
Specifications and information are subject to change without notice
WJ Communications, Inc
Phone 1-800-WJ1-4401
FAX: 408-577-6621
e-mail: sales@wj.com
Web site: www.wj.com
October 2004 Rev 1
ECP103
1 Watt, High Linearity InGaP HBT Amplifier
Product Information
The Communications Edge
TM
Product Features
x
2300 - 2700 MHz
x
+30.5 dBm P1dB
x
+46 dBm Output IP3
x
10 dB Gain @ 2450 MHz
x
9 dB Gain @ 2600 MHz
x
Single Positive Supply (+5V)
x
Available in SOIC-8 or 16pin
4mm QFN package
Applications
x
W-LAN
x
RFID
x
DMB
x
Fixed Wireless
Product Description
The ECP103 is a high dynamic range driver amplifier in
a low-cost surface mount package. The InGaP/GaAs
HBT is able to achieve superior performance for various
narrowband-tuned application circuits with up to +46
dBm OIP3 and +30.5 dBm of compressed 1-dB power.
The part is housed in an industry standard SOIC-8 SMT
package. All devices are 100% RF and DC tested.
The ECP103 is targeted for use as a driver amplifier in
wireless infrastructure where high linearity and medium
power is required. An internal active bias allows the
ECP103 to maintain high linearity over temperature and
operate directly off a single +5V supply. This
combination makes the device an excellent candidate for
driver amplifier stages in wireless-LAN, digital
multimedia broadcast, or fixed wireless applications. The
device can also be used in next generation RFID readers.
Functional Diagram
ECP103D
ECP103G
Specifications
(1)
Parameter
Units Min Typ Max
Operational Bandwidth
MHz
2300
2700
Test Frequency
MHz
2450
Gain
dB
10
Input Return Loss
dB
18
Output Return Loss
dB
8
Output P1dB
dBm
+30.5
Output IP3
(2)
dBm
+46
Noise Figure
dB
6.3
Test Frequency
MHz
2600
Gain
dB
9
Output P1dB
dBm
+30
Output IP3
(2)
dBm
+45
Operating Current Range , Icc
(3)
mA
400
450
500
Device Voltage, Vcc
V
5
1. Test conditions unless otherwise noted: T = 25�C, Vsupply = +5 V in a tuned application circuit.
2. 3OIP measured with two tones at an output power of +15 dBm/tone separated by 1 MHz. The
suppression on the largest IM3 product is used to calculate the 3OIP using a 2:1 rule.
3. This corresponds to the quiescent current or operating current under small-signal conditions into
pins 6, 7, and 8. It is expected that the current can increase by an additional 90 mA at P1dB. Pin 1
is used as a reference voltage for the internal biasing circuitry. It is expected that Pin 1 will pull
10.8 mA of current when used with a series bias resistor of R1=51
�
. (ie. total device current
typically will be 461 mA.)
Typical Performance
(4)
Parameter
Units
Typical
Frequency
MHz
2450
2600
S21 � Gain
dB
10
9
S11
dB
15
15
S22
dB
8
8
Output P1dB
dBm
30.5
30.0
Output IP3
dBm
46
45
W-CDMA Channel Power
@ -45 dBc ACPR
dBm
22.5
Noise Figure
dB
7
7
7
Supply Bias
(3)
+5 V @ 450 mA
4. Typical parameters reflect performance in a tuned application circuit at +25
�
C.
Absolute Maximum Rating
Ordering Information
Parameters
Rating
Part No.
Description
Operating Case Temperature
-40 to +85
qC
ECP103D
1 Watt InGaP HBT Amplifier (16p 4mm Pkg)
Storage Temperature
-65 to +150
qC
ECP103G
1 Watt InGaP HBT Amplifier (Soic-8 Pkg)
RF Input Power (continuous)
+26 dBm
ECP103D-PCB2450 2450 MHz Evaluation Board
Device Voltage
+8 V
ECP103D-PCB2650 2600 MHz Evaluation Board
Device Current
900 mA
ECP103G-PCB2450 2450 MHz Evaluation Board
Device Power
5 W
ECP103G-PCB2650 2600 MHz Evaluation Board
Operation of this device above any of these parameters may cause permanent damage.
