INPUT LOW VOLTAGE: Logic 0; All inputs
V
IL
-0.3
0.8
V
22
INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT: Any input 0V
£ V
IN
£ V
DD
(All
other pins not under test = 0V) For inputs: A0-A12, BA0,
BA1, RAS#, CAS#,WE#, CKE0
I
I
A
-10
10
µA
33
INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT: Any input 0V
£ V
IN
£ V
DD
(All other pins not under test = 0V) For inputs: S#, DQMB
I
I
B
-5
5
µA
33
OUTPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT: DQs are disabled;
0V
£ V
OUT
£ V
DD
Q
I
OZ
-10
10
µA
33
OUTPUT LEVELS:
Output High Voltage (I
OUT
= -4mA)
V
OH
2.4
≠
V
Output Low Voltage (I
OUT
= 4mA)
V
OL
≠
0.4
V
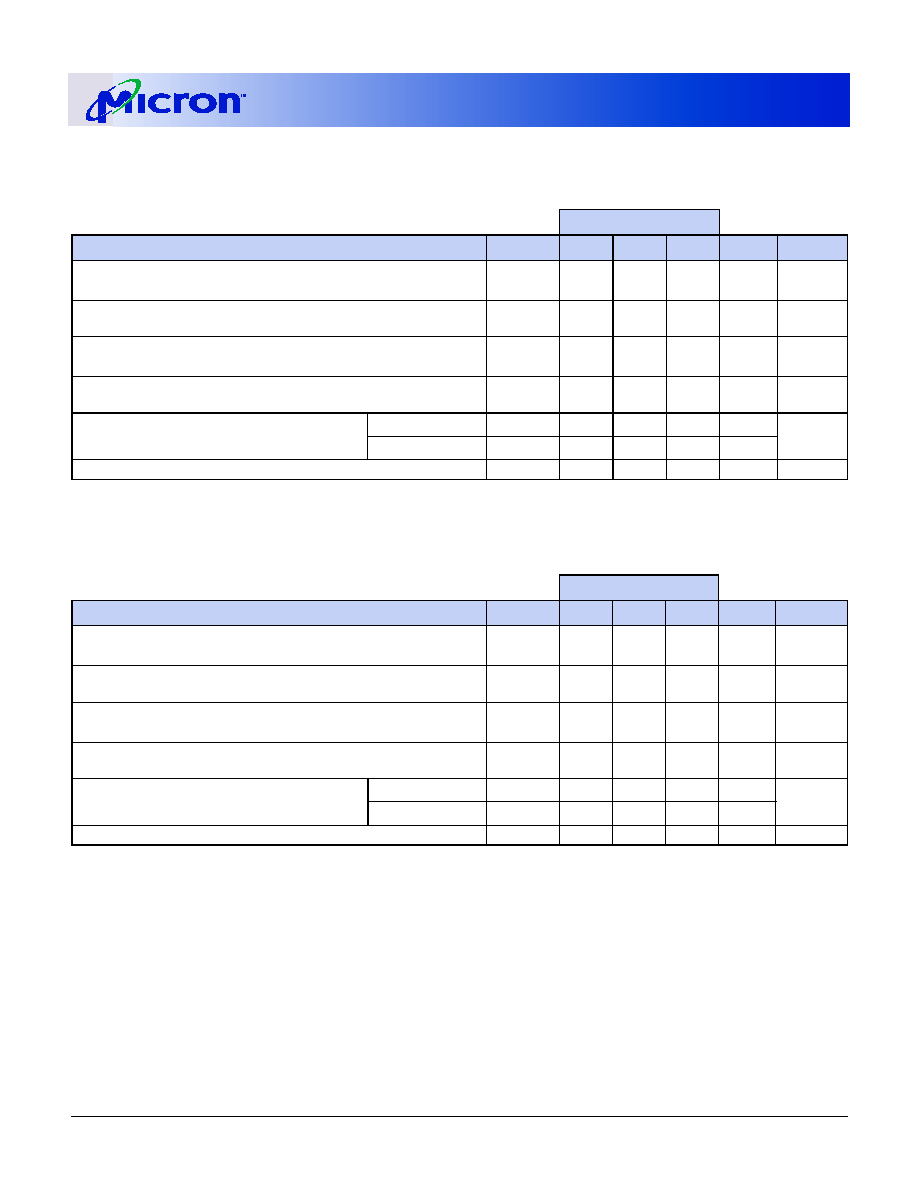
Table 11: I
DD
Specifications and Conditions (128MB)
SDRAM components only
Notes: 1, 6, 11, 13; notes appear on page 15; 0
∞C £ T
A
£ +70∞C; V
DD
= V
DD
Q - +3.3V ±0.3V
MAX
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
-13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
OPERATING CURRENT: Active Mode; Burst = 2; READ or WRITE;
t
RC =
t
RC (MIN)
I
DD1
1,250
2,070
1,710
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Power-Down Mode; All device banks idle;
CKE = LOW
I
DD2
36
36
36
mA
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Active Mode; CKE = HIGH; CS# = HIGH; All
device banks active after
t
RCD met; No accesses in progress
I
DD3
810
810
630
mA
3, 12, 19,
30
OPERATING CURRENT: Burst Mode; Continuous burst; READ or
WRITE; All device banks active
I
DD4
2,700
2,520
2,160
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
AUTO REFRESH CURRENT CS# = HIGH;
CKE = HIGH
t
RFC =
t
RFC (MIN)
I
DD5
4,140
3,780
3,420
mA
3, 12, 18,
19, 30, 31
t
RFC = 15.6 µs
I
DD6
54
54
54
mA
SELF REFRESH CURRENT: CKE
£ 0.2V
I
DD7
18
18
18
mA
4
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
12
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Table 12: I
DD
Specifications and Conditions (256MB)
SDRAM components only
Notes: 1, 6, 11, 13; notes appear on page 15; 0
∞C £ T
A
£ +70∞C; V
DD
= V
DD
Q - +3.3V ±0.3V
MAX
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
-13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
OPERATING CURRENT: Active Mode; Burst = 2; READ or WRITE;
t
RC =
t
RC (MIN)
I
DD1
2,880
2,700
2,520
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Power-Down Mode; All device banks idle;
CKE = LOW
I
DD2
36
36
36
mA
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Active Mode; CKE = HIGH; CS# = HIGH; All
device banks active after
t
RCD met; No accesses in progress
I
DD3
900
900
720
mA
3, 12, 19,
30
OPERATING CURRENT: Burst Mode; Continuous burst; READ or
WRITE; All device banks active
I
DD4
2,970
2,700
2,520
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
AUTO REFRESH CURRENT CS# = HIGH;
CKE = HIGH
t
RFC =
t
RFC (MIN)
I
DD5
5,940
5,580
4,860
mA
3, 12, 18,
19, 30, 31
t
RFC = 15.6 µs
I
DD6
54
54
54
mA
SELF REFRESH CURRENT: CKE
£ 0.2V
I
DD7
36
36
36
mA
4
Table 13: I
DD
Specifications and Conditions (512MB)
SDRAM components only
Notes: 1, 6, 11, 13; notes appear on page 15; 0
∞C £ T
A
£ +70∞C; V
DD
= V
DD
Q - +3.3V ±0.3V
MAX
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
-13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
OPERATING CURRENT: Active Mode; Burst = 2; READ or WRITE;
