 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: ML7020 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
This version: Nov. 2000
Previous version: Feb. 2000
ML7020
1200 bps MODEM for Remote Control Systems
1/19
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ML7020 is a 1200 bps modem LSI developed for remote control systems. The functions incorporated are
those of a 1200 bps FSK modem conforming to ITU-T Recommendations V.23, DTMF signal generation and
detection, call progress tone (CPT) generation and detection. Each functional block can be controlled via a 4-bit
processor interface
.
FEATURES
∑
Single 5 V power supply operation (V
DD
: 4.5 to 5.5 V)
∑
Low power consumption: During operation: 5 mA typ.
During the power down mode: 7
µ
A typ.
∑
Built-in 1200 bps modem conforming to ITU-T V.23 recommendations
∑
Built-in DTMF signal generator with a switchable 6-dB attenuator
∑
Built-in DTMF detector (the input can be selected from either the line or the terminal)
∑
Built-in call progress tone generator. The output frequency can be selected from 400 Hz and 800 Hz.
∑
Built-in call progress tone detector
∑
Three analog input systems (switchable)
∑
Analog output for the line is of the differential type and can drive a 600
line transformer.
∑
Analog output for the terminal is of the single-ended type and can drive a 1.2 k
load.
∑
Built-in switch for selecting the 600
termination
∑
4-Bit processor interface
∑
Built-in oscillator circuit for a 3.579545 MHz crystal
∑
Package: 32-Pin plastic SSOP (SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K) (Product name: ML7020MB)
FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
2/19
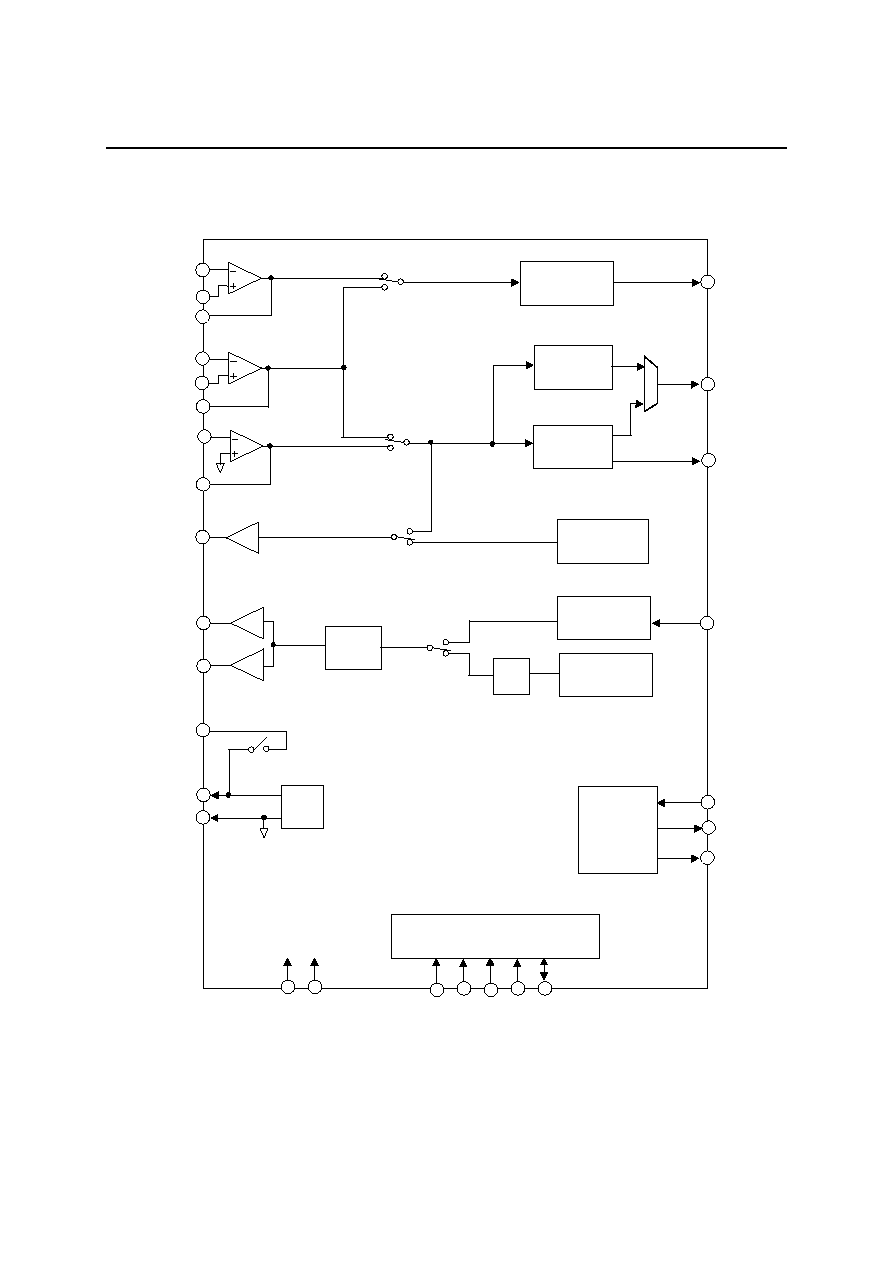
BLOCK DIAGRAM
* CPT: Call progress tone
* The state shown of each switch is that when the register is set to "0".
DTMF
Reception
TO
TI≠
TI+
TIO
MCU I/F
V
DD
GND
CSB
RDB
WR
B
A1, A0
D3 to D0
1.2 k
LI1≠
LI1+
LI1O
LI2≠
LI2O
SG
SGC
1.2 k
≠1
LO≠
+1
SWI
SGO
LO+
Oscillator
Circuit
CPT
Detection
Modem
Reception
SP
RD
DETB
CPT
Transmission
Modem
Transmission
DTMF
Transmission
Post-
LPF
XD
SW1
SW2
SW4
SW5
SW3
Input Amplifier 1
Input Amplifier 2
Input Amplifier 3
Output Amplifier 1
Output Amplifier 2
Output Amplifier 3
ATT
X1
X2
CLKO