1
2
3
4
12
11
10
9
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
N/C
RF OUT
RF OUT
N/C
Vref
N/C
RF IN
N/C
V
b
i
a
s
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
Vref
N/C
RF IN
N/C
Vbias
RF OUT
RF OUT
N/C

Specifications and information are subject to change without notice
WJ Communications, Inc
Phone 1-800-WJ1-4401
FAX: 408-577-6621
e-mail: sales@wj.com
Web site: www.wj.com
October 2004 Rev 1
ECP103
1 Watt, High Linearity InGaP HBT Amplifier
Product Information
The Communications Edge
TM
Typical Device Data � ECP103G (Soic-8 Package)
S-Parameters (V
cc
= +5 V, I
cc
= 450 mA, T = 25
�
C, calibrated to device leads)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Frequency (GHz)
Gain and Maximum Stable Gain
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
G
a
i
n
(
d
B
)
DB(|S[2,1]|)
DB(GMax)
0
1
.
0
1
.
0
-
1
.
0
1
0
.
0
10.0
-1
0.
0
5
.
0
5.0
-5
.0
2
.
0
2.
0
-2
.0
3
.
0
3.
0
-3
.0
4
.
0
4.
0
-4
.0
0
.
2
0.
2
-0.
2
0
.
4
0.
4
-0
.4
0
.
6
0
.
6
-
0
.6
0
.
8
0
.
8
-
0
.
8
S11
Swp Max
5.05GHz
Swp Min
0.05GHz
0
1
.
0
1
.
0
-
1
.
0
1
0
.
0
10.0
-1
0.
0
5
.
0
5.0
-5
.0
2
.
0
2.
0
-2
.0
3
.
0
3.
0
-3
.0
4
.
0
4.
0
-4
.0
0
.
2
0.
2
-0.
2
0
.
4
0.
4
-0
.4
0
.
6
0.
6
-
0
.6
0
.
8
0
.
8
-
0
.
8
S22
Swp Max
5.05GHz
Swp Min
0.05GHz
Notes:
The gain for the unmatched device in 50 ohm system is shown as the trace in black color. For a tuned circuit for a particular frequency,
it is expected that actual gain will be higher, up to the maximum stable gain. The maximum stable gain is shown in the dashed red line.
The impedance loss plots are shown from 0.05 � 5.05 GHz, with markers placed in 0.5 GHz increments.
S-Parameters (V
cc
= +5 V, I
cc
= 450 mA, T = 25
�
C, unmatched 50 ohm system, calibrated to device leads)
Freq (MHz)
S11 (dB)
S11 (ang)
S21 (dB)
S21 (ang)
S12 (dB)
S12 (ang)
S22 (dB)
S22 (ang)
50
-1.23
-177.95
24.07
122.55
-40.25
17.32
-1.26
-130.4
100
-1.01
178.17
19.55
116.55
-39.49
10.63
-1.33
-155.43
200
-1.01
172.63
15.55
112.97
-40.13
15.98
-1.17
