 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: ML7005 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

° Semiconductor
ML7005
1/24
° Semiconductor
ML7005
DTMF Transceiver
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ML7005 is a multi-functional DTMF transceiver LSI with built-in a DTMF signal generator,
a DTMF signal receiver, a call progress tone generator, a call progress tone detector, and a FAX
(FX) signal detector.
Each functional block can be controlled by an external MCU via a 4-bit processor interface.
The ML7005 does not contains a modem. However, the DTMF system data transmission is
possible at less than 66 bps by setting the DTMF receiver to the high-speed detection mode.
The ML7005 operates with low-power consumption and is suitable for remote control systems,
especially for ACR (Automatic Cost Routing) controllers.
FEATURES
∑ Wide range of power supply voltage : +2.7 V to +5.5 V
∑ Low power consumption
Operating mode
: 4.0 mA (V
DD
= 3 V) Typ.
Operating mode
: 5.0 mA (V
DD
= 5 V) Typ.
Power down mode : 1 mA Typ.
∑ The 4-bit processor interface supports both the Intel processor mode in which a read signal and
a write signal are used independently of each other, and the Motorola processor mode in which
a read signal and a write signal are used in common.
∑ The DTMF receiver can select either the high-speed detection mode (signal repeat time: more
than 60 ms) or the normal detection mode (signal repeat time: more than 90 ms).
∑ Built-in call progress tone generator
∑ Built-in FAX signal (FX: 1300 Hz) detector
∑ The DTMF signal generator, DTMF signal detector, call progress tone generator, and call
progress tone detector can operate concurrently.
∑ Built-in 3.579545 MHz crystal oscillator circuit
∑ Package :
32-pin plastic SSOP (SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K) (Product name: ML7005MB)
E2A0050-29-81
This version: Aug. 1999
Previous version: May 1999

° Semiconductor
ML7005
2/24
BLOCK DIAGRAM
≠
+
PRE
LPF
FX
Detector
FXDIM
FXDIO
+
≠
PRE
LPF
CPT
Detector
CPDIP
CPDIO
CPDIM
+
≠
PRE
LPF
DTMF
Receiver
DTRIP
DTRIO
DTRIM
≠
+
LPF
DTMF
Generator
DTAI
DTAO
DTGO
CPT
Generator
≠
+
CPAI
CPAO
SG
Generator
SG
V
DD
GND
Status
Register
PTYPE
D0
D1
D3
D2
WR
READ
ALE
CS
Control
Register
FXD0
CPD0
X1
X2
CLKO
PD
Processor
Interface
CPTGO

° Semiconductor
ML7005
3/24
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
32-Pin Plastic SSOP
17
WR
32
CPDIO
31
CPDIM
30
CPDIP
29
FXDIO
28
FXDIM
27
FXDO
26
DTAO
25
DTAI
24
DTGO
23
GND
22
CPDO
21
D0
20
D1
19
D2
18
D3
16
ALE
1
DTRIO
2
DTRIM
3
DTRIP
4
SG
5
CPAO
6
CPAI
7
CPTGO
8
PTYPE
9
V
DD
10
PD
11
X1
12
X2
13
CLKO
14
READ
15
CS

° Semiconductor
ML7005
4/24
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin
Symbol
Type
Description
1
O
DTRIO
Output pin for DTMF signal receiver input amplifier.
See the figure 8 for adjusting the receive signal level. See the figure 10 when the
DTMF signal receiver is not used.
2
I
DTRIM
Inverting input pin for DTMF signal receiver input amplifier.
3
I
DTRIP
Non-inverting input pin for DTMF signal receiver input amplifier.
4
O
SG
Output pin for signal ground.
The output voltage is half of V
DD
.
Connect SG and GND by a 1 µF capacitor.
This pin goes to a high impedance state when in power down mode.
5
O
CPAO
Output pin for amplifier used for adjusting the transmit output level of CPT
(Call Progress Tone) signal generator. The non-inverting input of this amplifier is
internally connected to SG. See the figure 11 for adjusting the transmit signal level.
When this amplifier is not used, the CPAO pin should be shorted to the CPAI pin.
6
I
CPAI
Inverting input pin for amplifier used to adjust the transmit level of the CPT signal
generator.
7
O
CPTGO
Analog output pin for CPT signal generator.
The tone amplitude is approximately - 3 dBm. The transmit signal level can be
changed by using the CPAO and CPAI pins. See the figure 11 for adjusting the
transmit signal level. Control the ON/OFF of CPT transmission by using CPGC of
the control register.
8
I
PTYPE
Input pin for selecting the processor mode.
This selection determines the functions of READ, CS, ALE, WR, D1 and D0 pins.
When this pin is "1", the Intel processor mode is selected. When this pin is "0", the
Motorola processor mode (MSM7524-compatible) is selected. This pin should be
fixed at "0" or "1".
9
--
V
DD
Power supply pin.
10
I
PD
Input pin for controlling the power down mode.
When this pin is set to "1", the entire LSI enters the power down mode and each
functional operation stops. The DC level of the analog output pin becomes undefined.
The digital output pins (FXD0, CPD0) and status register indicate a non-detection
state. At that time, the control register CR and DTMF transmit register DTMFT are
cleared. ("0" is written)
The internal circuits (timer, etc. for each detector) also are reset.
After turning on the power, set this pin to "1" to reset the LSI before using this LSI.
When this pin is set to "0", the normal operation starts.
11
I
X1
X1 and X2 are connected to a 3.579545 MHz crystal.
See "Oscillation Circuit" of the FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION for reference.
12
O
X2
13
O
CLKO
3.579545 MHz clock output pin. This pin can drive one ML7005 device.