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
3/19
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
V
DD
TIO
TI≠
TI+
LI1O
LI1≠
LI1+
SWI
SGO
LI2O
LI2≠
TO
LO+
LO≠
SGC
GND
SP
DETB
RD
XD
X1
X2
CLKO
D3
D2
D1
D0
A1
A0
WRB
RDB
CSB
32-Pin plastic SSOP

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
4/19
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No.
Symbol
I/O
Description
1
V
DD
Power supply pin. Connect a +5 V power supply to this pin.
2
TIO
O
The output pin of the input amplifier 1. See Figure 1. For the sake of noise
reduction, connect a capacitor between this pin and TI≠ (3) so as to attenuate
high frequency components above 10 kHz.
3
TI≠
I
The inverting input pin for the input amplifier 1. When the input amplifier 1 is not
used, connect pin TIO (2) to pin TI≠ (3), and connect pin TI+ (4) to pin SGO.
4
TI+
I
The non-inverting input pin for the input amplifier 1.
5
LI1O
O
The output pin for the input amplifier 2. See Figure 1. For the sake of noise
reduction, connect a capacitor between this pin and LI1≠ (6) so as to attenuate
high frequency components above 10 kHz.
6
LI1≠
I
The inverting input pin for the input amplifier 2. When the input amplifier 2 is not
used, connect pin LI1O (5) and LI1≠ (6), and connect pin LI+ (7) to pin SGO.
7
LI1+
I
The non-inverting input pin for the input amplifier 2.
8
SWI
I
The input pin for SW3. This pin is connected internally to SGO (9) when SW3 is
to be made ON.
9
SGO
O
The signal ground output pin for external circuits. A voltage of about V
DD
/2 is
output from this pin.
10
LI2O
O
The output pin for the input amplifier 3. See Figure 1. For the sake of noise
reduction, connect a capacitor between this pin and LI2≠ (10) so as to attenuate
high frequency components above 10 kHz.
11
LI2≠
I
The inverting input pin for the input amplifier 3.
When the input amplifier 3 is not used, connect pin LI2O (10) and LI2≠ (11).
12
TO
O
The output pin of the output amplifier 1.
Can drive a load of 1.2 k
or more.
13
LO+
O
The non-inverting output pin for the output amplifier 2. See Figure 2 for details
of connecting a peripheral circuit.
14
LO≠
O
The inverting output pin of the output amplifier 2. See Figure 2 for details of
connecting a peripheral circuit.
15
SGC
O
The signal ground output pin for internal circuits. A voltage of about V
DD
/2 is
output from this pin.
Connect a 1
µ
F capacitor between SGC (15) and GND (16).
16
GND
The ground pin for the LSI. Connect a 0 V input to this pin.
17
CSB
I
The chip select pin for the processor interface.
Reading and writing are possible when this input is "0". Reading and writing are
disabled when this input is "1".
18
RDB
I
The read control pin for the processor interface.
Data can be read from the LSI when this pin is "0".
19
WRB
I
The write control pin for the processor interface.
Data is written into this LSI at the rising edge of the WR signal.
20
A0
I
The address input pin A0 for the processor interface.

