 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: WM8731 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Document Outline
- WM8731
- Portable Internet Audio CODEC with Headphone Driver and Programmable Sample Rates
- Advanced Information, Rev 2.0, February 2001
- DESCRIPTION
- FEATURES
- APPLICATIONS
- BLOCK DIAGRAM
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- TABLE OF FIGURES
- TABLE OF TABLES
- PIN CONFIGURATION
- ORDERING INFORMATION
- PIN DESCRIPTION
- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
- RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
- ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- POWER CONSUMPTION
- MASTER CLOCK TIMING
- DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE Ö MASTER MODE
- DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE Ö SLAVE MODE
- MPU INTERFACE TIMING
- DEVICE DESCRIPTION
- INTRODUCTION
- AUDIO SIGNAL PATH
- DEVICE OPERATION
- AUDIO DATA SAMPLING RATES
- ACTIVATING DSP AND DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE
- SOFTWARE CONTROL INTERFACE
- POWER DOWN MODES
- REGISTER MAP
- DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
- DAC FILTER RESPONSES
- ADC FILTER RESPONSES
- DIGITAL DE-EMPHASIS CHARACTERISTICS
- RECOMMENDED EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
- PACKAGE DIMENSIONS

WM8731
Portable Internet Audio CODEC with
Headphone Driver and Programmable Sample Rates
Advanced Information, Rev 2.0, February 2001
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Lutton Court, Bernard Terrace, Edinburgh, EH8 9NX, UK
Tel: +44 (0) 131 667 9386
Fax: +44 (0) 131 667 5176
Email: sales@wolfson.co.uk
www.wolfsonmicro.com
Advanced Information data sheets
contain preliminary data on new products
in the preproduction phase of
development. Supplementary data will be
published at a later date.
2001 Wolfson Microelectronics Ltd
.
DESCRIPTION
The WM8731 is a low power stereo CODEC with an
integrated headphone driver. It offers the user the unique
ability to independently program the ADC and DAC sample
rates from a single clock source. The WM8731 is designed
specifically for portable MP3 audio and speech players and
recorders. The WM8731 is also ideal for MD, CD-RW
machines and DAT recorders.
Stereo line and mono microphone level audio inputs are
provided, along with a mute function, programmable line
level volume control and a bias voltage output suitable for
an electret type microphone.
Stereo 24-bit multi-bit sigma delta ADCs and DACs are
used with oversampling digital interpolation and decimation
filters. Digital audio input word lengths from 16-32 bits and
sampling rates from 8kHz to 96kHz are supported.
Stereo audio outputs are buffered for driving headphones
from a programmable volume control, line level outputs are
also provided along with anti-thump mute and power
up/down circuitry.
The device is controlled via a 2 or 3 wire serial interface.
The interface provides access to all features including
volume controls, mutes, de-emphasis and extensive power
management facilities. The device is available in a small 28-
pin SSOP package.
FEATURES
∑
Audio
Performance
-
97dB SNR (`A' weighted @ 48kHz) ADC
-
100dB SNR (`A' weighted @ 48kHz) DAC
-
1.42 ≠ 3.6V Digital Supply Operation
-
2.7 ≠ 3.6V Analogue Supply Operation
∑
ADC and DAC Sampling Frequency: 8kHz ≠ 96kHz
∑
Selectable ADC High Pass Filter
∑
2 or 3-Wire MPU Serial Control Interface
∑
Programmable Audio Data Interface Modes
-
I
2
S, Left, Right Justified or DSP
-
16/20/24/32 bit Word Lengths
-
Master or Slave Clocking Mode
∑
Stereo Audio Inputs and Outputs
∑
Microphone Input and Electret Bias with Side Tone Mixer
∑
Input and Output Volume and Mute Controls
∑
Highly Efficient Headphone Driver
∑
Playback Mode Power Consumption < 18mW
∑
Analogue Pass Through Power Consumption < 9mW
∑
28-Pin SSOP Package
APPLICATIONS
∑
Portable MP3 Players and Recorders
∑
CD and Minidisc Recorders
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MUX
MUX
VOL
VOL
ADC
ADC
DIGITAL
FILTERS
DIGTAL AUDIO INTERFACE
CONTROL INTERFACE
DAC
DAC
VOL/
MUTE
VOL/
MUTE
H/P
DRIVER
H/P
DRIVER
CS
B
SD
I
N
SC
LK
RHPOUT
LHPOUT
ROUT
LOUT
RLINEIN
LLINEIN
VMID
DBV
DD
(3
.3V
)
DG
ND
AVDD
AGND
0dB/
20dB
MICIN
+12 to -34.5dB,
1.5dB Steps
CLK
O
UT
+6 to -73dB
1 dB Steps
HPVDD
HPGND
+6 to -73dB
1 dB Steps
+12 to -34.5dB,
1.5dB Steps
DCV
DD
(1
.5V
)
ADCL
RC
DA
CLR
C
BCL
K
DACD
AT
ADCD
AT
OSC
XT
I
/
MCL
K
XT
O
MO
DE
MICBIAS
MUTE
Bypass
Bypass
Side Tone
Side Tone
CLKIN
DIVIDER
(Div x1, x2)
CLKOUT
DIVIDER
(Div x1, x2)
ATTEN/
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
ATTEN/
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
WM8731

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................... 1
FEATURES ............................................................................................................ 1
APPLICATIONS ..................................................................................................... 1
BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................................................................. 1
PIN CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................... 6
ORDERING INFORMATION .................................................................................. 6
PIN DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................ 6
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS......................................................................... 7
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS ..................................................... 7
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................................... 8
TERMINOLOGY................................................................................................... 10
POWER CONSUMPTION .................................................................................... 11
MASTER CLOCK TIMING ................................................................................... 12
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE ≠ MASTER MODE
13
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE ≠ SLAVE MODE
14
MPU INTERFACE TIMING
15
DEVICE DESCRIPTION....................................................................................... 17
INTRODUCTION
17
AUDIO SIGNAL PATH
18
LINE INPUTS .......................................................................................................................................... 18
MICROPHONE INPUT ............................................................................................................................ 20
MICROPHONE BIAS............................................................................................................................... 21
ADC ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
ADC FILTERS ......................................................................................................................................... 23
DAC FILTERS ......................................................................................................................................... 23
DAC ......................................................................................................................................................... 24
LINE OUTPUTS ...................................................................................................................................... 24
HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER...................................................................................................................... 26
BYPASS MODE ...................................................................................................................................... 28
SIDETONE MODE................................................................................................................................... 29
DEVICE OPERATION
30
DEVICE RESETTING .............................................................................................................................. 30
CLOCKING SCHEMES ........................................................................................................................... 30
CORE CLOCK......................................................................................................................................... 30
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR........................................................................................................................ 31

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
3
CLOCKOUT ............................................................................................................................................ 31
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACES .............................................................................................................. 32
MASTER AND SLAVE MODE OPERATION .......................................................................................... 35
AUDIO DATA SAMPLING RATES
36
NORMAL MODE SAMPLE RATES ........................................................................................................ 37
128/192fs NORMAL MODE .................................................................................................................... 39
512/768fs NORMAL MODE .................................................................................................................... 39
USB MODE SAMPLE RATES................................................................................................................. 40
ACTIVATING DSP AND DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE
41
SOFTWARE CONTROL INTERFACE
41
SELECTION OF SERIAL CONTROL MODE .......................................................................................... 41
3-WIRE (SPI COMPATIBLE) SERIAL CONTROL MODE ...................................................................... 42
2-WIRE SERIAL CONTROL MODE........................................................................................................ 42
POWER DOWN MODES
43
REGISTER MAP
45
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS............................................................... 50
TERMINOLOGY
50
DAC FILTER RESPONSES ................................................................................. 51
ADC FILTER RESPONSES ................................................................................. 52
ADC HIGH PASS FILTER
53
DIGITAL DE-EMPHASIS CHARACTERISTICS................................................... 54
RECOMMENDED EXTERNAL COMPONENTS .................................................. 55
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS .................................................................................... 56

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
4
TABLE OF FIGURES
Figure 1 System Clock Timing Requirements ............................................................................ 12
Figure 2 Clock Out Timing Requirements................................................................................... 12
Figure 3 Master Mode Connection .............................................................................................. 13
Figure 4 Digital Audio Data Timing ≠ Master Mode ................................................................... 13
Figure 5 Slave Mode Connection................................................................................................. 14
Figure 6 Digital Audio Data Timing ≠ Slave Mode...................................................................... 14
Figure 7 Program Register Input Timing - 3-Wire MPU Serial Control Mode .......................... 15
Figure 8 Program Register Input Timing ≠ 2-Wire MPU Serial Control Mode ......................... 16
Figure 9 Line Input Schematic ..................................................................................................... 18
Figure 10 Line Input Application Drawing .................................................................................. 19
Figure 11 Microphone Input Schematic ...................................................................................... 20
Figure 12 Microphone Input and Bias Application Drawing ..................................................... 21
Figure 13 Microphone Bias Schematic ....................................................................................... 22
Figure 14 Multi-Bit Oversampling Sigma Delta ADC Schematic............................................... 22
Figure 15 ADC Digital Filter .......................................................................................................... 23
Figure 16 DAC Filter Schematic ................................................................................................... 23
Figure 17 Multi-Bit Oversampling Sigma Delta Schematic ....................................................... 24
Figure 18 Line Output Schematic ................................................................................................ 25
Figure 19 Line Outputs Application Drawing ............................................................................. 26
Figure 20 Headphone Amplifier Schematic ................................................................................ 26
Figure 21 Headphone Output Application Drawing ................................................................... 28
Figure 22 Signal Routing in Bypass Mode................................................................................... 28
Figure 23 Side Tone Mode Schematic......................................................................................... 29
Figure 24 Crystal Oscillator Application Circuit.......................................................................... 31
Figure 25 Left Justified Mode........................................................................................................ 32
Figure 26 I2S Mode........................................................................................................................ 33
Figure 27 Right Justified Mode ..................................................................................................... 33
Figure 28 DSP Mode....................................................................................................................... 33
Figure 29 Master Mode ................................................................................................................. 36
Figure 30 Slave Mode..................................................................................................................... 36
Figure 31 3-Wire Serial Interface................................................................................................... 42
Figure 32 2-Wire Serial Interface.................................................................................................. 42
Figure 33 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 0 ....................................................... 51
Figure 34 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 0................................................................................. 51
Figure 35 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 1 ....................................................... 51
Figure 36 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 1................................................................................. 51
Figure 37 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 2 ....................................................... 51
Figure 38 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 2................................................................................. 51
Figure 39 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 3 ....................................................... 52
Figure 40 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 3................................................................................. 52
Figure 41 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 0 ....................................................... 52
Figure 42 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 0................................................................................. 52
Figure 43 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 1 ....................................................... 52
Figure 44 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 1................................................................................. 52
Figure 45 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 2 ....................................................... 53
Figure 46 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 2................................................................................. 53
Figure 47 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 3 ....................................................... 53
Figure 48 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 3................................................................................. 53
Figure 49 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (32kHz) .............................................................. 54
Figure 50 De-Emphasis Error (32kHz) .......................................................................................... 54
Figure 51 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (44.1kHz) ........................................................... 54
Figure 52 De-Emphasis Error (44.1kHz) ....................................................................................... 54
Figure 53 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (48kHz) .............................................................. 54
Figure 54 De-Emphasis Error (48kHz) .......................................................................................... 54
Figure 55 External Components Diagram.................................................................................... 55

