 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: TDA1308A | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Document Outline
- FEATURES
- GENERAL DESCRIPTION
- QUICK REFERENCE DATA
- ORDERING INFORMATION
- BLOCK DIAGRAM
- PINNING
- LIMITING VALUES
- THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
- QUALITY SPECIFICATION
- CHARACTERISTICS
- TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
- PACKAGE OUTLINES
- SOLDERING
- DEFINITIONS
- DISCLAIMERS

DATA SHEET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 2002 Feb 27
2002 Jul 19
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA1308; TDA1308A
Class AB stereo headphone driver

2002 Jul 19
2
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
FEATURES
∑
Wide temperature range
∑
No switch ON/OFF clicks
∑
Excellent power supply ripple rejection
∑
Low power consumption
∑
Short-circuit resistant
∑
High performance
≠ high signal-to-noise ratio
≠ high slew rate
≠ low distortion
∑
Large output voltage swing.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA1308; TDA1308A is an integrated class AB stereo
headphone driver contained in an SO8, DIP8 or a TSSOP8
plastic package. The device is fabricated in a 1 mm CMOS
process and has been primarily developed for portable
digital audio applications.
The difference between the TDA1308 and the TDA1308A
is that the TDA1308A can be used at low supply voltages.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
V
DD
= 5 V; V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= 25
∞
C; f
i
= 1 kHz; R
L
= 32
; unless otherwise specified.
Notes
1. V
DD
= 5 V; V
O(p-p)
= 3.5 V (at 0 dB).
2. V
DD
= 2.4 V; V
O(p-p)
= 1.62 V (at
-
4.8 dBV); for TDA1308A only.
3. V
DD
= 2.4 V; V
O(p-p)
= 1.19 V (at
-
7.96 dBV); for TDA1308A only.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage
TDA1308
single
3.0
5.0
7.0
V
dual
1.5
2.5
3.5
V
supply voltage
TDA1308A
single
2.4
5.0
7.0
V
dual
1.2
2.5
3.5
V
V
SS
negative supply voltage
-
1.5
-
2.5
-
3.5
V
I
DD
supply current
no load
-
3
5
mA
P
tot
total power dissipation
no load
-
15
25
mW
P
o
maximum output power
THD < 0.1%; note 1
-
60
-
mW
(THD + N)/S
total harmonic distortion
plus noise-to-signal ratio
note 1
-
0.03
0.06
%
-
-
70
-
65
dB
R
L
= 5 k
; note 2
-
-
92
-
89
dB
R
L
= 5 k
; note 3
-
-
52
-
40
dB
R
L
= 5 k
-
-
101
-
dB
S/N
signal-to-noise ratio
100
110
-
dB
cs
channel separation
-
70
-
dB
R
L
= 5 k
-
105
-
dB
PSRR
power supply ripple rejection f
i
= 100 Hz; V
ripple(p-p)
= 100 mV
-
90
-
dB
T
amb
ambient temperature
-
40
-
+85
∞
C

2002 Jul 19
3
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
ORDERING INFORMATION
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME
DESCRIPTION
VERSION
TDA1308
DIP8
plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil)
SOT97-1
TDA1308T
SO8
plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm
SOT96-1
TDA1308AT
SO8
plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm
SOT96-1
TDA1308TT
TSSOP8
plastic thin shrink small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3 mm
SOT505-1
handbook, halfpage
2
1
3
4
8
7
6
5
INA(neg)
TDA1308(A)
OUTA
MKA779
VSS
VDD
INA(pos)
INB(neg)
INB(pos)
OUTB
Fig.1 Block diagram.
PINNING
SYMBOL
PIN
DESCRIPTION
OUTA
1
output A
CD)
2
inverting input A
INA(pos)
3
non-inverting input A
V
SS
4
negative supply
INB(pos)
5
non-inverting input B
INB(neg)
6
inverting input B
OUTB
7
output B
V
DD
8
positive supply
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
MKA780
TDA1308(A)
VDD
OUTB
INA(neg)
INB(neg)
INB(pos)
VSS
INA(pos)
OUTA
Fig.2 Pin configuration.

