 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: TX5002 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

Æ
RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com
Page 1 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
∑
Designed for Short-Range Wireless Data Communications
∑
Supports RF Data Transmission Rates Up to 115.2 kbps
∑
3 V, Low Current Operation plus Sleep Mode
∑
Stable, Easy to Use, Low External Parts Count
∑
Complies with Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS)
The TX5002 hybrid transmitter is ideal for short-range wireless data applications where robust operation,
small size, low power consumption and low cost are required. All critical RF functions are contained in the
hybrid, simplifying and speeding design- in. The TX5002 includes provisions for both on-off keyed (OOK) and
amplitude-shift keyed (ASK) modulation. The TX5002 employs SAW filtering to suppress output harmonics,
facilitating compliance with FCC Part 15 and similar regulations.
Rating
Value
Units
Power Supply and All Input/Output Pins
-0.3 to +4.0
V
Non-Operating Case Temperature
-50 to +100
∞C
Soldering Temperature (10 seconds / 5 cycles max.)
260
∞C
418.00 MHz
Hybrid
Transmitter
TX5002
SM-20L Case
Electrical Characteristics
Characteristic
Sym
Notes
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
Units
Operating Frequency
f
o
417.80
418.20
MHz
Modulation Types
OOK & ASK
OOK Data Rate
10
kbps
ASK Data Rate
115.2
kbps
Transmitter Performance
Peak RF Output Power, 250 µA TXMOD Current
P
O
0
dBm
Peak Current, 250 µA TXMOD Current
I
TP
7.5
mA
OOK Turn On/Turn Off Times
t
ON
/t
OFF
20/15
µs
ASK Output Rise/Fall Times
t
TR
/t
TF
1.1/1.1
µs
2nd - 4th Harmonic Outputs
-50
dBm
5th - 10th Harmonic Outputs
-55
dBm
Non-harmonic Spurious Outputs
-50
dBm
Sleep Mode Current
I
S
0.7
µA
Sleep to Transmit Switch Time
t
TOR
21
µs
Transmit to Sleep Switch Time
t
RTO
15
µs
Control Input Logic Low Level
200
mV
Control Input Logic High Level
1
Vcc - 300
mV
Power Supply Voltage Range
V
CC
2.2
3.7
Vdc
Operating Ambient Temperature
T
A
-40
+85
∞C

RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com Page 2 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
Notes:
1. Do not allow the voltage applied to a control input pin to exceed Vcc + 200 mV.
2. The companion receiver to the TX5002 is the RX5002. Please see RFM's web site at www.rfm.com for details.
CAUTION: Electrostatic Device. Observe precautions when handling.
Item
Symbol
OOK
ASK
ASK
Units
Notes
Nominal NRZ Data Rate
DR
NOM
2.4
19.2
115.2
kbps
see page 1
Minimum Signal Pulse
SP
MIN
416.67
52.08
8.68
µs
single bit
Maximum Signal Pulse
SP
MAX
1666.68
208.32
34.72
µs
4 bits of same value
TXMOD Resistor
R
TXM
8.2
8.2
8.2
K
±5%, for 0 dBm output
DC Bypass Capacitor
C
DCB
4.7
4.7
4.7
µF
tantalum
RF Bypass Capacitor 1
C
RFB1
27
27
27
pF
±5% NPO
RF Bypass Capacitor 2
C
RFB2
100
100
100
pF
±5% NPO
RF Bypass Bead
L
RFB
Fair-Rite
Fair-Rite
Fair-Rite
vendor
2506033017YO or equivalent
Series Tuning Inductor
L
AT
56
56
56
nH
50 ohm antenna
Shunt Tuning/ESD Inductor
L
ESD
220
220
220
nH
50 ohm antenna
Transmitter Set-Up, 3.0 Vdc, -40 to +85 ∞C
Modulation Input
TOP VIEW
GND
3
CNT
RL0
CNT
RL1
P
WIDTH
P
RATE
THLD
1
THLD
2
RREF
GND2
TX
MOD
RX
DATA
LPF
ADJ
CMP
IN
BB
OUT
PK
DET
AGC
CAP
VCC
1
VCC
2
RFIO
GND1
+ 3
VDC
Transmitter OOK Configuration
1
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
+ 3
VDC
R
TXM
C
RFB2
C
DCB
L
AT
L
ESD
C
RFB1
L
RFB
+
T/S
Modulation Input
TOP VIEW
GND
3
CNT
RL0
CNT
RL1
P
WIDTH
P
RATE
THLD
1
THLD
2
RREF
GND2
TX
MOD
RX
DATA
LPF
ADJ
CMP
IN
BB
OUT
PK
DET
AGC
CAP
VCC
1
VCC
2
RFIO
GND1
+ 3
VDC
Transmitter ASK Configuration
1
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
+ 3
VDC
R
TXM
C
RFB2
C
DCB
L
AT
L
ESD
C
RFB1
L
RFB
+
T/S
RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com Page 3 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
Figure 1
Transmitter Theory of Operation
Introduction
RFM's TX-series hybrid transmitters are specifically designed for short-
range wireless data communication applications. These transmitters pro-
vide robust operation, very small size, low power consumption and low im-
plementation cost. All critical RF functions are contained in the hybrid,
simplifying and speeding design-in. The transmitters can be readily con-
figured to support a wide range of data rates and protocol requirements.
