 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: TDA8588J | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

DATA SHEET
Product specification
2004 Feb 24
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt
power amplifier and multiple
voltage regulator

2004 Feb 24
2
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
FEATURES
Amplifiers
∑
I
2
C-bus control
∑
Can drive a 2
load with a battery voltage of up to 16 V
and a 4
load with a battery voltage of up to 18 V
∑
DC load detection, open, short and present
∑
AC load (tweeter) detection
∑
Programmable clip detect; 1 % or 4 %
∑
Programmable thermal protection pre-warning
∑
Independent short-circuit protection per channel
∑
Low gain line driver mode (20 dB)
∑
Loss-of-ground and open V
P
safe
∑
All outputs protected from short-circuit to ground, to V
P
or across the load
∑
All pins protected from short-circuit to ground
∑
Soft thermal-clipping to prevent audio holes
∑
Low battery detection.
Voltage regulators
G
ENERAL
∑
I
2
C-bus control
∑
Good stability for any regulator with almost any output
capacitor value
∑
Five voltage regulators (microcontroller, display,
mechanical digital, mechanical drive and audio)
∑
Choice of non-adjustable 3.3 or 5 V microcontroller
supply (REG2) versions reducing risk of overvoltage
damage
∑
Choice of non-adjustable 3.3 or 5 V digital signal
processor supply (REG3) versions reducing risk of
overvoltage damage
∑
Selectable output voltages for regulators 1, 4 and 5
∑
Low dropout voltage PNP output stages
∑
High supply voltage ripple rejection
∑
Low noise for all regulators
∑
Two power switches (antenna switch and amplifier
switch)
∑
Regulator 2 (microcontroller supply) operational during
load-dump and thermal shut-down
∑
Low quiescent current (only regulator 2 is operational)
∑
Reset output (push-pull output stage)
∑
Adjustable reset delay time
∑
Backup functionality.
P
ROTECTION
∑
If connection to the battery voltage is reversed, all
regulator voltages will be zero
∑
Able to withstand voltages at the output of up to 18 V
(supply line may be short-circuited)
∑
Thermal protection to avoid thermal breakdown
∑
Load-dump protection
∑
Regulator outputs protected from DC short-circuit to
ground or to supply voltage
∑
All regulators protected by foldback current limiting
∑
Power switches protected from loss-of-ground.
APPLICATIONS
∑
Boost amplifier and voltage regulator for car radios and
CD/MD players.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Amplifiers
The TDA8588 has a complementary quad audio power
amplifier that uses BCDMOS technology. It contains four
amplifiers configured in Bridge Tied Load (BTL) to drive
speakers for front and rear left and right channels. The
I
2
C-bus allows diagnostic information of each amplifier and
its speaker to be read separately. Both front and both rear
channel amplifiers can be configured independently in line
driver mode with a gain of 20 dB (differential output).
Voltage regulators
The TDA8588 has a multiple output voltage regulator with
two power switches.
The voltage regulator contains the following:
∑
Four switchable regulators and one permanently active
regulator (microcontroller supply)
∑
Two power switches with loss-of-ground protection
∑
A reset output that can be used to communicate with a
microcontroller.
The quiescent current has a very low level of 150
µ
A with
only regulator 2 active.

2004 Feb 24
3
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX. UNIT
Amplifiers
V
P1
, V
P2
operating supply voltage
8
14.4
18
V
I
q(tot)
total quiescent current
-
270
400
mA
P
o(max)
maximum output power
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 14.4 V; V
IN
= 2 V
RMS square wave
44
46
-
W
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 15.2 V; V
IN
= 2 V
RMS square wave
49
52
-
W
R
L
= 2
; V
P
= 14.4 V; V
IN
= 2 V
RMS square wave
83
87
-
W
THD
total harmonic distortion
-
0.01
0.1
%
V
n(o)(amp)
noise output voltage in amplifier mode
-
50
70
µ
V
V
n(o)(LN)
noise output voltage in line driver mode
-
25
35
µ
V
Voltage regulators
S
UPPLY
V
P
supply voltage
regulator 1, 3, 4 and 5 on
10
14.4
18
V
regulator 2 on
4
-
-
V
jump starts for t
10 minutes
-
-
30
V
load dump protection for
t
50 ms and t
r
2.5 ms
-
-
50
V
overvoltage for shut-down
20
-
-
V
I
q(tot)
total quiescent supply current
standby mode; V
P
= 14.4 V
-
150
190
µ
A
V
OLTAGE REGULATORS
V
O(REG1)
output voltage of regulator 1
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA;
selectable via I
2
C-bus
IB2[D3:D2] = 01
-
8.3
-
V
IB2[D3:D2] = 10
-
8.5
-
V
IB2[D3:D2] = 11
-
8.7
-
V
V
O(REG2)
output voltage of regulator 2
0.5 mA
I
O
350 mA
TDA8588J; TDA8588AJ
-
5.0
-
V
TDA8588BJ
-
3.3
-
V
V
O(REG3)
output voltage of regulator 3
0.5 mA
I
O
300 mA
TDA8588J
-
5.0
-
V
TDA8588AJ; TDA8588BJ
-
3.3
-
V
V
O(REG4)
output voltage of regulator 4
maximum current
1.6 A;
0.5 mA
I
O
800 mA;
selectable via I
2
C-bus
IB2[D7:D5] = 001
-
5.0
-
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 010
-
6.0
-
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 011
-
7.0
-
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 100
-
8.6
-
V

2004 Feb 24
4
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
ORDERING INFORMATION
Note
1. Permanent output voltage of regulator 2 and output voltage of regulator 3, respectively.
V
O(REG5)
output voltage of regulator 5
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA;
selectable via I
2
C-bus
IB1[D7:D4] = 0001
-
6.0
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0010
-
7.0
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0011
-
8.2
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0100
-
9.0
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0101
-
9.5
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0110
-
10.0
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 0111
-
10.4
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 1000
-
12.5
-
V
IB1[D7:D4] = 1001
-
V
P
-
1
-
V
P
OWER SWITCHES
V
drop(SW1)
dropout voltage of switch 1
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.6
1.1
V
V
drop(SW2)
dropout voltage of switch 2
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.6
1.1
V
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
(1)
NAME
DESCRIPTION
VERSION
REGULATOR 2
REGULATOR 3
TDA8588J
DBS37P
plastic DIL-bent-SIL power package;
37 leads (lead length 6.8 mm)
SOT725-1
5 V
5 V
TDA8588AJ
5 V
3.3 V
TDA8588BJ
3.3 V
3.3 V
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX. UNIT

2004 Feb 24
5
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
BLOCK DIAGRAM
mdb586
V
reg2
40
µ
s
BACKUP
SWITCH
ENABLE
LOGIC
TDA8588
STANDBY/ MUTE
I
2
C-BUS
INTERFACE
CLIP DETECT/ DIAGNOSTIC
REGULATOR 1
REGULATOR 3
REGULATOR 2
REGULATOR 4
REGULATOR 5
SWITCH 1
SWITCH 2
MUTE
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
35
28
27
26
20
6
25
9
7
17
19
5
3
21
23
16
8
13
SGND
SVR
IN4
IN3
IN2
IN1
STB
SCL
SDA
RESCAP
V
P
BUCAP
ACGND
PGND1
PGND3
PGND4
10
14
12
15
11
22
4
2
1
18
24
32
29
34
33
31
30
37
REG2
REG1
REG3
REG4
REG5
SW1
SW2
RST
V
P1
DIAG
OUT1
+
OUT1
-
OUT2
+
OUT2
-
OUT3
+
OUT3
-
OUT4
+
OUT4
-
V
P2
GND
36
VP
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
TEMPERATURE &
LOAD DUMP
PROTECTION VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
TEMPERATURE & LOAD
DUMP PROTECTION
AMPLIFIER
PGND2/TAB
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2004 Feb 24
6
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
PINNING
SYMBOL
PIN
DESCRIPTION
PGND2/TAB
1
power ground 2 and connection for heatsink
SDA
2
I
2
C-bus data input and output
OUT3
-
3
channel 3 negative output
SCL
4
I
2
C-bus clock input
OUT3+
5
channel 3 positive output
V
P2
6
power supply voltage 2 to amplifier
OUT1
-
7
channel 1 negative output
PGND1
8
power ground 1
OUT1+
9
channel 1 positive output
SVR
10
half supply voltage filter capacitor
IN1
11
channel 1 input
IN3
12
channel 3 input
SGND
13
signal ground
IN4
14
channel 4 input
IN2
15
channel 2 input
ACGND
16
AC ground
OUT2+
17
channel 2 positive output
PGND3
18
power ground 3
OUT2
-
19
channel 2 negative output
V
P1
20
power supply voltage 1 to amplifier
OUT4+
21
channel 4 positive output
STB
22
standby or operating or mute mode select input
OUT4
-
23
channel 4 negative output
PGND4
24
power ground 4
DIAG
25
diagnostic and clip detection output, active LOW
RST
26
reset output
SW2
27
antenna switch; supplies unregulated power to car aerial motor
RESCAP
28
reset delay capacitor
SW1
29
amplifier switch; supplies unregulated power to amplifier(s)
REG1
30
regulator 1 output; supply for audio part of radio and CD player
REG3
31
regulator 3 output; supply for signal processor part (mechanical digital) of CD player
GND
32
combined voltage regulator, power and signal ground
REG4
33
regulator 4 output; supply for mechanical part (mechanical drive) of CD player
REG5
34
regulator 5 output; supply for display part of radio and CD player
V
P
35
power supply to voltage regulator
BUCAP
36
connection for backup capacitor
REG2
37
regulator 2 output; supply voltage to microcontroller

2004 Feb 24
7
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
TDA8588
PGND2/TAB
SDA
OUT3
-
SCL
OUT3
+
V
P2
OUT1
-
PGND1
OUT1
+
SVR
IN1
IN3
SGND
IN4
IN2
ACGND
OUT2
+
PGND3
OUT2
-
V
P1
OUT4
+
STB
OUT4
-
PGND4
DIAG
RST
SW2
RESCAP
SW1
REG1
REG3
GND
001aaa258
REG4
REG5
V
P
BUCAP
REG2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
Fig.2 Pin configuration.