2002 Jul 19
4
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
Notes
1. Human body model: C = 100 pF; R = 1500
; 3 pulses positive plus 3 pulses negative.
2. Machine model: C = 200 pF: L = 0.5 mH: R = 0
; 3 pulses positive plus 3 pulses negative.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
"UZW-BO/FQ-0601". The numbers of the quality specification can be found in the "Quality Reference
Handbook". The handbook can be ordered using the code 9398 510 63011.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage
0
8.0
V
t
SC(O)
output short-circuit duration
T
amb
= 25
∞
C; P
tot
= 1 W
20
-
s
T
stg
storage temperature
-
65
+150
∞
C
T
amb
operating ambient temperature
-
40
+85
∞
C
V
esd
electrostatic discharge
note 1
-
2000
+2000
V
note 2
-
200
+200
V
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
VALUE
UNIT
R
th j-a
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air
DIP8
109
K/W
SO8
210
K/W
TSSOP8
220
K/W
handbook, full pagewidth
MKA781
A1
A2
M2
M3
M6
M5
M4
I1
Cm
VDD
INA/B(neg)
INA/B(pos)
OUTA/B
VSS
D4
M1
D3
D2
D1
Fig.3 Equivalent schematic diagram.

2002 Jul 19
5
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
CHARACTERISTICS
V
DD
= 5 V; V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= 25
∞
C; f
i
= 1 kHz; R
L
= 32
; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
Supplies
V
DD
supply voltage
TDA1308
single
3.0
5.0
7.0
V
dual
1.5
2.5
3.5
V
supply voltage
TDA1308A
single
2.4
5.0
7.0
V
dual
1.2
2.5
3.5
V
V
SS
negative supply voltage
-
1.5
-
2.5
-
3.5
V
I
DD
supply current
no load
-
3
5
mA
P
tot
total power dissipation
no load
-
15
25
mW
DC characteristics
V
I(os)
input offset voltage
-
10
-
mV
I
bias
input bias current
-
10
-
pA
V
CM
common mode voltage
0
-
3.5
V
G
v
open-loop voltage gain
R
L
= 5 k
-
70
-
dB
I
O
maximum output current
(THD + N)/S < 0.1%
-
60
-
mA
R
O
output resistance
-
0.25
-
V
O
output voltage swing
note 1
0.75
-
4.25
V
R
L
= 16
1.5
-
3.5
V
R
L
= 5 k
0.1
-
4.9
V
PSRR
power supply rejection ratio
f
i
= 100 Hz;
V
ripple(p-p)
= 100 mV
-
90
-
dB
cs
channel separation
-
70
-
dB
R
L
= 5 k
-
105
-
dB
C
L
load capacitance
-
-
200
pF
AC characteristics
(THD + N)/S total harmonic distortion plus
noise-to-signal ratio
note 2
-
-
70
-
65
dB
-
0.03
0.06
%
note 3
-
-
52
-
40
dB
-
0.25
1.0
%
R
L
= 5 k
;
note 2
-
-
101
-
dB
-
0.0009
-
%
S/N
signal-to-noise ratio
100
110
-
dB
f
G
unity gain frequency
open-loop; R
L
= 5 k
-
5.5
-
MHz
P
o
maximum output power
(THD + N)/S < 0.1%
-
60
-
mW
C
i
input capacitance
-
3
-
pF
SR
slew rate
unity gain inverting
-
5
-
V/
µ
s
B
power bandwidth
unity gain inverting
-
20
-
kHz

2002 Jul 19
6
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
Notes
1. Values are proportional to V
DD
; (THD + N)/S < 0.1%.
2. V
DD
= 5.0 V; V
O(p-p)
= 3.5 V (at 0 dB).
3. V
DD
= 2.4 V; V
O(p-p)
= 1.13 V (at
-
7.96 dBV); for TDA1308A only.
TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
MKA782
1
2
3
5
6
7
4
8
RL
VOUTA
VDD
VINA
VINB
Vref
(typ. 2.5 V)
RL
VOUTB
3.9 k
3.9 k
3.9 k
3.9 k
100
µ
F
100
µ
F
C6
100
µ
F
TDA1308(A)
Fig.4 Measurement circuit for inverting application.