° Semiconductor
ML7005
5/24
Pin
Symbol
Type
Description
14
I
READ
Input pin for processor interface.
When PTYPE is "1" (Intel processor mode) :
This pin is the read control input pin. When this pin is set to "0", data in the
specified register is output to the bus lines (D3 to D0). At that time, CS must be "0".
See the figure 4 for processor interface timing.
When PTYPE is "0" (Motorola processor mode) :
This pin is the clock input pin (equivalent to SCLK of the MSM7524).
When in Write mode, data in D3 to D0 is written to the specified register at the
falling edge of the READ signal.
When in Read mode, data in the specified register is output to D3 to D0 when the
READ signal is "1", and D3 to D0 is opened when the READ signal is "0".
The READ signal is not necessarily a periodical signal.
See the figure 5 for processor interface timing.
15
I
CS
Chip select input pin for processor interface.
When the CS signal is "0", read and write operations are possible.
When the CS signal is "1", read and write operations are impossible.
16
I
ALE
Input pin for processor interface.
When PTYPE is "1" (Intel processor mode) :
This pin is the address latch enable input pin.
The register address data in D1 to D0 is latched at the falling edge of ALE.
When PTYPE is "0" (Motorola processor mode) :
This pin is the address data input pin (equivalent to AD0 of the MSM7524).
When this pin is "1", data can be written to the control register (CR) and data can
be read from the status register (STR).
When this pin is "0", data can be written to the DTMF transmit register (DTMFT)
and data can be read from the DTMF receive register (DTMFR).
17
I
WR
Input pin for processor interface.
When PTYPE is "1" (Intel processor mode) :
This pin is the Write control input.
Data in the data bus lines (D3 to D0) is written to the specified register. At that time,
CS must be "0".
When PTYPE is "0" (Motorola processor mode) :
This is the signal input pin for controlling the Read and Write modes
(equivalent to R/W of the MSM7524).
When this pin is "1", the LSI enters the Read mode. When this pin is "0", the LSI
enters the Write mode.
18 - 21
I/O
D3 - D0
4-bit data bus I/O pins for processor interface.
When PTYPE is "1" (Intel processor mode), D1 and D0 are also used for addressing.
22
O
CPDO
Digital output pin for CPT detector.
When a 400 Hz signal is input to the CPDIP and CPDIM pins, this pin is "1".
When the DOEN register is "0", this pin is fixed at "0".
23
--
GND
Ground pin.
24
O
DTGO
Analog output pin for DTMF signal generator.
The tone amplitude is approximately - 9.0 dBm for a low group and approximately
- 7.0 dBm for a high group. The transmit signal level can be changed by using the
DTAI and DTAO pins. See the figure 11 for adjusting the transmit signal level.
Control the ON/OFF of signal transmission by using MFC of the control register.

° Semiconductor
ML7005
6/24
Pin
Symbol
Type
Description
25
I
DTAI
Inverting input pin for operational amplifier used for adjusting the transmit output
level of the DTMF signal generator. The non-inverting input of this amplifier is
internally connected to SG. See the figure 11 for adjusting the transmit signal level.
When this amplifier is not used, the DTAO pin should be shorted to the DTAI pin.
26
O
DTAO
Output pin for operational amplifier used for adjusting the transmit output level of
the DTMF signal generator.
27
O
FXDO
Digital output pin for FAX signal (FX) detector.
When a 1300 Hz signal is input to the FXDIM, this pin is "1".
When a call progress tone (CPT) is received (CPD0="1"), this pin is forced to be "0".
When the DOEN register is "0", this pin is fixed at "0".
28
I
FXDIM
Inverting input pin for input amplifier used for detecting the FAX signal (FX).
See the figure 9 for adjusting the receive signal level.
When the FX detector is not used, the FXDIM pin should be shorted to the FXDIO pin.
29
O
FXDIO
Output pin for input amplifier used for detecting the FAX signal (FX).
30
I
CPDIP
Non-inverting input pin for input amplifier used for detecting the CPT.
See the figure 8 for adjusting the receive signal level.
When the CPT detector is not used, see the figure 10.
31
I
CPDIM
Inverting input pin for input amplifier used for detecting the CPT.
32
O
CPDIO
Output pin for input amplifier used for detecting the CPT.