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
5
TABLE OF TABLES
Table 1 Powerdown Mode Current Consumption Examples .................................................... 11
Table 2 Line Input Software Control............................................................................................ 19
Table 3 Microphone Input Software Control............................................................................... 21
Table 4 ADC Software Control ..................................................................................................... 22
Table 5 ADC Software Control ..................................................................................................... 23
Table 6 DAC Software Control ..................................................................................................... 24
Table 7 Output Software Control ................................................................................................. 25
Table 8 Headphone Output Software Control ............................................................................ 27
Table 9 Bypass Mode Software Control...................................................................................... 29
Table 10 Side Tone Mode Table ................................................................................................... 29
Table 11 Software Control of Reset............................................................................................. 30
Table 12 Software Control of Core Clock.................................................................................... 30
Table 13 Programming CLKOUT.................................................................................................. 31
Table 14 Digital Audio Interface Control ..................................................................................... 35
Table 15 Programming Master/Slave Modes .............................................................................. 35
Table 16 Sample Rate Control...................................................................................................... 37
Table 17 Normal Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table.................................................................. 38
Table 18 Normal Mode Actual Sample Rates.............................................................................. 39
Table 19 128fs Normal Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table........................................................ 39
Table 20 USB Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table....................................................................... 40
Table 21 USB Mode Actual Sample Rates .................................................................................. 41
Table 22 Activating DSP and Digital Audio Interface................................................................. 41
Table 23 Control Interface Mode Selection................................................................................. 41
Table 24 2-Wire MPU Interface Address Selection..................................................................... 42
Table 25 Power Conservation Modes Software Control ........................................................... 43
Table 26 Standby Mode ................................................................................................................ 44
Table 27 Poweroff Mode ............................................................................................................... 45
Table 28 Mapping of Program Registers..................................................................................... 45
Table 29 Register Map Description.............................................................................................. 50
Table 30 Digital Filter Characteristics ......................................................................................... 50

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
6
PIN CONFIGURATION
ORDERING INFORMATION
DEVICE
TEMP. RANGE
PACKAGE
XWM8731EDS
-10 to +70
o
C
28-pin SSOP
1
AVDD
2
AGND
3
MICBIAS
4
VMID
5
MICIN
6
RLINEIN
7
LLINEIN
8
DCVDD
9
MODE
10
CSB
SDIN
SCLK
XTO
XTI/MCLK
15
CLKOUT
DGND
ADCLRC
ADCDAT
DACDAT
DACLRC
BCLK
DBVDD
LHPOUT
HPGND
HPVDD
RHPOUT
LOUT
ROUT
11
12
13
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
28
27
26
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN
NAME
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
1
DBVDD
Supply
Digital Buffers VDD
2
CLKOUT
Digital Output
Buffered Clock Output
3
BCLK
Digital Input/Output
Digital Audio Bit Clock, Pull Down, (see Note 1)
4
DACDAT
Digital Input
DAC Digital Audio Data Input
5
DACLRC
Digital Input/Output
DAC Sample Rate Left/Right Clock, Pull Down (see Note 1)
6
ADCDAT
Digital Output
ADC Digital Audio Data Output
7
ADCLRC
Digital Input/Output
ADC Sample Rate Left/Right Clock, Pull Down (see Note 1)
8
HPVDD
Supply
Headphone VDD
9
LHPOUT
Analogue Output
Left Channel Headphone Output
10
RHPOUT
Analogue Output
Right Channel Headphone Output
11
HPGND
Ground
Headphone GND
12
LOUT
Analogue Output
Left Channel Line Output
13
ROUT
Analogue Output
Right Channel Line Output
14
AVDD
Supply
Analogue VDD
15
AGND
Ground
Analogue GND
16
VMID
Analogue Output
Mid-rail reference decoupling point
17
MICBIAS
Analogue Output
Electret Microphone Bias
18
MICIN
Analogue Input
Microphone Input (AC coupled)
19
RLINEIN
Analogue Input
Right Channel Line Input (AC coupled)
20
LLINEIN
Analogue Input
Left Channel Line Input (AC coupled)
21
MODE
Digital Input
Control Interface Selection, Pull Up (see Note 1)
22
CSB
Digital Input
3-Wire MPU Chip Select/ 2-Wire MPU interface address selection,
active low, Pull up (see Note 1)
23
SDIN
Digital Input/Output
3-Wire MPU Data Input / 2-Wire MPU Data Input
24
SCLK
Digital Input
3-Wire MPU Clock Input / 2-Wire MPU Clock Input
25
XTI/MCLK
Digital Input
Crystal Input or Master Clock Input (MCLK)
26
XTO
Digital Output
Crystal Output
27
DCVDD
Supply
Digital Core VDD
28
DGND
Ground
Digital GND
Note:
1.
Pull Up/Down only present when Control Register Interface ACTIVE=0 to conserve power.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
7
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Absolute Maximum Ratings are stress ratings only. Permanent damage to the device may be caused by continuously operating at
or beyond these limits. Device functional operating limits and guaranteed performance specifications are given under Electrical
Characteristics at the test conditions specified
ESD Sensitive Device. This device is manufactured on a CMOS process. It is therefore generically susceptible
to damage from excessive static voltages. Proper ESD precautions must be taken during handling and storage
of this device.
CONDITION
MIN
MAX
Digital supply voltage
-0.3V
+3.63V
Analogue supply voltage
-0.3V
+3.63V
Voltage range digital inputs
DGND -0.3V
DVDD +0.3V
Voltage range analogue inputs
AGND -0.3V
AVDD +0.3V
Master Clock Frequency (see Note 4)
40MHz
Operating temperature range, T
A
-10
∞
C
+70
∞
C
Storage temperature
-65
∞
C
+150
∞
C
Package body temperature (soldering 10 seconds)
+240
∞
C
Package body temperature (soldering 2 minutes)
+183
∞
C
Notes:
1.
Analogue and digital grounds must always be within 0.3V of each other.
2.
The digital supply core voltage (DCVDD) must always be less than or equal to the analogue supply voltage (AVDD) or
digital supply buffer voltage (DBVDD).
3.
The digital supply buffer voltage (DBVDD) must always be less than or equal to the analogue supply voltage (AVDD).
4. When
CLKIDIV2=1
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Digital supply range (Core)
DCVDD
1.42
3.6
V
Digital supply range (Buffer)
DBVDD
2.7
3.6
V
Analogue supply range
AVDD, HPVDD
2.7
3.6
V
Ground
DGND,AGND,HPGND
0
V
Total analogue supply current
IAVDD, IHPVDD
DCVDD, DBVDD,
AVDD,
HPVDD= 3.3V
13
mA
Digital supply current
IDCVDD, IDBVDD
DCVDD, DBVDD,
AVDD,
HPVDD= 3.3V
3
mA
Standby Current Consumption
10
uA

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
8
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Digital Logic Levels (CMOS Levels)
Input LOW level
V
IL
.3 x DBVDD
V
Input HIGH level
V
IH
.7 x DBVDD
V
Output LOW
V
OL
0.10 x
DBVDD
V
Output HIGH
V
OH
.9 x DBVDD
V
Power On Reset Threshold (DCVDD)
DCVDD Threshold On -> Off
V
th
0.7
0.9
1.2
V
Hysteresis
V
IH
0.3
V
DCVDD Threshold Off -> On
V
OL
0.6
V
Analogue Reference Levels
Reference voltage (VMID)
V
VMID
AVDD/2 ≠
50mV
AVDD/2
AVDD/2 +
50mV
V
Potential divider resistance
R
VMID
40k
50k
60k
Ohms
Line Input to ADC
Input Signal Level (0dB)
V
INLINE
1.0
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
SNR (Note 1,3)
A-weighted, 0dB gain
@ fs = 48kHz
93
97
dB
SNR (Note 1,3)
A-weighted, 0dB gain
@ fs = 96kHz
94
dB
SNR (Note 1,3)
A-weighted, 0dB gain
@ fs = 48kHz, AVDD =
2.7V
90
dB
Dynamic Range (Note 3)
DR
A-weighted, -60dB full
scale input
93
97
dB
THD
-1dB input, 0dB gain
-85
-80
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB
ADC channel separation
1kHz input
90
dB
Programmable Gain Maximum
Programmable Gain Minimum
1kHz input
Rsource < 50 Ohms
+12
-34.5
dB
Programmable Gain Step Size
Guaranteed Monotonic
1.5
dB
Mute attenuation
0dB, 1kHz input
80
dB
0dB gain
40k
50k
Ohms
Input Resistance
R
INLINE
12dB gain
10k
20k
Ohms
Input Capacitance
C
INLINE
10
pF
Microphone Input to ADC @ 0dB Gain, fs = 8kHz (40k ohm Source Impedance. See Figure 11)
Input Signal Level (0dB)
V
INMIC
1.0
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
SNR (Note 1,3)
A-weighted, 0dB gain
85
90
dB
Dynamic Range (Note 3)
DR
A-weighted, -60dB full
scale input
85
90
dB
THD
0dB input, 0dB gain
-80
-75
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
9
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Programmable Gain Boost
MICBOOST bit
set
1kHz input
Rsource < 50 Ohms
34
dB
Mic Path gain (MICBOOST gain
is additional to this nominal
gain)
MICBOOST = 0
Rsource < 50 Ohms
14
dB
Mute attenuation
0dB, 1kHz input
80
dB
Input Resistance
R
INMIC
8k
10k
12k
Ohms
Input Capacitance
C
INMIC
10
pF
Microphone Bias
Bias Voltage
V
MICBIAS
.75*AVDD ≠
100mV
0.75*AVDD
.75*AVDD +
100mV
V
Bias Current Source
I
MICBIAS
3
mA
Output Noise Voltage
Vn
1K to 20kHz
25
nV/
Hz
Line Output for DAC Playback Only (Load
= 10k ohms. 50pF)
0dBfs Full scale output voltage
At LINE outputs
1.0 x
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
SNR (Note 1,2,3)
A-weighted,
@ fs = 48kHz
90
100
dB
SNR (Note 1,2,3)
A-weighted
@ fs = 96kHz
98
dB
SNR (Note 1,2,3)
A-weighted,
@ fs = 48kHz, AVDD
= 2.7V
93
dB
Dynamic Range (Note 3)
DR
A-weighted, -60dB
full scale input
85
90
dB
1kHz, 0dBfs
-88
-80
dB
THD
1kHz, -3dBfs
-92
-86
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB
DAC channel separation
100
dB
Analogue Line Input to Line Output (Load
= 10k ohms. 50pF, No Gain on Input ) Bypass Mode
0dB Full scale output voltage
1.0 x
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
SNR (Note 1, 3)
90
95
dB
1kHz, 0dB
-86
-80
dB
THD
1kHz, -3dB
-92
-86
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB
Mute attenuation
1kHz, 0dB
80
dB
Stereo Headphone Output
0dB Full scale output voltage
1.0 x
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
Max Output Power RL = 32
ohms
P
O
30
mW
Max Output Power RL = 16
ohms
P
O
40
mW