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
5/19
Pin No.
Symbol
I/O
Description
21
A1
I
The address input pin A1 for the processor interface.
22
D0
IO The data input/output pin D0 for the processor interface.
23
D1
IO The data input/output pin D1 for the processor interface.
24
D2
IO The data input/output pin D2 for the processor interface.
25
D3
IO The data input/output pin D3 for the processor interface.
26
CLKOUT
O
The 3.579545 MHz oscillator circuit output pin.
27
X2
O
28
X1
I
The pins for connecting a 3.579545 MHz crystal. The capacitors and the
feedback resistor are internally connected to these pins. When inputting an
external clock, connect the input to the X1 pin via a 1000 pF capacitor and leave
the pin X2 open.
29
XD
I
The modem transmit data input pin.
The "1" level corresponds to the mark data and the "0" level corresponds to the
space data.
30
RD
O
The modem receive data output pin. The mark and space data are the same as
for XD. A mark is output when no carrier is detected.
31
DETB
O
The pin for outputting the carrier detect signal of the modem or the call progress
tone detector output.
The detection result corresponding to the respective operating mode is output
from this pin. A "0" indicates detection and a "1" indicates non-detection.
32
SP
O
The DTMF reception detection output pin.
A "0" indicates detection and a "1" indicates non-detection.

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
6/19
Figure 1 Input amplifier 1 to 3 interface
Figure 2 Output amplifier 2, 3 interface example
VREF
SGO
TI+
R1
R2
TI≠
TIO
Terminal
Input amplifier 1
C1
R3
R4
LI1≠
LI1O
Line 1
Input amplifier 2
C2
R5
R6
LI2≠
LI2O
Line 2
Input amplifier 3
C3
Example: The cutoff
frequency is fc = 10 kHz,
when R1 = R2 = 30 k
(gain = 1), and C1 is 500 pF
Example: The cutoff
frequency is fc = 10 kHz,
when R3 = R4 = 30 k
(gain = 1), and C2 is 500 pF
Example: The cutoff
frequency is fc = 10 kHz,
when R5 = R6 = 30 k
(gain = 1), and C3 is 500 pF
0.022
µ
F
LO≠
(≠10.0 dBm)
(≠10.0 dBm)
LO+
600
600
:
600
≠10.0 dBm
Output amplifier 2
Output amplifier 3
(When the transformer loss is 0 dB)