° Semiconductor
ML7005
7/24
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Rating
Unit
Power Supply Voltage
V
DD
≠0.3 to +7.0
V
Ta = 25∞C
With respect to GND
Input Voltage
V
I
≠0.3 to V
DD
+ 0.3
Storage Temperature
T
stg
≠55 to +150
∞C
--
Output Short Current
I
SHT
35
mA
Short to V
DD
or GND
Power Dissipation
P
D
100
mW
--
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
Power supply voltage
V
DD
3.6
V
--
Operating Temperature Range
T
OP
∞C
--
Input Clock Frequency Deviation
f
CLK
%
Input Clock duty
DUTY
%
X1, X2 Load Capacitance
C1, C2
pF
SG Bypass Capacitance
C3
V
DD
Bypass Capacitance
C4
mF
C5
Digital Input Fall Time
T
IF
--
Digital Ouput Load Capacitance
C
DL1
--
pF
C
DL2
--
Frequency Deviation
--
--
ppm
An external clock is applied to
X1
--
SG - GND
V
DD
- GND
FCDO, CPDO, D3 to D0
CLKO
+25∞C ±5∞C
--
--
--
20
--
--
--
Min.
Max.
2.7
5.5
+85
+0.1
60
22
--
--
--
--
50
--
40
--
20
≠100
+100
≠30
≠0.1
40
18
1
10
0.1
Digital Input Rise Time
T
IR
ns
PD, READ, CS,
ALE, WR, D3 to D0
--
50
--
Temperature Characteristics
--
--
≠30∞C to +85∞C
≠100
+100
Equivalent Series Resistance
--
--
W
--
--
90
Load Capacitance
--
16
pF
--
--
--
Crystal
° Semiconductor
ML7005
8/24
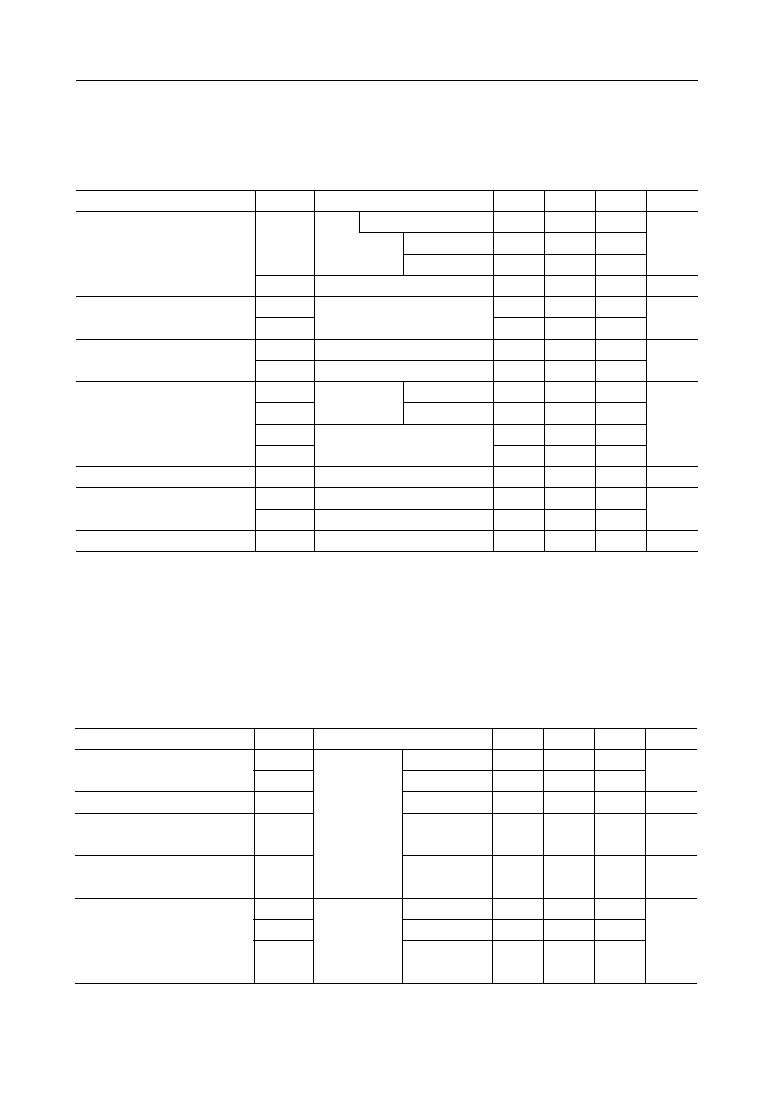
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC and Digital Interface Characteristics
AC CHARACTERISTICS
AC Characteristics 1 DTMF Signal Generator
*1 DTRIM, DTRIP, CPAI, DTAI, FXDIM, CPDIP, CPDIM
*2 DTRIO, CPAO, CPTGO, DTGO, DTAO, FXDIO, CPDIO
*3 DTRIO, CPAO, CPTGO, DTGO, DTAO, FXDIO, CPDIO, SG
Parameter
Symbol Condition or Applicable pin
Typ.
Unit
Power Supply Current
I
DD1
--
I
DD2
mA
--
Digital Input Voltage
V
IH
V
V
IL
Digital Input Current
I
IH
mA
I
IL
Digital Output Voltage
V
OH
V
V
OL
V
OLCK
0.06
Analog Input Resistance
R
IN
10
MW
Power Down Mode
V
I
= 0 V
Other than
CLK0
*1
1
--
--
0
0
Min.
Max.
--
9.0
40
V
DD
0.3V
DD
+10
+10
0.0
0.2
--
--
--
0.7 V
DD
0.0
≠10
≠10
V
OHCK
CLKO, CL £ 20pF
V
DD
≠ 0.06
V
DD
V
DD
≠ 0.2
Analog Output DC Potential
V
SG