2004 Feb 24
8
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8588 is a multiple voltage regulator combined
with four independent audio power amplifiers configured in
bridge tied load with diagnostic capability. The output
voltages of all regulators except regulators 2 and 3 can be
controlled via the I
2
C-bus. However, regulator 3 can be set
to 0 V via the I
2
C-bus. The output voltage of regulator 2
(microcontroller supply) and the maximum output voltage
of regulator 3 (mechanical digital and microcontroller
supplies) can both be either 5 V or 3.3 V depending on the
type number. The maximum output voltages of both
regulators are fixed to avoid any risk of damaging the
microcontroller that may occur during a disturbance of the
I
2
C-bus.
The amplifier diagnostic functions give information about
output offset, load, or short-circuit. Diagnostic functions
are controlled via the I
2
C-bus. The TDA8588 is protected
against short-circuit, over-temperature, open ground and
open V
P
connections. If a short-circuit occurs at the input
or output of a single amplifier, that channel shuts down,
and the other channels continue to operate normally. The
channel that has a short-circuit can be disabled by the
microcontroller via the appropriate enable bit of the
I
2
C-bus to prevent any noise generated by the fault
condition from being heard.
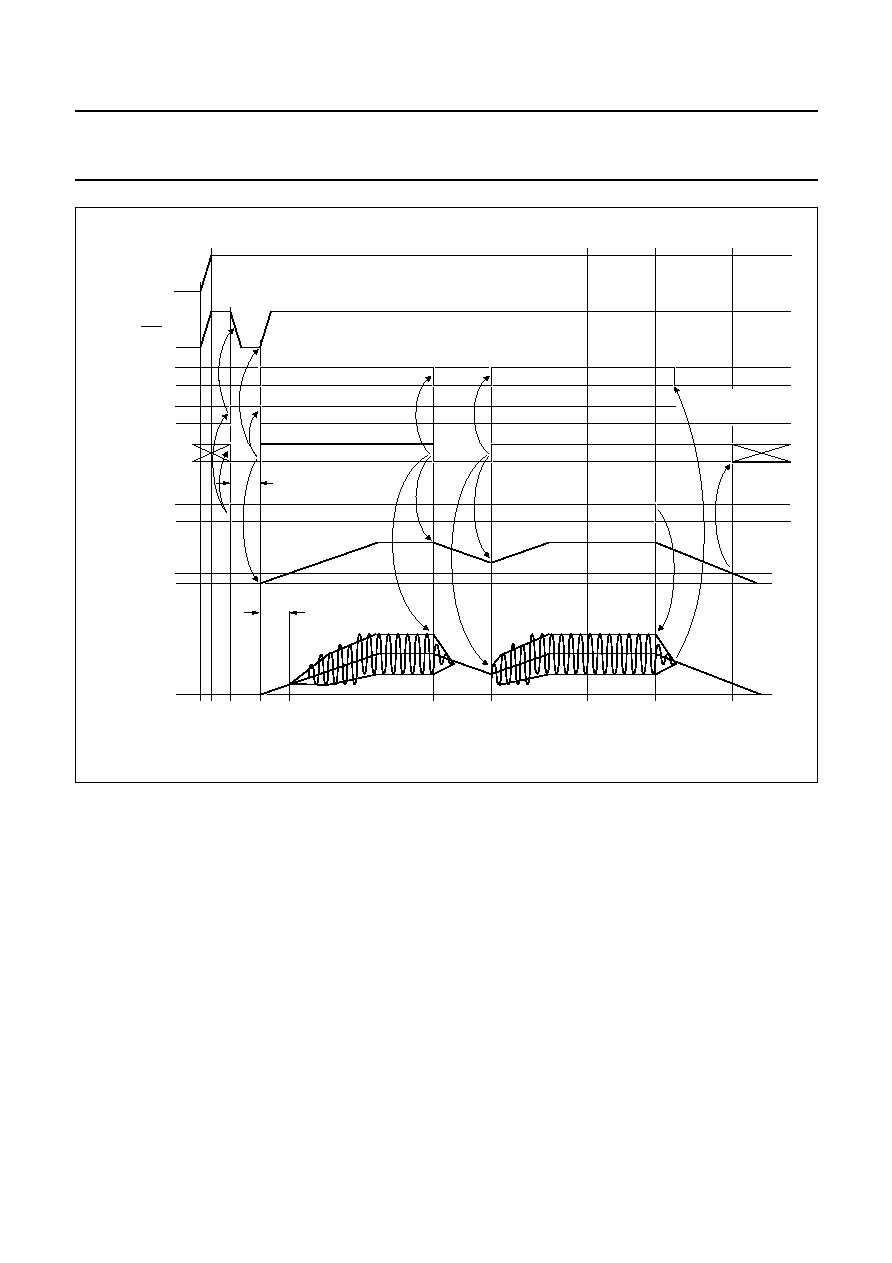
Start-up
At power on, regulator 2 will reach its final voltage when
the backup capacitor voltage exceeds 5.5 V independently
of the voltage on pin STB. When pin STB is LOW, the total
quiescent current is low, and the I
2
C-bus lines are high
impedance.
When pin STB is HIGH, the I
2
C-bus is biased on and then
the TDA8588 performs a power-on reset. When bit D0 of
instruction byte IB1 is set, the amplifier is activated, bit D7
of data byte 2 (power-on reset occurred) is reset, and
pin DIAG is no longer held LOW.
Start-up and shut-down timing (see Fig.12)
A capacitor connected to pin SVR enables smooth start-up
and shut-down, preventing the amplifier from producing
audible clicks at switch-on or switch-off. The start-up and
shut-down times can be extended by increasing the
capacitor value.
If the amplifier is shut down using pin STB, the amplifier is
muted, the regulators and switches are switched off, and
the capacitor connected to pin SVR discharges. The low
current standby mode is activated 2 seconds after pin STB
goes LOW.
Power-on reset and supply voltage spikes (see Fig.13
and Fig.14)
If the supply voltage drops too low to guarantee the
integrity of the data in the I
2
C-bus latches, the power-on
reset cycle will start. All latches will be set to a pre-defined
state, pin DIAG will be pulled LOW to indicate that a
power-on reset has occurred, and bit D7 of data byte 2 is
also set for the same reason. When D0 of instruction
byte 1 is set, the power-on flag resets, pin DIAG is
released and the amplifier will then enter its start-up cycle.
Diagnostic output
Pin DIAG indicates clipping, thermal protection
pre-warning of amplifier and voltage regulator sections,
short-circuit protection, low and high battery voltage.
Pin DIAG is an open-drain output, is active LOW, and must
be connected to an external voltage via an external pull-up
resistor. If a failure occurs, pin DIAG remains LOW during
the failure and no clipping information is available. The
microcontroller can read the failure information via the
I
2
C-bus.
AMPLIFIERS
Muting
A hard mute and a soft mute can both be performed via the
I
2
C-bus. A hard mute mutes the amplifier within 0.5 ms. A
soft mute mutes the amplifier within 20 ms and is less
audible. A hard mute is also activated if a voltage of 8 V is
applied to pin STB.
Temperature protection
If the average junction temperature rises to a temperature
value that has been set via the I
2
C-bus, a thermal
protection pre-warning is activated making pin DIAG LOW.
If the temperature continues to rise, all four channels will
be muted to reduce the output power (soft thermal
clipping). The value at which the temperature mute control
activates is fixed; only the temperature at which the
thermal protection pre-warning signal occurs can be
specified by bit D4 in instruction byte 3. If implementing
the temperature mute control does not reduce the average
junction temperature, all the power stages will be switched
off (muted) at the absolute maximum temperature T
j(max)
.
Offset detection
Offset detection can only be performed when there is no
input signal to the amplifiers, for instance when the
external digital signal processor is muted after a start-up.
The output voltage of each channel is measured and

2004 Feb 24
9
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
compared with a reference voltage. If the output voltage of
a channel is greater than the reference voltage, bit D2 of
the associated data byte is set and read by the
microcontroller during a read instruction. Note that the
value of this bit is only meaningful when there is no input
signal and the amplifier is not muted. Offset detection is
always enabled.
Speaker protection
If one side of a speaker is connected to ground, a missing
current protection is implemented to prevent damage to
the speaker. A fault condition is detected in a channel
when there is a mismatch between the power current in the
high side and the power current in the low side; during a
fault condition the channel will be switched off.
The load status of each channel can be read via the
I
2
C-bus: short to ground (one side of the speaker
connected to ground), short to V
P
(one side of the speaker
connected to V
P
), and shorted load.
Line driver mode
An amplifier can be used as a line driver by switching it to
low gain mode. In normal mode, the gain between
single-ended input and differential output (across the load)
is 26 dB. In low gain mode the gain between single-ended
input and differential output is 20 dB.
Input and AC ground capacitor values
The negative inputs to all four amplifier channels are
combined at pin ACGND. To obtain the best performance
for supply voltage ripple rejection and unwanted audible
noise, the value of the capacitor connected to pin ACGND
must be as close as possible to 4 times the value of the
input capacitor connected to the positive input of each
channel.
Load detection
DC-
LOAD DETECTION
When DC-load detection is enabled, during the start-up
cycle, a DC-offset is applied slowly to the amplifier outputs,
and the output currents are measured. If the output current
of an amplifier rises above a certain level, it is assumed
that there is a load of less than 6
and bit D5 is reset in
the associated data byte register to indicate that a load is
detected.
Because the offset is measured during the amplifier
start-up cycle, detection is inaudible and can be performed
every time the amplifier is switched on.
AC-
LOAD DETECTION
AC-load detection can be used to detect that AC-coupled
speakers are connected correctly during assembly. This
requires at least 3 periods of a 19 kHz sine wave to be
applied to the amplifier inputs. The amplifier produces a
peak output voltage which also generates a peak output
current through the AC-coupled speaker. The 19 kHz sine
wave is also audible during the test. If the amplifier detects
three current peaks that are greater than 550 mA, the
AC-load detection bit D1 of instruction byte IB1 is set to
logic 1. Three current peaks are counted to avoid false
AC-load detection which can occur if the input signal is
switched on and off. The peak current counter can be reset
by setting bit D1 of instruction byte IB1 to logic 0.
To guarantee AC-load detection, an amplifier current of
more than 550 mA is required. AC-load detection will
never occur with a current of less than 150 mA. Figure 3
shows which AC loads are detected at different output
voltages. For example, if a load is detected at an output
voltage of 2.5 V peak, the load is less than 4
. If no load
is detected, the output impedance is more than 14
.
L
OAD DETECTION PROCEDURE
1. At start-up, enable the AC- or DC-load detection by
setting D1 of instruction byte 1 to logic 1.
mrc331
10
10
2
Z
o(load)
(
)
1
V
o(peak)
(V)
0
10
7.5
2.5
5
(2)
(1)
no load present
load present
undefined
Fig.3
Tolerance of AC-load detection as a
function of output voltage.
(1) I
O(peak)
= < 150 mA.
(2) I
O(peak)
= > 550 mA.

2004 Feb 24
10
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
2. After 250 ms the DC load is detected and the mute is
released. This is inaudible and can be implemented
each time the IC is powered on.
3. When the amplifier start-up cycle is completed (after
1.5 s), apply an AC signal to the input, and DC-load
bits D5 of each data byte should be read and stored by
the microcontroller.
4. After at least 3 periods of the input signal, the load
status can be checked by reading AC-detect bits D4 of
each data byte.
The AC-load peak current counter can be reset by
setting bit D1 of instruction byte IB1 to logic 0 and then
to logic 1. Note that this will also reset the DC-load
detection bits D5 in each data byte.
Low headroom protection
The normal DC output voltage of the amplifier is set to half
the supply voltage and is related to the voltage on
pin SVR. An external capacitor is connected to pin SVR to
suppress power supply ripple. If the supply voltage drops
(at vehicle engine start), the DC output voltage will follow
slowly due to the affect of the SVR capacitor.
The headroom voltage is the voltage required for correct
operation of the amplifier and is defined as the voltage
difference between the level of the DC output voltage
before the V
P
voltage drop and the level of V
P
after the
voltage drop (see Fig.4).
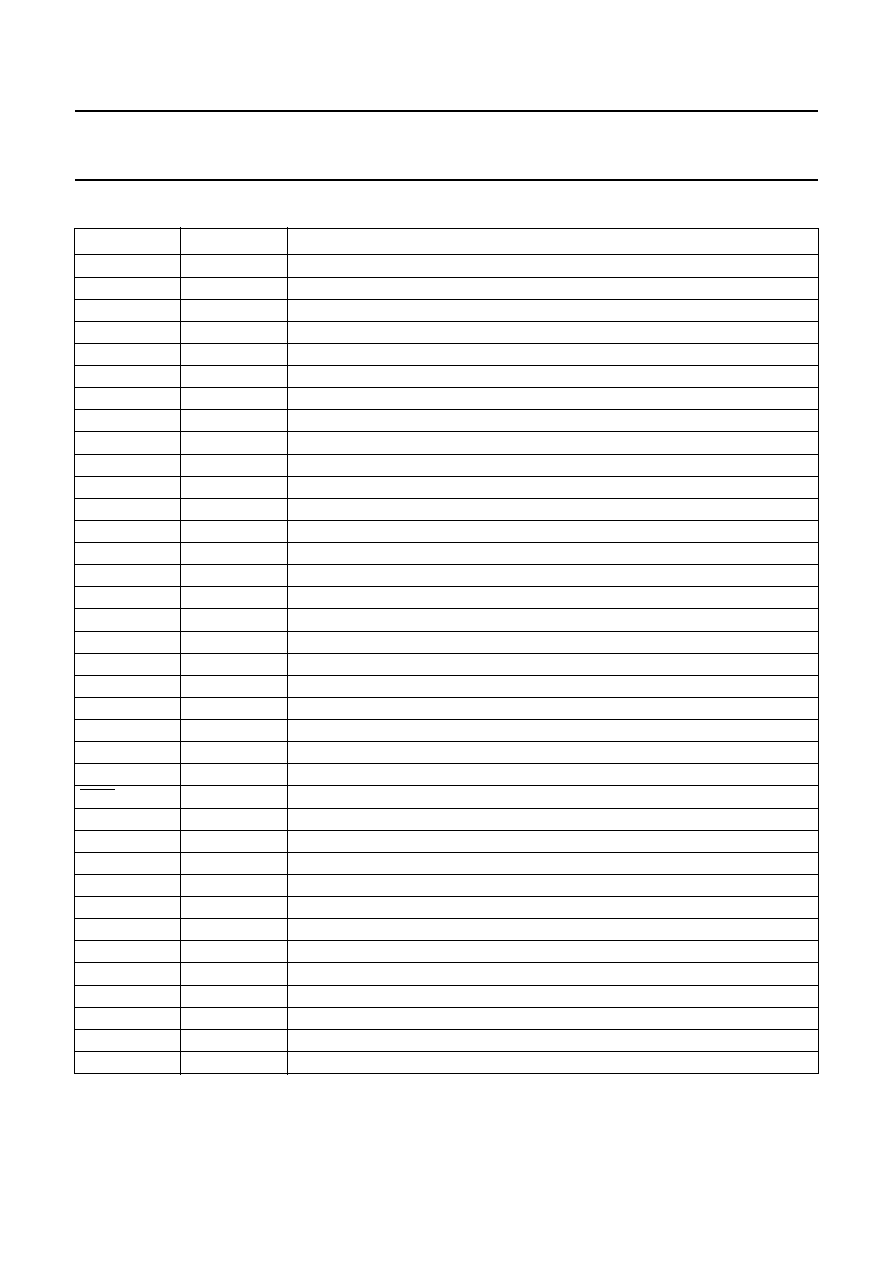
At a certain supply voltage drop, the headroom voltage will
be insufficient for correct operation of the amplifier. To
prevent unwanted audible noises at the output, the
headroom protection mode will be activated (see Fig.4).
This protection discharges the capacitors connected to
pins SVR and ACGND to increase the headroom voltage.
V
(V)
t (sec)
SVR voltage
vehicle engine start
headroom voltage
amplifier
DC output voltage
V
P
mdb515
14
8.4
7
Fig.4 Amplifier output during supply voltage.