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
7/19
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Rating
Unit
Power supply voltage
V
DD
--
≠0.3 to +7.0
V
Permissible power
dissipation
P
D
--
to 130
mW
Output short circuit current
I
SHT
Shorted to V
DD
or ground.
to 60
mA
Analog input voltage
V
AIN
--
≠0.3 to V
DD
+ 0.3
V
Digital input voltage
V
DIN
--
≠0.3 to V
DD
+ 0.3
V
Storage temperature range
T
stg
--
≠55 to +150
∞C
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Power supply voltage
V
DD
--
4.5
5.0
5.5
V
Operating temperature range
T
a
--
≠40
--
+85
∞C
High level input voltage
V
IH
Digital input pins
0.8
◊
V
DD
--
V
DD
V
Low level input voltage
V
IL
Digital input pins
0
--
0.2
◊
V
DD
V
Digital input rise time
t
ir
Digital input pins
--
--
50
ns
Digital input fall time
t
if
Digital input pins
--
--
50
ns
Digital output load
C
DL
Digital output pins
--
--
100
pF
Bypass capacitor for SGC
C
SG
Between SGC and GND
1
--
--
µ
F
Bypass capacitor for V
DD
C
VG
Between V
DD
and ground
10
--
--
µ
F
Oscillating frequency
--
--
--
3.579545
--
MHz
Frequency deviation
--
25 ±5∞C
≠100
--
+100
ppm
Temperature
characteristics
--
In the temperature range ≠40 to
+85∞C
≠50
--
+50
ppm
Equivalent series
resistor
--
--
--
--
90
Crys
ta
l
Production load
capacitance
--
--
--
16
--
pF
Input clock frequency
deviation
f
CLK
≠0.1
--
+0.1
%
Input clock duty ratio
DUTY
Values when an X1 external clock
is input
40
--
60
%

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
8/19
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC Characteristics
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
I
DD1
During operation (modem
transmission/reception mode)*1
0
5.0
10.0
mA
I
DD2
During operation (tone 1 mode)*1
0
5.0
10.0
mA
I
DD3
During operation (tone 2, tone 3
modes)*1
0
6.0
11.0
mA
Power supply current
I
DD4
During power down
0
7.0
100
µ
A
I
IH
V
I
= V
DD
--
--
2.0
µ
A
Input leak current
I
IL
V
I
= 0 V
--
--
0.5
µ
A
High level output
voltage
V
OH
I
OH
= ≠100
µ
A
V
DD
≠0.1
--
V
DD
V
Low level output
voltage
V
OL
I
OL
= 100
µ
A
0
0.05
0.1
V
Input capacitance
C
IN
--
--
5
--
pF
*1: See Table 3 for details of the modes.
Analog Interface
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Input resistance
R
IN
TI≠, TI+, LI1≠, LI1+, LI2≠
10
--
--
M
R
L1
TIO, LI1O, LI2O
20
--
--
k
R
L2
TO (Output amplitude 1 Vpp or less)
1.2
--
--
k
Output load resistance
R
L3
LO≠, LO+ (differential outputs)
1.2
--
--
k
Output load
capacitance
C
L
Analog outputs
--
--
100
pF
R
OX1
TIO, LI1O, LI2O, TO
--
10
--
Output impedance
R
OX2
LO≠, LO+, SGO
--
10
--
V
O1
TIO, LI1O, LI2O, TO, LO≠, LO+, SGC
--
V
DD
/2
--
V
Output DC voltage
V
O2
SGO
V
DD
/2
≠0.1
V
DD
/2
V
DD
/2
+0.1
V
V
S1
4 to 8 kHz
--
≠60
≠20
dBm
V
S2
8 to 12 kHz
--
≠80
≠40
dBm
Out-of-band spurious
response
V
S3
LO≠, LO+
(Differential outputs) 12 kHz to (4 kHz
each)
--
≠80
≠60
dBm
SW3 impedance
R
SW3
SW3
--
15
30
Output current
I
SGO
SGO pin (including via SW3)
≠0.6
--
0.6
mA