V
DD
/2
SG
V
DD
/2≠0.1
V
DD
/2≠0.1
V
AO
V
DD
/2
V
--
--
Analog Output Load Resistance
R
OUT
--
KW
20
--
mA
4.0
--
--
5.0
--
--
*2
*3
I
OL
= 100 mA
I
OH
= ≠100 mA
V
DD
= 3 V
V
DD
= 5 V
Operating Mode
--
--
V
DD
0.5
V
DD
≠ 0.5
0.0
V
I
= V
DD
V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
DTMF Tone Transmit Amplitude
V
DTTL
dBm
V
DTTH
f
DDT
≠7.0
Out-of-Band Spurious
V
S1
P≠51
dB
Measured at
DTGO
With respect to
output signal
level measured
at DTGO
Min.
Max.
≠8.5
≠5.5
--
P≠20
V
DTDF
≠9.0
≠7.5
≠10.5
V
S2
P≠60
--
P≠40
V
S3
P≠75
--
P≠60
High Group Tone
Low Group Tone
2.0
--
3.0
+1.5
1.0
≠1.5
V
DTTH
≠ V
DTTL
To Nominal
Frequency
THD
DT
≠40
≠23
--
Harmonics -
Fundamental
4kHz to 8kHz
8kHz to 12kHz
12 kHz to each
4 kHz band
Tone Transmit Amplitude Ratio
Tone Frequency Accuracy
Total Harmonic Distortion
dB
%
dB
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
*1
*1 0dBm = 0.775 Vrms (For all AC characteristics)
° Semiconductor
ML7005
9/24
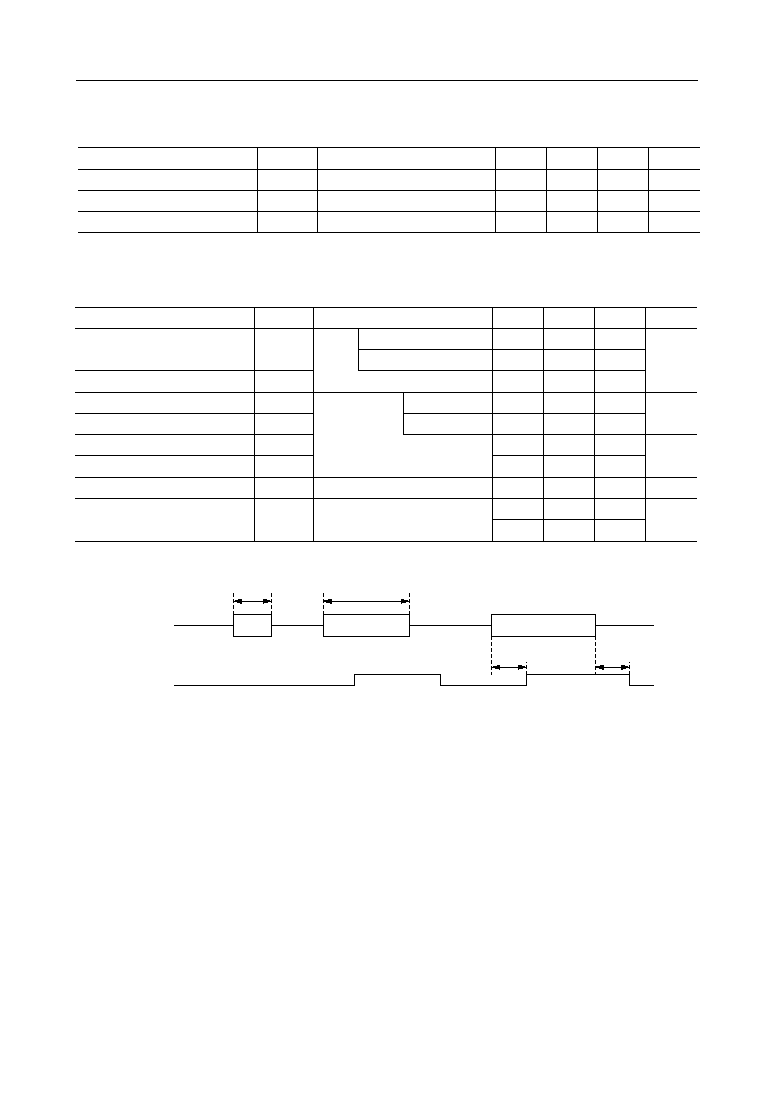
AC Characteristics 2 Call Progress Tone (CPT) Generator
AC Characteristics 3 Call Progress Tone (CPT) Detector
Figure 1 CPT Detect Timing
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
Tone Transmit Amplitude
V
CPT
≠2.5
dBm
--
Output Frequency
f
CPT
Hz
--
400
Min.
Max.
≠4
≠1
420
380
Total Harmonic Distortion
THD
CPT
dB
Harmonics - Fundamental
≠39
≠23
--
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
CPT Detect Amplitude
V
DETCP
--
--
Min.
Max.
≠46
≠6
dBm
--
0
≠46
--
≠60
--
f
in
= 350 to 450 Hz at CPDIO
2.7 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
4.5 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
CPT Non-detect Amplitude
V
REJCP
Time to Detect
t
DETCP
Time to Reject
t
REJCP
CPT Detect Delay Time
t
DELCP
CPT Detect Hold Time
t
HOLCP
CPT Detect Frequency
f
DETCP
CPT Non-detect Frequency
f
RETCP
ms
--
--
10
--
--
30
Non-detect
Detect
18
18
30
30
10
10
--
--
--
290
530
--
Hz
--
--
450
350
Hz
See Figure 1.
ms
CPDI
CPDO
(CPDR)
t
REJCP
t
DETCP
t
DELCP
t
HOLCP