2004 Feb 24
11
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
VOLTAGE REGULATORS
The voltage regulator section contains:
∑
Four switchable regulators and one permanent active
regulator
∑
Two power switches with loss-of-ground protection
∑
Reset push-pull output
∑
Backup functionality.
The quiescent current condition has a very low current
level of 150
µ
A typical with only regulator 2 active. The
TDA8588 uses low dropout voltage regulators for use in
low voltage applications.
All of the voltage regulators except for the standby
regulator can be controlled via the I
2
C-bus. The voltage
regulator section of this device has two power switches
which are capable of delivering unregulated 400 mA
continuous current, and has several fail-safe protection
modes. It conforms to peak transient tests and protects
against continuous high voltage (24 V), short-circuits and
thermal stress. A reset warning signal is asserted if
regulator 2 is out of regulation. Regulator 2 will try to
maintain output for as long as possible even if a thermal
shut-down or any other fault condition occurs. During
overvoltage stress conditions, all outputs except
regulator 2 will switch off and the device will be able to
supply a minimum current for an indefinite amount of time
sufficient for powering the memory of a microcontroller.
Provision is made for an external reserve supply capacitor
to be connected to pin BUCAP which can store enough
energy to allow regulator 2 to supply a microcontroller for
a period long enough for it to prepare for a loss-of-voltage.
Regulator 2
Regulator 2 is intended to supply the microcontroller and
has a low quiescent current. This supply cannot be shut
down in response to overvoltage stress conditions, and is
not I
2
C-bus controllable to prevent the microcontroller from
being damaged by overvoltage which could occur during a
disturbance of the I
2
C-bus. This supply will not shut down
during load dump transients or during a high
thermal-protection condition.
Backup capacitor
The backup capacitor is used as a backup supply for the
regulator 2 output when the battery supply voltage (V
P
)
cannot support the regulator 2 voltage.
Backup function
The backup function is implemented by a switch function,
which behaves like an ideal diode between pins V
P
and BUCAP; the forward voltage of this ideal diode
depends on the current flowing through it. The backup
function supplies regulator 2 during brief periods when no
supply voltage is present on pin V
P
. It requires an external
capacitor to be connected to pin BUCAP and ground.
When the supply voltage is present on pin V
P
this
capacitor will be charged to a level of V
P
-
0.3 V. When the
supply voltage is absent from pin V
P
, this charge can then
be used to supply regulator 2 for a brief period (t
backup
)
calculated using the formula:
Example: V
P
= 14.4 V, V
O(REG2)
= 5 V, R
L
= 1 k
and
C
backup
= 100
µ
F provides a t
backup
of 177 ms.
When an overvoltage condition occurs, the voltage on
pin BUCAP is limited to approximately 24 V; see Fig.5.
t
backup
C
backup
R
L
V
P
V
O REG2
(
)
0.5
≠
(
)
≠
V
O REG2
(
)
---------------------------------------------------------
◊
◊
=

2004 Feb 24
12
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
V
(V)
t (sec)
t
backup
out of regulation
V
O(REG2)
V
BUCAP
V
P
mdb512
Fig.5 Backup capacitor function.
t
backup
C
backup
V
P
V
O REG2
(
)
≠
0.5
≠
I
L
----------------------------------------------------
◊
=
Reset output
A reset pulse is generated at pin RST when the output
voltage of regulator 2 rises above the reset threshold
value. The reset output is a push-pull output that both
sources and sinks current. The output voltage can switch
between ground and V
O(REG2)
, and operates at a low
regulator 2 voltage or V
BUCAP
. The RST signal is controlled
by a low-voltage detection circuit which, when activated,
pulls pin RST LOW (reset active) when V
O(REG2)
is
V
th(rst)
. If V
O(REG2)
V
th(rst)
, pin RST goes HIGH. The
reset pulse is delayed by 40
µ
s internally. To extend the
delay and to prevent oscillations occurring at the threshold
voltage, an external capacitor can be connected to
pin RESCAP. Note that a reset pulse is not generated
when V
O(REG2)
falls below the reset threshold value.
Reset delay capacitor
A Reset Delay Capacitor (RDC) connected to
pin RESCAP can be used to extend the delay period of the
reset pulse and to ensure that a clean reset signal is sent
to the microcontroller. The RDC is charged by a current
source. The reset output (pin RST) will be released
(pin RST goes HIGH) when the RDC voltage crosses the
RDC threshold value.
Power switches
There are two power switches that provide an unregulated
DC voltage output for amplifiers and an aerial motor
respectively. The switches have internal protection for
over-temperature conditions and are activated by setting
bits D2 and D3 of instruction byte IB1 to logic 1. The
regulated outputs will supply pulsed current loads that can
contaminate the line with high frequency noise, so it is
important to prevent any cross-coupling between the
regulated outputs, particularly with the 8.3 V audio supply,
and the unregulated outputs.
In the ON state, the switches have a low impedance to the
battery voltage. When the battery voltage is higher than
22 V, the switches are switched off. When the battery
voltage is below 22 V the switches are set to their original
condition.
2004 Feb 24
13
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Protection
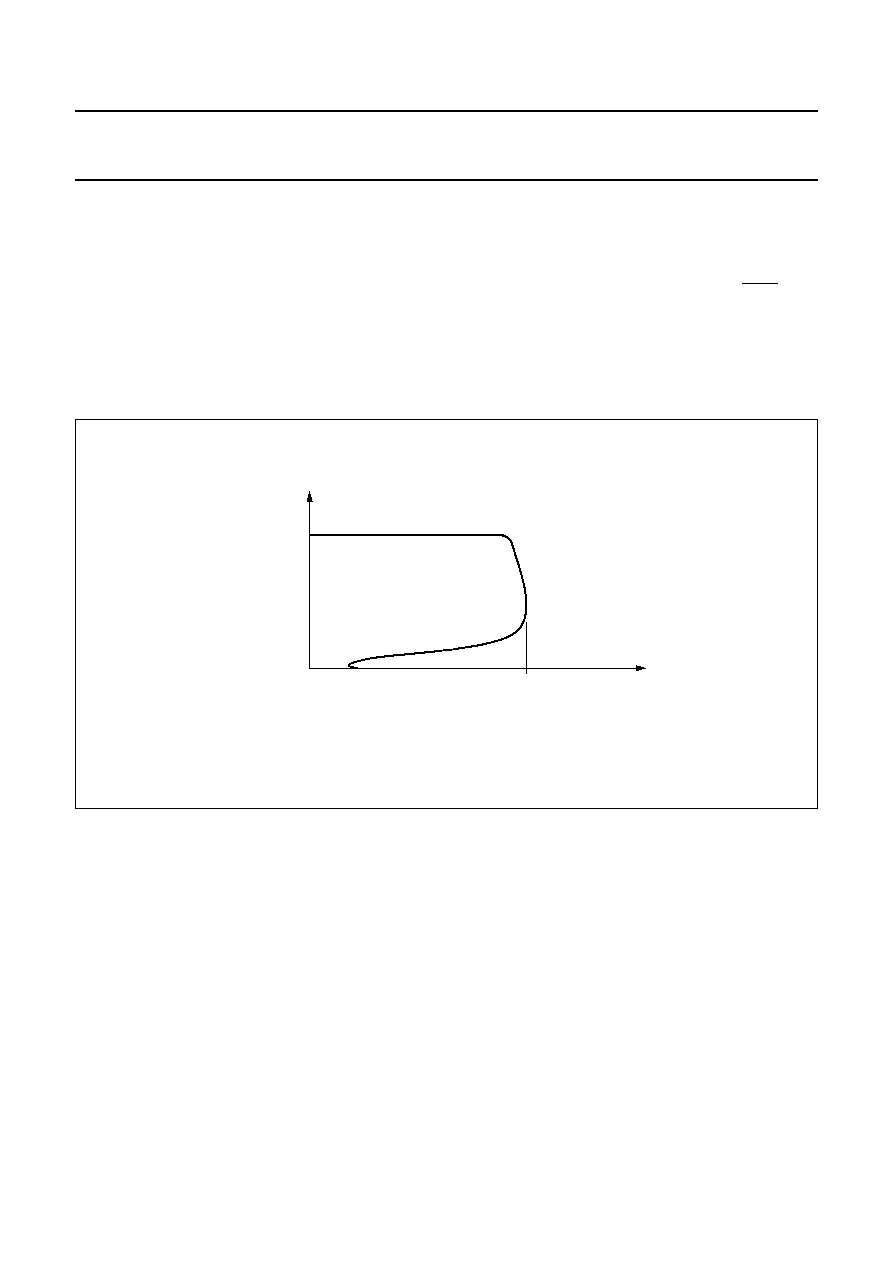
All regulator and switch outputs are fully protected by
foldback current limiting against load dumps and
short-circuits; see Fig.6. During a load dump all regulator
outputs, except the output of regulator 2, will go low.
The power switches can withstand `loss-of-ground'. This
means that if pin GND becomes disconnected, the switch
is protected by automatically connecting its outputs to
ground.
Temperature protection
If the junction temperature of a regulator becomes too
high, the amplifier(s) are switched off to prevent unwanted
noise signals being audible. A regulator junction
temperature that is too high is indicated by pin DIAG going
LOW and is also indicated by setting bit D6 in data byte 2.
If the junction temperature of the regulator continues to
rise and reaches the maximum temperature protection
level, all regulators and switches will be disabled except
regulator 2.
handbook, full pagewidth
VO(REGn)
Isc
Ilimit
IO(REGn)
MDB513
Fig.6 Foldback current protection.
2004 Feb 24
14
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
I
2
C-BUS SPECIFICATION
handbook, halfpage
MDB516
MSB
LSB
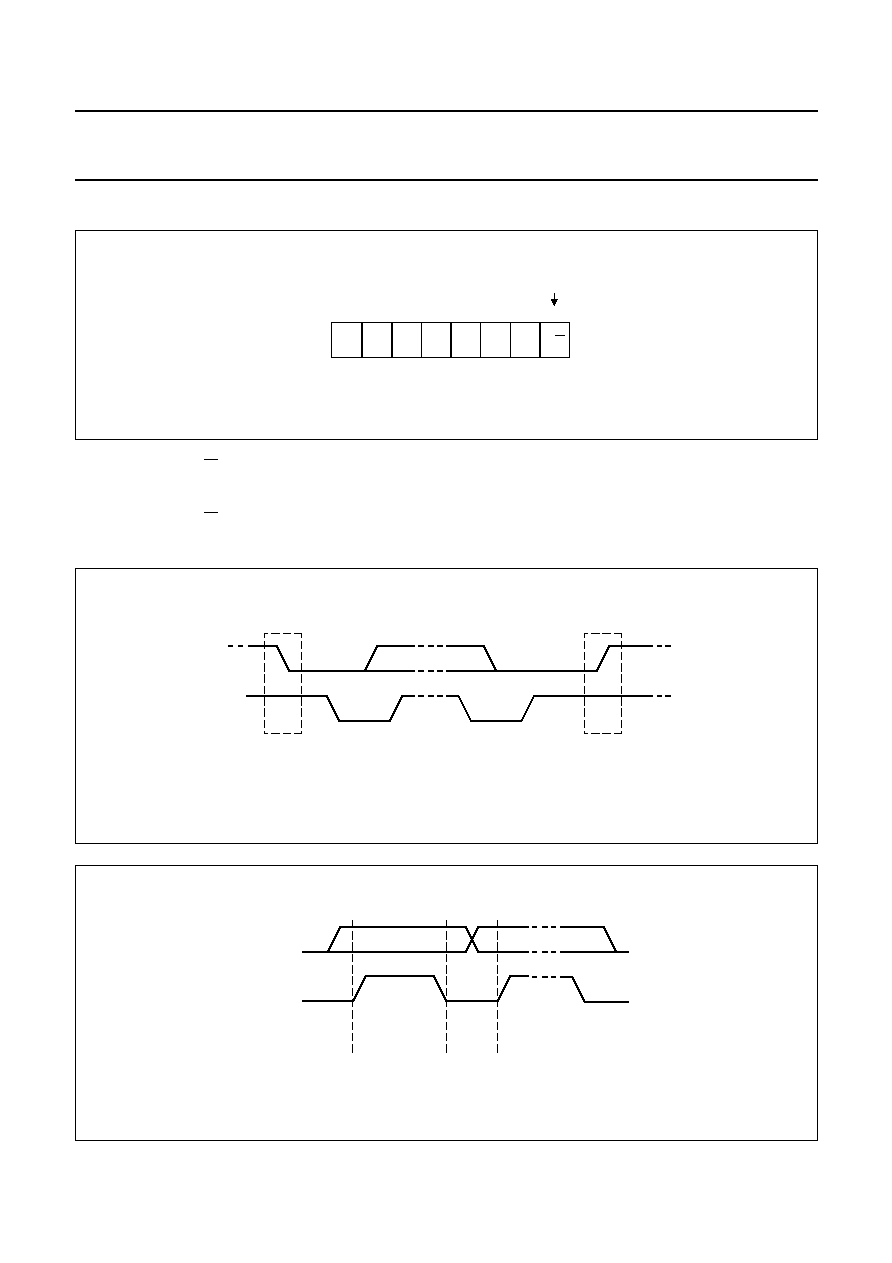
0 = write
1 = read
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
R/W
Fig.7 Address byte.
If address byte bit R/W = 0, the TDA8588 expects 3 instruction bytes: IB1, IB2 and IB3; see Table 1 to Table 6.
After a power-on, all instruction bits are set to zero.
If address byte bit R/W = 1, the TDA8588 will send 4 data bytes to the microcontroller: DB1, DB2, DB3 and DB4; see
Table 7 to Table 10.
MBA608
SDA
SCL
P
STOP condition
SDA
SCL
S
START condition
Fig.8 Definition of start and stop conditions.
MBA607
data line
stable;
data valid
change
of data
allowed
SDA
SCL
Fig.9 Bit transfer.

