 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: 6N139 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

s
Features
s
Applications
s
Outline Dimensions
6N139
1. High current transfer ratio
( CTR: MIN. 500 % at I
F
2. High speed response
( t
PHL
3. High commom mode rejection voltage
( CM
H
: TYP. 500V/
µ
s )
4. TTL compatible output
1. Interfaces for computer peripherals
3. Telephone sets
4. Signal transmission between circuits of
different potentials and impedances
*2 Pulse width <=1
µ
s, 300pps
*3 Decreases at the rate of 0.7mA /∞C if the external temperature is more than 25∞C
*5 For 10 seconds
6N139
( Unit : mm )
( Ta = 25∞C)
Internal connection
diagram
6N139
Parameter
Symbol
Rating
Unit
Input
Forward current
I
F
20
*1
Peak forward current
I
F
40
*2
Peak transient forward current
I
FM
1
A
Reverse voltage
V
R
5
V
Power dissipation
P
35
mW
Output
Supply voltage
V
CC
- 0.5 to + 18
V
Output voltage
V
O
- 0.5 to + 18
V
Emitter-base reverse
V
EBO
0.5
V
*3
Average output current
I
O
60
Power dissipation
P
O
100
mW
*4
Isolation voltage
V
iso
Operating temperature
T
opr
0 to + 70
∞C
Storage temperature
T
stg
- 55 to + 125
∞C
*5
Soldering temperature
T
sol
260
∞C
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.
"
"
In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
0.5TYP.
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
1 NC
2 Anode
3 Cathode
4 NC
5 GND
High Sensitivity, High Speed
OPIC Photocoupler
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and signal-
processing circuit integrated onto a single chip.
* " OPIC "
( Optical IC ) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
= 1.6mA )
5. Recognized by UL , file No. E64380
s
Absolute Maximum Ratings
withstand voltage ( Pin 5 to 7 )
mA
mA
mA
*1 50% duty cycle, Pulse width: 1ms
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
2. Computers, measuring instruments, control
equipment
2 500
*4 40 to 60% RH, AC for 1 minute
Primary Side Mark
( Sunken place
)
: TYP. 0.2
µ
s at R
L
= 270
)
V
rms
6 V
O
7 V
B
8 V
CC
=
0 to 13
∞
6.5
±
0.5
1.2
±
0.3
0.85
±
0.3
0.8
±
0.2
9.22
±
0.5
7.62
±
0.3
0.26
±
0.1
2.54
±
0.25
0.5
±
0.1
3.5
±
0.5
3.7
±
0.5

6N139
s
Electro-optical Characteristics
s
Switching Characteristics
and output current expressed in % .
V
F
/
Ta
( Ta = 25∞C, V
CC
= 5V)
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
Unit
t
PHL
R
L
= 4.7k
, I
F
= 0.5mA
-
5
25
µ
s
R
L
= 270
, I
F
= 12mA
-
0.3
1
µ
s
t
PLH
R
L
= 4.7k
, I
F
= 0.5mA
-
10
60
µ
s
R
L
= 270
, I
F
= 12mA
-
1.5
7
µ
s
CM
H
I
F
= 0, V
CM
= 10V
P-P
R
L
= 2.2k
-
500
-
V/
µ
s
CM
L
I
F
= 1.6 mA , V
CM
= 10V
P-P
R
L
= 2.2k
-
- 500
-
V/
µ
s
Output (1)
( 0)
*4
Propagation delay time
Output ( 0)
(1)
*4
Propagation delay time
Instantaneous common mode
rejection voltage " Output ( 0) "
rejection voltage " Output (1)"
*5
Instantaneous common mode
*6
*5
*6
Pulse input
=
1/10
100
I
F
1
2
3
4
R
L
V
CC
V
O
C
L
=
15pF
5V
1.5V
V
OL
t
PLH
t
V
O
0
I
F
1.5V
Note ) Typical value : at Ta = 25∞C, V
CC
= 5V
( Ta = 0 to + 70∞C unless otherwise specified )
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
Unit
Current transfer ratio
CTR(1) I
F
400
-
%
CTR(2) I
F
500
-
%
V
OL
(1)
I
O
-
0.1
0.4
V
V
OL
(2)
I
O
-
0.1
0.4
V
V
(2)
I
O
-
0.4
V
I
F
= 0, V
CC
= V
O
= 18V
-
0.05
100
µ
A
I
F
-
0.5
-
mA
I
F
= 0, V
CC
= 5V, V
O
= open
-
10
-
nA
I
F
-
1.5
1.7
V
I
F
-
- 1.9
-
mV/∞C
R
I
R
= 10
µ
A, Ta = 25∞C
5.0
-
-
V
V
F
= 0, f = 1MHz
-
60
-
pF
V
I-O
= 3kV DC
-
-
1.0
µ
A
V
I-O
= 500V DC
-
10
12
-
f = 1MHz
-
0.6
-
pF
8
7
6
5
duty ratio
Pulse generator
*5 Instantaneous common mode rejection voltage " output (1)" represents a common mode voltage variation that can hold the
*6 Instantaneous common mode rejection voltage " output ( 0) " represents a common mode voltage variation that can hold the
output above (1) level ( V
O
> 2.0V).