TX-series transmitters feature excellent suppression of output harmonics
and virtually no other RF emissions, making them easy to certify to short-
range (unlicensed) radio regulations.
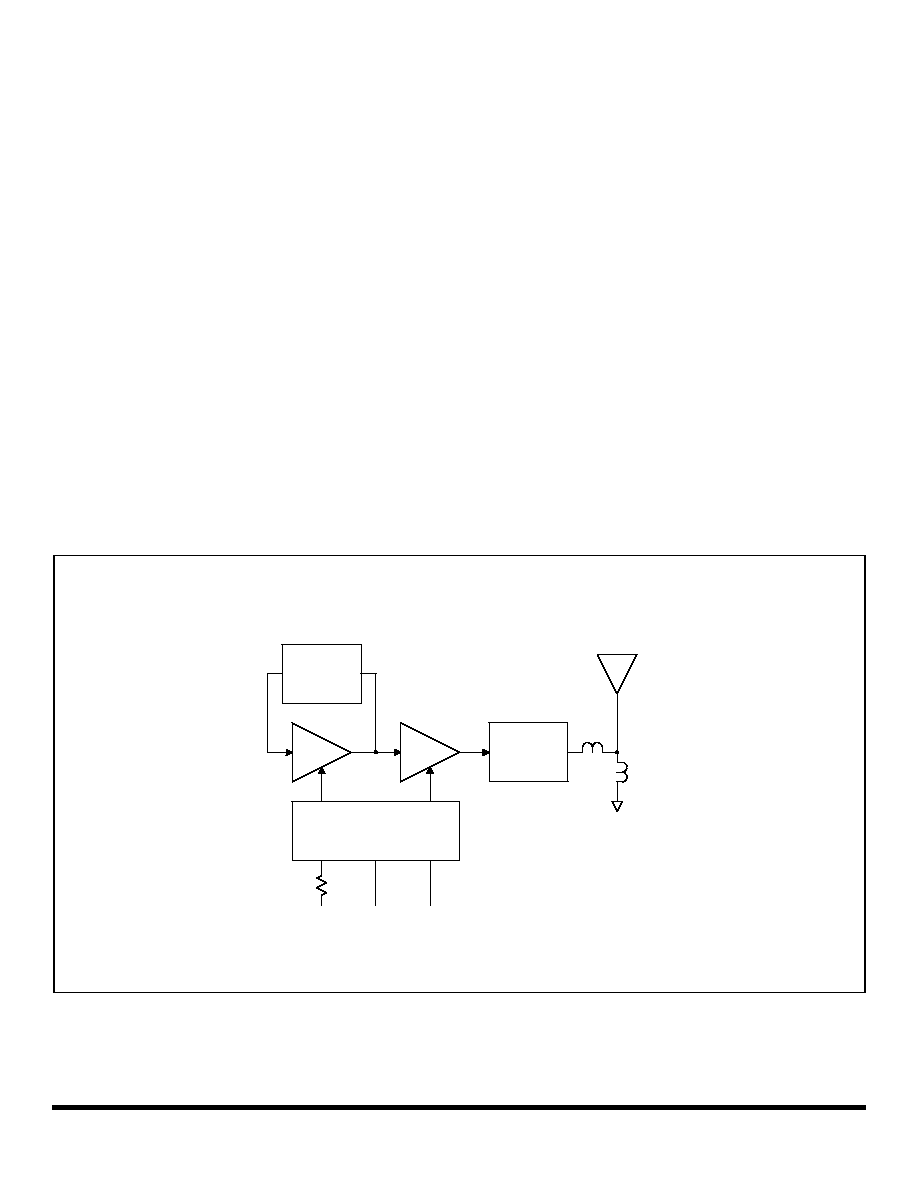
Transmitter Block Diagram
Figure 1 is the general block diagram of the transmitter. Please refer to Fig-
ure 1 for the following discussions.