-169.92
400
-1.03
163.72
12.03
98.68
-38.83
10.31
-0.93
179.61
600
-1.21
155.20
9.86
85.80
-39.30
-4.249
-0.66
173.43
800
-1.34
146.17
8.11
73.18
-37.70
-2.398
-0.83
168.67
1000
-1.52
136.69
6.92
61.43
-37.73
-16.27
-0.95
166.34
1200
-2.00
126.65
6.13
49.60
-37.14
-14.34
-1.05
165.13
1400
-2.65
115.04
5.80
37.55
-36.23
-28.50
-1.04
164.55
1600
-3.86
97.52
6.01
21.48
-36.45
-46.08
-1.11
166.24
1800
-6.72
86.05
6.17
1.700
-34.63
-68.99
-1.10
164.44
2000
-14.09
94.99
6.15
-23.83
-35.91
-100.68
-1.00
162.35
2200
-9.98
166.89
4.98
-52.92
-36.75
-147.66
-0.77
158.42
2400
-4.27
157.68
2.52
-80.08
-39.10
171.86
-0.79
154.12
2600
-2.13
142.95
-0.42
-100.8
-37.80
123.26
-0.81
149.03
2800
-1.24
130.88
-3.40
-116.44
-38.58
89.55
-0.84
144.09
3000
-0.82
120.68
-6.09
-128.99
-39.37
67.22
-0.92
138.4
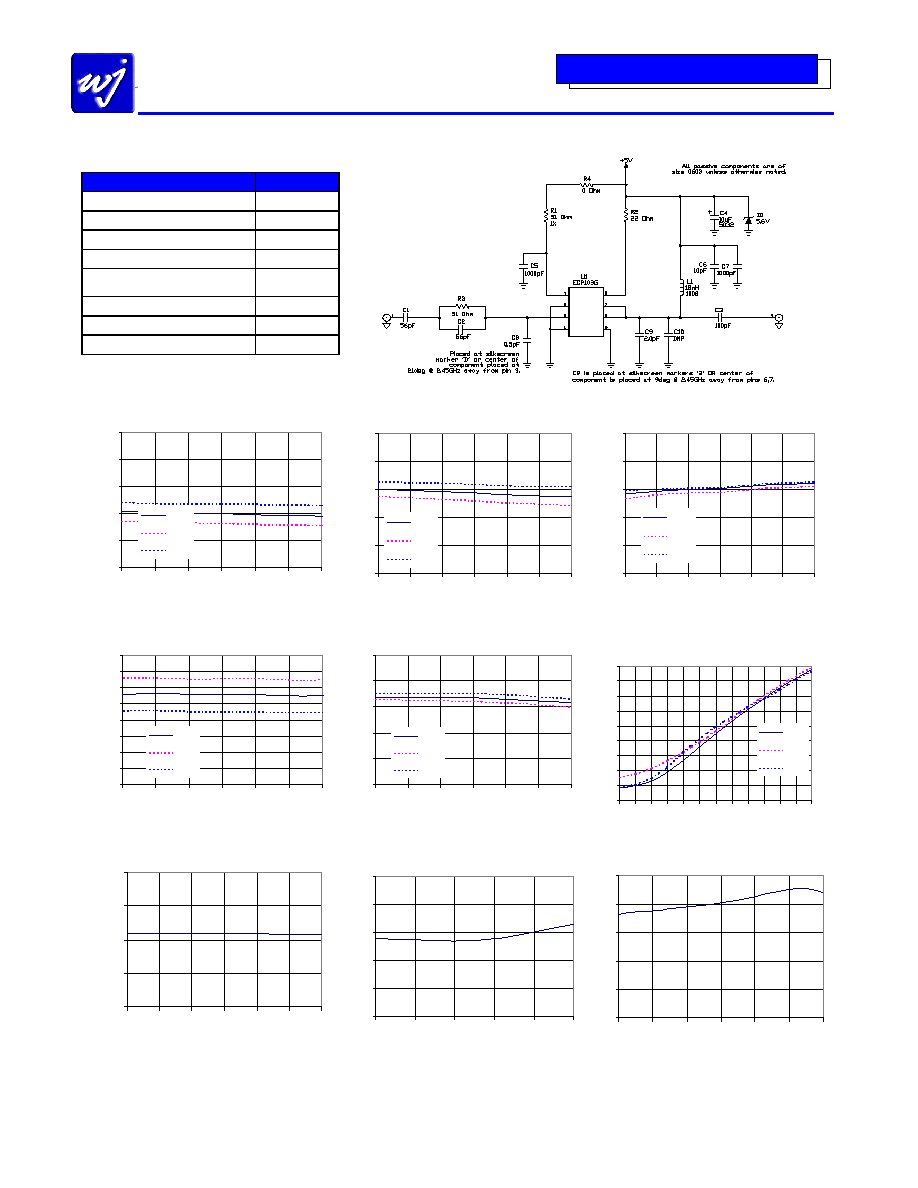
Application Circuit PC Board Layout
Circuit Board Material: Top RF layer is .014" Getek, 4 total layers (0.062" thick) for mechanical rigidity
1 oz copper, Microstrip line details: width = .026", spacing = .026"
The silk screen markers `A', `B', `C', etc. and `1', `2', `3', etc. are used as placemarkers for the input and output tuning shunt
capacitors � C8 and C9. The markers and vias are spaced in .050" increments.
Specifications and information are subject to change without notice
WJ Communications, Inc
�
Phone 1-800-WJ1-4401
�
FAX: 408-577-6621
�
e-mail: sales@wj.com
�
Web site: www.wj.com
October 2004 Rev 1
ECP103
1 Watt, High Linearity InGaP HBT Amplifier
Product Information
The Communications Edge
TM
2450 MHz Application Circuit (ECP103G-PCB2450)
Typical RF Performance at 25
qC
Frequency
2450 MHz
S21 � Gain
10 dB
S11 � Input Return Loss
-14 dB
S22 � Output Return Loss
-10 dB
Output P1dB
+30.5 dBm
Output IP3
(+17 dBm / tone, 1 MHz spacing)
+46 dBm
Noise Figure
7 dB
Device / Supply Voltage
+5 V
Quiescent Current
(1)
450 mA
1. This corresponds to the quiescent current or operating current under
small-signal conditions into pins 6, 7, and 8.