t
RC =
t
RC (MIN)
I
DD1
2,430
2,250
2,250
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Power-Down Mode; All device banks idle;
CKE = LOW
I
DD2
36
36
36
mA
30
STANDBY CURRENT: Active Mode; CKE = HIGH; CS# = HIGH; All
device banks active after
t
RCD met; No accesses in progress
I
DD3
720
720
720
mA
3, 12, 19,
30
OPERATING CURRENT: Burst Mode; Continuous burst; READ or
WRITE; All device banks active
I
DD4
2,430
2,430
2,430
mA
3, 18, 19,
30
AUTO REFRESH CURRENT CS# = HIGH;
CKE = HIGH
t
RFC =
t
RFC (MIN)
I
DD5
5,130
4,860
4,860
mA
3, 12, 18,
19, 30, 31
t
RFC = 15.6 µs
I
DD6
63
63
63
mA
SELF REFRESH CURRENT: CKE
£ 0.2V
I
DD7
45
45
45
mA
4

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
13
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Table 14: CAPACITANCE (128MB, 256MB, and 512MB)
Note: 2; notes appear on page 15
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Input Capacitance: A0-A12, BA0, BA1, RAS#, CAS#, WE#, CKE0
C
I1
≠
8
≠
pF
Input Capacitance: S0#, S2#, DQMB0-DQMB7
C
I2
≠
4
≠
pF
Input Capacitance: CK0
C
I3
≠
16
≠
pF
Input Capacitance: SCL, SA0-SA2, SDA
C
I4
≠
≠
10
pF
Input Capacitance: CK1-CK3
C
I5
≠
12
≠
pF
Input Capacitance: REGE
C
I6
1.5
-
12
pF
Input/Output Capacitance: DQ0-DQ63, CB0-CB3, CB4-CB7
C
IO
8
≠
12
pF
Table 15: SDRAM Component Electrical Characteristics and Recommended AC
Operating Conditions
Notes: 5, 6, 8, 9, 11; notes appear on page 15
AC CHARACTERISTICS
-13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
PARAMETER
SYMBOL MIN
MAX
MIN
MAX
MIN
MAX
Access time from CLK(pos.edge)
CL=3
t
AC(3)
5.4
5.4
6
ns
27
CL=2
t
AC(2)
5.4
6
6
ns
Address hold time
t
AH
0.8
0.8
1
ns
Address setup time
t
AS
1.5
1.5
2
ns
CLK high-level width
t
CH
2.5
2.5
3
ns
CLK low-level width
t
CL
2.5
2.5
3
ns
Clock cycle time
CL=3
t
CK(3)
7
7.5
8
ns
23
CL = 2
t
CK(2)
7.5
10
10
ns
23
CKE hold time
t
CKH
0.8
0.8
1
ns
CKE setup time
t
CKS
1.5
1.5
2
ns
CS#, RAS#, CAS#, WE#, DQM hold time
t
CMH
0.8
0.8
1
ns
CS#, RAS#, CAS#, WE#, DQM setup time
t
CMS
1.5
1.5
2
ns
Data-in hold time
t
DH
0.8
0.8
1
ns
Data-in setup time
t
DS
1.5
1.5
2
ns
Data-out high-impedance time
CL = 3
t
HZ(3)
5.4
5.4
6
ns
10
CL = 2
t
HZ(2)
5.4
6
6
ns
10
Data-out low-impedance time
t
LZ
1
1
1
ns
Data-out hold time (load)
t
OH
3
3
3
ns
Data-out hold time (no load)
t
OH
N
1.8
1.8
1.8
ns
28
ACTIVE to PRE CHARGE command
t
RAS
37
120,000
44
120,000
50
120,000
ns
29
ACTIVE to ACTIVE command period
t
RC
60
66
70
ns
ACTIVE to READ or WRITE delay
t
RCD
15
20
20
ns
Refresh period (8,192 rows)
t
REF
64
64
64
ms
AUTO REFRESH period
t
RFC
66
66
70
ns
PRE CHARGE command period
t
RP
15
20
20
ns
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
14
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
ACTIV bank a to ACTIVE bank b command
t
RRD
14
15
20
ns
Transition time
t
T
0.3
1.2
0.3
1.2
0.3
1.2
ns
7
WRITE recovery time
t
WR
1 CLK
+ 7ns
1 CLK
+ 7.5ns
1 CLK
+ 7ns
ns
24
14
15
15
ns
25
Exit SELF REFRESH to ACTIVE command
t
XSR
67
75
80
ns
20
Table 15: SDRAM Component Electrical Characteristics and Recommended AC
Operating Conditions (Continued)
Notes: 5, 6, 8, 9, 11; notes appear on page 15
AC CHARACTERISTICS
-13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
PARAMETER
SYMBOL MIN