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
10
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
SNR (Note 3)
A-weighted
90
97
dB
1kHz, R
L
= 32 ohms @
P
O
= 10mW rms
0.1
60
%
dB
THD
1kHz, R
L
= 32 ohms @
P
O
= 20mW rms
1.0
40
%
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB
Programmable Gain Maximum
Programmable Gain Minimum
1kHz
6
-73
dB
Programmable Gain Step Size
1kHz
1
dB
Mute attenuation
1kHz, 0dB
80
dB
Microphone Input to Headphone Output Side Tone Mode
0dB Full scale output voltage
1.0 x
AVDD/3.3
Vrms
SNR (Note 1, 3)
90
95
dB
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
PSSR
1kHz 100mVpp
50
dB
20Hz to 20kHz
100mVpp
45
dB
Programmable Attenuation
Maximum
Programmable Attenuation
Minimum
1kHz
15
6
dB
Programmable Attenuation Step
Size
1kHz
3
dB
Mute attenuation
1kHz, 0dB
80
dB
Notes:
1.
Ratio of output level with 1kHz full scale input, to the output level with the input short circuited, measured `A' weighted
over a 20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth using an Audio analyser.
2.
Ratio of output level with 1kHz full scale input, to the output level with all zeros into the digital input, measured `A'
weighted over a 20Hz to 20kHz bandwidth.
3.
All performance measurements done with 20kHz low pass filter, and where noted an A-weight filter. Failure to use
such a filter will result in higher THD+N and lower SNR and Dynamic Range readings than are found in the Electrical
Characteristics. The low pass filter removes out of band noise; although it is not audible it may affect dynamic
specification values.
4.
VMID decoupled with 10uF and 0.1uF capacitors (smaller values may result in reduced performance).
TERMINOLOGY
1.
Signal-to-noise ratio (dB) - SNR is a measure of the difference in level between the full scale output and the output
with no signal applied. (No Auto-zero or Automute function is employed in achieving these results).
2. Dynamic range (dB) - DR is a measure of the difference between the highest and lowest portions of a signal.
Normally a THD+N measurement at 60dB below full scale. The measured signal is then corrected by adding the 60dB
to it. (e.g. THD+N @ -60dB= -32dB, DR= 92dB).
3.
THD+N (dB) - THD+N is a ratio, of the rms values, of (Noise + Distortion)/Signal.
4.
Channel Separation (dB) - Also known as Cross-Talk. This is a measure of the amount one channel is isolated from
the other. Normally measured by sending a full scale signal down one channel and measuring the other.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
11
POWER CONSUMPTION
CURRENT CONSUMPTION
MODE
DESCRIPTION
PO
W
E
R
O
FF
CL
KOUT
P
D
OS
CP
D
OUTP
D
DACP
D
ADCP
D
MIC
P
D
LIN
E
IN
PD
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Record and Playback
All active
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
13
TBD
mA
Oscillator disabled
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
12
mA
Oscillator and
CLKOUT disabled,
No microphone
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
11
mA
Playback Only
Playback Only
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
7
TBD
mA
Playback Only
Oscillator and
CLKOUT disabled
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
6
mA
Record Only
Record Only
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
9
mA
Line Record Only
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
8
mA
Record Only,
Oscillator disabled
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
7
mA
Microphone Record
Only,
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
9
mA
Microphone Record
Only, Oscillator
disabled
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
8
mA
Side Tone
Microphone to
Headphone Out
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
3
mA
Microphone to
Headphone Out,
Oscillator disabled
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
2
mA
Analogue Bypass
Line In to Line Out
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
3
mA
Line In to Line Out,
Oscillator disabled
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
2
mA
Standby
Standby
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1.5
TBD
mA
Standby, Oscillator
and CLKOUT
disabled
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0.05
mA
Power Down
Power Down
1
0
0
X
1
1
X
X
1.5
mA
Power Down,
Oscillator and
CLKOUT disabled
1
1
1
X
1
1
X
X
0.01
TBD
mA
Table 1 Powerdown Mode Current Consumption Examples
Notes:
1.
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C. Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz,
XTI/MCLK = 256fs (12.288MHz).
2.
All figures are quiescent, with no signal.
3.
The power dissipation in the headphone itself not included in the above table.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
12
MASTER CLOCK TIMING
XTI/MCLK
t
XTIL
t
XTIH
t
XTIY
Figure 1 System Clock Timing Requirements
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
System Clock Timing Information
XTI/MCLK System clock pulse width
high
t
XTIH
18
ns
XTI/MCLK System clock pulse width
low
t
XTIL
18
ns
XTI/MCLK System clock cycle time
t
XTIY
54
ns
XTI/MCLK Duty cycle
40:60
60:40
XTI/MCLK
t
COP
CLKOUT
CLKOUT
(DIV X2)
Figure 2 Clock Out Timing Requirements
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
System Clock Timing Information
CLKOUT propagation delay from
XTI/MCLK falling edge
t
COP
0
10
ns

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
13
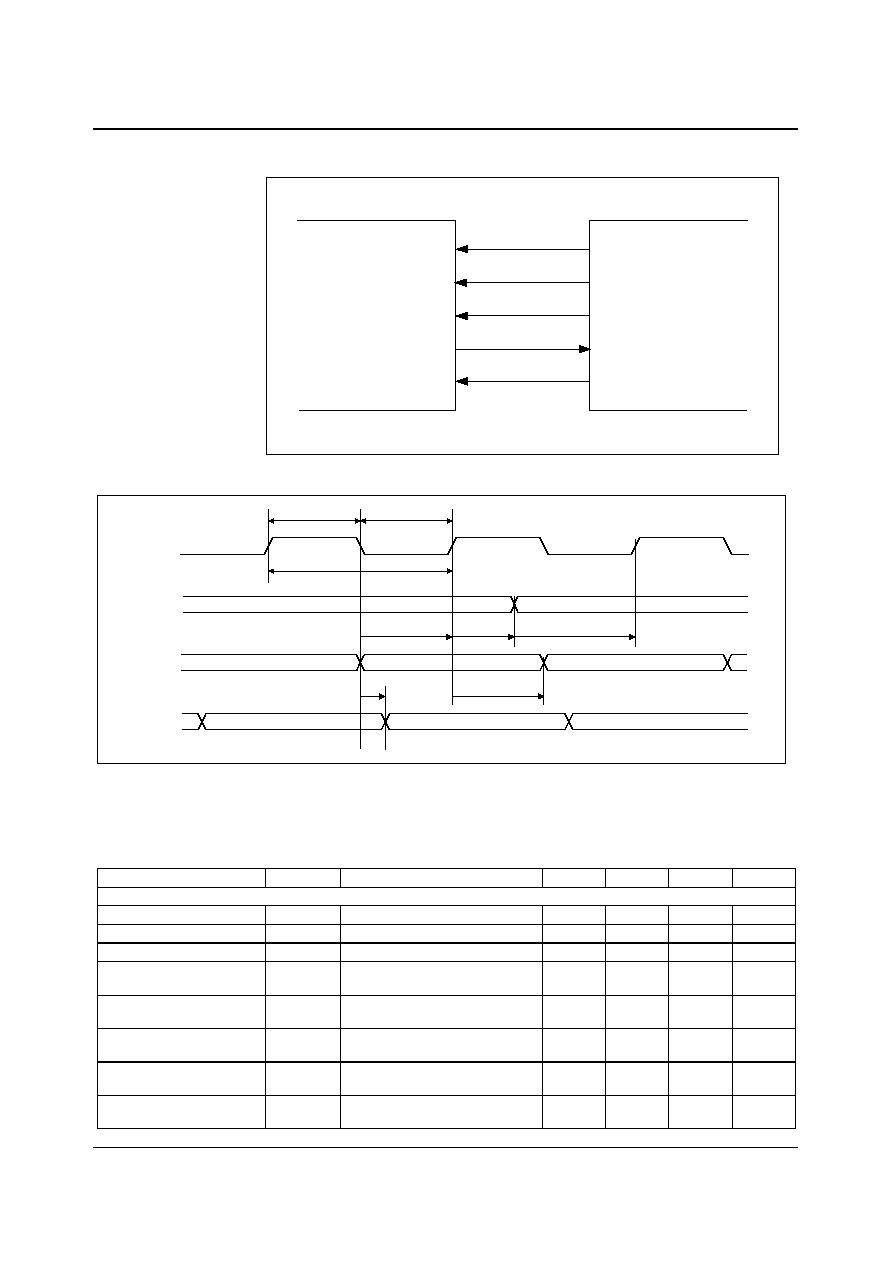
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE ≠ MASTER MODE
BCLK
ADCDAT
ADCLRC
DACDAT
DACLRC
WM8731
CODEC
DSP
ENCODER/
DECODER
Note: ADC and DAC can run at different rates
Figure 3 Master Mode Connection
BCLK
(Output)
ADCDAT
ADCLRC/
DACLRC
(Outputs)
t
DL
DACDAT
t
DDA
t
DHT
t
DST
Figure 4 Digital Audio Data Timing ≠ Master Mode
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Audio Data Input Timing Information
ADCLRC/DACLRC
propagation delay from
BCLK falling edge
t
DL
0
10
ns
ADCDAT propagation delay
from BCLK falling edge
t
DDA
0
10
ns
DACDAT setup time to
BCLCK rising edge
t
DST
10
ns
DACDAT hold time from
BCLK rising edge
t
DHT
10
ns
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
14
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE ≠ SLAVE MODE
BCLK
ADCDAT
ADCLRC
DACDAT
DACLRC
WM8731
CODEC
DSP
ENCODER/
DECODER
Note: The ADC and DAC can run at different rates
Figure 5 Slave Mode Connection
BCLK
DACLRC/
ADCLRC
t
BCH
t
BCL
t
BCY
DACDAT
ADCDAT
t
LRSU
t
DS
t
LRH
t
DH
t
DD
Figure 6 Digital Audio Data Timing ≠ Slave Mode
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Audio Data Input Timing Information
BCLK cycle time
t
BCY
50
ns
BCLK pulse width high
t
BCH
20
ns
BCLK pulse width low
t
BCL
20
ns
DACLRC/ADCLRC set-up
time to BCLK rising edge
t
LRSU
10
ns
DACLRC/ADCLRC hold
time from BCLK rising edge
t
LRH
10
ns
DACDAT set-up time to
BCLK rising edge
t
DS
10
ns
DACDAT hold time from
BCLK rising edge
t
DH
10
ns
ADCDAT propagation delay
from BCLK falling edge
t
DD
0
10
ns

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
15
MPU INTERFACE TIMING
CSB
SCLK
SDIN
t
CSL
t
DHO
t
DSU
t
CSH
t
SCY
t
SCH
t
SCL
t
SCS
LSB
t
CSS
Figure 7 Program Register Input Timing - 3-Wire MPU Serial Control Mode
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Program Register Input Information
SCLK rising edge to CSB rising
edge
t
SCS
60
ns
SCLK pulse cycle time
t
SCY
80
ns
SCLK pulse width low
t
SCL
20
ns
SCLK pulse width high
t
SCH
20
ns
SDIN to SCLK set-up time
t
DSU
20
ns
SCLK to SDIN hold time
t
DHO
20
ns
CSB pulse width low
t
CSL
20
ns
CSB pulse width high
t
CSH
20
ns
CSB rising to SCLK rising
t
CSS
20
ns