S21 vs. Frequency
8
10
12
14
16
18
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
Frequency (MHz)
S
2
1
(
d
B
)
+25�C
+85�C
-40�C
S11 vs. Frequency
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
Frequency (MHz)
S
1
1
(
d
B
)
+25�C
+85�C
-40�C
S22 vs. Frequency
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
1930
1940
1950
1960 1970 1980 1990
Frequency (MHz)
S
2
2
(
d
B
)
+25 �C
+85 �C
-40�C
Noise Figure vs. Frequency
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
Frequency (MHz)
N
F
(
d
B
)
+25�C
+85�C
-40�C
P1 dB vs. Frequency
25
27
29
31
33
35
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
Frequency (MHz)
P
1
d
B
(
d
B
m
)
+25�C
+85�C
-40�C
ACPR vs. Channel Power
IS-95, 9 Ch. Fwd. �885 KHz offset, 30 KHz Meas BW, 1960 MHz
-85
-80
-75
-70
-65
-60
-55
-50
-45
-40
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
Output Channel Power (dBm)
A
C
P
R
(
d
B
c
)
+25�C
+85�C
-40�C
OIP3 vs. Frequency
+25�C, 15 dBm / tone
35
40
45
50
55
1930
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
Frequency (MHz)
O
I
P
3
(
d
B
m
)
OIP3 vs. Temperature
freq. = 1960, 1961 MHz, +15 dBm
35
39
43
47
51
55
-40
-15
10
35
60
85
Temperature ( �C)
O
I
P
3
(
d
B
m
)
OIP3 vs. Output Power
freq. = 1960, 1961 MHz, +25�C
30
34
38
42
46
50
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
Output Power (dBm)
O
I
P
3
(
d
B
m
)

Specifications and information are subject to change without notice
WJ Communications, Inc
�
Phone 1-800-WJ1-4401
�
FAX: 408-577-6621
�
e-mail: sales@wj.com
�
Web site: www.wj.com
October 2004 Rev 1
ECP103
1 Watt, High Linearity InGaP HBT Amplifier
Product Information
The Communications Edge
TM
ECP103G (SOIC-8 Package) Mechanical Information
Outline Drawing
Land Pattern
Thermal Specifications
Parameter
Rating
Operating Case Temperature
-40 to +85
q C
Thermal Resistance, Rth
(1)
33
q C / W
Junction Temperature, Tjc
(2)
159
q C
Notes:
1. The thermal resistance is referenced from the junction-
to-case at a case temperature of 85
�
C. Tjc is a function
of the voltage at pins 6 and 7 and the current applied to
pins 6, 7, and 8 and can be calculated by:
Tjc = Tcase + Rth * Vcc * Icc
2. This corresponds to the typical biasing condition of +5V,
450 mA at an 85
�
C case temperature. A minimum
MTTF of 1 million hours is achieved for junction
temperatures below 247
�
C.
Product Marking
The component will be marked with an
"ECP103G" designator with an alphanumeric
lot code on the top surface of the package.
Tape and reel specifications for this part are
located on the website in the "Application
Notes" section.
ESD / MSL Information
ESD Rating: Class 1B
Value:
Passes between 500 and 1000V
Test:
Human Body Model (HBM)
Standard:
JEDEC Standard JESD22-A114
MSL Rating: Level 3 at +235
�
C convection reflow
Standard:
JEDEC Standard J-STD-020
Functional Diagram
Function
Pin No.
Vref
1
Input
3
Output
6, 7
Vbias
8
GND
Backside Paddle
N/C or GND
2, 4, 5
Mounting Config. Notes
1. A heatsink underneath the area of the PCB for the mounted
device is strictly required for proper thermal operation.
Damage to the device can occur without the use of one.
2. Ground / thermal vias are critical for the proper performance
of this device. Vias should use a .35mm (#80 / .0135" )
diameter drill and have a final plated thru diameter of .25
mm (.010" ).
3. Add as much copper as possible to inner and outer layers
near the part to ensure optimal thermal performance.
4. Mounting screws can be added near the part to fasten the
board to a heatsink. Ensure that the ground / thermal via
region contacts the heatsink.
5. Do not put solder mask on the backside of the PC board in
the region where the board contacts the heatsink.
6. RF trace width depends upon the PC board material and
construction.