° Semiconductor
ML7005
10/24
AC Characteristics 4 FAX Signal (FX) Detector
Figure 2 FX Detect Timing
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
FX Detect Amplitude
V
DETFX
--
--
Min.
Max.
≠40
≠6
dBm
--
0
≠40
--
≠60
--
f
in
= 1280 to 1320 Hz at FXDIO
2.7 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
4.5 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
FX Non-detect Amplitude
V
REJFX
Time to Detect
t
DETFX
Time to Reject
t
REJFX
FX Detect Delay Time
t
DELFX
FX Detect Hold Time
t
HOLFX
FX Detect Frequency
f
DETFX
FX Non-detect Frequency
f
REJFX
ms
--
--
30
--
--
65
Non-detect
Detect
50
50
65
65
35
35
--
--
--
1200
1380
--
Hz
--
--
1320
1280
Hz
See Figure 2.
FXDI
FXDO
(FXDR)
t
REJFX
t
DETFX
t
DELFX
t
HOLFX

° Semiconductor
ML7005
11/24
AC Characteristics 5 DTMF Receiver
*1 See the figure 3 for timing.
The input level includes the entire range indicated in V
DETDT1
and V
DETDT2
.
The input frequency includes the entire range indicated in f
DETDT
.
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
DTMF Detect Amplitude
V
DETDT1
--
Min.
Max.
≠42
≠10
dBm
--
0
≠42
--
≠60
--
Per Frequency at DTRIO
2.7 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
4.5 V £ V
DD
£ 5.5 V
DTMF Non-detect Amplitude
V
REJDT
Signal Repetition Time
t
CYCDT0
t
CYCDT1
Time to Detect
t
DETDT0
t
DETDT1
ms
--
90
--
--
--
60
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
Detect Frequency
f
DETDT
--
+1.8
≠1.8
Non-detect Frequency
f
REJDT
--
--
3.8
--
≠3.8
--
--
+6.0
≠6.0
V
High
Group - V
Low
Group
Level Twist
V
TWIST
≠12
--
--
N/S (N : 0.3 to 3.4 kHz)
Noise to Signal Ratio
V
N/S
45
--
--
360 to 440 Hz
Dial Tone Rejection Ratio
V
REJDT
%
dB
Time to Reject
t
REJDT0
t
REJDT1
--
49
--
--
--
35
Acceptable Drop Out Time
t
BRKDT10
t
BRKDT11
t
BRKDT20
t
BRKDT21
Interdigit Pause Time
t
POSDT0
t
POSDT1
Detect Delay Time
t
DELDT0
t
DELDT1
Detect Hold Time
t
HOLDT0
t
HOLDT1
SP Delay Time
t
SP
--
--
10
--
--
24
--
21
--
--
30
--
--
--
0.4
--
--
0.4
--
--
3
--
--
10
26
12
37
41
24
49
20
15
27
28
24
35
To Nominal Frequency
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
DTTIM = "0"
DTTIM = "1"
Detect
Non-detect
SP = "1"
(Before output)
SP = "0"
(During output)
0.6
0.2
1.0
DTTIM = "1", "0"
*1
V
DETDT2

° Semiconductor
ML7005
12/24
Timing When DTMF is received
DTMF Receive Data
SP
AIN Signal
t
CYCDT
t
DETDT
t
POSDT
t
REJDT
t
BRKDT1
t
DELDT
t
SP
t
HOLDT
t
BRKDT2
Figure 3 Timing When DTMF is Received
t
DETDT
: Time to Detect
When Time to Detect is the specified value of t
DETDT
or more, the DTMF signal is
normally received.
t
REJDT
: Time to Reject
When Time to Reject is the specified value of t
REJDT
or less, the input signal is ignored
and the SP and DTMF receive data are not output.
t
POSDT
: Interdigit Pause
When there is no input signal for the period of t
POSDT
or more, the DTMF receive data
and SP are reset. Even if the receive data is changed, when Interdigit Pause Time is the
value of t
POSDT
or less (including the change without Drop Out), SP remains at "0" and
the DTMF receive data may maintain its initial value.
t
BRKDT1
: Acceptable Drop Out Time 1
Acceptable Drop Out Time 1 is applied between when the input signal comes and when
SP becomes "0". Even if there is no input signal for the period of t
BRKDT1
or less, the SP
and DTMF receive data are normally output.
t
BRKDT2
: Acceptable Drop Out Time 2
Acceptable Drop Out Time 2 is applied when SP is "0" (when receive data is output).
Even if there is no input signal during signal reception for the period of t
BRKDT2
or less,
SP and DTMF receive data are not reset.
t
CYCDT
: Signal Repetition Time
Signal Repetition Time should be the specified value of t
CYCDT
or more so that a signal
is normally received.
t
DELDT
: Detect Delay Time
The DTMF receive data is output with a delay of the specified value of t
DELDT
after the
input signal appears.
t
HOLDT
: Detect Hold Time The SP and DTMF receive data outputs stop with a delay of the
specified value of t
HOLDT
after the input signal disappears.
t
SP
:
SP Delay Time
The SP data is output with a delay of the specified value of t
SP
after the DTMF receive
data is output. The DTMF receive data should be latched after detecting the fall of SP.

° Semiconductor
ML7005
13/24
Processor Interface Charactceristics (Intel Processor Mode)
Figure 4 Processor Interface Timing (Intel Processor Mode : PTYPE="1")
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
Address Data Setup Time
t
AL
--
ns
--
Address Data Hold Time
t
LA
ns
--
--
Min.
Max.
80
--
--
30
ALE Signal Time
t
LL
ns
--
--
--
80
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
Chip Select Setup Time before Read
t
CRS
ns
--
--
--
30
Chip Select Hold Time after Read
t
CRH
ns
--
--
--
30
READ Data Output Delay Time
t
RD
ns
V
OL
£ 0.4 V, V
OH
V
DD
≠ 0.4 V
90
180
0
Data Float Time after Read
t
RDF
ns
--
37
60
5
READ Signal Time
t
RW
ns
--
--
--
200
Chip Select Setup Time before Write
t
CWS
ns
--
--
--
30
Chip Select Hold Time after Write
t
CWH
ns
--
--
--
30
WR Signal Time
t
WW
ns
--
--
--
140
Data Setup Time before Write
t
DW
ns
--
--
--
80
Data Hold Time
t
WD
ns
--
--
--
30
ALE
t
LL
t
LL
t
RW
t
WW
READ
WR
D0 to D3
CS
t
AL
t
LA
t
RD
t
RDF
t
AL
t
LA
t
DW
t
WD
t
CRS
t
CRH
t
CWH
t
CWS
ADDRESS
READ DATA
ADDRESS
WRITE DATA