MAX
MIN
MAX
MIN
MAX
Table 16: AC Functional Characteristics
Notes: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11; notes appear on page 15
PARAMETER
SYMBOL -13E
-133
-10E
UNITS
NOTES
READ/WRITEc ommand to READ/WRITE command
t
CCD
1
1
1
t
CK
17
CKE to clock disable or power-down entry mode
t
CKED
1
1
1
t
CK
14, 32
CKE to clock enable or power-down exit setup mode
t
PED
1
1
1
t
CK
14, 32
DQM to input data delay
t
DQD
0
0
0
t
CK
17, 32
DQM to data mask during WRITEs
t
DQM
0
0
0
t
CK
17, 32
DQM to data high-impedance during READs
t
DQZ
2
2
2
t
CK
17, 32
WRITE command to input data delay
t
DWD
0
0
0
t
CK
17, 32
Data-in to ACTIVEcommand
t
DAL
4
5
4
t
CK
15, 21, 32
Data-in to PRE CHARGEcommand
t
DPL
2
2
2
t
CK
16, 21, 32
Last data-in to burst STOP command
t
BDL
1
1
1
t
CK
17, 32
Last data-in to new READ/WRITE command
t
CDL
1
1
1
t
CK
17, 32
Last data-in to PRECHARGEcommand
t
RDL
2
2
2
t
CK
16, 21, 32
LOAD MODE REGISTER command t o ACTIVE or REFRESH command
t
MRD
2
2
2
t
CK
26
Data-out to high-impedance from PRECHARGE
command
CL=3
t
ROH(3)
3
3
3
t
CK
17, 32
CL = 2
t
ROH(2)
2
2
2
t
CK
17, 32

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
15
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Notes
1. All voltages referenced to V
SS
.
2. This parameter is sampled. V
DD
, VV
DD
Q = +3.3V; f
= 1 MHz, T
A
= 25∞C; pin under test biased at 1.4V.
3. I
DD
is dependent on output loading and cycle
rates. Specified values are obtained with mini-
mum cycle time and the outputs open.
4. Enables on-chip refresh and address counters.
5. The minimum specifications are used only to
indicate cycle time at which proper operation
over the full temperature range is ensured; (0∞C
£
T
A
£ +70∞C).
6. An initial pause of 100µs is required after power-
up, followed by two AUTO Refresh commands,
before proper device operation is ensured. (V
DD
and V
DD
Q must be powered up simultaneously.
V
SS
and V
SS
Q must be at same potential.) The two
AUTO Refresh command wake-ups should be
repeated any time the tREF refresh requirement is
exceeded.
7. AC characteristics assume
t
T = 1ns.
8. In addition to meeting the transition rate specifi-
cation, the clock and CKE must transit between
V
IH
and V
IL
(or between V
IL
and V
IH
)
IN
a mono-
tonic manner.
9. Outputs measured at 1.5V with equivalent load:
10.
t
HZ defines the time at which the output achieves
the open circuit condition; it is not a reference to
V
OH
or V
OL
. The last valid data element will meet
t
OH before going High-Z.
11. AC timing and Idd tests have V
IL
= 0V and V
IH
= 3V,
with timing referenced to 1.5V crossover point. If
the input transition time is longer than 1 ns, then
the timing is referenced at V
IL
(MAX) and V
IH
(MIN) and no longer at the 1.5V crossover point.
12. Other input signals are allowed to transition no
more than once every two clocks and are other-
wise at valid V
IH
or V
IL
levels.
13. I
DD
specifications are tested after the device is
properly initialized.
14. Timing actually specified by
t
CKS; clock(s) speci-
fied as a reference only at minimum cycle rate.
15. Timing actually specified by
t
WR plus
t
RP; clock(s)
specified as a reference only at minimum cycle
rate.
16. Timing actually specified by
t
WR.
