 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: TZA1049 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
DATA SHEET
Product specification
2004 Mar 09
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TZA1049
4-channel BTL driver for
CD/DVD drives

2004 Mar 09
2
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
CONTENTS
1
FEATURES
2
APPLICATIONS
3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4
ORDERING INFORMATION
5
BLOCK DIAGRAM
6
PINNING
7
FUNCTIONAL DATA
7.1
General notes
8
LIMITING VALUES
9
CHARACTERISTICS
10
TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
11
PACKAGE OUTLINE
12
SOLDERING
12.1
Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
12.2
Reflow soldering
12.3
Wave soldering
12.4
Manual soldering
12.5
Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
13
DATA SHEET STATUS
14
DEFINITIONS
15
DISCLAIMERS

2004 Mar 09
3
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
1
FEATURES
∑
Two Bridge-Tied Load (BTL) driver channels for sled
and spindle motors and actuators
∑
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) input
∑
Integral thermal shut-down circuit
∑
Integral mute control
∑
Two regulated reference voltage outputs for other chips
in system; 3.3 V and 1.8 V respectively
∑
HSOP28 package.
2
APPLICATIONS
∑
BTL driver for CD and DVD players.
3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TZA1049 is a four-channel BTL driver IC for driving
motors and actuators in CD and DVD players.
Two reference voltage outputs are also available for
peripheral ICs such as servo and pick-up head drivers.
The spindle motor control inputs to the IC can be either
differential or single-ended.
4
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME
DESCRIPTION
VERSION
TZA1049TH
HSOP28
plastic, heatsink small outline package; 28 leads
SOP007

2004 Mar 09
4
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
5
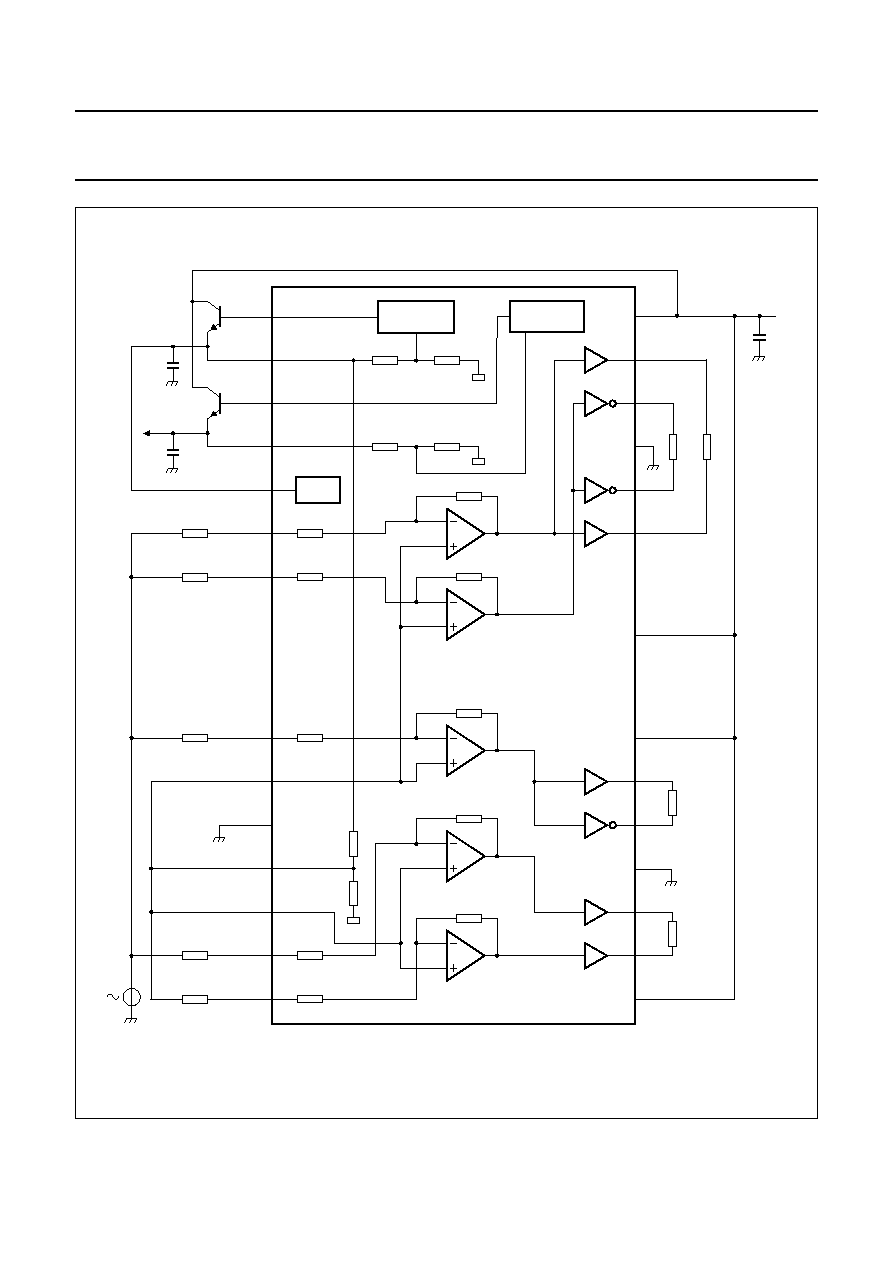
BLOCK DIAGRAM