output above ( 0) level ( V
O
< 0.8V).
*1
Logic ( 0) output voltage
Logic (1) output current
Logic ( 0) supply current
Logic (1) supply current
Input forward voltage
Input forward voltage temperature coefficient
Input reverse voltage
Input capacitance
OL
I
OH
I
CCL
I
CCH
V
F
BV
C
IN
I
I-O
R
I-O
C
I-O
(input-output )
Leak current
Isolation resistance
( input-output )
Capacitance ( input-output )
*3
*3
*3
*1 Current transfer ratio is a ratio of input current
*2
*3 Measured as 2-pin element ( Short 1,2,3,4 and 5, 6, 7, 8. )
*2
= 0.5mA, V
O
= 1.6mA, V
O
= 6.4mA, V
CC
= 0.4V, V
CC
= 4.5V
= 0.4V, V
CC
= 4.5V
= 4.5V, I
F
= 15mA, V
CC
= 4.5V, I
F
= 24mA, V
CC
= 4.5V, I
F
= 1.6mA
= 5mA
= 12mA
= 1.6mA, V
CC
= open
= 5V, V
O
= 1.6mA, Ta = 25∞C
= 1.6mA
*4 Test circuit for Propagation Delay Time
I
F
monitor
PHL
Ta = 25∞C, 45% RH, t = 5s
1 800
1 600
0.1

6N139
I
F
B
V
FF
A
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V
CM
V
CC
=
5V
V
o
R
L
2V
0.8V
CM
H
V
O
V
O
CM
L
V
CM
0V
t
r
t
10V
10%
90%
5V
V
OL
I
F
I
F
10%
90%
f
=
0
10
30
20
0
0
100
25
50
70
75
Fig. 1 Forward Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
F
(
mA
)
Ambient temperature T
a
(∞C)
0
120
0
60
25
50
75
70
100
100
80
40
35
20
P
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs.
Ambient Temperature
Power dissipation P
O
, P
tot
(
mW
)
Ambient temperature T
a
(∞C)
50∞C
25∞C
70∞C
1.0
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
F
(
mA
)
Forward voltage V
F
(V)
Fig. 3 Forward Current vs. Forward Voltage
Forward current I
Forward current I
*
6 Test Circuit for Instantaneous Common Mode Rejection Voltage
=
1.6mA
0
0
3.0mA
2.5mA
2.0mA
1.0mA
10
20
30
40
2
0.5mA
1.5mA
3.5mA
4.0mA
4.5mA
Output current I
O
(
mA
)
Output voltage V
O
(V)
Fig. 4 Output Current vs. Output Voltage
50
60
1
P
O
T
a
= 0∞C
T
a
= 25∞C
V
CC
= 5V
I
F
= 5mA
P
O
(MAX.