2004 Feb 24
15
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
mce641
ACK
MSB
MSB
-
1
MSB
MSB
-
1
LSB
+
1
LSB
LSB
+
1
1
2
7
8
9
1
2
7
8
9
1
2
7
8
9
1
2
7
8
9
: generated by master (microcontroller)
To stop the transfer, after the last acknowledge (A)
a stop condition (P) must be generated
To stop the transfer, the last byte must not be acknowledged
and a stop condition (P) must be generated
: generated by slave (TDA8588)
: start
: stop
: acknowledge
: read / write
S
P
A
R/W
SCL
SDA
SCL
SDA
ACK
ACK
MSB
MSB
-
1
MSB
MSB
-
1
LSB
+
1
LSB
LSB
+
1
ACK
S
A
A
A
P
A
P
ADDRESS
WRITE DATA
READ DATA
W
S
ADDRESS
R
I
2
C-WRITE
I
2
C-READ
Fig.10 I
2
C-bus read and write modes.

2004 Feb 24
16
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Table 1
Instruction byte IB1
Table 2
Regulator 5 (display) output voltage control
Table 3
Instruction byte IB2
Table 4
Regulator 4 (mechanical drive) output voltage
control
Table 5
Regulator 1 (audio) output voltage control
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
regulator 5 output voltage control
(see Table 2)
D6
D5
D4
D3
SW2 control
0 = SW2 off
1 = SW2 on
D2
SW1 control
0 = SW1 off
1 = SW1 on
D1
AC- or DC-load detection switch
0 = AC- or DC-load detection off; resets
DC-load detection bits and AC-load
detection peak current counter
1 = AC- or DC-load detection on
D0
amplifier start enable (clear power-on reset
flag; D7 of DB2)
0 = amplifier OFF; pin DIAG remains LOW
1 = amplifier ON; when power-on occurs,
bit D7 of DB2 is reset and pin DIAG is
released
BIT
OUTPUT (V)
D7
D6
D5
D4
0
0
0
0
0 (off)
0
0
0
1
6.0
0
0
1
0
7.0
0
0
1
1
8.2
0
1
0
0
9.0
0
1
0
1
9.5
0
1
1
0
10.0
0
1
1
1
10.4
1
0
0
0
12.5
1
0
0
1
V
P
-
1
(switch)
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
regulator 4 output voltage control (see
Table 4)
D6
D5
D4
regulator 3 (mechanical digital) control
0 = regulator 3 off
1 = regulator 3 on
D3
regulator 1 output voltage control (see
Table 5)
D2
D1
soft mute all amplifier channels (mute delay
20 ms)
0 = mute off
1 = mute on
D0
hard mute all amplifier channels (mute delay
0.4 ms)
0 = mute off
1 = mute on
BIT
OUTPUT (V)
D7
D6
D5
0
0
0
0 (off)
0
0
1
5
0
1
0
6
0
1
1
7
1
0
0
8.6
BIT
OUTPUT (V)
D3
D2
0
0
0 (off)
0
1
8.3
1
0
8.5
1
1
8.7

2004 Feb 24
17
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Table 6
Instruction byte IB3
Table 7
Data byte DB1
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
clip detection level
0 = 4 % detection level
1 = 1 % detection level
D6
amplifier channels 1 and 2 gain select
0 = 26 dB gain (normal mode)
1 = 20 dB gain (line driver mode)
D5
amplifier channels 3 and 4 gain select
0 = 26 dB gain (normal mode)
1 = 20 dB gain (line driver mode)
D4
amplifier thermal protection pre-warning
0 = warning at 145
∞
C
1 = warning at 122
∞
C
D3
disable channel 1
0 = enable channel 1
1 = disable channel 1
D2
disable channel 2
0 = enable channel 2
1 = disable channel 2
D1
disable channel 3
0 = enable channel 3
1 = disable channel 3
D0
disable channel 4
0 = enable channel 4
1 = disable channel 4
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
amplifier thermal protection pre-warning
0 = no warning
1 = junction temperature above pre-warning
level
D6
amplifier maximum thermal protection
0 = junction temperature below 175
∞
C
1 = junction temperature above 175
∞
C
D5
channel 4 DC load detection
0 = DC load detected
1 = no DC load detected
D4
channel 4 AC load detection
0 = no AC load detected
1 = AC load detected
D3
channel 4 load short-circuit
0 = normal load
1 = short-circuit load
D2
channel 4 output offset
0 = no output offset
1 = output offset
D1
channel 4 V
P
short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to V
P
1 = short-circuit to V
P
D0
channel 4 ground short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to ground
1 = short-circuit to ground

2004 Feb 24
18
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Table 8
Data byte DB2
Table 9
Data byte DB3
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
Power-on reset occurred or amplifier status
0 = amplifier on
1 = POR has occurred; amplifier off
D6
regulator thermal protection pre-warning
0 = no warning
1 = regulator temperature too high; amplifier
off
D5
channel 3 DC load detection
0 = DC load detected
1 = no DC load detected
D4
channel 3 AC load detection
0 = no AC load detected
1 = AC load detected
D3
channel 3 load short-circuit
0 = normal load
1 = short-circuit load
D2
channel 3 output offset
0 = no output offset
1 = output offset
D1
channel 3 V
P
short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to V
P
1 = short-circuit to V
P
D0
channel 3 ground short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to ground
1 = short-circuit to ground
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
-
D6
-
D5
channel 2 DC load detection
0 = DC load detected
1 = no DC load detected
D4
channel 2 AC load detection
0 = no AC load detected
1 = AC load detected
D3
channel 2 load short-circuit
0 = normal load
1 = short-circuit load
D2
channel 2 output offset
0 = no output offset
1 = output offset
D1
channel 2 V
P
short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to V
P
1 = short-circuit to V
P
D0
channel 2 ground short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to ground
1 = short-circuit to ground
2004 Feb 24
19
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Table 10 Data byte DB4
BIT
DESCRIPTION
D7
-
D6
-
D5
channel 1 DC load detection
0 = DC load detected
1 = no DC load detected
D4
channel 1 AC load detection
0 = no AC load detected
1 = AC load detected
D3
channel 1 load short-circuit
0 = normal load
1 = short-circuit load
D2
channel 1 output offset
0 = no output offset
1 = output offset
D1
channel 1 V
P
short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to V
P
1 = short-circuit to V
P
D0
channel 1 ground short-circuit
0 = no short-circuit to ground
1 = short-circuit to ground
2004 Feb 24
20
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
Notes
1. Human body model: R
s
= 1.5 k
; C = 100 pF; all pins have passed all tests to 2500 V to guarantee 2000 V,
according to class II.
2. Machine model: R
s
= 10
; C = 200 pF; L = 0.75 mH; all pins have passed all tests to 250 V to guarantee 200 V,
according to class II.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
supply voltage
operating
-
18
V
not operating
-
1
+
50
V
with load dump protection
0
50
V
V
SDA
, V
SCL
voltage on pins SDA and SCL
operating
0
7
V
V
IN
, V
SVR
,
V
ACGND
,
V
DIAG
voltage on pins INn, SVR, ACGND and DIAG operating
0
13
V
V
STB
voltage on pin STB
operating
0
24
V
I
OSM
non-repetitive peak output current
-
10
A
I
ORM
repetitive peak output current
-
6
A
V
sc
AC and DC short-circuit voltage
short-circuit of output pins across
loads and to ground or supply
-
18
V
V
rp
reverse polarity voltage
voltage regulator only
-
-
18
V
P
tot
total power dissipation
T
case
= 70
∞
C
-
80
W
T
j
junction temperature
-
150
∞
C
T
stg
storage temperature
-
55
+150
∞
C
T
amb
ambient temperature
-
40
+85
∞
C
V
esd
electrostatic discharge voltage
note 1
-
2000
V
note 2
-
200
V