mce478
1
V
CC
7
V
CC
V
CC
11
GND
V
CC
2
x1
32.3 k
32.3 k
32.3 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
32.3 k
32.3 k
x1
x1
x1
x1
x1
x0.5
x0.5
RADOUTN
3
FOCOUTP
8
9
10
5
FOCOUTN
6
RADOUTP
SLOUTP
SLOUTN
12
13
MOTOUTP
MOTOUTN
14
4
28
22
18
27
26
21
20
19
24
23
17
16
15
25
GND
VOUT3.3
SLIN
VFBIN3.3
VOUT1.8
MUTE
RADIN
FOCIN
VBIASIN
GND
MOTBIAS
VBIASOUT
MOTIN1
MOTIN2
VFBIN1.8
3.3 V
GENERATOR
MUTE
TZA1049
1.8 V
GENERATOR
Fig.1 Block diagram.

2004 Mar 09
5
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
6
PINNING
SYMBOL
PIN
DESCRIPTION
V
CC
1
supply voltage
RADOUTN
2
radial coil driver negative output
FOCOUTP
3
focus coil driver positive output
GND
4
ground
FOCOUTN
5
focus coil driver negative output
RADOUTP
6
radial coil driver positive output
V
CC
7
supply voltage
V
CC
8
supply voltage
SLOUTP
9
sled motor driver positive output
SLOUTN
10
sled motor driver negative output
GND
11
ground
MOTOUTP
12
spindle motor driver positive output
MOTOUTN
13
spindle motor driver negative output
V
CC
14
supply voltage
MOTIN2
15
spindle motor driver input 2
MOTIN1
16
spindle motor driver input 1
MOTBIAS
17
spindle motor bias input
VBIASOUT
18
1.65 V bias voltage output
GND
19
ground
VBIASIN
20
bias voltage input
SLIN
21
sled motor driver input
FOCIN
22
focus coil driver input
RADIN
23
radial coil driver input
MUTE
24
mute control input
VFBIN1.8
25
1.8 V generator/regulator feedback voltage input
VOUT1.8
26
1.8 V generator/regulator output
VFBIN3.3
27
3.3 V generator/regulator feedback voltage input
VOUT3.3
28
3.3 V generator/regulator output

2004 Mar 09
6
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
7
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1
General notes
1. The integral thermal shut-down circuit mutes the
output current when the chip temperature reaches
175
∞
C (typical). The hysteresis is set to 25
∞
C
(typical), so the circuit will restart when the chip
temperature falls to 150
∞
C (typical).