)
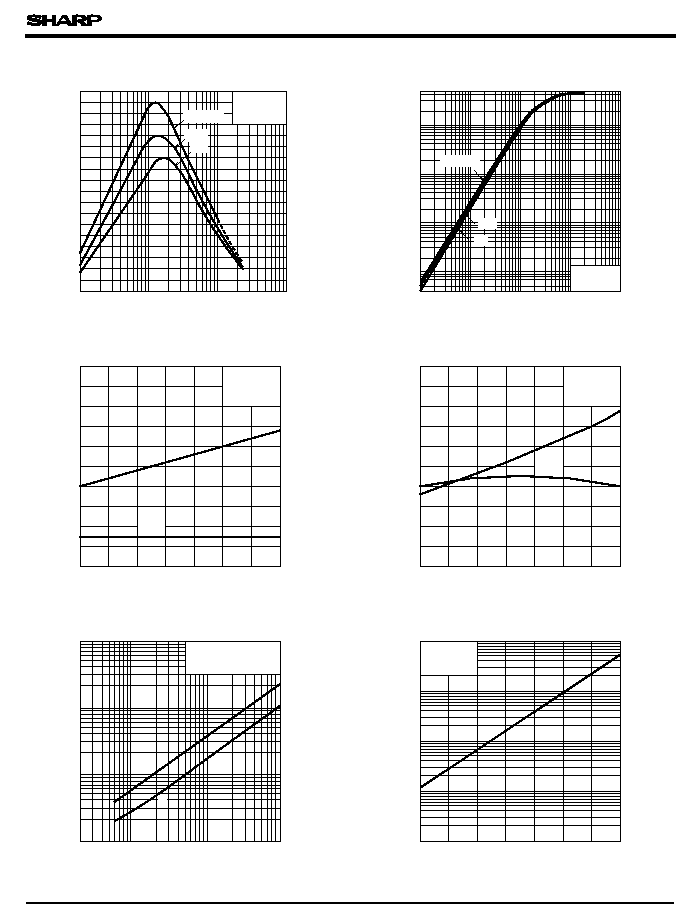
6N139
200
0.1
Current transfer ratio CTR
(
%
)
1
10
100
800
600
400
25∞C
0∞C
Fig. 5 Current Transfer Ratio vs.
Forward Current
Forward current I
F
( mA )
0
1
2
10
20
30
40
70
0
60
50
I
F
= 12mA
R
L
= 270
Ambient temperature T
a
(∞C)
1/f = 100
µ
s
0
5
10
10
20
30
40
70
0
60
50
I
F
= 0.5mA
R
L
= 4.7k
Ambient temperature T
a
(∞C)
1/f = 1ms
1
0.1
10
t
r
t
f
1
10
100
1000
Rise time, fall time t
r
, t
f
(
µ
s
)
L
( k
)
Propagation delay time t
PHL
, t
PLH
(
µ
s
)
Propagation delay time t
PHL
, t
PLH
Adjust I
F
to V
OL
= 2V
T
a
= 25∞C
Ambient Temperature
Fig. 7-a Propagation Delay Time vs.
Fig. 8 Rise Time, Fall Time vs.
Fig. 7-b Propagation Delay Time vs.
Ambient Temperature
0.004
0.01
100
50
10
1
0.1
10
1
0.1
0.01
0∞C
25∞C
Fig. 6 Output Current vs. Forward Current
Output current I
O
(
mA
)
Forward current I
F
( mA )
10
- 10
0
10
- 9
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
10
- 8
10
- 7
10
- 6
Ambient Temperature
Fig. 9 Logic (1) Supply Current vs.
CCH
(
A
)
Ambient temperature T
a
(∞C)
I
F
= 0mA
V
CC
= 15V
V
O
= OPEN
Logic
(1
)
supply current I
T
a
= 70∞C
V
O
= 0.4V
V
CC
= 4.5V
T
a
= 70∞C
V
O
= 0.4V
V
CC
= 5.0V
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
1 000
Load Resistance
Load resistance R
(
µ
s
)

6N139
I
F
90
%
90
%
2V
Pulse
input
Duty ratio
=
1
/
10
10
%
10
%
5V
5V
Input
Output
(saturated)
1.5V
1.5V
V
OL
I
F
O
V
O
t
PHL
t
t
f
t
Output
Pulse
oscillator
V
CC
V
O
R
L
100
*7 Test Circuit for Rise Time, Fall Time vs. Load Resistance
I
F
monitor
C
L
=
15
PF
( 1) It is recommended that a by-pass capacitor of more than 0.01
µ
F be added between V
CC
and
GND near the device in order to stabilize power supply line.
( 2) Transistor of detector side in bipolar configuration is apt to be affected by static electricity
for its minute design. When handling them, general counterplan against static electricity
should be taken to avoid breakdown of devices or degradation of characteristics.
s
Precautions for Use
PLH
r
(non-saturated)
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
( 3) As for other general cautions, please refer to the chapter " Precautions for Use " .