2002 Jul 19
7
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
handbook, full pagewidth
MKA783
1
2
3
5
6
7
4
8
R5
10 k
R6
10 k
C3
1
µ
F
R1
22 k
C8
C7
R4
C4
R3
C5
1 nF
R2
BCK
WS
DATA
VDD
Vref
5
4
1
2
3
6
7
8
3.9 k
33 k
C2
10
µ
F
C1
100 nF
3.9 k
1 nF
100
µ
F
100
µ
F
C6
100
µ
F
TDA1308(A)
TDA1545A
Fig.5 Example of application with TDA1545A (stereo continuous calibration DAC).
handbook, halfpage
0
40
80
MKA784
10
-
2
10
-
3
fi (Hz)
Gv
(dB)
10
-
4
10
-
5
10
-
6
10
-
7
10
-
8
no load
RL = 32
Fig.6
Open-loop gain as a function of input
frequency.
handbook, halfpage
-
130
-
110
-
70
-
90
MKA785
10
-
2
10
-
1
10
-
3
10
-
4
10
-
5
fi (Hz)
Gv
(dB)
32
RL = 16
5 k
Fig.7 Crosstalk as a function of input frequency.

2002 Jul 19
8
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
handbook, halfpage
3
Po
(mW)
4
VDD (V)
5
100
10
20
40
60
MKA786
RL = 16
32
8
Fig.8 Output power as a function of supply voltage.
handbook, halfpage
-
110
-
90
-
70
-
50
MKA787
10
-
1
10
-
2
10
-
3
10
-
4
10
-
5
fi (Hz)
(THD
+
N)/S
(dB)
RL = 5 k
;
VO(p-p) = 3.5 V
RL = 32
;
Po = 50 mW
RL = 16
;
Po = 50 mW
Fig.9 Total harmonic distortion plus noise-to-signal ratio as a function of input frequency.

2002 Jul 19
9
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
handbook, halfpage
-
40
-
80
-
100
-
60
MKA788
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
RL = 8
16
32
5 k
fi = 1 kHz
VO(p-p) (V)
(THD
+
N)/S
(dB)
Fig.10 Total harmonic distortion plus noise-to-signal ratio as a function of output voltage level.

2002 Jul 19
10
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
PACKAGE OUTLINES
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC
JEDEC
EIAJ
SOT97-1
95-02-04
99-12-27
UNIT
A
max.
1
2
b
1
(1)
(1)
(1)
b
2
c
D
E
e
M
Z
H
L
mm
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
min.
A
max.
b
max.
w
M
E
e
1
1.73
1.14
0.53
0.38
0.36
0.23
9.8
9.2
6.48
6.20
3.60
3.05
0.254
2.54
7.62
8.25
7.80
10.0
8.3
1.15
4.2
0.51
3.2
inches
0.068
0.045
0.021
0.015
0.014
0.009
1.07
0.89
0.042
0.035
0.39
0.36
0.26
0.24
0.14
0.12
0.01
0.10
0.30
0.32
0.31
0.39
0.33
0.045
0.17
0.020
0.13
b
2
050G01
MO-001
SC-504-8
M
H
c
(e )
1
M
E
A
L
seating plane
A
1
w
M
b
1
e
D
A
2
Z
8
1
5
4
b
E
0
5
10 mm
scale
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
pin 1 index
DIP8: plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil)
SOT97-1

