 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: TDA4862 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
w
= New type
Type
Ordering Code
Package
w
TDA 4862
Q67000-A8368-A205
P-DIP-8-1
w
TDA 4862 G
Q67006-A8369-A703
P-DSO-8-1
Power-Factor Controller (PFC)
TDA 4862
IC for High Power Factor
and Active Harmonic Filter
Advanced Information
Bipolar IC
P-DIP-8-1
P-DSO-8-1
Features
∑ IC for sinusoidal line-current consumption
∑ Power factor approaching 1
∑ Controls boost converter as an active
harmonics filter
∑ Internal start-up with low current consumption
∑ Zero current detector for discontinuous
operation mode
∑ High current totem pole gate driver
∑ Trimmed
±
1.4% internal reference
∑ Undervoltage lock-out with hysteresis
∑ Very low start-up current consumption
∑ Pin compatible to world standard
∑ Fast overvoltage regulator
∑ Current sense input with internal low pass filter
Semiconductor Group
1
1998-02-16
TDA 4862
Semiconductor Group
2
1998-02-16
Description
The TDA 4862 is excellent convenient for designing a preconverter in ballasts and
switched mode power supplies with sinusoidal line current consumption and a power
factor approaching unity.
The TDA 4862 controls a boost converter as an active harmonics filter in a discontinuous
mode (free oscillating triangular shaped current mode).
The TDA 4862 comprises an internal start-up timer, a high gain voltage amplifier, an one
quadrant multiplier for approaching unity power factor, a zero current detector, PWM and
logic circuitry, and totem pole MOSFET gate driver.
Protective features are: input undervoltage lockout with hysteresis,
V
CC
zener clamp,
cycle-by-cycle current limiting, output voltage limiting for fast and slow load changes up
to open circuit, and a sinking gate driver current activated whenever undervoltage mode
occurs.
The output voltage of this preconverter is regulated with high accuracy. Therefore the
device can be used for world-wide line voltages without switches.
The TDA 4862 is the improved version of the TDA 4817 with a pinout equivalent to world
standard.