7. Use 1 oz. Copper minimum.
8
All dimensions are in millimeters (inches). Angles are in
degrees.
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
MTTF vs. GND Tab Temperature
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
50
60
70
80
90
100
Tab temperature (� C)
M
T
T
F
(
m
i
l
l
i
o
n
h
r
s
)

Specifications and information are subject to change without notice
WJ Communications, Inc
�
Phone 1-800-WJ1-4401
�
FAX: 408-577-6621
�
e-mail: sales@wj.com
�
Web site: www.wj.com
October 2004 Rev 1
ECP103
1 Watt, High Linearity InGaP HBT Amplifier
Product Information
The Communications Edge
TM
ECP103D (16-pin 4x4mm Package) Mechanical Information
Outline Drawing
Land Pattern
0.65mm
TYP.
TYP.
SOLDERMASK SWELL TO BE 0.5mm
FROM OUTSIDE EDGE OF ALL PADS
GROUND PLANE AREA FOR VIAS
2.23mm X 2.23mm
RECOMMENDED PAD
0.76mm X 0.34mm
DEVICE GROUND PAD
2.0mm X 2.0mm
4.00mm
16L 4.0mm X 4.0mm PACKAGE
0.25mm DIA. THERMAL GROUND VIA HOLE VIAS ARE PLACED
ON A 0.65mm GRID. VIAS ARE TO BE CONNECTED TO TOP,
BOTTOM, AND INTERNAL GROUND PLANES IN ORDER TO
MAXIMIZE HEAT DISSIPATION. FOR .031" THK FR4 MATERIAL,
VIA BARREL PLATING TO BE MIN. 0.0014 THICK. VIAS TO BE
PLUGGED WITH EITHER CONDUCTIVE OR NON-CONDUCTIVE
EPOXY TO PREVENT SOLDER. DRAINS THROUGH VIA IN
REFLOW PROCESS
Thermal Specifications
Parameter
Rating
Operating Case Temperature
-40 to +85
q C
Thermal Resistance, Rth
(1)
33
q C / W
Junction Temperature, Tjc
(2)
159
q C
Notes:
1. The thermal resistance is referenced from the junction-
to-case at a case temperature of 85
�
C. Tjc is a function
of the voltage at pins 10 and 11 and the current applied
to pins 10, 11, and 16 and can be calculated by:
Tjc = Tcase + Rth * Vcc * Icc
2. This corresponds to the typical biasing condition of +5V,
450 mA at an 85
�
C case temperature. A minimum
MTTF of 1 million hours is achieved for junction
temperatures below 247
�
C.
Product Marking
The component will be marked with an
" ECP103D" designator with an alphanumeric
lot code on the top surface of the package.
Tape and reel specifications for this part are
located on the website in the " Application
Notes" section.
ESD / MSL Information
ESD Rating: Class 1B
Value:
Passes between 500 and 1000V
Test:
Human Body Model (HBM)
Standard:
JEDEC Standard JESD22-A114
MSL Rating: Level 3 at +235
�
C convection reflow
Standard:
JEDEC Standard J-STD-020
Functional Diagram
Function
Pin No.
Vref
1
RF Input
3
RF Output
10, 11
Vbias
16
GND
Backside Paddle
N/C or GND
2, 4-9, 12-15
Mounting Config. Notes
1. A heatsink underneath the area of the PCB for the mounted
device is strictly required for proper thermal operation.
Damage to the device can occur without the use of one.
2. Ground / thermal vias are critical for the proper performance
of this device. Vias should use a .35mm (#80 / .0135" )
diameter drill and have a final plated thru diameter of .25
mm (.010" ).
3. Add as much copper as possible to inner and outer layers
near the part to ensure optimal thermal performance.
4. Mounting screws can be added near the part to fasten the
board to a heatsink. Ensure that the ground / thermal via
region contacts the heatsink.
5. Do not put solder mask on the backside of the PC board in
the region where the board contacts the heatsink.
6. RF trace width depends upon the PC board material and
construction.
7. Use 1 oz. Copper minimum.
8
All dimensions are in millimeters (inches). Angles are in
degrees.
MTTF vs. GND Tab Temperature
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
50
60
70
80
90
100
Tab temperature (� C)
M
T
T
F
(
m
i
l
l
i
o
n
h
r
s
)
1
2
3
4
12
11
10
9
16
15
14
13
5
6
7
8
N/C
RF OUT
RF OUT
N/C
Vref
N/C
RF IN
N/C
V
b
i
a
s
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C
N
/
C