17. Required clocks are specified by JEDEC function-
ality and are not dependent on any timing param-
eter.
18. The Idd current will increase or decrease propor-
tionally according to the amount of frequency
alteration for the test condition.
19. Address transitions average one transition every
two clocks.
20. CLK must be toggled a minimum of two times
during this period.
21. Based on
t
CK = 10ns for -10E, and
t
CK = 7.5ns for -
133 and -13E.
22. Vih overshoot: V
IH
(MAX) = V
DD
Q + 2V for a pulse
width
£ 3ns, and the pulse width cannot be
greater than one third of the cycle rate. V
IL
under-
shoot: V
IL
(MIN) = -2V for a pulse width
£ 3ns.
23. The clock frequency must remain constant (stable
clock is defined as a signal cycling within timing
constraints specified for the clock pin) during
access or precharge states (READ, WRITE, includ-
ing
t
WR, and PRECHARGE commands). CKE may
be used to reduce the data rate.
24. Auto precharge mode only. The precharge timing
budget (
t
RP) begins 7ns for -13E; 7.5ns for -133
and 7ns for -10E after the first clock delay, after
the last WRITE is executed. May not exceed limit
set for precharge mode.
25. Precharge mode only.
26. JEDEC and PC100 specify three clocks.
27.
t
AC for -133/-13E at CL = 3 with no load is 4.6ns
and is guaranteed by design.
28. Parameter guaranteed by design.
29. The value of
t
RAS. use in -13E speed grade module
SPDs is calculated from
t
RC -
t
RP = 45ns.
30. For -10E, CL= 2 and tCK = 10ns; for -133, CL = 3
and
t
CK = 7.5ns; for -13E, CL = 2 and
t
CK = 7.5ns.
31. CKE is HIGH during refresh command period
t
RFC (MIN) else CKE is LOW. The I
DD
6 limit is
actually a nominal value and does not result in a
fail value.
32. This AC timing function will show an extra clock
cycle when in registered mode.
33. Leakage number reflects the worst case leakage
possible through the module pin, not what each
memory device contributes.
Q
50pF
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
16
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
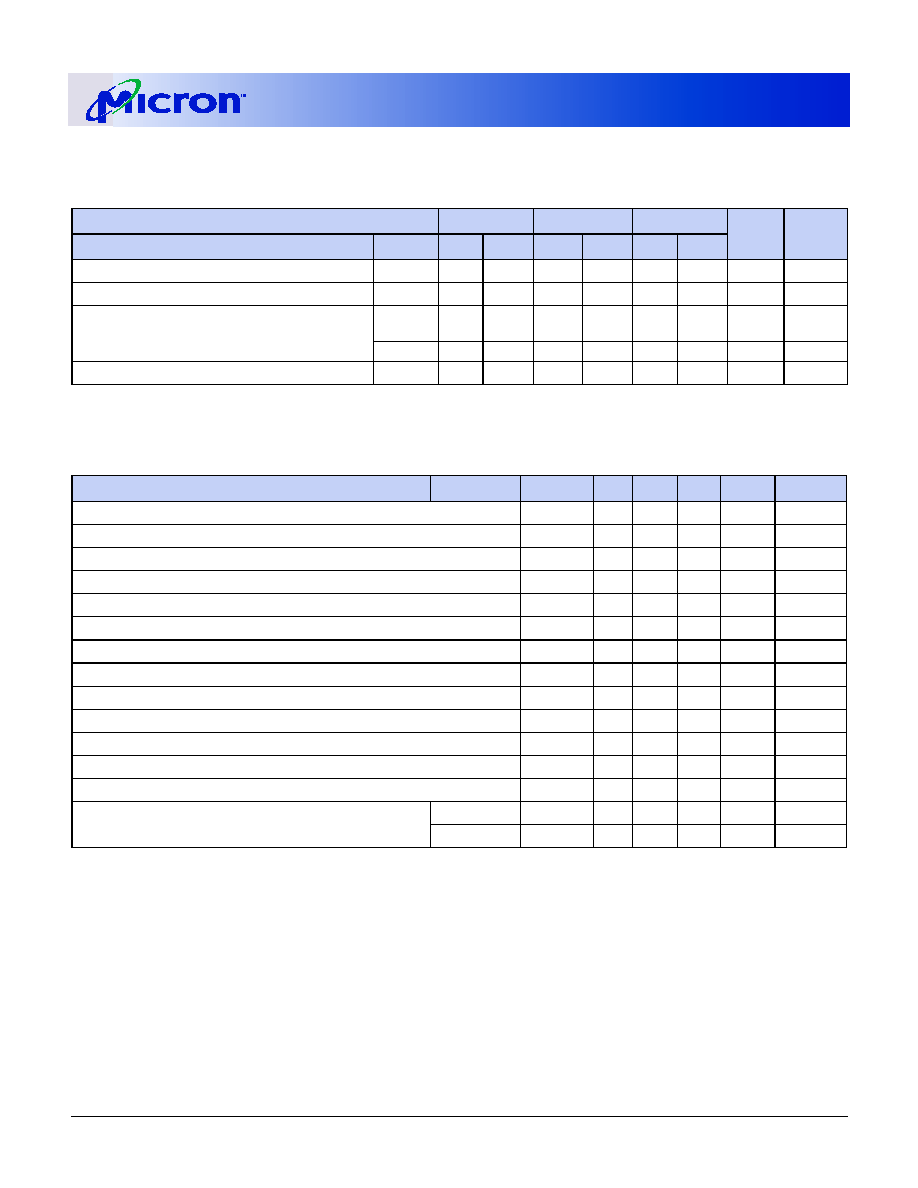
SPD Clock and Data Conventions
Data states on the SDA line can change only during
SCL LOW. SDA state changes during SCL HIGH are
reserved for indicating start and stop conditions (as
shown in Figure 6, Data Validity, and Figure 7, Defini-
tion of Start and Stop).