2004 Feb 24
21
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
"General Quality Specification for Integrated Circuits SNW-FQ-611D".
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
VALUE
UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient
in free air
40
K/W
R
th(j-c)
thermal resistance from junction to case
see Fig.11
0.75
K/W
handbook, halfpage
MDB514
Amplifier
0.5 K
/
W
0.2 K
/
W
1 K
/
W
Voltage regulator
Virtual junction
Case
Fig.11 Equivalent thermal resistance network.
2004 Feb 24
22
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
CHARACTERISTICS
Amplifier section
T
amb
= 25
∞
C; V
P
= 14.4 V; R
L
= 4
; measured in the test circuit Fig.26; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
Supply voltage behaviour
V
P1
, V
P2
operating supply voltage
R
L
= 4
8
14.4
18
V
R
L
= 2
8
14.4
16
V
I
q(tot)
total quiescent current
no load
-
280
400
mA
I
stb
standby current
-
10
50
µ
A
V
O
DC output voltage
-
7.2
-
V
V
P(mute)
low supply voltage mute
6.5
7
8
V
V
hr
headroom voltage
when headroom protection is
activated; see Fig.4
-
1.4
-
V
V
POR
power-on reset voltage
see Fig.13
-
5.5
-
V
V
OO
output offset voltage
mute mode and power on
-
100
0
+100
mV
Mode select (pin STB)
V
stb
standby mode voltage
-
-
1.3
V
V
oper
operating mode voltage
2.5
-
5.5
V
V
mute
mute mode voltage
8
-
V
P
V
I
I
input current
V
STB
= 5 V
-
4
25
µ
A
Start-up, shut-down and mute timing
t
wake
wake-up time from standby
before first I
2
C-bus transmission
is recognised
via pin STB; see Fig.12
-
300
500
µ
s
t
mute(off)
time from amplifier switch-on to
mute release
via I
2
C-bus (IB1 bit D0);
C
SVR
= 22
µ
F; see Fig.12
-
250
-
ms
t
d(mute-on)
delay from mute to on
soft mute; via I
2
C-bus
(IB2 bit D1 = 1 to 0)
10
25
40
ms
hard mute; via I
2
C-bus
(IB2 bit D0 = 1 to 0)
10
25
40
ms
via pin STB; V
STB
= 4 to 8 V
10
25
40
ms
t
d(on-mute)
delay from on to mute
soft mute; via I
2
C-bus
(IB2 bit D1 = 0 to 1)
10
25
40
ms
hard mute; via I
2
C-bus
(IB2 bit D0 = 0 to 1)
-
0.4
1
ms
via pin STB; V
STB
= 4 to 8 V
-
0.4
1
ms
I
2
C-bus interface
V
IL
LOW-level input voltage on pins
SCL and SDA
-
-
1.5
V
V
IH
HIGH-level input voltage on pins
SCL and SDA
2.3
-
5.5
V
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage on
pin SDA
I
L
= 3 mA
-
-
0.4
V
2004 Feb 24
23
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
f
SCL
SCL clock frequency
-
-
400
kHz
Diagnostic
V
DIAG
diagnostic pin LOW output
voltage
fault condition; I
DIAG
= 200
µ
A
-
-
0.8
V
V
o(offset)
output voltage when offset is
detected
±
1.5
±
2
±
2.5
V
THD
clip
THD clip detection level
IB3 bit D7 = 0
-
4
-
%
IB3 bit D7 = 1
-
1
-
%
T
j(warn)
average junction temperature for
pre-warning
IB3 bit D4 = 0
135
145
155
∞
C
IB3 bit D4 = 1
112
122
132
∞
C
T
j(mute)
average junction temperature for
3 dB muting
V
IN
= 0.05 V
150
160
170
∞
C
T
j(off)
average junction temperature
when all outputs are switched off
165
175
185
∞
C
Z
o(load)
impedance when a DC load is
detected
-
-
6
Z
o(open)
impedance when an open DC
load is detected
500
-
-
I
o(load)
amplifier current when an AC load
is detected
550
-
-
mA
I
o(open)
amplifier current when an open
AC load is detected
-
-
150
mA
Amplifier
P
o
output power
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 14.4 V; THD = 0.5 % 20
21
-
W
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 14.4 V; THD = 10 %
27
28
-
W
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 14.4 V;
V
IN
= 2 V RMS square wave
(maximum power)
44
46
-
W
R
L
= 4
; V
P
= 15.2 V;
V
IN
= 2 V RMS square wave
(maximum power)
49
52
-
W
R
L
= 2
; V
P
= 14.4 V; THD = 0.5 % 37
41
-
W
R
L
= 2
; V
P
= 14.4 V; THD = 10 %
51
55
-
W
R
L
= 2
; V
P
= 14.4 V;
V
IN
= 2 V RMS square wave
(maximum power)
83
87
-
W
THD
total harmonic distortion
P
o
= 1 W to 12 W; f = 1 kHz;
R
L
= 4
-
0.01
0.1
%
P
o
= 1 W to 12 W; f = 10 kHz
-
0.2
0.5
%
P
o
= 4 W; f = 1 kHz
-
0.01
0.03
%
line driver mode; V
o
= 2 V (RMS);
f = 1 kHz; R
L
= 600
-
0.01
0.03
%
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT

2004 Feb 24
24
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Voltage regulator section
T
amb
= 25
∞
C; V
P
= 14.4 V; measured in the test circuit Fig.26; unless otherwise specified.
cs
channel separation (crosstalk)
f = 1 Hz to 10 kHz; R
source
= 600
50
60
-
dB
P
o
= 4 W; f = 1 kHz
-
80
-
dB
SVRR
supply voltage ripple rejection
f = 100 Hz to 10 kHz;
R
source
= 600
55
70
-
dB
CMRR
common mode ripple rejection
amplifier mode;
V
common
= 0.3 V (p-p);
f = 1 kHz to 3 kHz; R
source
= 0
40
70
-
dB
V
cm(max)(rms)
maximum common mode voltage
level (rms value)
f = 1 kHz
-
-
0.6
V
V
n(o)(LN)
noise output voltage in line driver
mode
filter 20 Hz to 22 kHz;
R
source
= 600
-
25
35
µ
V
V
n(o)(amp)
noise output voltage in amplifier
mode
filter 20 Hz to 22 kHz;
R
source
= 600
-
50
70
µ
V
G
v(amp)
voltage gain in amplifier mode
single-ended in to differential out
25
26
27
dB
G
v(LN)
voltage gain in line driver mode
single-ended in to differential out
19
20
21
dB
Z
i
input impedance
C
IN
= 220 nF
55
70
-
k
mute
mute attenuation
V
O(on)
/V
O(mute)
80
90
-
dB
V
o(mute)
output voltage mute
V
IN
= 1 V (RMS)
-
70
-
µ
V
B
p
power bandwidth
-
1 dB; THD = 1 %
-
20
-
kHz
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
Supply
V
P
supply voltage
regulator 1, 3, 4 and 5 on
10.0
14.4
18
V
regulator 2
switched on
4
-
-
V
in regulation
6.3
-
50
V
overvoltage for shut-down
18.1
22
-
V
I
q(tot)
total quiescent supply
current
standby mode; note 1
-
150
190
µ
A
Reset output (push-pull stage, pin RST)
V
REG2(th)(r)
rising threshold voltage
of regulator 2
V
P
is rising;
I
O(REG2)
= 50 mA
V
O(REG2)
-
0.2
V
O(REG2)
-
0.1
V
O(REG2)
-
0.04
V
V
REG2(th)(f)
falling threshold voltage
of regulator 2
V
P
is falling;
I
O(REG2)
= 50 mA
V
O(REG2)
-
0.25
V
O(REG2)
-
0.15
V
O(REG2)
-
0.1
V
I
sink(L)
LOW-level sink current
V
RST
0.8 V
1
-
-
mA
I
source(H)
HIGH-level source
current
V
RST
= V
O(REG2)
-
0.5 V;
V
P
= 14.4 V
200
600
-
µ
A
t
r
rise time
note 2
-
2
50
µ
s
t
f
fall time
note 2
-
10
50
µ
s
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT

2004 Feb 24
25
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Reset delay (pin RESCAP)
I
ch
charge current
V
RESCAP
= 0 V
1
4
8
µ
A
I
dch
discharge current
V
RESCAP
= 3 V; V
P
4.3 V
1
7
-
mA
V
th(rst)
reset signal threshold
voltage
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588J
2.5
3
3.5
V
TDA8588BJ
1.6
2.1
2.6
V
t
d(rst)
reset signal delay
without C
RESCAP
; note 3
-
40
-
µ
s
C
RESCAP
= 47 nF; note 3;
see Fig.15
15
35
100
ms
Regulator 1: REG1 (audio; I
O
= 5 mA)
V
O(REG1)
output voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA;
12 V < V
P
< 18 V;
IB2[D3:D2] = 01
7.9
8.3
8.7
V
IB2[D3:D2] = 10
8.1
8.5
8.9
V
IB2[D3:D2] = 11
8.3
8.7
9.1
V
V
O(LN)
line regulation voltage
12 V
V
P
18 V
-
-
50
mV
V
O(load)
load regulation voltage
5 mA
I
O
400 mA
-
-
100
mV
SVRR
supply voltage ripple
rejection
f
ripple
= 120 Hz;
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p)
50
60
-
dB
V
drop
dropout voltage
V
P
= 7.5 V; note 4
I
O
= 200 mA
-
0.4
0.8
V
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.6
2.5
V
I
limit
current limit
V
O
7 V; note 5
400
700
-
mA
I
sc
short-circuit current
R
L
0.5
; note 6
70
190
-
mA
Regulator 2: REG2 (microprocessor; I
O
= 5 mA)
V
O(REG2)
output voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
350 mA;
10 V
V
P
18 V
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588J
4.75
5.0
5.25
V
TDA8588BJ
3.1
3.3
3.5
V
V
O(LN)
line regulation voltage
10 V
V
P
18 V
-
3
50
mV
V
O(load)
load regulation voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
300 mA
-
-
100
mV
SVRR
supply voltage ripple
rejection
f
ripple
= 120 Hz;
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p)
40
50
-
dB
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT

2004 Feb 24
26
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
V
drop
dropout voltage
I
O
= 200 mA
V
BUCAP
= 4.75 V; note 7
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588J
-
0.5
0.8
V
TDA8588BJ
-
1.75
2
V
I
O
= 350 mA;
V
BUCAP
= 4.75 V; note 7
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588J
-
0.5
1.3
V
TDA8588BJ
-
1.75
2.7
V
I
limit
current limit
V
O
2.8 V; note 5
400
1000
-
mA
I
sc
short-circuit current
R
L
0.5
; note 6
160
300
-
mA
Regulator 3: REG3 (mechanical digital; I
O
= 5 mA)
V
O(REG3)
output voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
300 mA;
10 V
V
P
18 V
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588BJ
3.1
3.3
3.5
V
TDA8588J
4.75
5.0
5.25
V
V
O(LN)
line regulation voltage
10 V
V
P
18 V
-
3
50
mV
V
O(load)
load regulation voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
300 mA
-
-
100
mV
SVRR
supply voltage ripple
rejection
f
ripple
= 120 Hz;
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p)
50
65
-
dB
V
drop
dropout voltage
V
P
= 4.75 V; I
O
= 200 mA;
note 4
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588BJ
-
1.45
1.65
V
TDA8588J
-
0.4
0.8
V
V
P
= 4.75 V; I
O
= 300 mA;
note 4
TDA8588AJ and
TDA8588BJ
-
1.45
1.65
V
TDA8588J
-
0.4
1.5
V
I
limit
current limit
V
O
2.8 V; note 5
400
700
-
mA
I
sc
short-circuit current
R
L
0.5
; note 6
135
210
-
mA
Regulator 4: REG4 (mechanical drive; I
O
= 5 mA)
V
O(REG4)
output voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
800 mA;
10 V
V
P
18 V
IB2[D7:D5] = 001
4.75
5.0
5.25
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 010
5.7
6.0
6.3
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 011
6.6
7.0
7.4
V
IB2[D7:D5] = 100
8.1
8.6
9.1
V
V
O(LN)
line regulation voltage
10 V
V
P
18 V
-
3
50
mV
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT