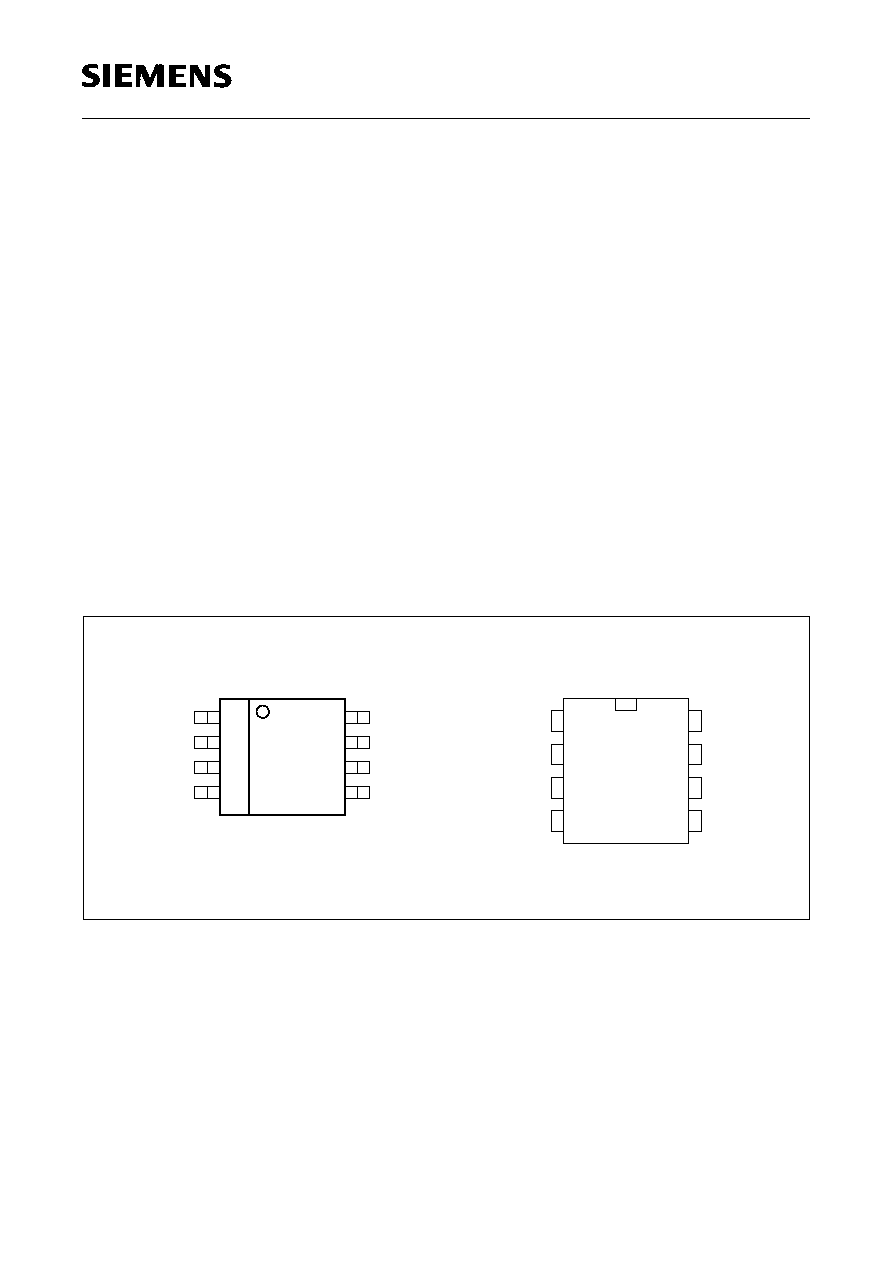
Figure 1
Pin Configuration (top view)
TDA 4862
TDA 4862 G
MULTIN
4
3
2
1
IEP01748
5
6
GND
DETIN
7
8
GTDRV
V
CC
AOUT
V
SENSE
V
SENSE
4
3
2
1
IEP01749
5
6
7
8
SENSE
MULTIN
AOUT
V
SENSE
V
CC
V
GTDRV
GND
DETIN
TDA 4862
Semiconductor Group
3
1998-02-16
Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin Symbol Function
1
V
SENSE
Voltage Amplifier Inverting Input;
V
SENSE
is connected via a resistive divider to the boost converter output.
With a capacitor connected to
V
AOUT
it forms an integrator.
2
V
AOUT
Voltage Amplifier Output;
V
AOUT
is connected internally to the first multiplier input. To prevent
overshoot the input voltage will be clamped at 5 V. Input voltage less
than 2.2 V is inhibiting the gate driver. If the current flowing into this pin
is exceeding an internal defined margin the multiplier output voltage is
reduced to prevent the MOSFET from overvoltage damage.
3
MULTIN Multiplier Input;
MULTIN is the second multiplier input and connected via a resistive
divider to the rectifier output voltage.
4
I
SENSE
Current Sense Minus;
I
SENSE
is connected to a sense resistor controlling the MOSFET source
current. The input is internally clamped at ≠ 0.3 V to prevent negative
input voltage interaction. An internal low pass filter suppresses voltage
spikes when turning the MOSFET on.
5
DETIN
Zero Current Detector Input;
DETIN is connected to an auxiliary winding monitoring the zero crossing
of the inductor current.
6
GND
Ground;
All voltages are measured with respect to GND.
V
CC
should be
bypassed directly to GND with a 0.1
µ
F or larger ceramic capacitor.
7
GTDRV
Gate Drive Output;
GTDRV is the output of a totem-pole circuitry for direct driving a
MOSFET. A clamping network bypasses low state source current and
high state sink current.
8
V
CC
Positive Supply Voltage;
V
CC
should be connected to a stable source slightly above the
V
CC
turn-ON threshold for normal operation. A 100 nF or lager ceramic
capacitor connected to
V
CC
absorbs supply current spikes required to
charge external MOSFET gate capacitances.