2. Mute mode is activated when the voltage at pin MUTE
is below 0.5 V, and deactivated when the voltage at
pin MUTE is above 1.2 V. In mute mode, both positive
and negative output terminals will be at
high-impedance state. However, the 3.3 V and 1.8 V
outputs are not affected.
3. It is recommended that a 220
µ
F decoupling capacitor
is connected between pins V
CC
and pin GND and
physically located as close as possible to these supply
pins.
4. The positive outputs of the focus, radial and sled driver
channels are in phase with their respective input
signals. The positive output of the spindle driver
channel is in phase with the input signal on
pin MOTIN1.
5. The values of the resistors connected to each input
channel must be equal to, or larger than, 4.7 k
to
ensure that the gain of each input stage is less than, or
equal to 1.
6. The GND pins are internally connected to heat
dissipation fins within the package. You must ensure
that these pins are connected to an external ground.
7. The 1.65 V bias voltage output from pin VBIASOUT is
derived from the internal 3.3 V generator/regulator,
and will be affected by any variation in the 3.3 V
generator/regulator voltage.
TZA1049TH
V
CC
VOUT3.3
RADOUTN
VFBIN3.3
FOCOUTP
VOUT1.8
GND
VFBIN1.8
FOCOUTN
MUTE
RADOUTP
RADIN
V
CC
FOCIN
V
CC
SLIN
SLOUTP
VBIASIN
SLOUTN
GND
GND
VBIASOUT
MOTOUTP
MOTBIAS
MOTOUTN
MOTIN1
V
CC
MOTIN2
mce479
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
18
17
20
19
22
21
24
23
26
25
28
27
Fig.2 Pin configuration.

2004 Mar 09
7