° Semiconductor
ML7005
14/24
Processor Interface Characteristics (Motorola Processor Mode)
Figure 5 Processor Interface Timing (Motorola Processor Mode)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
Unit
READ Signal Period
t
CYC
--
ms
--
READ Signal Pulse Width
t
HI
ns
"H" period
--
Min.
Max.
1
--
--
200
t
LO
"L" period
--
--
200
(V
DD
= 2.7 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠30 to +85∞C)
ALE
t
AS
ALE ∆ READ
--
--
80
t
AH
READ ∆ ALE
--
--
20
CS
t
CS
CS ∆ READ
--
--
80
t
CH
READ ∆ CS
--
--
20
WR
t
WRS
WR ∆ READ
--
--
80
t
WRH
READ ∆ WR
--
--
20
D3 to D0
(Write)
t
DWS
D3 to D0 ∆ READ
--
--
80
t
DWH
READ ∆ D3 to D0
--
--
30
D3 to D0
(Read)
t
DRD
READ ∆ D3 to D0
V
OL
£ 0.4 V,
V
OH
V
DD
≠ 0.4 V
90
180
0
t
DRH
D3 to D0 ∆ READ
37
60
5
See
Figure 5
SETUP Time
HOLD Time
SETUP Time
HOLD Time
SETUP Time
HOLD Time
SETUP Time
HOLD Time
Delay Time
Hold Time
READ
(Clock)
ALE
(Address)
CS
WR
(Read /
Write)
t
HI
t
LO
D3 to D0
DATA
"Write"
t
CYC
t
DWS
t
DWH
t
WRH
t
WRS
t
CH
t
CS
t
AH
t
AS
t
HI
t
LO
DATA
"Read"
t
CYC
t
DRH
t
WRH
t
WRS
t
CH
t
CS
t
AH
t
AS
t
DRD

° Semiconductor
ML7005
15/24
REGISTER DESCRIPTION
Register Interface Description
The ML7005 contains a 4-bit DTMF transmit data register (DTMFT), a 4-bit DTMF receive data
register (DTMFR), a 4-bit control register (CR), and a 4-bit status register (STR). The DTMFT and
CR registers are for Write-only and the DTMFR and STR registers are for Read-only.
When the PTYPE pin is "1", accessing the registers is possible in the Intel processor mode. When
the PTYPE pin is "0", accessing the registers is possible in the Motorola processor mode.
In the Intel processor mode (PTYPE="1"), when CS is "0", data can be written to the DTMFT and
CR registers by fetching data from D3 to D0 at the rising edge of the WR signal. When CS is "0",
the contents of DTMFR and STR can be transferred to D3 to D0 by setting READ to "0".
In the Motorola processor mode (PTYPE="0"), when CS and WR are "0", data can be written to
the DTMFT and CR registers by fetching D3 to D0 data and ALE at the falling edge of READ.
When CS is "0" and WR is "1", the contents of DTMFR and STR are transferred to D3 to D0 by
latching ALE at the rising edge of READ.
When the PD pin is set to "1" the DTMFT and CR registers are reset.
Table 1 Outline of Registers
Note:
The contents of the DTMFT and CR registers cannot be read.
Table 2 Register Names
Register
name
Accessing
(address) in Intel
processor mode
Description
Accessing in
Motorola
processor mode
Writing to DTMFT
WR
ALE
D0
D1
Reading from DTMFR
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
DTMFT
DTMFR
Writing to CR
0
1
0
1
CR
Reading from STR
1
1
1
1
STR
Register name
D0
D1
D2
D3
DTT0
DTR0
DTT1
DTR1
DTT2
DTR2
DTT3
DTR3
DTMFT
DTMFR
MFC
DOEN
DTTIM
CPGC
CR
DETF
CPDR
FXDR
SP
STR

° Semiconductor
ML7005
16/24
DTMFT and DTMFR Registers
16 kinds of DTMF transmit signals can be determined by setting the DTMFT register.
16 kinds of DTMF receive signals can be monitored from the DTMFR register.
The table 3 shows the DTMF signal codes.
Even if the DTMF transmit code is changed while the DTMF signal is being transmitted
(MFC="1"), the output frequency is not changed.
Table 3 DTMF Signal Code List
High group
signal (Hz)
Low group
signal (Hz)
1209
1336
697
697
1477
697
1209
770
DIGIT
1
2
3
4
DTT0
DTR0
1
0
1
0
DTT1
DTR1
0
1
1
0
DTT2
DTR2
0
0
0
1
DTT3
DTR3
0
0
0
0
1336
770
5
1
0
1
0
1477
770
6
0
1
1
0
1209
852
7
1
1
1
0
1336
852
8
0
0
0
1
1477
852
9
1
0
0
1
1336
941
0
0
1
0
1
1209
941
*
1
1
0
1
1477
941
#
0
0
1
1
1633
697
A
1
0
1
1
1633
770
B
0
1
1
1
1633
852
C
1
1
1
1
1633
941
D
0
0
0
0