SPD Start Condition
All commands are preceded by the start condition,
which is a HIGH-to-LOW transition of SDA when SCL
is HIGH. The SPD device continuously monitors the
SDA and SCL lines for the start condition and will not
respond to any command until this condition has been
met.
SPD Stop Condition
All communications are terminated by a stop condi-
tion, which is a LOW-to-HIGH transition of SDA when
SCL is HIGH. The stop condition is also used to place
the SPD device into standby power mode.
SPD Acknowledge
Acknowledge is a software convention used to indi-
cate successful data transfers. The transmitting device,
either master or slave, will release the bus after trans-
mitting eight bits. During the ninth clock cycle, the
receiver will pull the SDA line LOW to acknowledge
that it received the eight bits of data (as shwon in Fig-
ure 8, Acknowledge Response from Receiver).
The SPD device will always respond with an
acknowledge after recognition of a start condition and
its slave address. If both the device and a write opera-
tion have been selected, the SPD device will respond
with an acknowledge after the receipt of each subse-
quent eight-bit word. In the read mode the SPD device
will transmit eight bits of data, release the SDA line and
monitor the line for an acknowledge. If an acknowl-
edge is detected and no stop condition is generated by
the master, the slave will continue to transmit data. If
an acknowledge is not detected, the slave will termi-
nate further data transmissions and await the stop
condition to return to standby power mode.
Figure 6: Data Validity
Figure 7: Definition of Start and Stop
Figure 8: Acknowledge Response from Receiver
SCL
SDA
DATA STABLE
DATA STABLE
DATA
CHANGE
SCL
SDA
START
BIT
STOP
BIT
SCL from Master
Data Output
from Transmitter
Data Output
from Receiver
9
8
Acknowledge

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
17
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
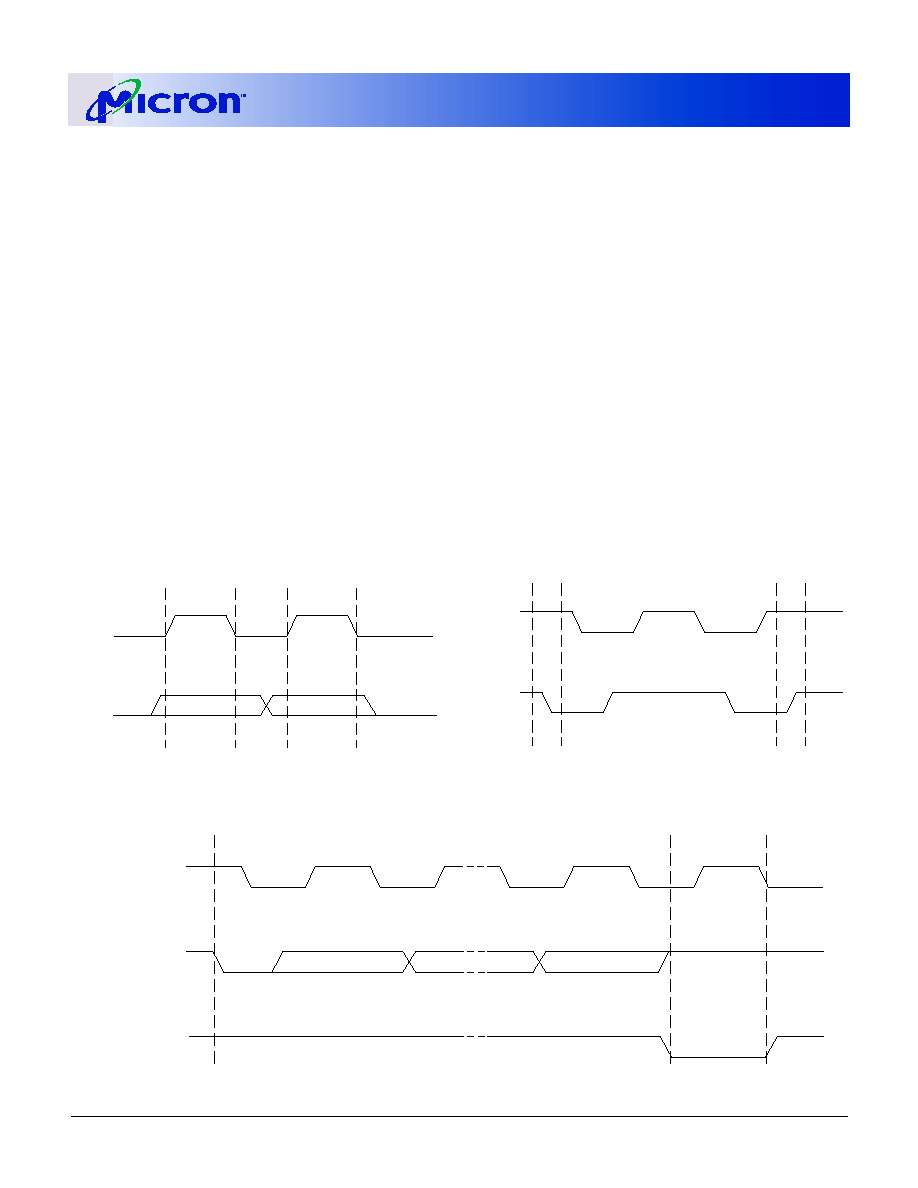
Figure 9: SPD EEPROM Timing Diagram
Table 17: EEPROM Device Select Code
Most significant bit (b7) is sent first)
SELECT CODE
DEVICE TYPE IDENTIFIER
CHIP ENABLE
RW
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
b2
b1
b0
Memory Area Select Code (Two Arrays)
1
0
1
0
SA2
SA1
SA0
RW
Protection Register Select Code
0
1
1
0
SA2
SA1
SA0
RW
Table 18: EEPROM Operating Modes
MODE
RW BIT
WC
BYTES
INITIAL SEQUENCE
Current Address Read
1
V
IH
or V
IL
1
Start, Device Select, RW = 1
Random Ddress Read
0
V
IH
or V
IL
1
Start, Device Select, RW = 0, Address
1
V
IH
or V
IL
Restart, Device Select, RW = 1
Sequential Read
1
V
IH
or V
IL
≥ 1