2002 Jul 19
11
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
UNIT
A
max.
A
1
A
2
A
3
b
p
c
D
(1)
E
(2)
(1)
e
H
E
L
L
p
Q
Z
y
w
v
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC
JEDEC
EIAJ
mm
inches
1.75
0.25
0.10
1.45
1.25
0.25
0.49
0.36
0.25
0.19
5.0
4.8
4.0
3.8
1.27
6.2
5.8
1.05
0.7
0.6
0.7
0.3
8
0
o
o
0.25
0.1
0.25
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
Notes
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
2. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
1.0
0.4
SOT96-1
X
w
M
A
A
1
A
2
b
p
D
H
E
L
p
Q
detail X
E
Z
e
c
L
v
M
A
(A )
3
A
4
5
pin 1 index
1
8
y
076E03
MS-012
0.069
0.010
0.004
0.057
0.049
0.01
0.019
0.014
0.0100
0.0075
0.20
0.19
0.16
0.15
0.050
0.244
0.228
0.028
0.024
0.028
0.012
0.01
0.01
0.041
0.004
0.039
0.016
0
2.5
5 mm
scale
SO8: plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm
SOT96-1
97-05-22
99-12-27

2002 Jul 19
12
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
UNIT
A1
A
max.
A2
A3
bp
L
HE
Lp
w
y
v
c
e
D
(1)
E
(2)
Z
(1)
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC
JEDEC
EIAJ
mm
0.15
0.05
0.95
0.80
0.45
0.25
0.28
0.15
3.10
2.90
3.10
2.90
0.65
5.10
4.70
0.70
0.35
6
∞
0
∞
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.94
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Notes
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
2. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.70
0.40
SOT505-1
99-04-09
w
M
bp
D
Z
e
0.25
1
4
8
5
A
A2
A1
Lp
(A3)
detail X
L
HE
E
c
v
M
A
X
A
y
2.5
5 mm
0
scale
TSSOP8: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3 mm
SOT505-1
1.10
pin 1 index