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
16
SDIN
SCLK
t
3
t
1
t
6
t
2
t
7
t
5
t
4
t
3
t
8
t
10
Figure 8 Program Register Input Timing ≠ 2-Wire MPU Serial Control Mode
Test Conditions
AVDD, HPVDD, DBVDD = 3.3V, AGND = 0V, DCVDD = 1.5V, DGND = 0V, T
A
= +25
o
C, Slave Mode, fs = 48kHz, XTI/MCLK =
256fs unless otherwise stated.
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
Program Register Input Information
SCLK Frequency
0
400
kHz
SCLK Low Pulsewidth
t
1
600
ns
SCLK High Pulsewidth
t
2
1.3
us
Hold Time (Start Condition)
t
3
600
ns
Setup Time (Start Condition)
t
4
600
ns
Data Setup Time
t
5
100
ns
SDIN, SCLK Rise Time
t
6
300
ns
SDIN, SCLK Fall Time
t
7
300
ns
Setup Time (Stop Condition)
t
8
600
ns
Data Hold Time
t
10
900
ns

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
17
DEVICE DESCRIPTION
INTRODUCTION
The WM8731 is a low power audio CODEC designed specifically for portable audio products. It's
features, performance and low power consumption make it ideal for portable MP3 players and
portable mini-disc players.
The CODEC includes line and microphone inputs to the on-board ADC, line and headphone outputs
from the on-board DAC, a crystal oscillator, configurable digital audio interface and a choice of 2 or 3
wire MPU control interface. It is fully compatible and an ideal partner for a range of industry standard
microprocessors, controllers and DSPs.
The CODEC includes three low noise inputs - mono microphone and stereo line. Line inputs have
+12dB to -34dB logarithmic volume level adjustments and mute. The Microphone input has -6dB to
34dB volume level adjustment. An electret microphone bias level is also available. All the required
input filtering is contained within the device with no external components required.
The on-board stereo analogue to digital converter (ADC) is of a high quality using a multi-bit high-
order oversampling architecture delivering optimum performance with low power consumption. The
output from the ADC is available on the digital audio interface. The ADC includes an optional digital
high pass filter to remove unwanted dc components from the audio signal.
The on-board digital to analogue converter (DAC) accepts digital audio from the digital audio
interface. Digital filter de-emphasis at 32kHz, 44.1kHz and 48kHz can be applied to the digital data
under software control. The DAC employs a high quality multi-bit high-order oversampling
architecture to again deliver optimum performance with low power consumption.
The DAC outputs, Microphone (SIDETONE) and Line Inputs (BYPASS) are available both at line
level and through a headphone amplifier capable of efficiently driving low impedance headphones.
The headphone output volume is adjustable in the analogue domain over a range of +6dB to ≠73dB
and can be muted.
The design of the WM8731 has given much attention to power consumption without compromising
performance. It includes the ability to power off selective parts of the circuitry under software control,
thus conserving power. Nine separate power save modes be configured under software control
including a standby and power off mode.
Special techniques allow the audio to be muted and the device safely placed into standby, sections
of the device powered off and volume levels adjusted without any audible clicks, pops or zipper
noises. Therefore standby and power off modes maybe used dynamically under software control,
whenever recording or playing is not required.
The device caters for a number of different sampling rates including industry standard 8kHz, 32kHz,
44.1kHz, 48kHz, 88.2kHz and 96kHz. Additionally, the device has an ADC and DAC that can operate
at different sample rates.
There are two unique schemes featured within the programmable sample rates of the WM8731:
Normal industry standard 256/384fs sampling mode may be used, with the added ability to mix
different sampling rates. Also a special USB mode is included, whereby all audio sampling rates can
be generated from a 12.00MHZ USB clock. Thus, for example, the ADC can record to the DSP at
44.1kHz and be played back from the CODEC at 8kHz with no external digital signal processing
required. The digital filters used at for both record and playback are optimised for each sampling rate
used.
The digitised output is available in a number of audio data formats I
2
S, DSP Mode (a burst mode in
which frame sync plus 2 data packed words are transmitted), MSB-First, left justified and MSB-First,
right justified. The digital audio interface can operate in both master or slave modes.
The software control uses either 2 or 3-wire MPU interface.
A crystal oscillator is included on board the device. The device can generate the system master clock
or alternatively it can accept an external master clock from the audio system.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
18
AUDIO SIGNAL PATH
LINE INPUTS
The WM8731 provides Left and Right channel line inputs (RLINEIN and LLINEIN). The inputs are
high impedance and low capacitance, thus ideally suited to receiving line level signals from external
hi-fi or audio equipment.
Both line inputs include independent programmable volume level adjustments and ADC input mute.
The scheme is illustrated in Figure 9. Passive RF and active Anti-Alias filters are also incorporated
within the line inputs. These prevent high frequencies aliasing into the audio band or otherwise
degrading performance.
12.5k
VMID
LINEIN
To
ADC
Figure 9 Line Input Schematic
The gain between the line inputs and the ADC is logarithmically adjustable from +12dB to ≠34.5dB in
1.5dB steps under software control. The ADC Full Scale input is 1.0V rms at AVDD = 3.3 volts. Any
voltage greater than full scale will possibly overload the ADC and cause distortion. Note that the full
scale input tracks directly with AVDD. The gain is independently adjustable on both Right and Left
Line Inputs. However, by setting the INBOTH bit whilst programming the volume control, both
channels are simultaneously updated with the same value. Use of INBOTH reduces the required
number of software writes required. The line inputs to the ADC can be muted in the analogue domain
under software control. The software control registers are shown Table 2. Note that the Line Input
Mute only mutes the input to the ADC, this will still allow the Line Input signal to pass to the line
output in Bypass Mode.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
19
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
4:0
LINVOL[4:0]
10111
( 0dB )
Left Channel Line Input Volume
Control
11111 = +12dB . . 1.5dB steps down
to 00000 = -34.5dB
7
LINMUTE
1
Left Channel Line Input Mute to ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
0000000
Left Line In
8
LRINBOTH
0
Left to Right Channel Line Input
Volume and Mute Data Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
LINVOL[4:0] and LINMUTE to
RINVOL[4:0] and RINMUTE
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
4:0
RINVOL[4:0]
10111
( 0dB )
Right Channel Line Input Volume
Control
11111 = +12dB . .1.5dB steps down
to 00000 = -34.5dB
7
RINMUTE
1
Right Channel Line Input Mute to
ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
0000001
Right Line In
8
RLINBOTH
0
Right to Left Channel Line Input
Volume and Mute Data Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
RINVOL[4:0] and RINMUTE to
LINVOL[4:0] and LINMUTE
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
Table 2 Line Input Software Control
The line inputs are biased internally through the operational amplifier to VMID. Whenever the line
inputs are muted or the device placed into standby mode, the line inputs are kept biased to VMID
using special anti-thump circuitry. This reduces any audible clicks that may otherwise be heard when
re-activating the inputs.
The external components required to complete the line input application is shown in the Figure 10.
AGND
AGND
R1
R2
C1
C2
AGND
LINEIN
Figure 10 Line Input Application Drawing

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
20
For interfacing to a typical CD system, it is recommended that the input is scaled to ensure that there
is no clipping of the signal. R1 = 5.6k, R2 = 5.6k, C1 = 220pF, C2 = 1
µ
F.
R1 and R2 form a resistive divider to attenuate the 2 Vrms output from a CD player to a 1 Vrms level,
so avoiding overloading the inputs. R2 also provides a discharge path for C2, thus preventing the
input to C2 charging to an excessive voltage which may otherwise damage any equipment connected
that is not suitably protected against high voltages. C1 forms an RF low pass filter for increasing the
rejection of RF interference picked up on any cables. C2 forms a DC blocking capacitor to remove
the DC path between the WM8731 and the driving audio equipment. C2 together with the input
impedance of the WM8731 form a high pass filter.
MICROPHONE INPUT
MICIN is a high impedance, low capacitance input suitable for connection to a wide range of
monophonic microphones of different dynamics and sensitivities.
The MICIN includes programmable volume adjustments and a mute function. The scheme is shown
in Figure 11. Passive RF and active Anti-Alias filters are also incorporated within the microphone
inputs. These allow a matched interface to the multi-bit oversampling ADC and preventing high
frequencies aliasing into the audio band or otherwise degrading performance.
50k
10k
VMID
MICIN
To
ADC
VMID
20dB GAIN BOOST
Figure 11 Microphone Input Schematic
There are 2 stages of gain made up of two low noise inverting operational amplifiers.
The 1
st
stage comprises a nominal gain of G1 = 50k/10k = 5. By adding an external resistor (Rmic) in
series with MICIN the gain of stage can be adjusted. For example adding Rmic = 40K sets the gain
of stage 1 to x1 (0dB). The equation below can be used to calculate the gain versus Rmic.
G1 = 50k/ (Rmic + 10k)
Or alternatively to calculate the value of Rmic to achieve a given gain, G1.
Rmic = (50k/G1) ≠ 10k
The internal 50k and 10k resistors have a tolerance of 15%. For Rmicext = 90k G = 0.5 (-6dB) and
for Rmicext = 0 G = x10 (14dB).
The 2
nd
stage comprises a 0dB gain stage that can be software configured to provide a fixed 20dB of
gain for low sensitivity microphones.
The microphone input can therefore be configured with a variable gain of between -6dB and 14dB on
the 1
st
stage, and an additional fixed 0dB or 20dB on the 2
nd
stage. This allows for all gains to the
input signal in the range ≠6dB to 34dB to be catered for.
The ADC Full Scale input is 1.0V rms at AVDD = 3.3 volts. Any voltage greater than full scale will
possibly overload the ADC and cause distortion. Note that the full scale input tracks directly with
AVDD. Stage 1 and Stage 2 gains should be configured so that the ADC receives a maximum signal
equal to its full scale for maximising the signal to noise.
The software control for the MICIN is shown in Table 3. Note that the Microphone Mute only mutes
the input to the ADC, this will still allow the Microphone Input signal to pass to the line output in
Sidetone Mode.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
21
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0
MICBOOST
0
Microphone Input Level Boost
1 = Enable Boost
0 = Disable Boost
0000100
Analogue Audio
Path Control
1
MUTEMIC
1
Line Input Mute to ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
Table 3 Microphone Input Software Control
The microphone input is biased internally through the operational amplifier to VMID. Whenever the
line inputs are muted the MICIN input is kept biased to VMID using special anti-thump circuitry. This
reduces any audible clicks that may otherwise be heard when re-activating the input.
The application drawing for the microphone is shown in Figure 12.
AGND
AGND
R1
R2
C1
C2
MICIN
MICBIAS
AGND
FROM
MICROPHONE
Rmic
Figure 12 Microphone Input and Bias Application Drawing
Recommended component values are C1 = 220pF (npo ceramic), C2 = 1
µ
F, R1 = 680 ohms, R2 =
47k. Rmic values depends on gain setting (see above).
R1 and R2 form part of the biasing network (refer to Microphone Bias section below). R1 connected
to MICBIAS is necessary only for electret type microphones that require a voltage bias. R2 should
always be present to prevent the microphone input from charging to a high voltage which may
damage the microphone on connection. R1 and R2 should be large so as not to attenuate the signal
from the microphone, which can have source impedance greater than 2k. C1 together with the
source impedance of the microphone and the input impedance of MICIN forms an RF filter. C2 is a
DC blocking capacitor to allow the microphone to be biased at a different DC voltage to the MICIN
signal.
MICROPHONE BIAS
The MICBIAS output provides a low noise reference voltage suitable for biasing electret type
microphones and the associated external resistor biasing network. Refer to the Microphone Input
section for an application drawing and further description.
The scheme for MICBIAS is shown in Figure 13. Note that there is a maximum source current
capability of 3mA available for the MICBIAS. This limits the smallest value of external biasing
resistors that can safely be used.
Note that the MICBIAS output is not active in standby mode.
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
22
VMID
MICBIAS
AGND
R
2R
Figure 13 Microphone Bias Schematic
ADC
The WM8731 uses a multi-bit oversampled sigma-delta ADC. A single channel of the ADC is
illustrated in the Figure 14.
FROM MICROPHONE
INPUT
FROM LINE INPUT
ANALOG
INTEGRATOR
INSEL
MULTI
BITS
TO ADC DIGITAL FILTERS
Figure 14 Multi-Bit Oversampling Sigma Delta ADC Schematic
The use of multi-bit feedback and high oversampling rates reduces the effects of jitter and high
frequency noise.
The ADC Full Scale input is 1.0V rms at AVDD = 3.3 volts. Any voltage greater than full scale will
possibly overload the ADC and cause distortion. Note that the full scale input tracks directly with
AVDD.
The device employs a pair of ADCs. The input can be selected from either the Line Inputs or the
Microphone input under software control. The two channels cannot be selected independently. The
control is shown in Table 4.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0000100
Analogue
Audio Path
Control
2
INSEL
0
Microphone/Line Input Select to ADC
1 = Microphone Input Select to ADC
0 = Line Input Select to ADC
Table 4 ADC Software Control
The digital data from the ADC is fed for signal processing to the ADC Filters.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
23
ADC FILTERS
The ADC filters perform true 24 bit signal processing to convert the raw multi-bit oversampled data
from the ADC to the correct sampling frequency to be output on the digital audio interface. Figure 15
illustrates the digital filter path.
FROM ADC
DIGITAL
HPF
DIGITAL
DECIMATION
FILTER
TO DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFACE
DIGITAL
DECIMATOR
HPFEN
Figure 15 ADC Digital Filter
The ADC digital filters contain a digital high pass filter, selectable via software control. The high-pass
filter response detailed in Digital Filter Characteristics. The software control is shown in Table 5.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0000101
Digital Audio
Path Control
0
ADCHPD
0
ADC High Pass Filter Enable
(Digital)
1 = Enable High Pass Filter
0 = Disable High Pass Filter
Table 5 ADC Software Control
There are several types of ADC filters, frequency and phase responses of these are shown in Digital
Filter Characteristics. The filter types are automatically configured depending on the sample rate
chosen. Refer to the sample rate section for more details.
DAC FILTERS
The DAC filters perform true 24 bit signal processing to convert the incoming digital audio data from
the digital audio interface at the specified sample rate to multi-bit oversampled data for processing by
the analogue DAC. Figure 16 illustrates the DAC digital filter path.
FROM DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFACE
MUTE
DIGITAL
INTERPOLATION
FILTER
TO LINE
OUTPUTS
DIGITAL
DE_EMPHASIS
DEEMP
DACMU
Figure 16 DAC Filter Schematic