2004 Feb 24
27
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
V
O(load)
load regulation voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA
-
-
100
mV
SVRR
supply voltage ripple
rejection
f
ripple
= 120 Hz;
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p)
50
65
-
dB
V
drop
dropout voltage
V
P
= V
O(REG4)
-
0.5 V;
I
O
= 800 mA; note 4
-
0.6
1
V
I
O(peak)
peak output current
t
3 s; V
O
= 4 V
1
1.5
-
A
I
limit
limit current
V
O
4 V; t
100 ms;
V
P
11.5 V; note 5
1.5
2
-
A
I
sc
short-circuit current
R
L
0.5
; note 6
240
400
-
mA
Regulator 5: REG5 (display; I
O
= 5 mA)
V
O(REG5)
output voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA
10 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0001
5.7
6.0
6.3
V
10 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0010
6.65
7.0
7.37
V
10 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0011
7.8
8.2
8.6
V
10.5 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0100
8.55
9.0
9.45
V
11 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0101
9.0
9.5
10.0
V
11.5 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0110
9.5
10.0
10.5
V
13 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 0111
9.9
10.4
10.9
V
14.2 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 1000
11.8
12.5
13.2
V
12.5 V
V
P
18 V;
IB1[D7:D4] = 1001
V
P
-
1
-
-
V
V
O(LN)
line regulation voltage
10 V
V
P
18 V
-
3
50
mV
V
O(load)
load regulation voltage
0.5 mA
I
O
400 mA
-
-
100
mV
SVRR
supply voltage ripple
rejection
f
ripple
= 120 Hz;
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p)
50
60
-
dB
V
drop
dropout voltage
V
P
= V
O(REG5)
-
0.5 V;
note 4
I
O
= 300 mA
-
0.4
0.8
V
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.5
2.3
V
I
limit
limit current
V
O
5.5 V; note 5
400
950
-
mA
I
sc
short-circuit current
R
L
0.5
; note 6
100
200
-
mA
Power switch 1: SW1 (antenna)
V
drop(SW1)
dropout voltage
I
O
= 300 mA
-
0.6
0.8
V
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.6
1.1
V
I
limit
limit current
V
8.5 V
0.5
1
-
A
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT

2004 Feb 24
28
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Notes
1. The quiescent current is measured in standby mode when R
L
=
.
2. The rise and fall times are measured with a 50 pF load capacitor.
3. The reset delay time depends on the value of the reset delay capacitor:
4. The dropout voltage of a regulator is the voltage difference between V
P
and V
O(REGn)
.
5. At current limit, V
O(REGn)
is held constant (see Fig.6).
6. The foldback current protection limits the dissipation power at short-circuit (see Fig.6).
7. The dropout voltage of regulator 2 is the voltage difference between V
BUCAP
and V
O(REG2)
.
Power switch 2: SW2 (amplifier)
V
drop(SW2)
dropout voltage
I
O
= 300 mA
-
0.6
0.8
V
I
O
= 400 mA
-
0.6
1.1
V
I
limit
limit current
V
O
8.5 V
0.5
1
-
A
Backup switch
I
DC(BU)
continuous current
V
BUCAP
6 V
0.4
1.5
-
A
V
clamp(BU)
clamping voltage
V
P
= 30 V;
I
O(REG2)
= 100 mA
-
24
28
V
V
drop
dropout voltage
I
O
= 500 mA;
(V
P
-
V
BUCAP
)
-
0.6
0.8
V
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
t
d rst
(
)
C
RESCAP
I
ch
------------------------
V
th rst
(
)
◊
=
C
RESCAP
750
10
3
◊
(
)
◊
s
[ ]
=
2004 Feb 24
29
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
mrc350
V
p
DIAG
Amplifier status
DB2 bit D7
V
O(REG3)
IB1 bit D0
IB2 bit D4
SVR
STB
Amplifier
output
t
mute(off)
t
wake
Regulator switched off
when amplifier is
completely muted
Soft
mute
Soft
mute
Fig.12 Start-up and shut-down timing.
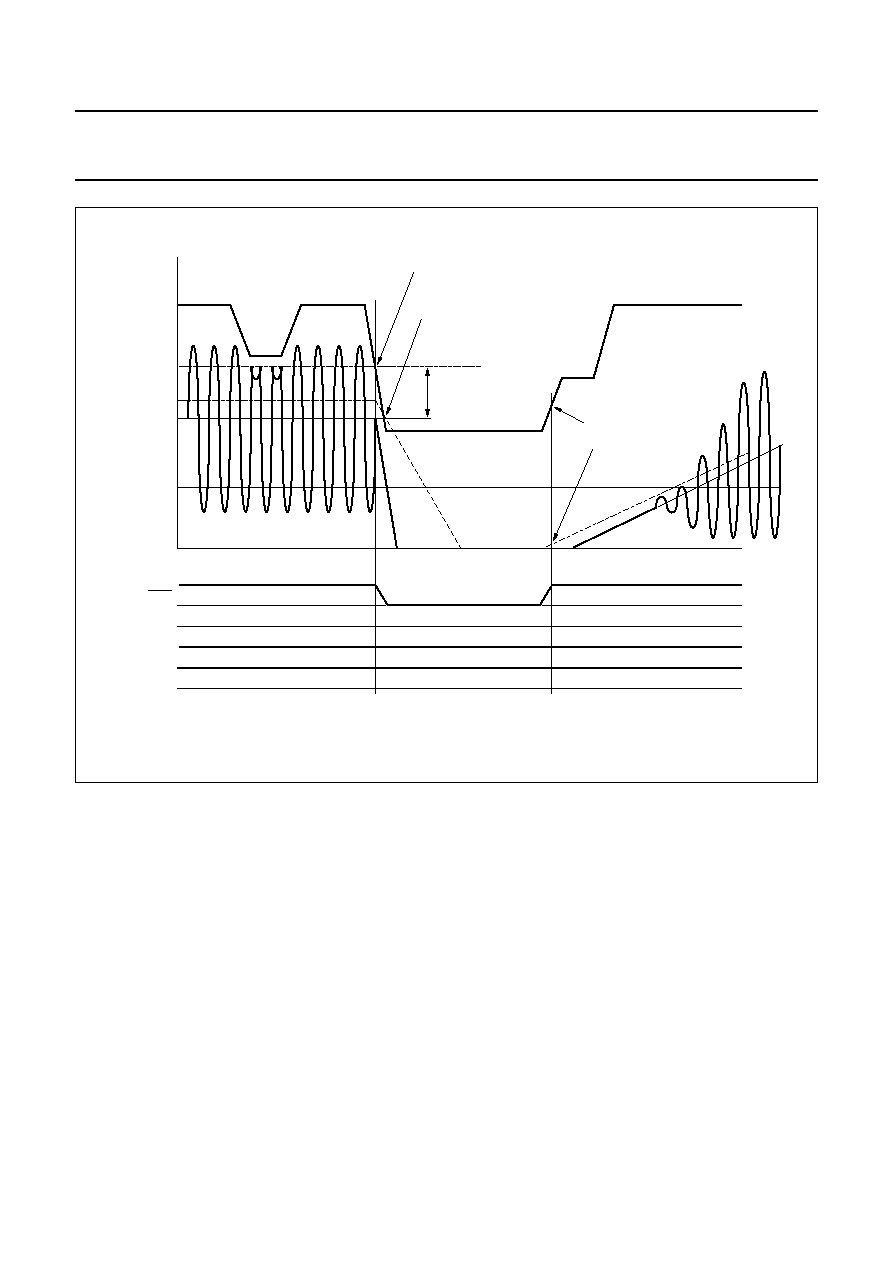
2004 Feb 24
30
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
handbook, full pagewidth
MRC348
VO
(V)
Headroom voltage
14.4
8.8
8.6
7.2
3.5
Vp
Low Vp mute activated
Headroom protection activated:
1) fast mute
2) discharge of SVR
SVR voltage
Output
voltage
Low Vp mute released
DIAG
DB2 bit D7
VO(REG3)
Fig.13 Low V
P
behaviour at V
P
> 5.5 V.

2004 Feb 24
31
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
POR activated
14.4
8.8
8.6
7.2
3.5
V
p
Low V
p
mute activated
SVR voltage
DIAG
DB2 bit D7
V
O(REG3)
5.5
POR has occured
mrc349
V
O
(V)
Fig.14 Low V
P
behaviour at V
P
< 5.5 V.
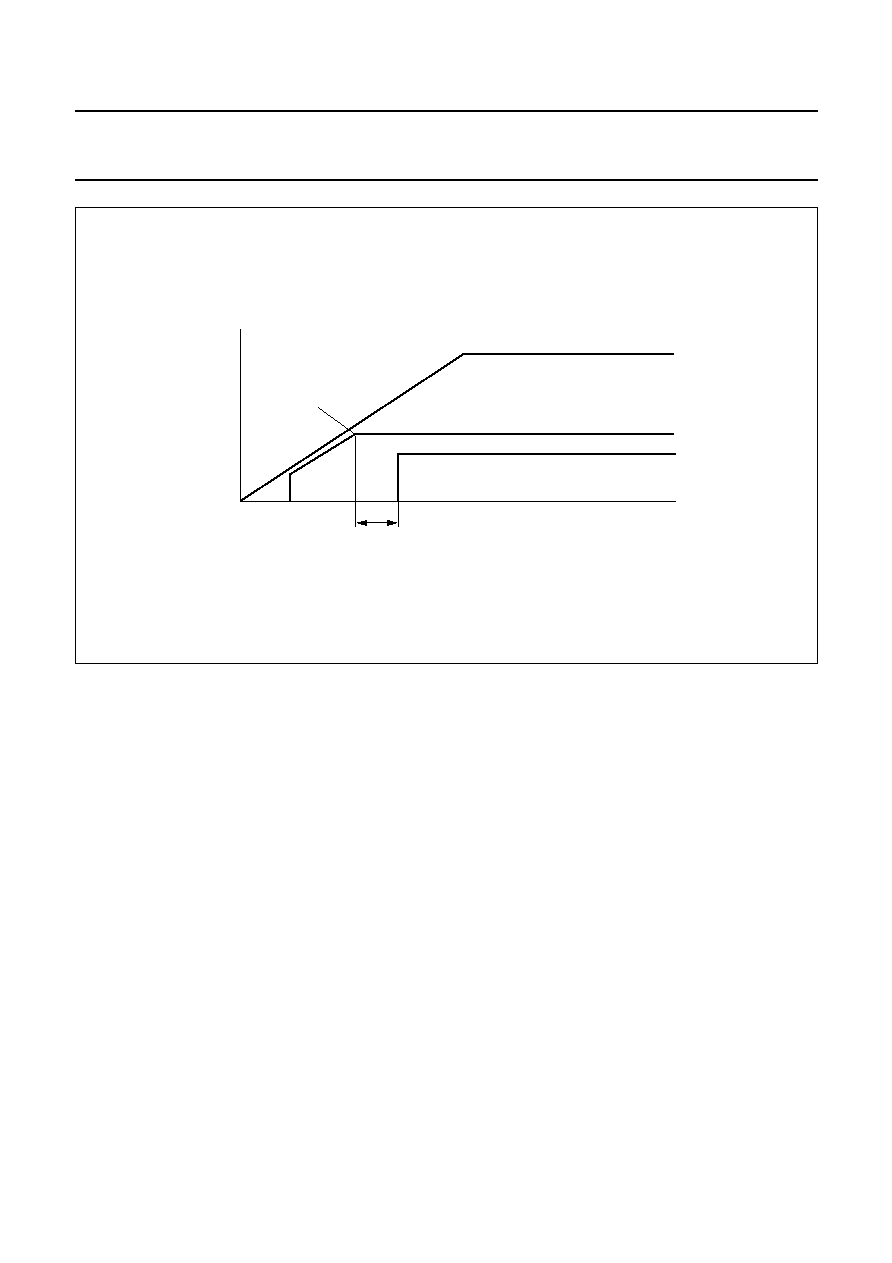
2004 Feb 24
32
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
mdb511
V
(V)
t (sec)
t
d(rst)
V
th(rst)
V
O(REG2)
V
P
V
RST
Fig.15 Reset delay function.