2002 Jul 19
13
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
SOLDERING
Introduction
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
"Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages"
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mount components are mixed on
one printed-circuit board. Wave soldering can still be used
for certain surface mount ICs, but it is not suitable for fine
pitch SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
Through-hole mount packages
S
OLDERING BY DIPPING OR BY SOLDER WAVE
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260
∞
C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joints for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
stg(max)
). If the
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
M
ANUAL SOLDERING
Apply the soldering iron (24 V or less) to the lead(s) of the
package, either below the seating plane or not more than
2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit
is less than 300
∞
C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between
300 and 400
∞
C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
Surface mount packages
R
EFLOW SOLDERING
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250
∞
C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 220
∞
C for
thick/large packages, and below 235
∞
C for small/thin
packages.
W
AVE SOLDERING
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
for surface mount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
∑
Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
∑
For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
≠ larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
≠ smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
∑
For packages with leads on four sides, the footprint must
be placed at a 45
∞
angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250
∞
C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
M
ANUAL SOLDERING
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300
∞
C. When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can
be soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds
between 270 and 320
∞
C.
2002 Jul 19
14
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
Suitability of IC packages for wave, reflow and dipping soldering methods
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
"Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods".
2. For SDIP packages, the longitudinal axis must be parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
3. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
4. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45
∞
angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, QFP and TQFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
6. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
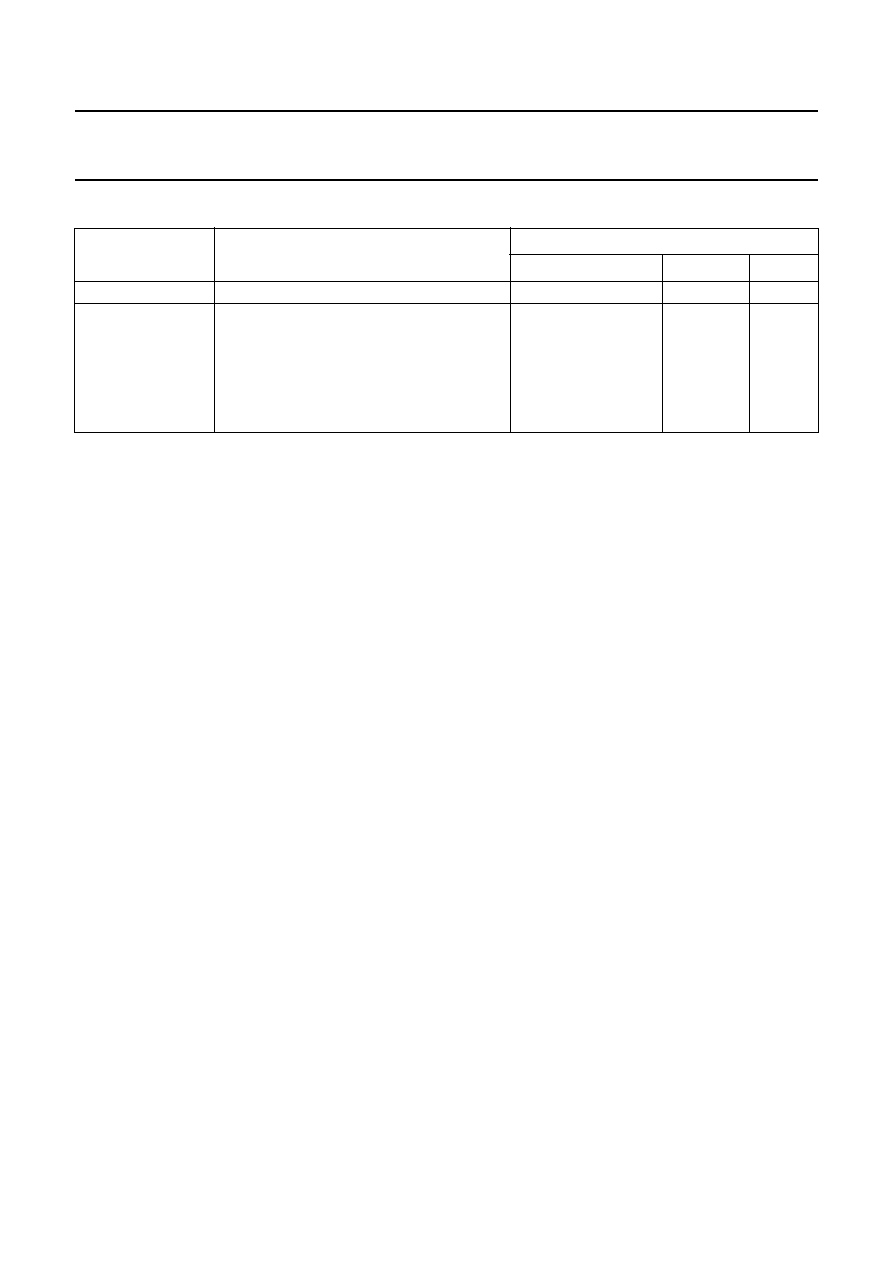
MOUNTING
PACKAGE
SOLDERING METHOD
WAVE
REFLOW
(1)
DIPPING
Through-hole mount DBS, DIP, HDIP, SDIP, SIL
suitable
(2)
-
suitable
Surface mount
BGA, HBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, TFBGA
not suitable
suitable
-
HBCC, HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTQFP,
HTSSOP, HVQFN, SMS
not suitable
(3)
suitable
-
PLCC
(4)
, SO, SOJ
suitable
suitable
-
LQFP, QFP, TQFP
not recommended
(4)(5)
suitable
-
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO
not recommended
(6)
suitable
-

2002 Jul 19
15
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Class AB stereo headphone driver
TDA1308; TDA1308A
DATA SHEET STATUS
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
DATA SHEET STATUS
(1)
PRODUCT
STATUS
(2)
DEFINITIONS
Objective data
Development
This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Preliminary data
Qualification
This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Product data
Production
This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Changes will be
communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification
The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition
Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
at these or at any other conditions above those given in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information
Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
no representation or warranty that such applications will be
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications
These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductors customers using or selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes
Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
the use of any of these products, conveys no licence or title
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warranties that
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.

© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2002
SCA74
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Philips Semiconductors ≠ a worldwide company
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Printed in The Netherlands
753503/03/pp
16
Date of release:
2002 Jul 19
Document order number:
9397 750 09985