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
24
The DAC digital filter can apply digital de-emphasis under software control, as shown in Table 6.The
DAC can also perform a soft mute where the audio data is digitally brought to a mute level. This
removes any abrupt step changes in the audio that might otherwise result in audible clicks in the
audio outputs.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
2:1
DEEMP[1:0]
00
De-emphasis Control
(Digital)
11 = 48kHz
10 = 44.1kHz
01 = 32kHz
00 = Disable
0000101
Digital
Audio Path
Control
3
DACMU
1
DAC Soft Mute Control
(Digital)
1 = Enable soft mute
0 = Disable soft mute
Table 6 DAC Software Control
DAC
The WM8731 employs a multi-bit sigma delta oversampling digital to analogue converter. The
scheme for the converter is illustrated in Figure 17.
FROM DAC
DIGITAL
FILTERS
TO LINE OUTPUT
Figure 17 Multi-Bit Oversampling Sigma Delta Schematic
The DAC converts the multi-level digital audio data stream from the DAC digital filters into high
quality analogue audio.
LINE OUTPUTS
The WM8731 provides two low impedance line outputs LLINEOUT and RLINEOUT, suitable for
driving typical line loads of impedance 10K and capacitance 50pF. The line output is used to
selectively sum the outputs from the DAC or/and the Line inputs in bypass mode.
The LLINEOUT and RLINEOUT outputs are only available at a line output level and are not level
adjustable in the analogue domain, having a fixed gain of 0dB. The level is fixed such that at the DAC
full scale level the output level is Vrms at AVDD = 3.3 volts. Note that the DAC full scale level tracks
directly with AVDD. The scheme is shown in Figure 18. The line output includes a low order audio
low pass filter for removing out-of band components from the sigma-delta DAC. Therefore no further
external filtering is required in most applications.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
25
VMID
FROM LINE
INPUTS
LINEOUT
FROM DAC
BYPASS
TO HEADPHONE AMP
DACSEL
FROM MICROPHONE
INPUT
SIDETONE
Figure 18 Line Output Schematic
The DAC output, Line Input and microphone are summed into the Line Output. In DAC mode only the
output from the DAC is routed to the line outputs. In Bypass mode the Line Input is summed into the
Line Outputs. In Side Tone mode the Microphone Input is summed into the Line Output. These
features can be used for either over-dubbing or, if the DAC is muted, as a pure analogue bypass or
Side Tone feature, so avoiding any digital signal processing.
The line output is muted by either muting the DAC (analogue) or Soft Muting (digital) and disabling
the BYPASS and SIDETONE paths. Refer to the DAC section for more details. Whenever the DAC
is muted or the device placed into standby mode the DC voltage is maintained at the line outputs to
prevent any audible clicks from being present.
The software control for the line outputs is shown in Table 7.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
3
BYPASS
1
Bypass Switch
1 = Enable Bypass
0 = Disable Bypass
4
DACSEL
0
DAC Select
1 = Select DAC
0 = Don't select DAC
0000100
Analogue
Audio Path
Control
5
SIDETONE
0
Side Tone Switch
1 = Enable SideTone
0 = Disable Side Tone
Table 7 Output Software Control
The recommended external components are shown in Figure 19.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
26
AGND
R1
C1
AGND
LINEOUT
R2
Figure 19 Line Outputs Application Drawing
Recommended values are C1 = 10
µ
F, R1 = 47k, R2 = 100 ohms.
C1 forms a DC blocking capacitor to the line outputs. R1 prevents the output voltage from drifting so
protecting equipment connected to the line output. R2 forms a de-coupling resistor preventing
abnormal loads from disturbing the device. Note that poor choice of dielectric material for C1 can
have dramatic effects on the measured signal distortion at the output
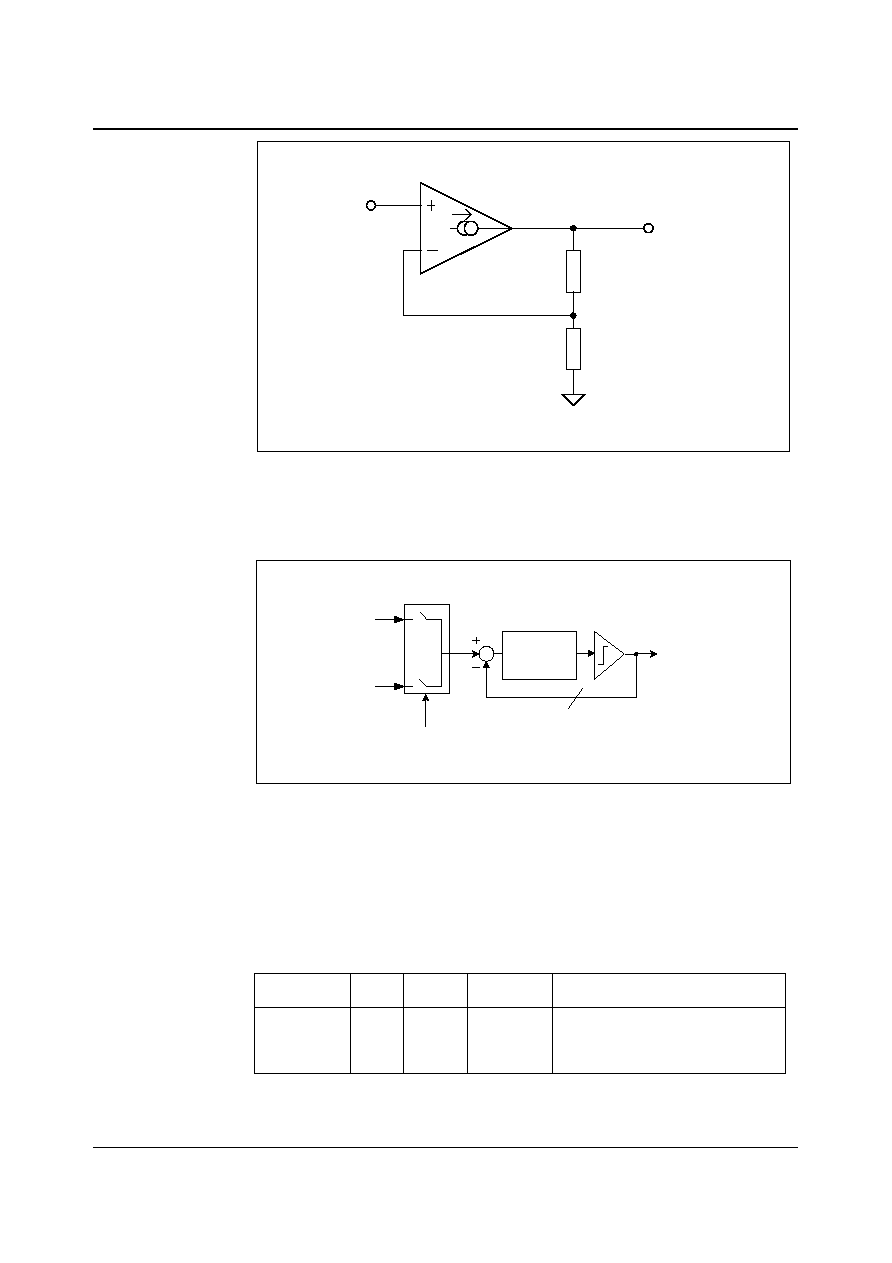
HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER
The WM8731 has a stereo headphone output available on LHPOUT and RHPOUT. The output is
designed specifically for driving 16 or 32 ohm headphones with maximum efficiency and low power
consumption. The headphone output includes a high quality volume level adjustment and mute
function.
The scheme of the circuit is shown in Figure 20.
VMID
HPOUT
FROM
DAC VIA
LINEOUT
Figure 20 Headphone Amplifier Schematic
LHPOUT and RHPOUT volumes can be independently adjusted under software control using the
LHPVOL[6:0] and RHPVOL[6:0] bits respectively of the headphone output control registers. The
adjustment is logarithmic with an 80dB range in 1dB steps from +6dB to ≠73dB.
The headphone outputs can be separately muted by writing codes less than 0110000 to
LHPVOL[6:0] or RHPVO[6:0]L bits. Whenever the headphone outputs are muted or the device
placed into standby mode, the DC voltage is maintained at the line outputs to prevent any audible
clicks from being present.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
27
A zero cross detect circuit is provided at the input to the headphones under the control of the LZCEN
and RZCEN bits of the headphone output control register. Using these controls the volume control
values are only updated when the input signal to the gain stage is close to the analogue ground level.
This minimises and audible clicks and zipper noise as the gain values are changed or the device
muted. Note that this circuit has no time out so if only DC levels are being applied to the gain stage
input of more than approximately 20mV, then the gain will not be updated. This zero cross function is
enabled when the LZCEN and RZCEN bit is set high during a volume register write. If there is
concern that a DC level may have blocked a volume change (one made with LZCEN or RZCEN set
high) then a subsequent volume write of the same value, but with the LZCEN or RZCEN bit set low
will force a volume update, regardless of the DC level.
LHPOUT and RHPOUT volume and zero-cross setting can be changed independently. Alternatively,
the user can lock the two channels together, allowing both to be updated simultaneously, halving the
number of serial writes required, provided that the same gain is needed for both channels. This is
achieved through writing to the HPBOTH bit of the control register. Setting LRHPBOTH whilst writing
to LHPVOL and LZCEN will simultaneously update the Right Headphone controls similarly. The
corresponding effect on updating RLHPBOTH is also achieved.
The software control is given in Table 8.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
6:0
LHPVOL[6:0]
1111001
( 0dB )
Left Channel Headphone Output
Volume Control
1111111 = +6dB
. . 1dB steps down to
0110000 = -73dB
0000000 to 0101111 = MUTE
7
LZCEN
0
Left Channel Zero Cross detect
Enable
1 = Enable
0 = Disable
0000010
Left
Headphone
Out
8
LRHPBOTH
0
Left to Right Channel Headphone
Volume, Mute and Zero Cross Data
Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
LHPVOL[6:0] and LZCEN to
RHPVOL[6:0] and RZCEN
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
6:0
RHPVOL[6:0]
1111001
( 0dB )
Right Channel Headphone Output
Volume Control
1111111 = +6dB
. . 1dB steps down to
0110000 = -73dB
0000000 to 0101111 = MUTE
7
RZCEN
0
Right Channel Zero Cross Detect
Enable
1 = Enable
0 = Disable
0000011
Right
Headphone
Out
8
RLHPBOTH
0
Right to Left Channel Headphone
Volume, Mute and Zero Cross Data
Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
RHPVOL[6:0] and RZCEN to
LHPVOL[6:0] and LZCEN
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
Table 8 Headphone Output Software Control