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
8
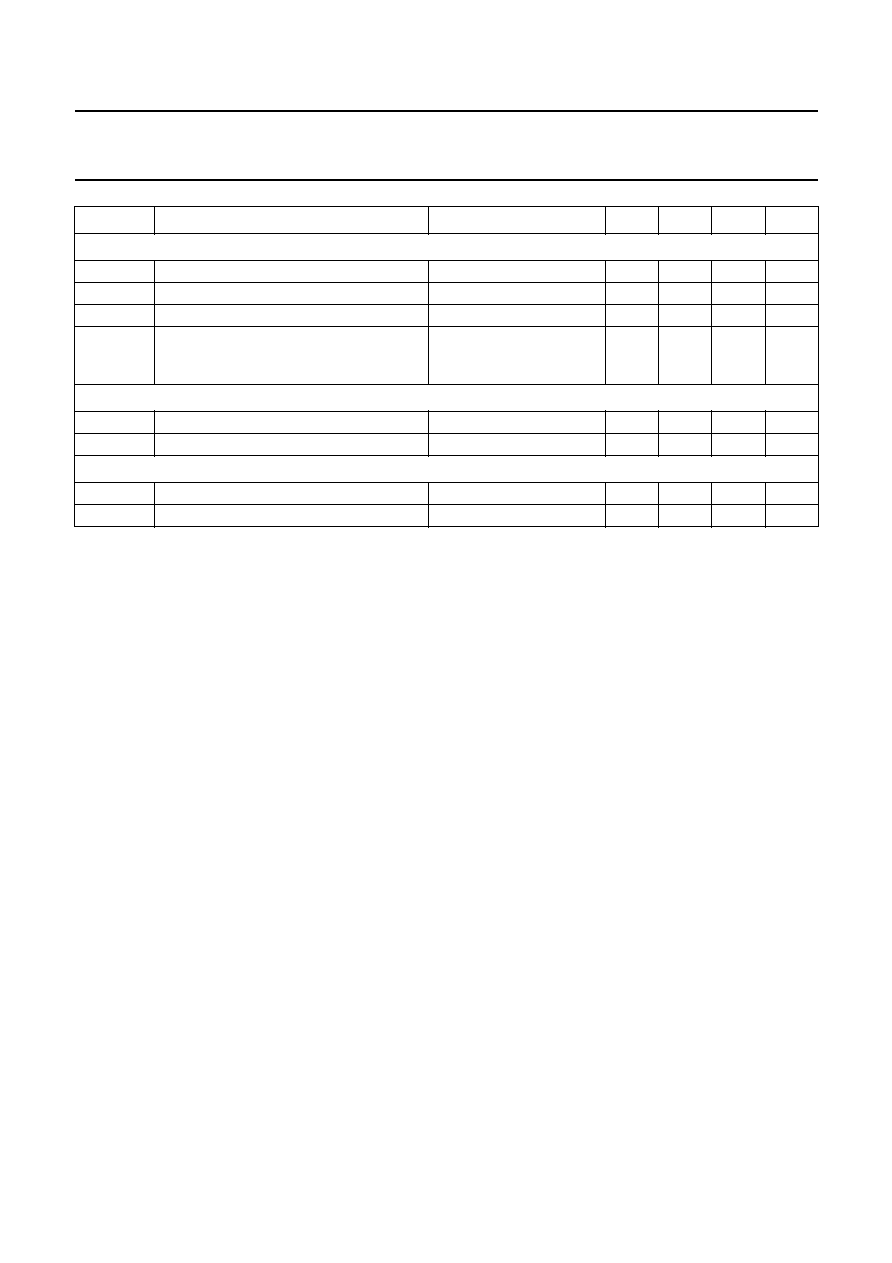
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
9
CHARACTERISTICS
T
amb
= 25
∞
C; V
CC
= 9 V; R
L
= 8
; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
V
CC
supply voltage
-
13.5
V
P
power dissipation
-
1.7
W
T
oper
operating temperature
-
40
+85
∞
C
T
stg
storage temperature
-
55
+150
∞
C
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
B
bandwidth
20
25
100
kHz
V
CC
power supply
6
9
13
V
PSRR
power supply rejection ratio
at V
CC
= 5 V
30
38
-
dB
I
q
quiescent current
unloaded
-
20.3
36
mA
I
stb
standby current
mute mode active;
unloaded
-
2.1
10
mA
V
MUTE(L)
low level voltage on pin MUTE; mute
mode active
0
-
0.8
V
V
MUTE(H)
high level voltage on pin MUTE; mute
mode inactive
2
-
5
V
Radial coil driver
V
OO(rad)
output offset voltage
-
±
20
±
50
mV
I
con(rad)
maximum constant current
R
L
= 8
250
300
-
mA
I
p(max)(rad)
maximum peak current
R
L
= 8
250
430
-
mA
G
rad
gain
V
CC
= 9 V;
V
i
= 700 mV (p-p);
R
ext
= 4.7 k
; note 1
6
7
8
dB
Focus coil driver
V
OO(foc)
output offset voltage
-
±
20
±
50
mV
I
con(foc)
maximum constant current
R
L
= 8
250
300
-
mA
I
p(max)(foc)
maximum peak current
R
L
= 8
370
430
-
mA
G
foc
gain
V
CC
= 9 V;
V
i
= 700 mV (p-p);
R
ext
= 4.7 k
; note 1
6
7
8
dB
Sled motor driver
V
OO(sle)
output offset voltage
-
±
20
±
50
mV
I
con(sle)
maximum constant current
R
L
= 8
200
300
-
mA
I
p(sle)
maximum peak current
R
L
= 8
370
430
-
mA
G
sle
gain
V
CC
= 9 V;
V
i
= 700 mV (p-p);