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
9/19
AC Characteristics (DTMF Section)
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
V
DTTL
Lower group
tone
≠7.0
≠4.5
≠3.0
dBm
Transmit level
V
DTTH
LO≠, LO+_Differential *1
Higher group
tone
≠5.5
≠2.5
≠1.0
dBm
Transmit signal level
relative value
V
DTDF
(Higher group tone) ≠ (lower group tone)
1
2
3
dB
Transmit signal frequency
deviation
f
DDT
Relative to the nominal frequency
≠1.5
--
+1.5
%
Transmit signal distortion
rate
THD
DT
(Harmonic waves) ≠ (fundamental wave)
--
--
≠23
dB
DTMF detection level
V
DETDT
For one frequency
≠42
--
≠6
dBm
DTMF non-detection level
V
REJDT
For one frequency
--
--
≠60
dBm
Detection frequency band
f
DETDT
Relative to the nominal frequency
--
--
±1.5
%
Non-detection frequency
band
f
REJDT
Relative to the nominal frequency
±3.8
---
--
%
Level difference between
two received frequencies
V
TWIST
(Higher group tone) ≠ (lower group tone)
≠6
--
+6
dB
Permissible received
noise level
L
OSSR6
(Noise level) ≠ (tone level) 0.3 to 3.4 kHz
--
≠12
--
dB
Received dial tone
elimination ratio
V
REJCP
380 to 420 Hz
37
53
--
dB
Signal repetition period
t
c
120
--
--
ms
t
s
Detection
49
--
--
ms
Input signal persistence
duration
t
l
Non-detection
--
--
24
ms
Signal quiet duration
t
p
30
--
--
ms
t
ba
SP = 0
--
--
0.4
ms
Instantaneous break
protection period
t
bb
SP = 1
--
--
10
ms
Detection delay time
t
g
During the tone 1, tone 2,
and loop back modes.
See Figure 3 and Table 3
for details.
24
41
49
ms
Detection hold time
t
d
24
28
35
ms
SP delay time
t
sp
0.2
0.6
1.0
ms
Signal repetition period
t
c
60
--
--
ms
t
s
Detection
35
--
--
ms
Input signal persistence
duration
t
l
Non-detection
--
--
10
ms
Signal quiet duration
t
p
During the tone 3 mode.
See Figure 3 and Table 3
for details.
21
--
--
ms
t
ba
SP = 0
--
--
0.4
ms
Instantaneous break
protection period
t
bb
SP = 1
--
--
3.0
ms
Detection delay time
t
g
12
26
37
ms
Detection hold time
t
d
15
20
27
ms
SP delay time
t
sp
0.2
0.6
1.0
ms
ATT attenuation
V
ATT
Relative to the ATT = "0" reference
≠7.5
≠6
≠4.5
dB
Note: 0 dBm = 0.775 Vrms
*1:
The value will be 6 dB smaller for pin LO+ or pin LO≠ alone.

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
10/19
Figure 3 DTMF reception timing
t
s
:
Input signal persistence duration (detection)
Normal reception is made when the input signal persistence duration is equal to t
s
or more.
t
I
:
Input signal persistence duration (non-detection)
The input signal is ignored when the input signal persistence duration is less than t
I
, and the SP and DTMF
receive data are not output.
t
p
:
Signal quiet duration
The DTMF receive data and SP are reset if the input continues to be in the no-signal condition for a
duration equal to t
p
or longer.
Also, even if the receive data changes during DTMF signal reception, SP continues to be "1" and the
DTMF receive data may remain in the initial value and may not change, if the signal quiet duration is less
than t
p
(including when it changes without any instantaneous break).
t
ba
: Instantaneous break protection period 1
This is applicable to the period after the input signal has arrived and until the timing when SP becomes "1".
In other words, SP and DTMF receive data are output normally even if a no-signal condition of a duration
less than t
ba
occurs.
t
bb
: Instantaneous break protection period 2
This is applicable when SP is "1" (during output of the receive data). In other words, SP and the DTMF
receive data are not reset even if a no-signal condition of a duration less than t
bb
occurs during signal
reception.
t
c
:
For ensuring normal reception, make sure that the signal repetition period is equal to t
c
or more.
t
g
:
Detection delay time
The DTMF receive data is output with a delay of t
g
relative to the appearance of the input signal.
t
d
:
Detection hold time
The output of SP or the DTMF receive data is stopped with a delay of t
d
after the termination of the input
signal.
t
sp
: SP delay time
SP is output after a delay of t
sp
relative to the output of the DTMF receive data. Therefore, latch the
DTMF receive data when the rising edge of SP is detected.
t
s
t
p
t
c
t
bb
t
d
t
g
DTMF signal
DTMF receive data
SP
t
l
t
sp
t
ba