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
28
The recommended external components required to complete the application are shown in Figure 21.
AGND
R1
C1
AGND
HPOUT
Figure 21 Headphone Output Application Drawing
Recommended values are C1 = 220uF (10V electrolytic), R1 = 47k
C1 forms a DC blocking capacitor to isolate the dc of the HPOUT from the headphones. R1 form a
pull down resistor to discharge C1 to prevent the voltage at the connection to the headphones from
rising to a level that may damage the headphones.
BYPASS MODE
The WM8731 includes a bypass mode whereby analogue line inputs are routed directly to the
analogue line outputs and headphone outputs. The scheme for this is in Figure 22.
12.5K
VMID
LINEIN
VMID
HPOUT
VMID
FROM
LINE
INPUTS
LINEOUT
FROM
DAC
BYPASS (ON)
DACSEL (OFF)
SIDETONE (OFF)
Figure 22 Signal Routing in Bypass Mode

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
29
The bypass mode is selected under software control using the BYPASS microphone bit as shown in
Table 9. In true bypass mode, the output from the DAC (DACSEL) and (SIDETONE) should be de-
selected from the line output block. However this can also be used to sum the DAC output, Line
Inputs together and microphone inputs. The analogue line input and headphone output volume
controls and mutes are still operational in bypass mode. The 0dB gain setting is recommended for
the Line Input volume control to avoid distortion. The maximum signal at any point in the bypass path
must be no greater than 1.0V rms at AVDD = 3.3V, to avoid distortion. This amplitude tracks linearly
with AVDD. This means that if the DAC is producing a 1Vrms signal, and it is being summed with
1Vrms line BYPASS signal, the resulting LINEOP signal will be clipped.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0000100
Analogue
Audio Path
Control
3
BYPASS
1
Bypass Switch (Analogue)
1 = Enable Bypass
0 = Disable Bypass
Table 9 Bypass Mode Software Control
SIDETONE MODE
The WM8731 also includes a side tone mode where the microphone input is routed to line and
headphone outputs. The scheme for this is shown in Figure 23.
The side tone mode allows the microphone input to be attenuated to the outputs for telephone and
headset applications.
VMID
HPOUT
50k
10k
VMID
MICIN
VMID
10dB GAIN BOOST
VMID
FROM
LINE
INPUTS
LINEOUT
FROM
DAC
BYPASS (OFF)
DACSEL (OFF)
SIDETONE (ON)
Figure 23 Side Tone Mode Schematic
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
5
SIDETONE
0
Side Tone Switch (Analogue)
1 = Enable Side Tone
0 = Disable Side Tone
0000100
Analogue
Audio Path
Control
7:6
SIDEATT[1:0]
00
Side Tone Attenuation
11 = -15dB
10 = -12dB
01 = -9dB
00 = -6dB
Table 10 Side Tone Mode Table

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
30
The side tone mode and attenuation is selected under software control using the SIDETONE bit as
shown in Table 10. In true side tone the output from the DAC (DACSEL) and line inputs (BYPASS)
should be deselected from the line output block. However, this can also be used to sum the DAC
output, line inputs and microphone inputs together. The microphone boost gain control and
headphone output volume control and mutes are still operational in side tone mode. The maximum
signal at any point in the side tone path must be no greater than 1.0V rms at VDD = 3.3V, to avoid
distortion. This amplitude tracks linearly with AVDD.
DEVICE OPERATION
DEVICE RESETTING
The WM8731 contains a power on reset circuit that resets the internal state of the device to a known
condition. The power on reset is applied as DCVDD powers on and released only after the voltage
level of DCVDD crosses a minimum turn off threshold. If DCVDD later falls below a minimum turn on
threshold voltage then the power on reset is re-applied. The threshold voltages and associated
hysteresis are shown in the Electrical Characteristics table.
The user also has the ability to reset the device to a known state under software control as shown in
the table below.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0001111
Reset Register
8:0
RESET
not reset
Reset Register
Writing 00000000 to register resets
device
Table 11 Software Control of Reset
When using the software reset. In 3-wire mode the reset is applied on the rising edge of CSB and
released on the next rising edge of SCLK. In 2-wire mode the reset is applied for the duration of the
ACK signal (approximately 1 SCLK period, refer to Figure 32).
CLOCKING SCHEMES
In a typical digital audio system there is only one central clock source producing a reference clock to
which all audio data processing is synchronised. This clock is often referred to as the audio system's
Master Clock. To allow WM8731 to be used in a centrally clocked system, the WM8731 is capable of
either generating this system clock itself or receiving it from an external source as will be discussed.
For applications where it is desirable that the WM8731 is the system clock source, then clock
generation is achieved through the use of a suitable crystal connected between the XTI/MCLK input
and XTO output pins (see CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR section).
For applications where a component other than the WM8731 will generate the reference clock, the
external system can be applied directly through the XTI/MCLK input pin with no software
configuration necessary. Note that in this situation, the oscillator circuit of the WM8731 can be safely
powered down to conserve power (see POWER DOWN section).
CORE CLOCK
The WM8731 DSP core can be clocked either by MCLK or MCLK divided by 2. This is controlled by
software as shown in Table 12 below.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0001000
Sampling
Control
6
CLKIDIV2
0
Core Clock divider select
1 = Core Clock is MCLK divided by 2
0 = Core Clock is MCLK
Table 12 Software Control of Core Clock
Having a programmable MCLK divider allows the device to be used in applications where higher
frequency master Clocks are available. For example the device can support 512fs master clocks
whilst fundamentally operating in a 256fs mode.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
31
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
The WM8731 includes a crystal oscillator circuit that allows the audio system's reference clock to be
generated on the device. This is available to the rest of the audio system in buffered form on
CLKOUT. The crystal oscillator is a low radiation type, designed for low EMI. A typical application
circuit is shown in Figure 24.
XTI/MCLK
XTO
DGND
DGND
Cp
Cp
Figure 24 Crystal Oscillator Application Circuit
For crystal frequencies in the 12MHz range, a Cp of 10pF is recommended. For crystal frequencies
in the 18MHz range, 15pF Cp is recommended.
The WM8731 crystal oscillator provides an extremely low jitter clock source. Low jitter clocks are a
requirement for high quality audio ADC and DACs, regardless of the converter architecture. The
WM8731 architecture is less susceptible than most converter techniques but still requires clocks with
less than approximately 1ns of jitter to maintain performance. In applications where there is more
than one source for the master clock, it is recommended that the clock is generated by the WM8731
to minimise such problems.
CLOCKOUT
The Core Clock is internally buffered and made available externally to the audio system on the
CLKOUT output pin. CLKOUT provides a replication of the Core Clock, but buffered as suitable for
driving external loads.
There is no phase inversion between XTI/MCLK, the Core Clock and CLOCKOUT but there will
inevitably be some delay. The delay will be dependent on the load that CLOCKOUT drives. Refer to
Electrical Characteristics.
CLKOUT can also be divided by 2 under software control, refer to Table 13. Note that if CLKOUT is
not required then the CLKOUT buffer on the WM8731 can be safely powered down to conserve
power (see POWER DOWN section). If the system architect has the choice between using F
CLKOUT
=
F
MCLK
or F
CLKOUT
= F
MCLK
/2 in the interface, the latter is recommended to conserve power. When the
divide by two is selected CLKOUT changes on the rising edge of MCLK. Please refer to Electrical
Characteristics for timing information.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0001000
Sampling
Control
7
CLKODIV2
0
CLKOUT divider select
1 = CLOCKOUT is Core Clock
divided by 2
0 = CLOCKOUT is Core Clock
Table 13 Programming CLKOUT
CLKOUT is disabled and set low whenever the device is in reset.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
32
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACES
WM8731 may be operated in either one of the 4 offered audio interface modes. These are:
∑
Right
justified
∑
Left
justified
∑
I2S
∑
DSP
mode
All four of these modes are MSB first and operate with data 16 to 32 bits.
Note that 32 bit data is not supported in right justified mode.
The digital audio interface takes the data from the internal ADC digital filter and places it on the
ADCDAT output. ADCDAT is the formatted digital audio data stream output from the ADC digital
filters with left and right channels multiplexed together. ADCLRC is an alignment clock that controls
whether Left or Right channel data is present on the ADCDAT lines. ADCDAT and ADCLRC are
synchronous with the BCLK signal with each data bit transition signified by a BCLK high to low
transition. BCLK maybe an input or an output dependent on whether the device is in master or slave
mode. Refer to the MASTER/SLAVE OPERATION section
The digital audio interface also receives the digital audio data for the internal DAC digital filters on the
DACDAT input. DACDAT is the formatted digital audio data stream output to the DAC digital filters
with left and right channels multiplexed together. DACLRC is an alignment clock that controls
whether Left or Right channel data is present on DACDAT. DACDAT and DACLRC are synchronous
with the BCLK signal with each data bit transition signified by a BCLK high to low transition. DACDAT
is always an input. BCLK and DACLRC are either outputs or inputs depending whether the device is
in master or slave mode. Refer to the MASTER/SLAVE OPERATION section
There are four digital audio interface formats accommodated by the WM8731. These are shown in
the figures below. Refer to the Electrical Characteristic section for timing information.
Left Justified mode is where the MSB is available on the first rising edge of BCLK following a ADCLR
or DACLRC transition.
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
DACLRC/
ADCLRC
BCLK
DACDAT/
ADCDAT
1/fs
n
3
2
1
n-2
n-1
LSB
MSB
n
3
2
1
n-2
n-1
LSB
MSB
Figure 25 Left Justified Mode
I2S mode is where the MSB is available on the 2nd rising edge of BCLK following a LRCLK
transition.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
33
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
DACLRC/
ADCLRC
BCLK
DACDAT/
ADCDAT
1/fs
n
3
2
1
n-2
n-1
LSB
MSB
n
3
2
1
n-2
n-1
LSB
MSB
1 BCLK
1 BCLK
Figure 26 I2S Mode
Right Justified mode is where the LSB is available on the rising edge of BCLK preceding a LRCLK
transition, yet MSB is still transmitted first.
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
DACLRC/
ADCLRC
BCLK
DACDAT/
ADCDAT
1/fs
n
3
2
1
n-2 n-1
LSB
MSB
n
3
2
1
n-2 n-1
LSB
MSB
Figure 27 Right Justified Mode
DSP mode is where the left channel MSB is available on either the 1
st
or 2
nd
rising edge of BCLK
(selectable by LRP) following a LRC transition high. Right channel data immediately follows left
channel data.
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
DACLRC/
ADCLRC
BCLK
DACDAT/
ADCDAT
n
3
2
1
n-2 n-1
LSB
MSB
n
3
2
1
n-2 n-1
1 BCLK
Input Word Length (IWL)
Note: Input word length is defined by the IWL register, LRP = 1
1/fs
Figure 28 DSP Mode