R
ext
= 4.7 k
; note 1
6
7
8
V/V
2004 Mar 09
8
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
Note
1. For gain measurements, only the channel being tested is active, the others are inactive; see Fig.4.
Spindle motor driver
V
OO(spin)
output offset voltage
-
±
10
±
50
mV
I
con(spin)
maximum constant current
R
L
= 4
400
430
-
mA
I
p(spin)
maximum peak current
R
L
= 4
560
600
-
mA
G
spin
gain
V
CC
= 9 V;
V
i
= 700 mV (p-p);
R
ext
= 4.7 k
; note 1
1
1.12
1.26
V/V
3.3 V generator
V
fb(3.3)
feedback voltage
3.1
3.3
3.5
V
I
O(3.3)
output current
3
4.4
5
mA
1.8 V generator
V
fb(1.8)
feedback voltage
1.7
1.8
1.9
V
I
O(1.8)
output current
3
4.2
5
mA
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
UNIT
2004 Mar 09
9
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
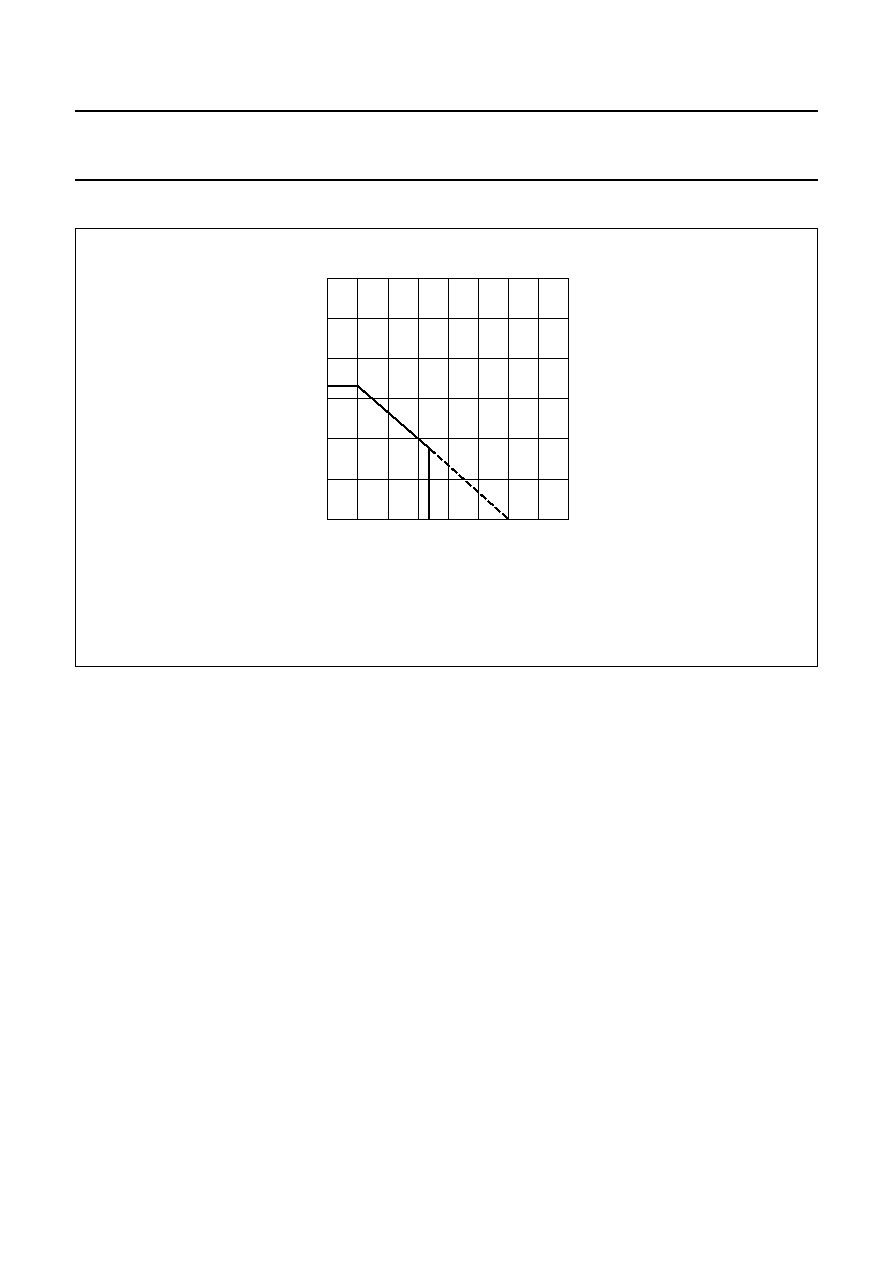
10 TEST AND APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, halfpage
0
3
2
1
0
50
100
P
(W)
200
150
Tamb (∞C)
MCE472
Fig.3 Power dissipation as a function of ambient temperature.