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
11/19
AC Characteristics (Modem Section)
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Modem transmit level
V
AOM
LO≠, LO+ Differential
≠6.0
≠4.0
≠2.0
dBm
Transmit signal level
relative value
V
DM
(Mark signal) ≠ (space signal)
≠1.5
0
+1.5
dB
f
M
--
XD = 1
1292
1300
1308
Hz
Transmit carrier
frequency
f
S
--
XD = 0
2092
2100
2108
Hz
Receive signal level
V
AI
Level of LI1O and LI2O
≠51
--
≠6
dBm
V
ON
Level of LI1O and LI2O
OFF
ON
--
≠44.5
≠42
dBm
Carrier detection level
V
OFF
1700 Hz
ON
OFF
≠51
≠46.5
--
dBm
Carrier detection
hysteresis
v
HYS
--
2
--
dB
Carrier detection delay
time
t
CDD
OFF
≠30 dBm
5
10
15
ms
Carrier detection hold
time
t
CDH
≠30 dBm
OFF
23
28
34
ms
Demodulation bias
distortion
D
BS
1200 bps, 1:1 pattern
≠10
--
+10
%
Note: RD is fixed at "1" when the carrier detector is OFF.
AC Characteristics (CLKO)
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
V
COH
0.9
◊
V
DD
--
V
DD
V
Output amplitude
V
COL
CL = 100 pF
0
--
0.1
◊
V
DD
V

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
12/19
AC Characteristics (Call Progress Tone Section)
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Transmit level
V
CPT
Pin TO
≠21.5
≠20.0
≠18.5
dBm
During 400 Hz output
380
400
420
Hz
Transmit frequency
f
CPT
Pin TO
During 800 Hz output
780
800
820
Hz
Distortion rate
THD
CPT
Pin TO
--
--
≠23
dB
Detection level
V
DETCP
400 Hz, level of LI1O and LI2O
≠46
--
≠6
dBm
Non-detection level
V
REJCP
400 Hz, level of LI1O and LI2O
--
--
≠60
dBm
Detection frequency
f
DETCP
--
360
--
440
Hz
510
--
--
Hz
Non-detection
frequency
f
rejCP
--
--
--
300
Hz
t
DETCP
Detection
30
--
--
ms
Detection
persistence period
t
REJCP
See Figure 4.
Non-detection
--
--
10
ms
Detection delay time
t
DELCP
10
17
30
ms
Detection hold time
t
HOLCP
10
17
30
ms
CPT input
t
REJCP
t
DETCP
DETB
t
DELCP
t
HOLCP
Figure 4 Call progress tone detection timing

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
13/19
AC Characteristics (Processor Interface)
(V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Write signal period
P
W
2000
--
--
ns
Write signal width
T
W
100
--
--
ns
Read signal width
T
R
200
--
--
ns
T
AW1
10
--
--
ns
Address data setup time
T
AR1
80
--
--
ns
T
AW2
50
--
--
ns
Address data hold time
T
AR2
10
--
--
ns
T
CW1
10
--
--
ns
Chip select setup time
T
CR1
80
--
--
ns
T
CW2
50
--
--
ns
Chip select hold time
T
CR2
10
--
--
ns
Data setup time
T
DW1
110
--
--
ns
Data hold time
T
DW2
20
--
--
ns
Data output delay time
t
pd1
20
60
150
ns
Data output hold time
t
pd2
See Figure 5.
20
40
100
ns
Figure 5 Processor interface timing
CSB
A1, A0
D0 to D3
WRB
RDB
T
AW1
T
CW1
T
AW2
T
CW2
T
W
T
AR1
T
CR1
T
AR2
T
CR2
T
R
T
DW1
T
DW2
t
pd1
t
pd2
Address
Address
Write data
Read data