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
34
In all modes DACLRC and ADCLRC must always change on the falling edge of BCLK, refer to Figure
25, Figure 26, Figure 27 and Figure 28.
Operating the digital audio interface in DSP mode allows ease of use for supporting the various
sample rates and word lengths. The only requirement is that all data is transferred within the correct
number of BCLK cycles to suit the chosen word length.
In order for the digital audio interface to offer similar support in the three other modes (Left Justified,
I2S and Right Justified), the DACLRC, ADCLRC and BCLK frequencies, continuity and mark-space
ratios need more careful consideration.
In Slave mode, DACLRC and ADCLRC inputs are not required to have a 50:50 mark-space ratio.
BCLK input need not be continuous. It is however required that there are sufficient BCLK cycles for
each DACLRC/ADCLRC transition to clock the chosen data word length. The non-50:50 requirement
on the LRCs is of use in some situations such as with a USB 12MHZ clock. Here simply dividing
down a 12MHz clock within the DSP to generate LRCs and BCLK will not generate the appropriate
DACLRC or ADCLRC since they will no longer change on the falling edge of BCLK. For example,
with 12MHz/32k fs mode there are 375 MCLK per LRC. In these situations DACLRC/ADCLRC can
be made non 50:50.
In Master mode, DACLRC and ADCLRC will be output with a 50:50 mark-space ratio with BCLK
output at 64fs. The exception again is in USB mode where BCLK is always 12MHz. So for example in
12MHz/32k fs mode there are 375 master clocks per LRC period. Therefore DACLRC and ADCLRC
outputs will have a mark space ratio of 187:188.
The ADC and DAC digital audio interface modes are software configurable as indicated in Table 13.
Note that dynamically changing the software format may result in erroneous operation of the
interfaces and is therefore not recommended.
The length of the digital audio data is programmable at 16/20/24 or 32 bits. Refer to the software
control table below. The data is signed 2's complement. Both ADC and DAC are fixed at the same
data length. The ADC and DAC digital filters process data using 24 bits. If the ADC is programmed to
output 16 or 20 bit data then it strips the LSBs from the 24 bit data. If the ADC is programmed to
output 32 bits then it packs the LSBs with zeros. If the DAC is programmed to receive 16 or 20 bit
data, the WM8731 packs the LSBs with zeros. If the DAC is programmed to receive 32 bit data, then
it strips the LSBs.
The DAC outputs can be swapped under software control using LRP and LRSWAP as shown in
Table 14. Stereo samples are normally generated as a Left/Right sampled pair. LRSWAP reverses
the order so that a Left sample goes to the right DAC output and a Right sample goes to the left DAC
output. LRP swaps the phasing so that a Right/Left sampled pair is expected and preserves the
correct channel phase difference.
To accommodate system timing requirements the interpretation of BCLK maybe inverted, this is
controlled vias the software shown in Table 14. This is especially appropriate for DSP mode.
ADCDAT lines are always outputs. They power up and return from standby low.
DACDAT is always an input. It is expected to be set low by the audio interface controller when the
WM8731 is powered off or in standby.
ADCLRC, DACLRC and BCLK can be either outputs or inputs depending on whether the device is
configured as a master or slave. If the device is a master then the DACLRC and BCLK signals are
outputs that default low. If the device is a slave then the DACLRC and BCLK are inputs. It is
expected that these are set low by the audio interface controller when the WM8731 is powered off or
in standby.
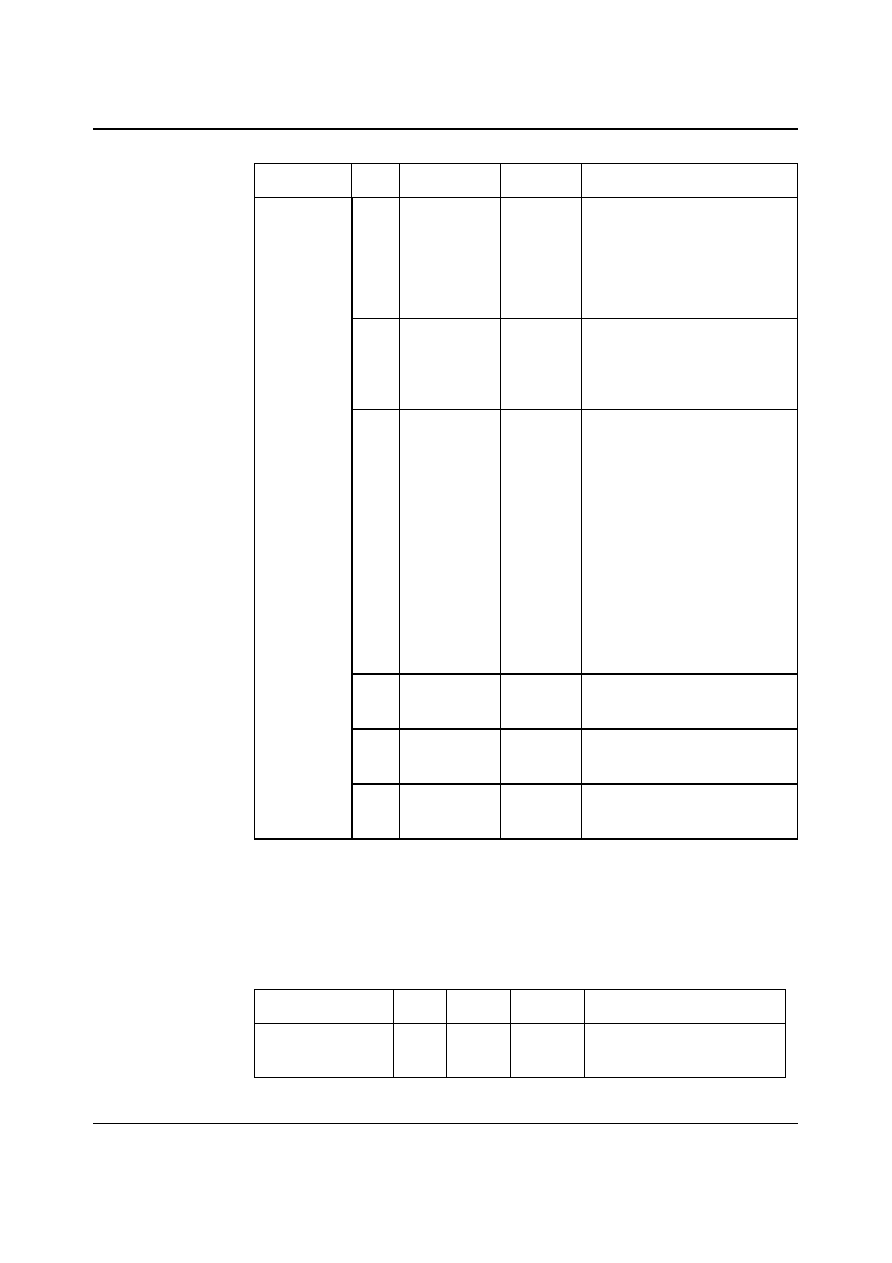
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
35
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
1:0
FORMAT[1:0]
10
Audio Data Format Select
11 = DSP Mode, frame sync + 2
data packed words
10 = I
2
S Format, MSB-First left-1
justified
01 = MSB-First, left justified
00 = MSB-First, right justified
3:2
IWL[1:0]
10
Input Audio Data Bit Length Select
11 = 32 bits
10 = 24 bits
01 = 20 bits
00 = 16 bits
4
LRP
0
DACLRC phase control (in left, right
or I2S modes)
1 = Right Channel DAC data when
DACLRC high
0 = Right Channel DAC data when
DACLRC low
(opposite phasing in I
2
S mode)
or
DSP mode A/B select (in DSP mode
only)
1 = MSB is available on 2nd BCLK
rising edge after DACLRC rising
edge
0 = MSB is available on 1st BCLK
rising edge after DACLRC rising
edge
5
LRSWAP
0
DAC Left Right Clock Swap
1 = Right Channel DAC Data Left
0 = Right Channel DAC Data Right
6
MS
0
Master Slave Mode Control
1 = Enable Master Mode
0 = Enable Slave Mode
0000111
Digital Audio
Interface
Format
7
BCLKINV
0
Bit Clock Invert
1 = Invert BCLK
0 = Don't invert BCLK
Table 14 Digital Audio Interface Control
Note: If right justified 32 bit mode is selected then the WM8731 defaults to 24 bits.
MASTER AND SLAVE MODE OPERATION
The WM8731 can be configured as either a master or slave mode device. As a master mode device
the WM8731 controls sequencing of the data and clocks on the digital audio interface. As a slave
device the WM8731 responds with data to the clocks it receives over the digital audio interface. The
mode is set with the MS bit of the control register as shown in Table 15.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0000111
Digital Audio Interface
Format
6
MS
0
Master Slave Mode Control
1 = Enable Master Mode
0 = Enable Slave Mode
Table 15 Programming Master/Slave Modes