° Semiconductor
ML7005
17/24
Control Register CR
Bit No.
Name
Description
D3
CPGC
This bit is used to control the ON/OFF of call progress tone transmitting.
"0" : The GPTGO output is OFF and the SG level is output.
"1" : The GPTGO output is ON and CPT is output.
D2
DTTIM
This bit is used to control the detect time of DTMF receiver.
"0" : Normal detect "1" : High-speed detect
When there is enough time, set to the normal detect mode (DTTIM = "0") because the
high-speed detect mode sometimes causes erroneous detection by noise or voice signal.
D1
DOEN
This bit is used to control the call progress tone detector and FX detector.
"0" : The CPDO and FXDO output pins and CPDR and FXDR registers are fixed to "0".
"1" : The CPDO and FXDO output pins and CPDR and FXDR registers become valid.
D0
MFC
This bit is used to control the ON/OFF of DTMF transmit output.
"0" : The DTGO output is OFF and the SG level is output.
"1" : The DTGO output is ON and the DTMF signal is output.
D3
CPGC
D2
DTTIM
D1
DOEN
D0
MFC

° Semiconductor
ML7005
18/24
Status Register STR
Bit No.
Name
Description
D3
SP
This bit is used to indicate whether the DTMF receive signal is being received.
"0" : Indicates that the valid DTMF signal is being received.
"1" : Indicates that the DTMF signal is not being received.
D2
FXDR
This bit is used to indicate whether the FAX signal (FX) is being received.
"0" : Indicates that the FAX signal (FX) is not being received.
"1" : Indicates that the valid FAX signal (FX: 1300 Hz) is being received.
When a call progress tone is received (CPDO="1"), this bit is forced to be "0".
When the DOEN register is "0", this bit also is fixed at "0". This bit has the same
function as that of the FXDO.
D1
CPDR
This bit is used to indicate whether the call progress tone is being received.
"0" : Indicates that the call progress tone is not being received.
"1" : Indicates that the valid call progress tone (400 Hz) is being received.
When the DOEN register is "0", this bit is fixed at "0". This bit has the same function
as that of the CPDO pin.
D0
DETF
This is a flag to indicate that a detector has changed its status from a non-detect state to
a detect state.
This bit is "1" when:
(1) SP is changed from "1" to "0",
(2) FXDR is changed from "0" to "1", or
(3) CPDR is changed from "0" to "1".
This bit remains "0" even if a 1300 Hz or 400 Hz signal is input, because the FXDR
and CPDR are fixed at "0" when the DOEN regsiter is "0".
When the processor has read the status register, this bit is reset to "0".
When the processor does not read the status register after a signal is detected, this bit is
"0" after the detected signal disappears.
D3
SP
D2
FXDR
D1
CPDR
D0
DETF

° Semiconductor
ML7005
19/24
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Oscillation Circuit
The X1 and X2 should be connected by a 3.579545 MHz crystal.
When the load capacitance of the crystal is 16pF, X1 and GND should be connected by a 20 pF
capacitor, and X2 and GND also should be connected by a 20 pF capacitor.
If necessary, an external clock should be input to X1 via a 1000 pF capacitor, and X2 should be
left open.
Figure 6 Crystal Connection
Figure 7 External Clock Connection
DTMF Receiver, CPT Detector Input Level Adjustment
Adjust the input level according to the method shown in the figure 8.
Determine the value of a usable resistor so that the levels of the outputs (DTIO, CPDIO) of each
amplifier at a maximum input level are less than the maximum detect level described in the AC
Characteristics.
X1
X2
C1
3.579545MHz
C2
X1
X2
3.579545MHz
Figure 8 DTMF, CPT Input Level Adjustment
+
≠
R
A
R
C
R
B
DTRIO
DTRIM
CA
IN
DTRIP
(CPDIM)
(CPDIP)
(CPDIO)
SG
R
A
100 kW
R
B
, R
C
50 kW
CA 0.1 mF
Gain = 1 +
R
B
R
C
£ 10
≠
+
R
D
DTRIP
CA
IN
DTRIM
(CPDIP)
(CPDIM)
SG
Gain =
R
E
R
D
£ 10
R
E
DTRIO
(CPDIO)

° Semiconductor
ML7005
20/24
Figure 9 FX Input Level Adjustment
Processing the Input Pin when the DTMF Receiver and CPT Detector are not Used
Process the Input pin according to the method shown in the figure 10.
≠
+
R
F
C8
IN
FXDIM
Gain =
R
G
R
F
£ 10
R
G
FXDIO
FX Detector Input Level Adjustment
Adjust the input level according to the method shown in the figure 9.
Determine the value of a usable resistor so that the output level of FXDIO is less than the
maximum detect level described in the AC Characteristics.
Figure 10 Processing the Unused Input Pin
≠
+
DTRIP
(CPDIP)
DTRIM
(CPDIM)
SG
DTRIO
(CPDIO)

° Semiconductor
ML7005
21/24
Figure 11 Analog Output Level Adjustment
Concurrent Operation of 4 Functions
The DTMF signal generator, DTMF signal detector, call progress tone generator, and call
progress tone detector can operate concurrently.
When both the DTMF signal generator and call progress tone generator operate concurrently, the
DTMF signal sometimes cannot be detected if the receive level of the DTMF signal is less than
-36 dBm.
Adjusting the Analog Output Level
Adjust the analog output level according to the method shown in the figure 11.
R
I
/R
H
1.6 is always required when V
DD
4.5 V.
In the case of R
I
/R
H
> 1, if R
I
/R
H
= A, the maximum analog output load resistance is 20*A (kW).
If V
DD
is less than 4.5 V, R
I
/R
H
1 is required.
≠
+
DTAI (CPAI)
OUT
Gain =
R
I
R
H
R
H
DTGO (CPDGO)
R
I
DTAO (CPAO)
Generator