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
14/19
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Description of Processor Interface
∑
List of Registers
Table 1 List of processor interface registers
A1
A0
R/W
D3
D2
D1
D0
0
0
W
PBG3
PBG2
PBG1
PBG0
0
1
R/W
SW1 CONT
MODE2
MODE1
MODE0
1
0
R/W
SW3 CONT
SW2 CONT
CPTG ON
CPT800
1
1
R/W
SW5 CONT
SW4 CONT
MOD-DT ON
ATT
0
0
R
PBR3
PBR2
PBR1
PBR0
* Data written into the registers other than the register [(A1, A0) = (0,0)] can be read out.
* Immediately after switching ON the power, use the LSI only after clearing the control registers
using the power down mode.
∑
PBG3 to 0/PBR3 to 0
The registers PBG3 to 0 are used for setting the DTMF transmit data.
The registers PBR3 to 0 are used for reading the DTMF receive data.
The output frequency does not change even if the code is changed during transmission.
Table 2 shows the data assignments.
Table 2 DTMF transmit/receive data assignments
D3
D2
D1
D0
PBG3/
PBR3
PBG2/
PBR2
PBG1/
PBR1
PBG0/
PBR0
CODE
Lower group
frequency (Hz)
Higher group
frequency (Hz)
0
0
0
1
1
697
1209
0
0
1
0
2
697
1336
0
0
1
1
3
697
1477
0
1
0
0
4
770
1209
0
1
0
1
5
770
1336
0
1
1
0
6
770
1477
0
1
1
1
7
852
1209
1
0
0
0
8
852
1336
1
0
0
1
9
852
1477
1
0
1
0
0
941
1336
1
0
1
1
941
1209
1
1
0
0
#
941
1477
1
1
0
1
A
697
1633
1
1
1
0
B
770
1633
1
1
1
1
C
852
1633
0
0
0
0
D
941
1633

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
15/19
∑
MODE2 to MODE0
These registers are used for setting the mode. The contents of setting are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 List of mode settings
Operation of different blocks
MODE2 MODE1 MODE0 Mode name Modulator
section
Demodulator
section
DTMF
transmission
DTMF
reception
CPT
transmission
CPT
reception
0
0
0
Modem
transmission
O
≠
≠
≠
O
≠
0
0
1
Modem
reception
≠
O
≠
≠
O
≠
0
1
0
Tone 1
(Note 1)
≠
≠
≠
O
O
≠
0
1
1
Tone 2
(Note 1)
≠
≠
O
O
O
O
1
0
0
Tone 3
(Note 1)
≠
≠
O
O
O
O
1
0
1
Loop back
(Note 2)
O
O
O
O
≠
≠
1
1
0
Test
LSI internal test
1
1
1
Power down
(Note 3)
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
≠
*[O]: Operating condition, [≠]: Power down condition
Note 1: Tone 1, 2, 3 modes
The DTMF detection timing is different in the tone 1, 2, loop back modes from that in the tone 3
mode.
In the tone 3 mode, the DTMF detection goes into the high speed detection mode. In this
mode, since the detector can make incorrect detection due to voice signals or noise, avoid
using the tone 3 mode if there is any margin available in the timing.
Note 2: Loop back mode
The modem loop back mode is initiated when SW5CONT is High and MOD-DT_ON is High.
(The data input in XD is output from RD via the internal circuits.)
The DTMF loop back mode is initiated when SW5CONT is Low and MOD-DT_ON is High.
(The data set in PBG3 to PBG0 is latched at the rising edge of MOD-DT_ON, and is output at
PBR3 to PBR0 via the internal circuits.)
Note 3: Power down mode
The conditions when the LSI is put in the power down mode are listed below.
Each blocks:
Stop operating and the internal circuits are reset.
Analog output pins:
Go to the high-impedance state
DETB, RD, CLKO pins:
High level
SP, X2 pins:
Low level
Processor interface registers:
Low level (excepting SW1CONT, MODE2, 1, 0)