70
◊
70
◊
1.6 mm glass epoxy board.
At temperatures above T
amb
= 25
∞
C, power dissipation is de-rated at 13.6 mW/
∞
C.
2004 Mar 09
10
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
mce480
8
8
1
V
CC
7
V
CC
V
CC
11
GND
V
CC
2
x1
32.3 k
32.3 k
32.3 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
24 k
4.7 k
4.7 k
4.7 k
4.7 k
4.7 k
32.3 k
32.3 k
x1
x1
x1
x1
x1
x0.5
x0.5
12 V
12 V
RADOUTN
220
µ
F
12 V
3 FOCOUTP
8
9
10
5
FOCOUTN
6
RADOUTP
SLOUTP
SLOUTN
12
13
MOTOUTP
MOTOUTN
14
4
28
22
18
27
26
21
20
19
24
23
17
16
15
Vs
25
Q1
Q2
3.3 V
1.8 V
47
µ
F
47
µ
F
GND
VOUT3.3
SLIN
VFBIN3.3
VOUT1.8
MUTE
RADIN
FOCIN
VBIASIN
GND
MOTBIAS
VBIASOUT
MOTIN1
MOTIN2
VFBIN1.8
3.3 V
GENERATOR
MUTE
TZA1049
1.8 V
GENERATOR
8
8
Fig.4 Gain test configuration.

2004 Mar 09
11
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
handbook, full pagewidth
MCE481
MUTE
FORWARD
MICROCONTROLLER
REVERSE
RADIAL
COIL
SERVO/COIL DRIVER
SPINDLE
MOTOR1
SPINDLE
MOTOR2
FOCUS
COIL
SLED
COIL
M
M
12 V
1
2
3
4
5
6
focus
coil
12 V
radial
coil
7
8
12 V
12 V
9
sled
motor
M
spindle
motor
loading
motor
10
11
12
13
28
Q1
Q2
3.3 V
1.8 V
47
µ
F
220
µ
F
47
µ
F
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
TZA1049
Fig.5 Spindle motor differential control application.

2004 Mar 09
12
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
handbook, full pagewidth
MCE482
MUTE
FORWARD
MICROCONTROLLER
REVERSE
RADIAL
COIL
SERVO/COIL DRIVER
SPINDLE
MOTOR1
FOCUS
COIL
SLED
COIL
M
M
12 V
1
2
3
4
5
6
focus
coil
12 V
radial
coil
7
8
12 V
12 V
9
sled
motor
M
spindle
motor
loading
motor
10
11
12
13
28
Q1
Q2
3.3 V
1.8 V
47
µ
F
220
µ
F
47
µ
F
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
TZA1049
Fig.6 Spindle motor single-ended application.

2004 Mar 09
13
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
11 PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT
A
max.
A
1
A
2
max
b
b
1
c
e
L
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC
JEDEC
JEITA
mm
2.31
0.20
0.05
2.2
5.25
5.05
0.45
0.30
0.30
0.23
7.75
7.49
0.8
1.1
y
0.089
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions are not included.