TDA 4862
Semiconductor Group
4
1998-02-16
Functional Description
Introduction
Conventional electronic ballasts and switching power supplies are designed with a
bridge rectifier and bulk capacitor. Their disadvantage is that the circuit draws power
from the line when the instantaneous AC voltage exceeds the capacitor's voltage. This
occurs near the line voltage peak and causes a high charge current spike with following
characteristics: the apparent power is higher than the real power that means low power
factor condition, the current spikes are non-sinusoidal with a high content of harmonics
causing line noise, the rectified voltage depends on load condition and requires a large
bulk capacitor, special efforts in noise suppression are necessary.
With the TDA 4862 preconverter a sinusoidal current is achieved which varies in direct
instantaneous proportion to the input voltage half sine wave and means a power factor
near 1. This is due to the appearance of almost any complex load like a resistive one at
the AC line. The harmonic distortions are reduced and comply with the IEC555 standard.
Operating Description
The TDA 4862 contains a wide bandwidth voltage amplifier used in a feedback loop, an
overvoltage regulator, an one quadrant multiplier with a wide linear operating range, a
current sense comparator, zero current detector, a PWM and logic circuitry, a totem-pole
MOSFET driver, an internal trimmed voltage reference, a restart timer and an
undervoltage lockout circuitry. These functional blocks are described below.
Voltage Amplifier
The voltage amplifier is internally compensated and yields a gain bandwidth of 0.8 MHz
and a phase margin of 80 degrees. The non-inverting input is biased at 2.5 V and is not
pinned out. The inverting input is sensing the output voltage via a resitive devider. The
voltage amplifier output
V
AOUT
and the inverting input
V
SENSE
are connected in a simplest
way via an external capacitor. It forms an integrator which monitors the average output
voltage over several line cycles. Typically the bandwidth is set below 20 Hz. ln order to
keep the output voltage constant the voltage amplifier output is connected to the
multiplier input for regulation.
Overvoltage Regulator
Fast changes of the output voltage can't be regulated by the integrator formed with the
voltage amplifier This occurs during initial start-up, sudden load removal, or output
arcing and leads to a current peak at the voltage amplifier input while the voltage
amplifier's differential input voltages remains zero. The peak current is flowing through
the external capacitor into
V
AOUT
. Exceeding an internal defined margin causes a
regulation circuitry to reduce the multiplier output voltage.

TDA 4862
Semiconductor Group
5
1998-02-16
Functional Description (cont'd)
MuItiplier
A one quadrant multiplier is the crucial circuitry that regulates the gate driver with respect
of the DC output voltage and the AC haversine input voltage of the preregulator. Both
inputs are designed for good linearity over a wide dynamic range, 0 V to 4.0 V for the
MULTIN and 2.5 V to 4.0 V for the
V
AOUT
.
Current Sense Comparator and RS Latch
The multiplier output voltage is compared with the current sense voltage which
represents the current through the MOSFET. The current sense comparator in addition
with the logic ensures that only a single pulse appears at the drive output during a
given cycle. The multiplier output and the current sense threshold are internally clamped
at 1.3 V. So the gate drive MOSFET is protected against critical operating, as they occur
during start up. To prevent the input from negative pulses a special protection circuitry
is implemented. Switch-on current peaks are reduced by an internal RC-Filter.
Zero Current Detector
The zero current detector senses the inductor current via an auxiliary winding and
ensures that the next on-time is initiated immediately when the inductor current has
reached zero. This diminishes the reverse recovery losses of the boost converter diode.
Output switch conduction is terminated when the voltage drop of the shunt resistor
reaches the threshold level of the multiplier output. So the boost current waveform has
a triangular shape and there are no deadtime gaps between the cycles. This leads to a
continuous AC line current limiting the peak current to twice of the average current.
To prevent false tripping the zero current detector is designed as a Schmitt trigger with
a hysteresis of 0.6 V. An internal 5 V clamp protects the input from overvoltage
breakdown, a 0.6 V clamp prevents substrate injection. An external resistor must be
used in series with the auxiliary winding to limit the current through the clamps.
Timer
A restart timer function was added to the IC to eliminate the need for an oscillator when
used in stand-alone applications. The timer starts or restarts the TDA 4862 if the drive
output has been off for more than 15
µ
s after the inductor current reaches zero.