Similar to Current or Random Address Read
Byte Write
0
V
IL
1
Start, Device Select, RW = 0
Page Write
0
V
IL
£ 16
Start, Device Select, RW = 0
SCL
SDA IN
SDA OUT
tLOW
tSU:STA
tHD:STA
tF
tHIGH
tR
tBUF
tDH
tAA
tSU:STO
tSU:DAT
tHD:DAT
UNDEFINED

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
18
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
NOTE:
1. The SPD EEPROM WRITE cycle time (
t
WRC) is the time from a valid stop condition of a write sequence to the end of
the EEPROM internal erase/program cycle. During the WRITE cycle, the EEPROM bus interface circuit is disabled, SDA
remains HIGH due to pull-up resistor, and the EEPROM does not respond to its slave address.
Table 19: Serial Presence-Detect EEPROM DC Operating Conditions
All voltages referenced to V
SS
; V
DD
= +3.3V ±0.3V
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
MIN
MAX
UNITS
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
V
DD
3
3.6
V
INPUT HIGH VOLTAGE: Logic 1; All inputs
V
IH
V
DD
x 0.7
V
DD
+ 0.5
V
INPUT LOW VOLTAGE: Logic 0; All inputs
V
IL
-1
V
DD
x 0.3
V
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE: I
OUT
= 3mA
V
OL
≠
0.4
V
INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT: V
IN
= GND to V
DD
I
LI
≠
10
µA
OUTPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT: V
OUT
= GND to V
DD
I
LO
≠
10
µA
STANDBY CURRENT: SCL = SDA = V
DD
- 0.3V; All other inputs = V
SS
or V
DD
I
SB
≠
30
µA
POWER SUPPLY CURRENT:
SCL clock frequency = 100 KHz
I
DD
≠
2
mA
Table 20: Serial Presence-Detect EEPROM AC Operating Conditions
All voltages referenced to V
SS
; V
DD
= +3.3V ±0.3V
PARAMETER/CONDITION
SYMBOL
MIN
MAX UNITS
NOTES
SCL LOW to SDA data-out valid
t
AA
0.3
3.5
µs
Time the bus must be free before a new transition cans tart
t
BUF
4.7
µs
Data-out hold time
t
DH
300
ns
SDA and SCL fall time
t
F
300
ns
Data-in hold time
t
HD:DAT
0
µs
Start condition hold time
t
HD:STA
4
µs
Clock HIGH period
t
HIGH
4
µs
Noise suppression time constant at SCL, SDA inputs
t
I
100
ns
Clock LOW period
t
LOW
4.7
µs
SDA and SCL rise time
t
R
1
µs
SCL clock frequency
t
SCL
100
KHz
Data-in setup time
t
SU:DAT
250
ns
Start condition setup time
t
SU:STA
4.7
µs
Stop condition setup time
t
SU:STO
4.7
µs
WRITEcycle time
t
WRC
10
ms
1

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
19
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Table 21: Serial Presence- Detect Matrix
"1"/"0": Serial Data, "driven to HIGH"/"driven to LOW"
BYTE
DESCRIPTION
ENTRY
(VERSION)
MT18LSDT1672G MT18LSDT3272G MT18LSDT6472G
0
Number of Bytes Used By Micron
128
80
80
80
1
Total Number of SPD Memory Bytes
256
08
08
08
2
Memory Type
SDRAM
04
04
04
3
Number of Row Addresses