Antenna Port
The only external RF components needed for the transmitter are the anten-
na and its matching components. Antennas presenting an impedance in
the range of 35 to 72 ohms resistive can be satisfactorily matched to the
RFIO pin with a series matching coil and a shunt matching/ESD protection
coil. Other antenna impedances can be matched using two or three com-
ponents. For some impedances, two inductors and a capacitor will be re-
quired. A DC path from RFIO to ground is required for ESD protection.
Transmitter Chain
The transmitter chain consists of a SAW coupled-resonator oscillator fol-
lowed by a modulated buffer amplifier. The SAW coupled resonator output
filter suppresses transmitter harmonics to the antenna.
Transmitter operation supports two modulation formats, on-off keyed
(OOK) modulation, and amplitude-shift keyed (ASK) modulation. When
OOK modulation is chosen, the transmitter output turns completely off be-
tween "1" data pulses. When ASK modulation is chosen, a "1" pulse is rep-
resented by a higher transmitted power level, and a "0" is represented by a
lower transmitted power level. OOK modulation provides compatibility with
first-generation ASH technology, and provides for power conservation.
ASK modulation must be used for high data rates (data pulses less than
200 µs). ASK modulation also reduces the effects of some types of inter-
ference and allows the transmitted pulses to be shaped to control modula-
tion bandwidth.
The modulation format is chosen by the state of the CNTRL0 and the
CNTRL1 mode control pins, as discussed below. In the OOK mode, the os-
cillator amplifier TXA1 and buffer amplifier TXA2 are turned off when the
voltage to the TXMOD input falls below 220 mV. In the OOK mode, the data
rate is limited by the 20/15 µs turn-on and turn-off time of the oscillator. In
the ASK mode TXA1 is biased ON continuously, and the output of TXA2 is
modulated by the TXMOD input current. Minimum output power occurs in
the ASK mode when the modulation driver sinks about 10 µA of current
from the TXMOD pin.
Transmitter Block Diagram
TXA1
TXA2
Antenna
SAW
Coupled
Resonator
SAW
CR
Filter
Modulation
& Bias Control
TX
IN
CN
TRL1
CN
TRL0
Tune/ESD
Ant
Tune
R
TXM

RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com Page 4 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
The transmitter RF output power is proportional to the input current to the
TXMOD pin. A series resistor is used to adjust the peak transmitter output
power. 0 dBm of output power requires about 250 µA of input current.
Transmitter Mode Control
The three transmitter operating modes ≠ transmit ASK, transmit OOK, and
power-down (sleep), are controlled by the Modulation & Bias Control func-
tion, and are selected with the CNTRL1 and CNTRL0 control pins. Setting
CNTRL1 high and CNTRL0 low place the unit in the ASK transmit mode.
Setting CNTRL1 low and CNTRL0 high place the unit in the OOK transmit
mode. Setting CNTRL1 and CNTRL0 both low place the unit in the power-
down mode. (Note that the resistor driving TXMOD must also be low in the
power-down mode to minimize power-down current.) CNTRL1 and
CNTRL0 are CMOS compatible inputs. These inputs must be held at a log-
ic level; they cannot be left unconnected.
Turn-On Timing
The maximum time required for either the OOK or ASK transmitter mode to
become operational is 5 ms after the supply voltage reaches 2.2 Vdc. The
total turn-on time to stable transmitter operation for a 10 ms power supply
rise time is 15 ms.
Sleep and Wake-Up Timing
The maximum transition time from either transmit mode to the sleep mode
(t
TOS
and t
TAS
) is 15 µs after CNTRL1 and CNTRL0 are both low (1 µs fall
time).
The maximum time required to switch from the sleep mode to either trans-
mit mode (t
STO
and t
STA
) is 21 µs. Most of this time is due to the start-up of
the transmitter oscillator.
0.000
0.000
.140
.270
.410
.0775
.1025
.1175
.1575
.1975
.2375
.2775
.3175
.3575
.3825
.4600
.1975
.1725
.2125
.2375
Dimensions in inches
SM-20L PCB Pad Layout
Dimension
mm
Inches
Min
Nom
Max
Min
Nom
Max
A
10.795
10.922
11.049
.425
.430
.435
B
9.525
9.652
9.779
.375
.380
.385
C
1.778
1.905
2.032
.070
.075
.080
D
3.048
3.175
3.302
.120
.125
.130
E
0.381
0.508
0.635
.015
.020
.025
F
0.889
1.016
1.143
.035
.040
.045
G
3.175
3.302
3.429
.125
.130
.135
H
1.778
1.905
2.032
.070
.075
0.80
SM-20L Package Drawing
C
D
E
F
G
A
B
H
3
4
5
6
7
9
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
19
Transmitter Pin Out
RFIO
8
2
10
20
1
18
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
TXMOD
NC
NC
NC
GND1
VCC1
GND2
VCC2
GND3
CNTRL0
CNTRL1

RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com Page 5 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
Pin Descriptions
Pin
Name
Description
1
GND1
GND1 is the RF ground pin. GND2 and GND3 should be connected to GND1 by short, low-inductance traces.