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
16/19
∑
SW1CONT
This is the switch for selecting the DTMF reception input.
0: The input amplifier 1 is connected to the DTMF reception circuit.
1: The input amplifier 2 is connected to the DTMF reception circuit.
∑
SW2CONT
This is the switch for selecting the modem reception and CPT detection inputs.
0: The input amplifier 2 is connected to the modem reception circuit and the CPT detection circuit.
1: The input amplifier 3 is connected to the modem reception circuit and the CPT detection circuit.
∑
SW3CONT
This is the switch for external circuits, and can be used for connecting the termination, etc.
0: The switch goes into the OFF state.
1: The switch goes into the ON state. (The SWI pin and the SGO pin are connected together.)
∑
SW4CONT
This is the switch for selecting the signal (TO) of the output amplifier 1.
0: The CPT transmit output is connected to the output amplifier 1.
1: The output signal of SW2 is connected to the output amplifier 1.
∑
SW5CONT
This is the switch for selecting the signal (LO≠, LO+) of the output amplifier 2.
0: The DTMF transmit output is connected to the output amplifier 2.
1: The modem transmit output is connected to the output amplifier 2.
Set this to "1" during the modem transmit mode and set this to "0" during the DTMF transmit mode.
∑
CPTG_ON
This register is used for the ON/OFF control of call progress tone transmission.
0: CPT transmission becomes OFF and the signal is not output.
1: CPT transmission becomes ON and the signal is output.
∑
CPT800
This selects the frequency of call progress tone transmission.
0: A 400 Hz signal is output.
1: An 800 Hz signal is output.
∑
MOD-DT_ON
This is used for the ON/OFF control of modem transmission or DTMF transmission.
The transmission function is made ON/OFF of the block corresponding to the selected mode.
0: Modem transmission or DTMF transmission become OFF and the signal is not output.
1: Modem transmission or DTMF transmission become ON and the signal is output.
In the DTMF transmission mode or in the DTMF loop back mode, PBG3 to 0 are latched at the rising edge of
MOD-DT_ON.
Set this to "0" during the modem reception mode and the tone 1 mode.
∑
ATT
This controls the attenuator of the DTMF transmission section.
0: No attenuator is inserted. The DTMF transmit signal is output as it is.
1: A ≠6 dB attenuator is inserted in the DTMF transmission section.

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
17/19
APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
To
terminal
V
DD
TIO
TI≠
TI+
LI1O
LI1≠
LI1+
SWI
SGO
LI2O
LI2≠
TO
LO+
LO≠
SGC
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
SP
DETB
RD
XD
X1
X2
CLKO
D3
D2
D1
D0
A1
A0
WRB
RDB
CSB
MCU I/F
3.579545 MHz
1
µ
F
30 k
ML7020
To line
From
terminal
From line
30 k
30 k
500 pF
500 pF
30 k
10
µ
F

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
18/19
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The surface mount type packages are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity
absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki's responsible sales person for the product
name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions (reflow method,
temperature and times).
SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K
Mirror finish
Package material
Epoxy resin
Lead frame material
42 alloy
Pin treatment Solder plating (
5µm)
Package weight (g)
0.60 TYP.
5
Rev. No./Last Revised
3/Dec. 5, 1996
(Unit: mm)

FEDL7020-02
1Semiconductor
ML7020
19/19
NOTICE
1.
The information contained herein can change without notice owing to product and/or technical
improvements. Before using the product, please make sure that the information being referred to is up-to-
date.
2.
The outline of action and examples for application circuits described herein have been chosen as an
explanation for the standard action and performance of the product. When planning to use the product,
please ensure that the external conditions are reflected in the actual circuit, assembly, and program designs.
3.
When designing your product, please use our product below the specified maximum ratings and within the
specified operating ranges including, but not limited to, operating voltage, power dissipation, and operating
temperature.
4.
Oki assumes no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any failure or unusual or unexpected operation
resulting from misuse, neglect, improper installation, repair, alteration or accident, improper handling, or
unusual physical or electrical stress including, but not limited to, exposure to parameters beyond the
specified maximum ratings or operation outside the specified operating range.
5.
Neither indemnity against nor license of a third party's industrial and intellectual property right, etc. is
granted by us in connection with the use of the product and/or the information and drawings contained
herein. No responsibility is assumed by us for any infringement of a third party's right which may result
from the use thereof.
6.
The products listed in this document are intended for use in general electronics equipment for commercial
applications (e.g., office automation, communication equipment, measurement equipment, consumer
electronics, etc.). These products are not authorized for use in any system or application that requires
special or enhanced quality and reliability characteristics nor in any system or application where the failure
of such system or application may result in the loss or damage of property, or death or injury to humans.
Such applications include, but are not limited to, traffic and automotive equipment, safety devices,
aerospace equipment, nuclear power control, medical equipment, and life-support systems.
7.
Certain products in this document may need government approval before they can be exported to particular
countries. The purchaser assumes the responsibility of determining the legality of export of these products
and will take appropriate and necessary steps at their own expense for these.
8.
No part of the contents contained herein may be reprinted or reproduced without our prior permission.
Copyright 2000 Oki Electric Industry Co., Ltd.


