12or13
0C
0C
0D
4
Number of Column Addresses
10or11
0A
0B
0B
5
Number of Module Ranks
1
01
01
01
6
Module Data Width
72
48
48
48
7
Module Data Width (Continued)
0
00
00
00
8
Module Voltage Interface Levels
LVTTL
01
01
01
9
SDRAM Cycle Time,
t
CK
(CAS Latency = 3)
7 (-13E)
7.5 (-133)
8 (-10E)
70
75
80
70
75
80
70
75
80
10
SDRAM Access From Clock,
t
AC
(CAS Latency = 3)
5.4 (-13E/-133)
6 (-10E)
54
60
54
60
54
60
11
Module Configuration Type
ECC
02
02
02
12
Refresh Rate/type
7.8/15.6µs/SELF
80
80
82
13
SDRAM Width (Primary SDRAM)
4
04
04
04
14
Error-Checking SDRAM Data Width
4
04
04
04
15
Minimum Clock Delay,
t
CCD
1
01
01
01
16
Burst Lengths Supported
1, 2, 4, 8, PAGE
8F
8F
8F
17
Number of Banks on SDRAM Device
4
04
04
04
18
CAS Latencies Supported
2, 3
06
06
06
19
CS Latency
0
01
01
01
20
WE Latency
0
01
01
01
21
SDRAM Module Attributes
-133
1F
1F
1F
22
SDRAM Device Attributes: General
0E
0E
0E
0E
23
SDRAM Cycle Time,
t
CK
(CAS Latency = 2)
7.5 (-13E)
10 (-133/-10E)
75
A0
75
A0
75
A0
24
SDRAM Access From Clock,
t
AC,
(CAS Latency = 2)
5.4 (-13E)
6 (-133/-10E)
54
60
54
60
54
60
25
SDRAM Cycle Time,
t
CK (CAS Latency = 1)
≠
00
00
00
26
SDRAM Access From Clock,
t
AC, (CAS
Latency = 1)
≠
00
00
00
27
Minimum Row Precharge Time,
t
RP
15 (-13E)
20 (-133/-10E)
0F
14
0F
14
0F
14
28
Minimum Row Active to Row Active,
t
RRD
14(-13E)
15 (-133)
20 (-10E)
0E
0F
14
0E
0F
14
0E
0F
14
29
Minimum RAS# to CAS# Delay,
t
RCD
15 (-13E)
20 (-133/-10E)
0F
14
0F
14
0F
14
30
Minimum RAS# Pulse Width,
t
RAS (See
note 1)
45 (-13E)
44 (-133)
50 (-10E)
2D
2C
32
2D
2C
32
2D
2C
32
31
Module Rank Density
128MB/
256MB/512MB
20
40
80

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
20
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
NOTE:
1. The value of
t
RAS used for the -13E module is calculated from
t
RC -
t
RP. Actual device spec. value is 37 ns.
32
Command Address Setup,
t
AS
1.5 (-13E/-133)
2 (-10E)
15
20
15
20
15
20
33
Command Address Hold,
t
AH
0.8 (--13E/133)
1 (-10E)
08
10
08
10
08
10
34
Data Signal Input Setup,
t
DS
1.5 (-13E/-133)
2 (-10E)
15
20
15
20
15
20
35
Data Signal Input Hold,
t
DH
0.8 (-13E/-133)
1 (-10E)
08
10
08
10
08
10
36-61
Reserved Bytes
00
00
00
62
SPD Revision
REV. 1.2
12
12
12
63
Checksum For Bytes 0-62
-13E
-133
-10E
91
D7
1F
B2
F8
40
F5
3B
83
64
Manufacturer's JEDEC ID Code
MICRON
2C
2C
2C
65-71
Manufacturer's JEDEC Code (Cont.)
FF
FF
FF
72
Manufacturing Location
01≠11
01≠0B
01≠0B
73-90
Module Part Number (ASCII)
Variable Data
Variable Data
Variable Data
91
PCB Identification Code
1≠9
01≠09
01≠09
01≠09
92
Identification Code (Continuted)
0
00
00
00
93
Year of Manufacture in BCD