° Semiconductor
ML7005
22/24
Register Settings for Each Mode
An example of register settings for each mode is shown below.
Table 4 Register Setting
Mode
Power ON
DTMF Detect
(High Speed)
CPT Detect
Description
(1) Wait until power supply is
stabilized
(2) PD pin = "1"
(internal circuit is reset)
(3) Wait 200 ms or more
(4) PD pin = "0"
(5) CR setting
(1) Detect timing setting
(2) STR monitoring
(when not detected)
(3) STR monitoring
(when detected)
(4) DTMF receive data reading
(5)
STR monitoring (when
detected and after reading STR)
(6) STR monitoring (after
making the input signal OFF)
(1) CPT detect enable setting
(2) STR monitoring
(when not detected)
(3) STR monitoring
(when detected)
Address in
Intel
processor
mode
D1, D0
--
--
--
--
10
10
11
11
01
11
11
10
11
11
ALE
WR
Motorola
processor
mode
D3
D2
D1
D0
Active
register
--
--
--
--
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
--
--
--
--
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
--
--
--
--
X
0
1
0
X
0
1
0
1
1
--
--
--
--
X
1
0
0
X
0
0
0
0
0
--
--
--
--
X
0
0
0
X
0
0
1
0
1
--
--
--
--
X
0
0
1
X
0
0
0
0
1
--
--
--
--
CR
CR
STR
STR
DTMFR
STR
STR
CR
STR
STR
(4) STR monitoring (when
detected and after reading STR)
11
1
1
1
0
1
0
STR
DTMF
Transmit
(1) DTMF transmit data setting
00
0
0
X
X
X
X
DTMFT
(2) DTMF transmit ON
10
1
0
0
0
0
1
CR
(3) Wait transmit ON time
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
(4) DTMF transmit OFF
10
1
0
0
0
0
0
CR
(5) Wait transmit OFF time
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
(6) To transmit next data,
return to (1)
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
CPT Transmit (1) CPT transmit ON
10
1
0
1
0
0
0
CR
(2) Wait transmit ON time
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
(3) CPT transmit OFF
10
1
0
0
0
0
0
CR

° Semiconductor
ML7005
23/24
APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
Note :
indicates connection to the SG pin.
1
R2
C6
DTMF Input
R1
2
DTRIO
DTRIM
3
4
DTRIP
SG
C3
ML7005
8
9
PTYPE
V
DD
C4
+2.7 to 5.5 V
C5
+
≠
C1
C2
3.579545 MHz
CPDIO
CPDIM
CPDIP
FXDIO
FXDIM
FXDO
DTAO
DTAI
DTGO
GND
CPDO
D0
D1
D2
D3
WR
32
31
30
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
R3
R4
R5
R6
C7
C8
CPT Input
FX Input
To MPU
CPAO
CPAI
CPTGO
5
6
7
10
PD
11
X1
12
X2
13
CLKO
14
READ
15
CS
16
ALE
29

° Semiconductor
ML7005
24/24
(Unit : mm)
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, TQFP, LQFP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP, and BGA are surface mount type
packages, which are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in
storage. Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki's responsible sales person
on the product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
0.60 TYP.
Mirror finish

NOTICE
1.
The information contained herein can change without notice owing to product and/or
technical improvements. Before using the product, please make sure that the information
being referred to is up-to-date.
2.
The outline of action and examples for application circuits described herein have been
chosen as an explanation for the standard action and performance of the product. When
planning to use the product, please ensure that the external conditions are reflected in the
actual circuit, assembly, and program designs.
3.
When designing your product, please use our product below the specified maximum
ratings and within the specified operating ranges including, but not limited to, operating
voltage, power dissipation, and operating temperature.
4.
Oki assumes no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any failure or unusual or
unexpected operation resulting from misuse, neglect, improper installation, repair, alteration
or accident, improper handling, or unusual physical or electrical stress including, but not
limited to, exposure to parameters beyond the specified maximum ratings or operation
outside the specified operating range.
5.
Neither indemnity against nor license of a third party's industrial and intellectual property
right, etc. is granted by us in connection with the use of the product and/or the information
and drawings contained herein. No responsibility is assumed by us for any infringement
of a third party's right which may result from the use thereof.
6.
The products listed in this document are intended for use in general electronics equipment
for commercial applications (e.g., office automation, communication equipment,
measurement equipment, consumer electronics, etc.). These products are not authorized
for use in any system or application that requires special or enhanced quality and reliability
characteristics nor in any system or application where the failure of such system or
application may result in the loss or damage of property, or death or injury to humans.
Such applications include, but are not limited to, traffic and automotive equipment, safety
devices, aerospace equipment, nuclear power control, medical equipment, and life-support
systems.
7.
Certain products in this document may need government approval before they can be
exported to particular countries. The purchaser assumes the responsibility of determining
the legality of export of these products and will take appropriate and necessary steps at their
own expense for these.
8.
No part of the contents contained herein may be reprinted or reproduced without our prior
permission.
9.
MS-DOS is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Copyright 1999 Oki Electric Industry Co., Ltd.
Printed in Japan
E2Y0002-29-62
