2004 Feb 24
33
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Performance diagrams
THD
AS A FUNCTION OF OUTPUT POWER
P
o
AT DIFFERENT FREQUENCIES
handbook, full pagewidth
10
2
10
1
10
-
1
10
-
2
10
-
3
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
10
2
MRC345
Po (W)
THD
(%)
(2)
(1)
(3)
Fig.16 THD as a function of P
o
.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
(1) f = 10 kHz.
(2) f = 1 kHz.
(3) f = 100 Hz.
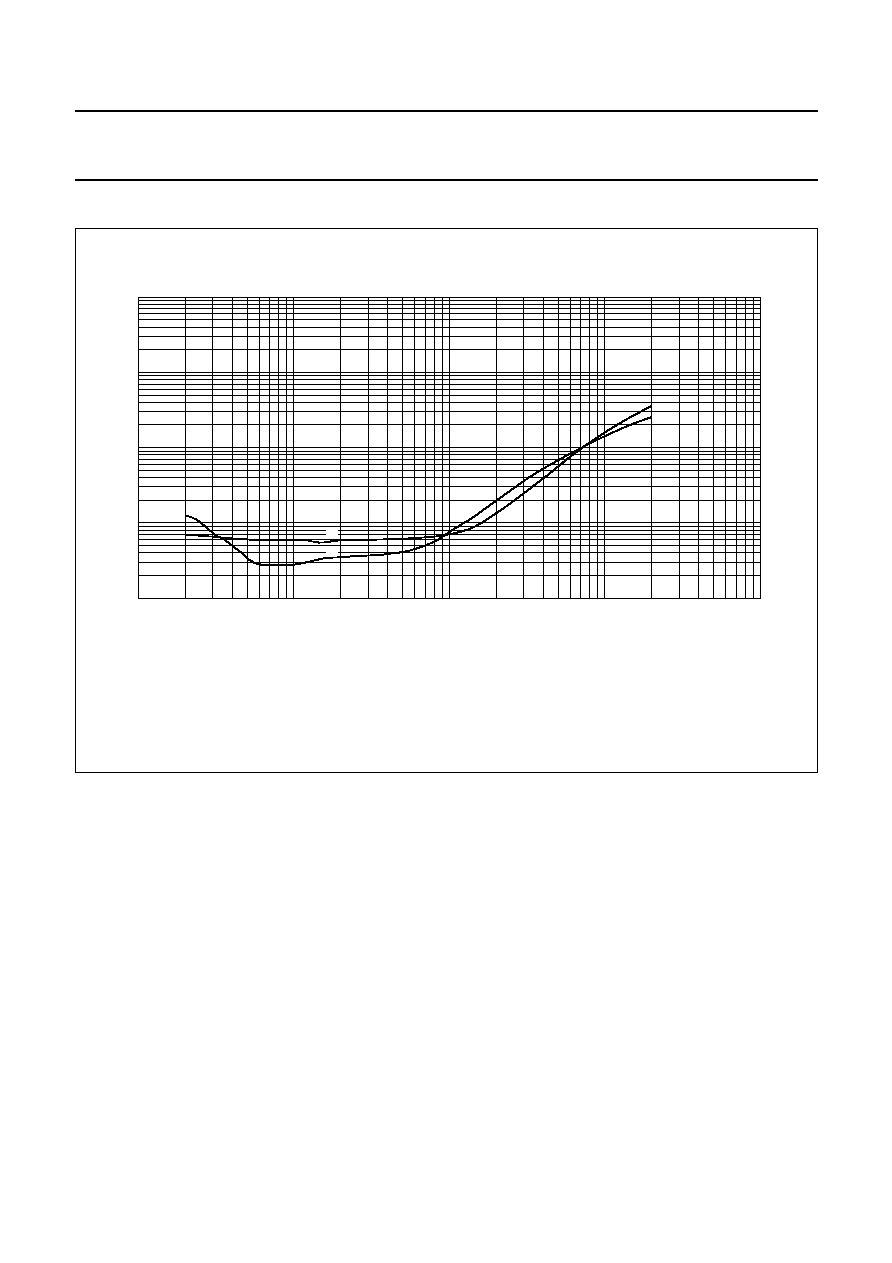
2004 Feb 24
34
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
THD
AS A FUNCTION OF FREQUENCY AT DIFFERENT OUTPUT POWERS
handbook, full pagewidth
MRC344
10
1
10
-
1
10
-
2
10
-
3
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
10
2
(2)
(1)
f (kHz)
THD
(%)
Fig.17 THD as a function of frequency.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
(1) P
o
= 1 W.
(2) P
o
= 10 W.

2004 Feb 24
35
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
L
INE DRIVER MODE
handbook, full pagewidth
MRC329
10
-
1
1
10
1
10
-
1
10
-
2
10
-
3
Vo(rms)
THD
(%)
10
2
(V)
Fig.18 THD as a function of V
o
in balanced line driver mode.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 600
.
f = 1 kHz.

2004 Feb 24
36
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
O
UTPUT POWER AS A FUNCTION OF FREQUENCY AT DIFFERENT
THD
LEVELS
handbook, full pagewidth
20
30
22
24
26
28
MRC330
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
10
2
f (kHz)
Po
(W)
(1)
(2)
(3)
Fig.19 P
o
as a function of frequency; R
L
= 4
.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
(1) THD = 10 %.
(2) THD = 5 %.
(3) THD = 0.5 %.

2004 Feb 24
37
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
handbook, full pagewidth
35
60
40
45
50
55
MRC335
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
10
2
f (kHz)
Po
(W)
(1)
(3)
(2)
Fig.20 P
o
as a function of frequency; R
L
= 2
.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
(1) THD = 10 %.
(2) THD = 5 %.
(3) THD = 0.5 %.

2004 Feb 24
38
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
O
UTPUT POWER
(P
O
)
AS A FUNCTION OF SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(V
P
)
001aaa283
40
60
20
80
100
P
o
(W)
0
V
P
(V)
8
20
16
12
10
18
14
(1)
(2)
(3)
Fig.21 P
o
as a function of supply voltage; R
L
= 4
.
(1) Maximum power.
(2) THD = 10 %.
(3) THD = 0.5 %.
f = 1 kHz.

2004 Feb 24
39
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
handbook, full pagewidth
20
100
0
8
12
16
20
40
60
80
MRC332
Vp (V)
Po
(W)
(1)
(2)
(3)
Fig.22 P
o
as a function of supply voltage; R
L
= 2
.
(1) Maximum power.
(2) THD = 10 %.
(3) THD = 0.5 %.
f = 1 kHz.

2004 Feb 24
40
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
S
UPPLY VOLTAGE RIPPLE REJECTION IN OPERATING AND MUTE MODES
handbook, full pagewidth
60
80
64
68
72
76
MRC333
10
-
1
1
10
f (kHz)
SVRR
(dB)
(1)
(2)
Fig.23 SVRR as a function of frequency.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
V
ripple
= 2 V (p-p).
R
source
= 600
.
(1) Operating mode.
(2) Mute mode.
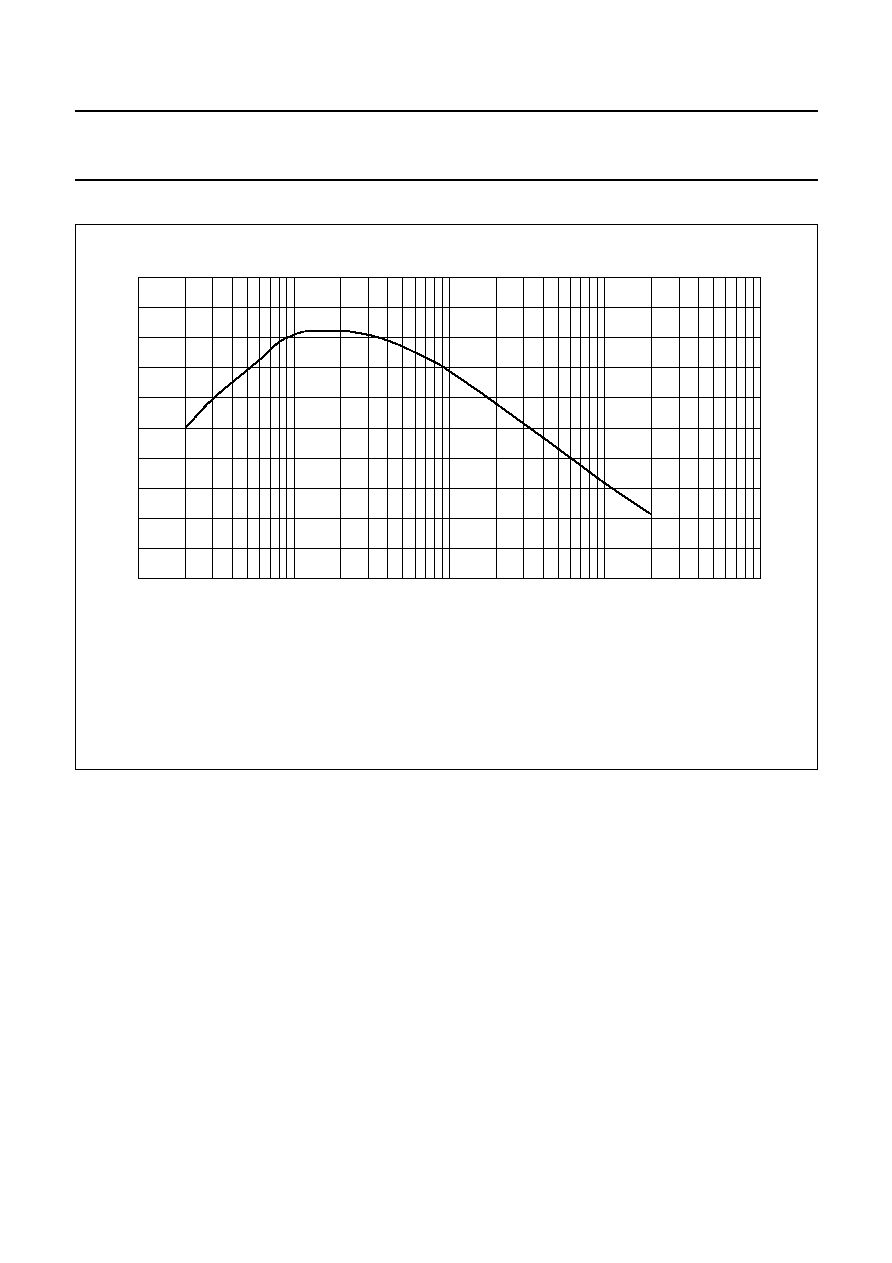
2004 Feb 24
41
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
C
HANNEL SEPARATION AS A FUNCTION OF FREQUENCY
handbook, full pagewidth
50
100
60
70
80
90
MRC351
10
-
2
10
-
1
1
10
f (kHz)
cs
(dB)
10
2
Fig.24 Channel separation.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
P
o
= 4 W.
R
source
= 600
.

2004 Feb 24
42
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
P
OWER DISSIPATION AND EFFICIENCY
handbook, full pagewidth
30
50
0
0
10
20
10
20
30
40
MRC342
Po (W)
Ptot
(W)
Fig.25 Amplifier dissipation as a function of output power; all channels driven.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
f = 1 kHz.

2004 Feb 24
43
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
handbook, full pagewidth
40
100
0
0
8
16
24
32
20
40
60
80
MRC343
Po (W)
(%)
Fig.26 Amplifier efficiency as a function of output power; all channels driven.
V
P
= 14.4 V.
R
L
= 4
.
f = 1 kHz.

2004 Feb 24
44
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
APPLICATION AND TEST INFORMATION
mdb587
V
reg2
40
µ
s
BACKUP
SWITCH
ENABLE
LOGIC
STANDBY/ MUTE
I
2
C-BUS
INTERFACE
CLIP DETECT/ DIAGNOSTIC
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
TEMPERATURE &
LOAD DUMP
PROTECTION VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
REGULATOR 1
REGULATOR 3
REGULATOR 2
REGULATOR 4
REGULATOR 5
SWITCH 1
SWITCH 2
MUTE
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
26 dB/
20 dB
PROTECTION/
DIAGNOSTIC
TEMPERATURE & LOAD
DUMP PROTECTION
AMPLIFIER
26 dB/
20 dB
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
35
28
27
26
20
6
25
9
7
17
19
5
3
21
23
16
8
13
SGND
SVR
IN4
IN3
IN2
IN1
STB
SCL
SDA
RESCAP
V
P
BUCAP
ACGND
PGND1 PGND2/TAB PGND3 PGND4
10
14
12
15
11
22
4
2
1
18
24
32
29
34
33
31
30
37
REG2
REG1
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
REG3
REG4
REG5
SW1
SW2
RST
V
P1
DIAG
OUT1
+
OUT1
-
OUT2
+
OUT2
-
OUT3
+
OUT3
-
OUT4
+
OUT4
-
V
P2
microcontroller
microcontroller
14.4 V
aerial
motor
amplifiers
display
mechanical
drive
mechanical
digital
audio
microcontroller
GND
36
V
P
1000
µ
F
(16 V)
220 nF
220
µ
F
(16 V)
14.4 V
220 nF
47 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
100 nF
10
µ
F
(50 V)
10 k
100 nF
RS
470 nF
RS
470 nF
RS
470 nF
RS
470 nF
2.2
µ
F
(4
◊
470 nF)
22
µ
F
TDA8588
220
nF
220
nF
2200
µ
F
(16 V)
(1)
Fig.26 Test and application diagram.
ACGND capacitor value must be close to 4
◊
input capacitor value.
For EMC reasons, a capacitor of 10 nF can be connected between each amplifier output and ground.
(1) See "Supply decoupling".