2
VCC1
VCC1 is the positive supply voltage pin for the transmitter output amplifier and the transmitter base-band circuitry. VCC1
is usually connected to the positive supply through a ferrite RF decoupling bead which is bypassed by an RF capacitor on
the
supply side. See the description of VCC2 (Pin 16) for additional information.
3
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
4
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
5
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
6
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
7
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
8
TXMOD
The transmitter RF output voltage is proportional to the input current to this pin. A series resistor is used to adjust the peak
transmitter output voltage. 0 dBm of output power requires 250 µA of input current. In the ASK mode, minimum output
power occurs when the modulation driver sinks about 10 µA of current from this pin. In the OOK mode, input signals less
than 220 mV completely turn the transmitter oscillator off. Internally, this pin appears to be a diode in series with a small
resistor. Peak transmitter output power P
O
for a 3 Vdc supply voltage is approximately:
P
O
= 16*(I
TXM
)
2
, where P
O
is in mW, and the peak modulation current I
TXM
is in mA
A ±5% resistor value is recommended. In the OOK mode, this pin is usually driven with a logic-level data input (unshaped
data pulses). OOK modulation is practical for data pulses of 200 µs or longer. In the ASK mode, this pin accepts analog
modulation (shaped or unshaped data pulses). ASK modulation is practical for data pulses 8.7 µs or longer. This pin must
be low in the power-down (sleep) mode. Please refer to the
ASH Transceiver Designer's Guide for additional information
on modulation techniques.
9
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
10
GND2
GND2 is an IC ground pin. It should be connected to GND1 by a short, low inductance trace.
11
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
12
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
13
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
14
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
15
NC
No connection. Printed circuit board pad may be grounded or floating.
16
VCC2
VCC2 is the positive supply voltage pin for the transmitter oscillator. Pin 16 must be bypassed with an RF capacitor, and
must also be bypassed with a 1 to 10 µF tantalum or electrolytic capacitor. Power supply voltage ripple should be limited to
10 mV peak-to-peak. See the
ASH Transceiver Designer's Guide for additional information.
17
CNTRL1
CNTRL1 and CNTRL0 select the transmit modes. CNTRL1 high and CNTRL0 low place the unit in the ASK transmit mode.
CNTRL1 low and CNTRL0 high place the unit in the OOK transmit mode. CNTRL1 and CNTRL0 both low place the unit in
the power-down (sleep) mode. CNTRL1 is a high-impedance input (CMOS compatible). An input voltage of 0 to 300 mV is
interpreted as a logic low. An input voltage of Vcc - 300 mV or greater is interpreted as a logic high. An input voltage
greater than Vcc + 200 mV should not be applied to this pin. A logic high requires a maximum source current of 40 µA. A
logic low requires a maximum sink current of 25 µA (1 µA in sleep mode). This pin must be held at a logic level; it cannot
be left unconnected.
18
CNTRL0
CNTRL0 is used with CNTRL1 to control the operating modes of the transmitter. See the description of CNTRL1 for more
information.
19
GND3
GND3 is an IC ground pin. It should be connected to GND1 by a short, low inductance trace.
20
RFIO
RFIO is the transmitter RF output pin. This pin is connected directly to the SAW filter transducer. Antennas presenting an
impedance in the range of 35 to 72 ohms resistive can be satisfactorily matched to this pin with a series matching coil and
a shunt matching/ESD protection coil. Other antenna impedances can be matched using two or three components. For
some impedances, two inductors and a capacitor will be required. A DC path from RFIO to ground is required for ESD pro-
tection.

RF Monolithics, Inc.
Phone: (972) 233-2903
Fax: (972) 387-8148
E-mail: info@rfm.com Page 6 of 6
RFM Europe
Phone: 44 1963 251383
Fax: 44 1963 251510
http://www.rfm.com
©1999 by RF Monolithics, Inc. The stylized RFM logo are registered trademarks of RF Monolithics, Inc.
TX5002-070705
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
I
TXM
in µA
V
TXM
vs I
TXM
0.85
0.90
0.95
1.00
1.05
1.10
1.15
1.20
V
TXM
in V
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
275
250
225
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
1.20
1.40
1.60
3 V
RF Output Power vs I
TXM
I
TXM
in µA
Output Power in mW
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
275
250
225