SOP007
03-07-28
D
(1)
E
(1)
18.67
18.41
H
E
10.02
9.62
L
p
1.0
0.4
b1
detail X
A
A1
A2
y
Lp
L
c
b
HSOP28: plastic, heatsink small outline package; 28 leads
SOP007
0
5
10 mm
scale
X
D
28
15
1
14
e
E
HE

2004 Mar 09
14
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
12 SOLDERING
12.1
Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
"Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages"
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering can still be used for
certain surface mount ICs, but it is not suitable for fine pitch
SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
12.2
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Driven by legislation and environmental forces the
worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is increasing.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 270
∞
C depending on solder paste material. The
top-surface temperature of the packages should
preferably be kept:
∑
below 225
∞
C (SnPb process) or below 245
∞
C (Pb-free
process)
≠ for all BGA, HTSSON-T and SSOP-T packages
≠ for packages with a thickness
2.5 mm
≠ for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume
350 mm
3
so called thick/large packages.
∑
below 240
∞
C (SnPb process) or below 260
∞
C (Pb-free
process) for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a
volume < 350 mm
3
so called small/thin packages.
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on packing,
must be respected at all times.
12.3
Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
for surface mount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
∑
Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
∑
For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
≠ larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
≠ smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
∑
For packages with leads on four sides, the footprint must
be placed at a 45
∞
angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from
3 to 4 seconds at 250
∞
C or 265
∞
C, depending on solder
material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
12.4
Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300
∞
C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320
∞
C.

2004 Mar 09
15
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
12.5
Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
Notes
1. For more detailed information on the BGA packages refer to the
"(LF)BGA Application Note" (AN01026); order a copy
from your Philips Semiconductors sales office.
2. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
"Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods".
3. These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must on no account
be processed through more than one soldering cycle or subjected to infrared reflow soldering with peak temperature
exceeding 217
∞
C
±
10
∞
C measured in the atmosphere of the reflow oven. The package body peak temperature
must be kept as low as possible.
4. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering. On versions with the heatsink on the bottom side, the solder
cannot penetrate between the printed-circuit board and the heatsink. On versions with the heatsink on the top side,
the solder might be deposited on the heatsink surface.
5. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45
∞
angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
6. Wave soldering is suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.8 mm; it is definitely not
suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