Variable Data
Variable Data
Variable Data
94
Week of Manufacture in BCD
Variable Data
Variable Data
Variable Data
95-98
Module Serial Number
Variable Data
Variable Data
Variable Data
99-125 Manufacturer-Specific Data (Rsvd)
≠
≠
≠
126
Identification Code (Continuted)
100/133 MHz
64
64
64
127
Year of Manufacture in BCD
8F
8F
8F
Table 21: Serial Presence- Detect Matrix (Continued)
"1"/"0": Serial Data, "driven to HIGH"/"driven to LOW"
BYTE
DESCRIPTION
ENTRY
(VERSION)
MT18LSDT1672G MT18LSDT3272G MT18LSDT6472G
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
21
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
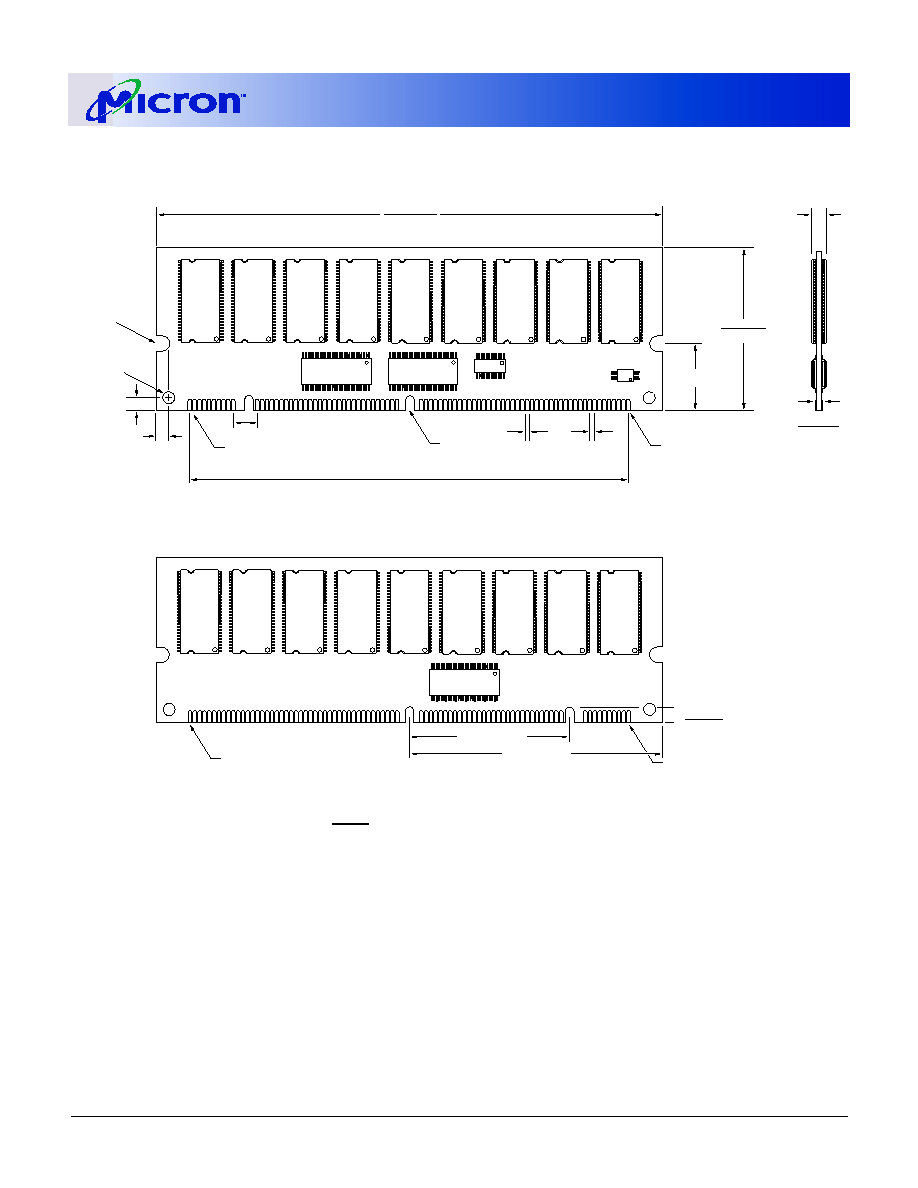
Figure 10: 168-Pin DIMM Dimensions (Standard PCB)
NOTE:
All dimensions in inches (millimeters)
or typical where noted.
1.705 (43.31)
1.695 (43.05)
.128 (3.25)
.118 (3.00)
(2X)
PIN 1
.700 (17.78)
TYP.
.118 (3.00)
(2X)
.118 (3.00) TYP.
.250 (6.35) TYP.
4.550 (115.57)
.050 (1.27)
TYP.
.118 (3.00)
TYP.
.040 (1.02)
TYP.
079 (2.00) R
(2X)
.039 (1.00) R(2X)
PIN 84
FRONT VIEW
BACK VIEW
PIN 168
PIN 85
2.625 (66.68)
1.661 (42.18)
.054 (1.37)
.046 (1.17)
5.256 (133.50)
5.244 (133.20)
.157 (4.00)
MAX
MAX
MIN

128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
22
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
Figure 11: 168-Pin DIMM Dimensions (Low-Profile PCB)
NOTE:
All dimensions in inches (millimeters)
or typical where noted.
Data Sheet Designation
Released (No Mark): This data sheet contains mini-
mum and maximum limits specified over the complete
power supply and temperature range for production
devices. Although considered final, these specifica-
tions are subject to change, as further product devel-
opment and data characterization sometimes occur.
FRONT VIEW
BACK VIEW
5.256 (133.50)
5.244 (133.20)
.320 (8.13)
MAX
.700 (17.78)
1.206 (30.63)
1.194 (30.33)
PIN 1
.250 (6.35)
4.550 (115.57)
.050 (1.27)
.040 (1.02)
.039 (1.00) R(2X)
PIN 84
.118 (3.00)
8 (3.00)
R
)
0)
X)
PIN 168
PIN 85
2.625 (66.68)
1.661 (42.18)
.128 (3.25)
.118 (3.00)
(2X)
.054 (1.37)
.046 (1.17)
U1
U2
U3
U4
U5
U12
U11
U10
U6
U7
U8
U9
U14
U15
U16
U17
U18
U24
U19
U20
U21
U22
U23
MAX
MIN

Æ
8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID 83707-0006, Tel: 208-368-3900
E-mail: prodmktg@micron.com, Internet: http://www.micron.com, Customer Comment Line: 800-932-4992
Micron, the M logo, and the Micron logo are trademarks and/or service marks of Micron Technology, Inc.
128MB, 256MB, 512MB (x72, ECC)
168-PIN REGISTERED SDRAM DIMM
16,32,Meg x 64 DDR SDRAM DIMMs (Footer Desc variable)
©2003, Micron Technology Inc.
SD18C16_32_64x72G_B.fm - Rev. B 1/03 EN
23






