2004 Feb 24
45
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Supply decoupling
(see Fig.26)
The high frequency 220 nF decoupling capacitors connected to power supply voltage pins 6 and 20 should be located
as close as possible to these pins.
It is important to use good quality capacitors. These capacitors should be able to suppress high voltage peaks that can
occur on the power supply if several audio channels are accidentally shorted to the power supply simultaneously, due to
the activation of current protection. Good results have been achieved using 0805 case-size capacitors (X7R material,
220 nF) located close to power supply voltage pins 6 and 20.
2004 Feb 24
46
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
PCB layout
handbook, full pagewidth
MDB533
Fig.27 Top of printed-circuit board layout of test and application circuit showing copper layer viewed from top.
handbook, full pagewidth
MDB534
Fig.28 Bottom of printed-circuit board layout of test and application circuit showing copper layer viewed from top.

2004 Feb 24
47
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
mdb588
CBU
REG3
REG1
SW1
SW2
RGND
1000
µ
F
220
µ
F
22
µ
F
2200
µ
F
2.2
µ
F
10
µ
F (50 V)
10
µ
F (50 V)
10
µ
F (50 V)
10
µ
F (50 V)
10
µ
F (50 V)
10
µ
F
Mode
DZ 5.6 V
470 nF
I
2
C supply
DIAG
GND
GND
Sense
SDA
+ 5 V
GND
SCL
V
P
V
P
4.7 k
470 nF
OUT
OUT
IN
SGND
RST
RESCAP
RESCAP
47 nF
on
off
on
off
REG2
REG5
REG4
TDA8588J
Fig.29 Top of printed-circuit board layout of test and application circuit showing components viewed from top.
handbook, full pagewidth
MDB536
100 nF
100 nF
100 nF
100 nF
10 k
47 k
220 nF
220 nF
220 nF
Fig.30 Bottom of printed-circuit board layout of test and application circuit showing components viewed from
bottom.

2004 Feb 24
48
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
Beep input circuit
Beep input circuit to amplify the beep signal from the microcontroller to all 4 amplifiers (gain = 0 dB). Note that this circuit
will not affect amplifier performance.
Noise
The outputs of regulators 1 to 5 are designed to give very low noise with good stability. The noise output voltage depends
on output capacitor C
o
. Table 11 shows the affect of the output capacitor on the noise figure.
Table 11 Regulator noise figures
Note
1. Measured in the frequency range 20 Hz to 80 kHz.
Stability
The regulators are made stable by connecting capacitors to the regulator outputs. The stability can be guaranteed with
almost any output capacitor if its Electric Series Resistance (ESR) stays below the ESR curve shown in Fig.32. If an
electrolytic capacitor is used, its behaviour with temperature can cause oscillations at extremely low temperature.
Oscillation problems can be avoided by adding a 47 nF capacitor in parallel with the electrolytic capacitor. The following
example describes how to select the value of output capacitor.
REGULATOR
NOISE FIGURE (
µ
V) at I
REG
= 10 mA; note 1
C
o
= 10
µ
F
C
o
= 47
µ
F
C
o
= 100
µ
F
1
225
195
185
2
750
550
530
3
120
100
95
4
225
195
185
5
320
285
270
mdb589
From
microcontroller
1.7 k
0.22
µ
F
100
2.2
µ
F
47 pF
TDA8588
ACGND
Fig.31 Application diagram for beep input.
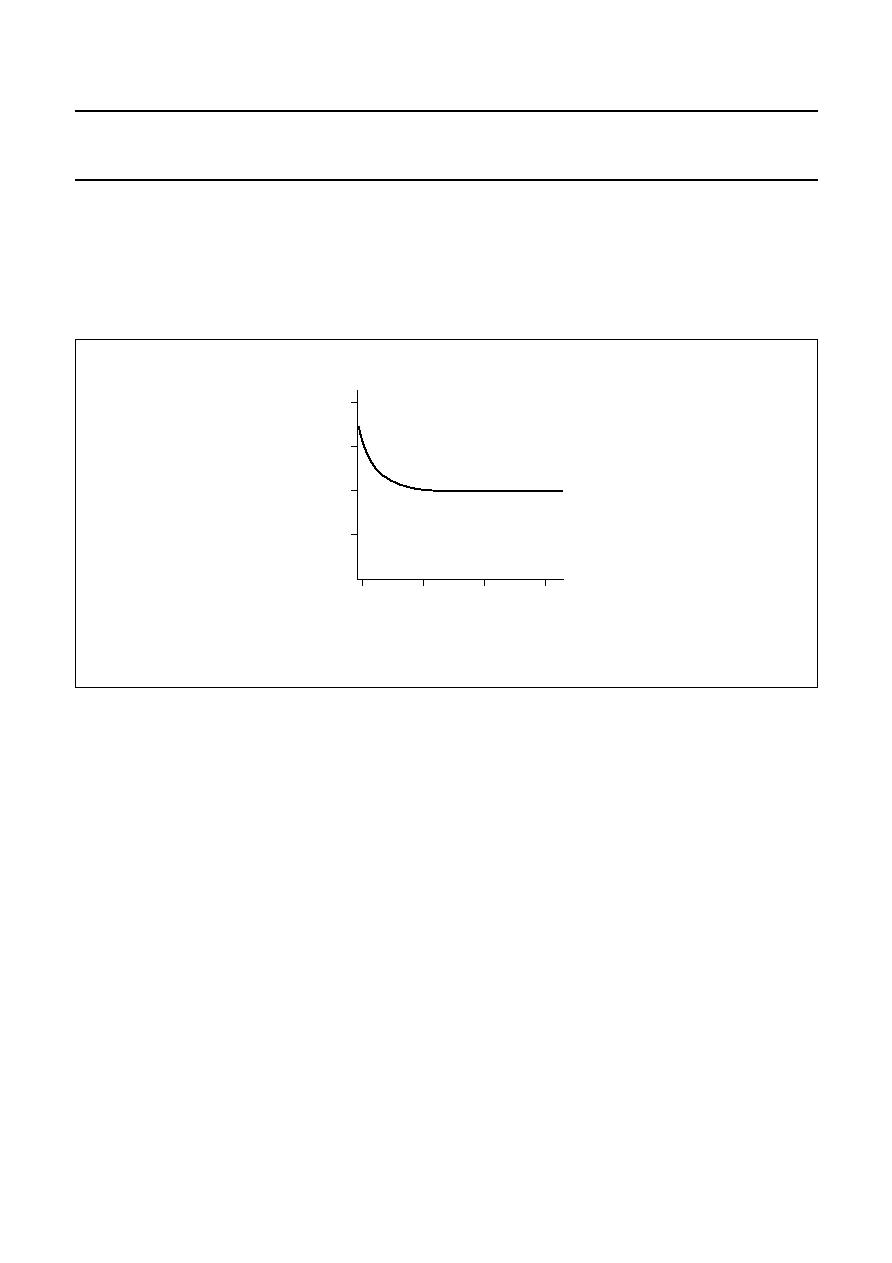
2004 Feb 24
49
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
E
XAMPLE REGULATOR
2
Regulator 2 is stabilized with an electrolytic output capacitor of 10
µ
F which has an ESR of 4
. At T
amb
=
-
30
∞
C the
capacitor value decreases to 3
µ
F and its ESR increases to 28
which is above the maximum allowed as shown
in Fig.32, and which will make the regulator unstable. To avoid problems with stability at low temperatures, the
recommended solution is to use tantalum capacitors. Either use a tantalum capacitor of 10
µ
F, or an electrolytic capacitor
with a higher value.
handbook, halfpage
0
0.1
1
10
C (
µ
F)
MGL912
stable region
maximum ESR
100
ESR
(
)
20
15
10
5
Fig.32 Curve for selecting the value of output capacitors for regulators 1 to 5.

2004 Feb 24
50
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT
A
D
(1)
E
(1)
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC
JEDEC
JEITA
mm
19
A2
4.65
4.35
bp
0.60
0.45
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
SOT725-1
- - -
- - -
- - -
0
10
20 mm
scale
L
E
A
c
A2
m
L3
L4
L2
Q
w
M
bp
d
Z
e1
e2
e
1
37
DBS37P: plastic DIL-bent-SIL power package; 37 leads (lead length 6.8 mm)
SOT725-1
v
M
D
x
h
Eh
non-concave
view B: mounting base side
B
D
c
Z
(1)
d
e
e1
e2
L3
Dh
Eh
L
m
0.5
0.3
42.2
41.7
37.8
37.4
12
2
15.9
15.5
1
4
1.15
0.85
L2
3.9
3.1
L4
22.9
22.1
8
3.30
2.65
2.1
1.8
3.4
3.1
4
6.8
Q
j
0.25
w
0.6
v
0.03
x
j
01-11-14
02-11-22

2004 Feb 24
51
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
SOLDERING
Introduction to soldering through-hole mount
packages
This text gives a brief insight to wave, dip and manual
soldering. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be
found in our
"Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit
Packages" (document order number 9398 652 90011).
Wave soldering is the preferred method for mounting of
through-hole mount IC packages on a printed-circuit
board.
Soldering by dipping or by solder wave
Driven by legislation and environmental forces the
worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is increasing.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from
3 to 4 seconds at 250
∞
C or 265
∞
C, depending on solder
material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
The total contact time of successive solder waves must not
exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
stg(max)
). If the
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
Manual soldering
Apply the soldering iron (24 V or less) to the lead(s) of the
package, either below the seating plane or not more than
2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit
is less than 300
∞
C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between
300 and 400
∞
C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
Suitability of through-hole mount IC packages for dipping and wave soldering methods
Notes
1. For SDIP packages, the longitudinal axis must be parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
2. For PMFP packages hot bar soldering or manual soldering is suitable.
PACKAGE
SOLDERING METHOD
DIPPING
WAVE
DBS, DIP, HDIP, RDBS, SDIP, SIL
suitable
suitable
(1)
PMFP
(2)
-
not suitable

2004 Feb 24
52
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
DATA SHEET STATUS
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
3. For data sheets describing multiple type numbers, the highest-level product status determines the data sheet status.
LEVEL
DATA SHEET
STATUS
(1)
PRODUCT
STATUS
(2)(3)
DEFINITION
I
Objective data
Development
This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
II
Preliminary data Qualification
This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
III
Product data
Production
This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Relevant changes will
be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification
(CPCN).
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification
The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition
Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
at these or at any other conditions above those given in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information
Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
no representation or warranty that such applications will be
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications
These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductors customers using or selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes
Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes in the products -
including circuits, standard cells, and/or software -
described or contained herein in order to improve design
and/or performance. When the product is in full production
(status `Production'), relevant changes will be
communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these
products, conveys no licence or title under any patent,
copyright, or mask work right to these products, and
makes no representations or warranties that these
products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work
right infringement, unless otherwise specified.

2004 Feb 24
53
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
I
2
C-bus controlled 4
◊
50 Watt power
amplifier and multiple voltage regulator
TDA8588J; TDA8588xJ
PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
2
C COMPONENTS
Purchase of Philips I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips' I
2
C patent to use the
components in the I
2
C system provided the system conforms to the I
2
C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.

© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004
SCA76
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Philips Semiconductors ≠ a worldwide company
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Printed in The Netherlands
R32/01/pp
54
Date of release:
2004 Feb 24
Document order number:
9397 750 11401





















