7. Wave soldering is suitable for SSOP, TSSOP, VSO and VSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than
0.65 mm; it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
8. Image sensor packages in principle should not be soldered. They are mounted in sockets or delivered pre-mounted
on flex foil. However, the image sensor package can be mounted by the client on a flex foil by using a hot bar
soldering process. The appropriate soldering profile can be provided on request.
9. Hot bar or manual soldering is suitable for PMFP packages.
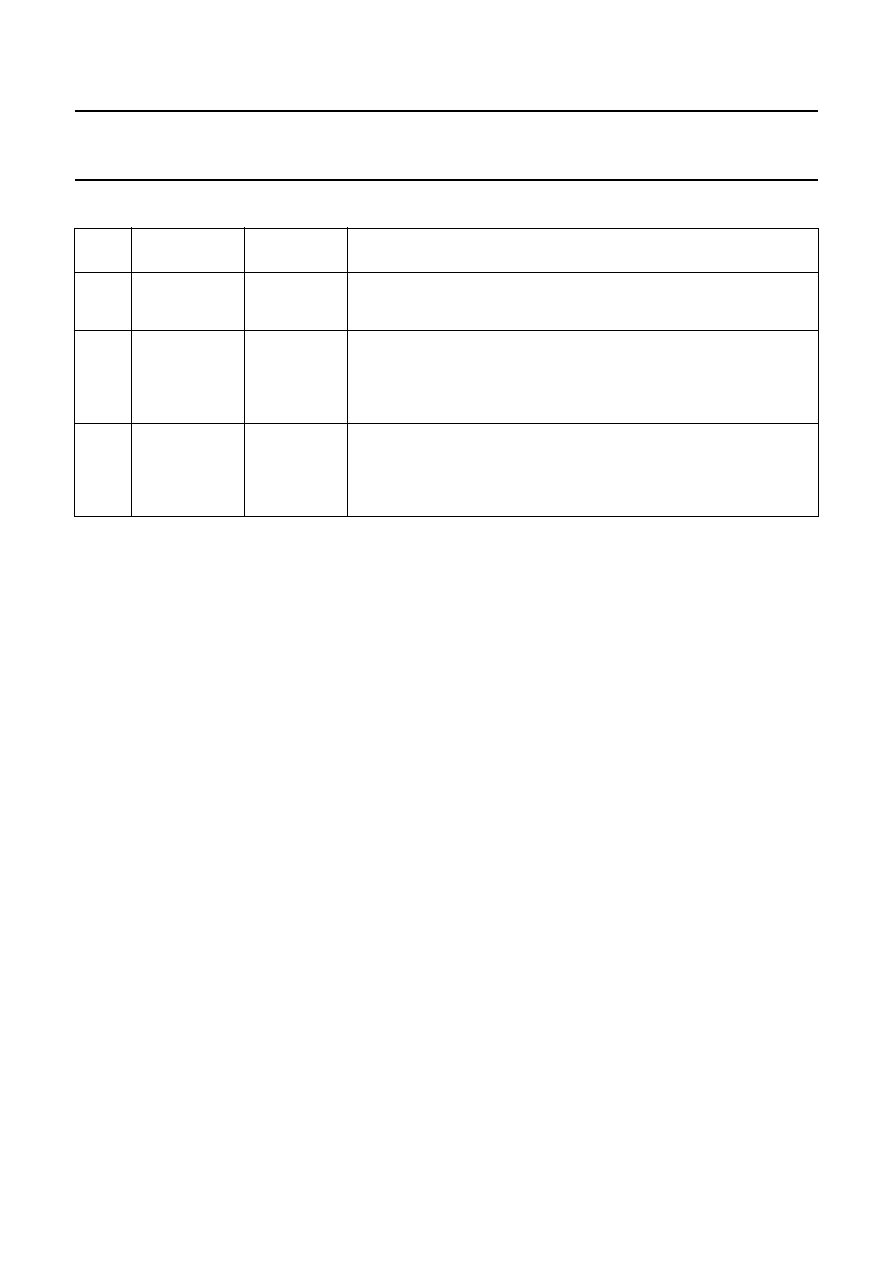
PACKAGE
(1)
SOLDERING METHOD
WAVE
REFLOW
(2)
BGA, HTSSON..T
(3)
, LBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, SSOP..T
(3)
, TFBGA,
USON, VFBGA
not suitable
suitable
DHVQFN, HBCC, HBGA, HLQFP, HSO, HSOP, HSQFP, HSSON,
HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, HVSON, SMS
not suitable
(4)
suitable
PLCC
(5)
, SO, SOJ
suitable
suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP
not recommended
(5)(6)
suitable
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO, VSSOP
not recommended
(7)
suitable
CWQCCN..L
(8)
, PMFP
(9)
, WQCCN..L
(8)
not suitable
not suitable
2004 Mar 09
16
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
4-channel BTL driver for CD/DVD drives
TZA1049
13 DATA SHEET STATUS
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
3. For data sheets describing multiple type numbers, the highest-level product status determines the data sheet status.
LEVEL
DATA SHEET
STATUS
(1)
PRODUCT
STATUS
(2)(3)
DEFINITION
I
Objective data
Development
This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
II
Preliminary data Qualification
This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
III
Product data
Production
This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Relevant changes will
be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification
(CPCN).
14 DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification
The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition
Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
at these or at any other conditions above those given in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information
Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
no representation or warranty that such applications will be
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
15 DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications
These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductors customers using or selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes
Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes in the products -
including circuits, standard cells, and/or software -
described or contained herein in order to improve design
and/or performance. When the product is in full production
(status `Production'), relevant changes will be
communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these
products, conveys no licence or title under any patent,
copyright, or mask work right to these products, and
makes no representations or warranties that these
products are free from patent, copyright, or mask work
right infringement, unless otherwise specified.

© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004
SCA76
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Philips Semiconductors ≠ a worldwide company
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
Printed in The Netherlands
R32/01/pp
17
Date of release:
2004 Mar 09
Document order number:
9397 750 11573
