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
36
As a master mode device the WM8731 controls the sequencing of data transfer (ADCDAT,
DACDAT) and output of clocks (BCLK, ADCLRC, DACLRC) over the digital audio interface. It uses
the timing generated from either its on-board crystal or the MCLK input as the reference for the clock
and data transitions. This is illustrated in Figure 29. ADCDAT is always an output from and DACDAT
is always an input to the WM8731 independent of master or slave mode.
BCLK
ADCDAT
ADCLRC
DACDAT
DACLRC
WM8731
CODEC
DSP
ENCODER/
DECODER
Note: ADC and DAC can run at different rates
Figure 29 Master Mode
As a slave device the WM8731 sequences the data transfer (ADCDAT, DACDAT) over the digital
audio interface in response to the external applied clocks (BCLK, ADCLRC, DACLRC). This is
illustrated in Figure 30.
BCLK
ADCDAT
ADCLRC
DACDAT
DACLRC
WM8731
CODEC
DSP
ENCODER/
DECODER
Note: The ADC and DAC can run at different rates
Figure 30 Slave Mode
Note that the WM8731 relies on controlled phase relationships between audio interface BCLK,
DACLRC and the master MCLK or CLKOUT. To avoid any timing hazards, refer to the timing section
for detailed information.
AUDIO DATA SAMPLING RATES
The WM8731 provides for two modes of operation (normal and USB) to generate the required DAC
and ADC sampling rates. Normal and USB modes are programmed under software control according
to the table below.
In Normal mode, the user controls the sample rate by using an appropriate MCLK or crystal
frequency and the sample rate control register setting. The WM8731 can support sample rates from
8ks/s up to 96ks/s.
In USB mode, the user must use a fixed MLCK or crystal frequency of 12MHz to generate sample
rates from 8ks/s to 96ks/s. It is called USB mode since the common USB (Universal Serial Bus)
clock is at 12MHz and the WM8731 can be directly used within such systems. WM8731 can
generate all the normal audio sample rates from this one Master Clock frequency, removing the need
for different master clocks or PLL circuits.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
37
Uniquely, the WM8731 offers the user the ability to sample the ADC and DAC at different rates under
software control in both Normal and USB modes. The reduces the burden on any controlling DSP.
However, the signal processing in the ADC and DAC over-sampling filters is tightly coupled together
in order to minimise power consumption. To this end, only the combinations of sample rates listed in
the following sections are supported. Note that these rates supported are anticipated to be the likely
combinations used in typical audio systems.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0
USB/
NORMAL
0
Mode Select
1 = USB mode (250/272fs)
0 = Normal mode (256/384fs)
1
BOSR
0
Base Over-Sampling Rate
USB Mode
0 = 250fs
1 = 272fs
Normal Mode
0 = 256fs
1 = 384fs
0001000
Sampling
Control
5:2
SR[3:0]
0000
ADC and DAC sample rate control;
See USB Mode and Normal Mode
Sample Rate sections for operation
Table 16 Sample Rate Control
NORMAL MODE SAMPLE RATES
In normal mode MCLK/crystal oscillator is set up according to the desired sample rates of the ADC
and DAC. For ADC or DAC sampling rates of 8, 32, 48 or 96kHz, MCLK frequencies of either
12.288MHz (256fs) or 18.432MHz (384fs) can be used. For ADC or DAC sampling rates of 8, 44.1 or
88.2kHz from MCLK frequencies of either 11.2896MHz (256fs) or 16.9344MHz (384fs) can be used.
The table below should be used to set up the device to work with the various sample rate
combinations. For example if the user wishes to use the WM8731 in normal mode with the ADC and
DAC sample rates at 48kHz and 48kHz respectively then the device should be programmed with
BOSR = 0, SR3 = 0, SR2 = 0, SR1 = 0 and SR0 = 0 with a 12.288MHz MCLK or with BOSR = 1,
SR3 = 0, SR2 = 0, SR1 = 0 and SR0 = 0 with a 18.432MHz MCLK. The ADC and DAC will then
operate with a Digital Filter of type 1, refer to Digital Filter Characteristics section for an explanation
of the different filter types.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
38
SAMPLING
RATE
ADC
DAC
MCLK
FREQUENCY
SAMPLE
RATE
REGISTER SETTINGS
DIGITAL
FILTER
TYPE
kHz
kHz
MHz
BOSR
SR3
SR2
SR1
SR0
12.288
0
0
0
0
0
48
48
18.432
1
0
0
0
0
1
12.288
0
0
0
0
1
48
8
18.432
1
0
0
0
1
1
12.288
0
0
0
1
0
8
48
18.432
1
0
0
1
0
1
12.288
0
0
0
1
1
8
8
18.432
1
0
0
1
1
1
12.288
0
0
1
1
0
32
32
18.432
1
0
1
1
0
1
12.288
0
0
1
1
1
96
96
18.432
1
0
1
1
1
2
11.2896
0
1
0
0
0
44.1
44.1
16.9344
1
1
0
0
0
1
11.2896
0
1
0
0
1
44.1
8
(Note 1)
16.9344
1
1
0
0
1
1
11.2896
0
1
0
1
0
8
(Note 1)
44.1
16.9344
1
1
0
1
0
1
11.2896
0
1
0
1
1
8
(Note 1)
8
(Note 1)
16.9344
1
1
0
1
1
1
11.2896
0
1
1
1
1
88.2
88.2
16.9344
1
1
1
1
1
2
Table 17 Normal Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table
Notes:
1.
8k not exact, actual = 8.018kHz
2.
All other combinations of BOSR and SR[3:0] that are not in the truth table are invalid
The BOSR bit represents the base over-sampling rate. This is the rate that the WM8731 digital signal
processing is carried out at. In Normal mode, with BOSR = 0, the base over-sampling rate is at
256fs, with BOSR = 1, the base over-sampling rate is at 384fs. This can be used to determine the
actual audio data rate produced by the ADC and required by the DAC.
Example scenarios are:
1.
with a requirement that the ADC data rate is 8kHz and DAC data rate is 48kHz, then choosing
MCLK = 12.288MHz the device is programmed with BOSR = 0 (256fs), SR3 = 0, SR2 = 0, SR1
= 1, SR0 = 0.The ADC output data rate will then be exactly 8kHz (derived from 12.288MHz/256
x1/6) and the DAC expects data at exactly 48kHz (derived from 12.288MHz/256)
2.
with a requirement that ADC data rate is 8kHz and DAC data rate is 44.1kHz, then choosing
MCLK = 16.9344MHz the device is programmed with BOSR = 1 (384fs), SR3 = 1, SR2 = 0, SR1
= 0, SR0 = 1. The ADC will no longer output data at exactly 8.000kHz, instead it will be
8.018kHz (derived from 16.9344MHz/384 x 2/11), the DAC still is at exactly 44.1kHz (derived
from 16.9344MHz/384). A slight (sub 0.5%) pitch shift will therefore result in the 8kHz audio
data and (importantly) the user must ensure that the data across the digital interface is correctly
synchronised at the 8.018kHz rate.
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
39
The exact sample rates achieved are defined by the relationships in Table 18 below.
ACTUAL SAMPLING RATE
BOSR=0
(256fs)
BOSR=1
(384fs)
TARGET
SAMPLING
RATE
MCLK=12.288
MCLK=11.2896
MCLK=18.432
MCLK=16.9344
kHz
kHz
kHz
kHz
kHz
8
8.018
8
8.018
8
12.288MHz/256 x 1/6
11.2896MHz/256 x 2/11
18.432MHz/384 x 1/6
16.9344MHz/384 x 2/11
32
32
32
12.288MHz/256 x 2/3
not available
18.432MHz/384x 2/3
not available
44.1
44.1
44.1
not available
11.2896MHz/256
not available
16.9344MHz /384
48
48
48
12.288MHz/256
not available
18.432MHz/384
not available
88.2
88.2
88.2
not available
11.2896MHz/384 x 2
not available
16.9344MHz /384 x 2
96
96
96
12.288MHz/256 x 2
not available
18.432MHz/384 x 2
not available
Table 18 Normal Mode Actual Sample Rates
128/192fs NORMAL MODE
The Normal Mode sample rates are designed for standard 256fs and 384fs MCLK rates. However the
WM8731 is also capable of being clocked from a 128 or 192fs MCLK for application over limited
sampling rates as shown in the table below.
SAMPLING
RATE
ADC
DAC
MCLK
FREQUENCY
SAMPLE
RATE
REGISTER SETTINGS
DIGITAL
FILTER
TYPE
kHz
kHz
MHz
BOSR
SR3
SR2
SR1
SR0
6.144
0
0
1
1
1
48
48
9.216
1
0
1
1
1
2
5.6448
0
1
1
1
1
44.1
44.1
8.4672
1
1
1
1
1
2
Table 19 128fs Normal Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table
512/768fs NORMAL MODE
512 fs and 768 fs MCLK rates can be accommodated by using the CLKIDIV2 bit. The core clock to
the DSP will be divided by 2 so an external 512/768 MCLK will become 256/384 fs internally and the
device otherwise operates as in Table 15 but with MCLK at twice the specified rate. See Table 12 for
software control.

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
40
USB MODE SAMPLE RATES
In USB mode the MCLK/crystal oscillator input is 12MHz only.
SAMPLING
RATE
ADC
DAC
MCLK
FREQUENCY
SAMPLE
RATE
REGISTER SETTINGS
DIGITAL
FILTER
TYPE
kHz
kHz
MHz
BOSR
SR3
SR2
SR1
SR0
48
48
12.000
0
0
0
0
0
0
44.1
(Note 2)
44.1
(Note 2)
12.000
1
1
0
0
0
1
48
8
12.000
0
0
0
0
1
0
44.1
(Note 2)
8
(Note 1)
12.000
1
1
0
0
1
1
8
48
12.000
0
0
0
1
0
0
8
(Note 1)
44.1
(Note 2)
12.000
1
1
0
1
0
1
8
8
12.000
0
0
0
1
1
0
8
(Note 1)
8
(Note 1)
12.000
1
1
0
1
1
1
32
32
12.000
0
0
1
1
0
0
96
96
12.000
0
0
1
1
1
3
88.2
(Note 3)
88.2
(Note 3)
12.000
1
1
1
1
1
2
Table 20 USB Mode Sample Rate Look-up Table
Notes:
1.
8k not exact, actual = 8.021kHz
2.
44.1k not exact, actual = 44.118kHz
3.
88.1k not exact, actual = 88.235kHz
4.
All other combinations of BOSR and SR[3:0] that are not in the truth table are invalid
The table above can be used to set up the device to work with various sample rate combinations. For
example if the user wishes to use the WM8731 in USB mode with the ADC and DAC sample rates at
48kHz and 48kHz respectively then the device should be programmed with BOSR = 0, SR3 = 0, SR2
= 0, SR1 = 0 and SR0 = 0. The ADC and DAC will then operate with a Digital Filter of type 0, refer to
Digital Filter Characteristics section for an explanation of the different filter types.
The BOSR bit represents the base over-sampling rate. This is the rate that the WM8731 digital signal
processing is carried out at and the sampling rate will always be a sub-multiple of this. In USB mode,
with BOSR = 0, the base over-sampling rate is defined at 250fs, with BOSR = 1, the base over-
sampling rate is defined at 272fs. This can be used to determine the actual audio sampling rate
produced by the ADC and required by the DAC.
Example scenarios are, :-
1.
with a requirement that the ADC data sampling rate is 8kHz and DAC data sampling rate is
48kHz the device is programmed with BOSR = 0 (250fs), SR3 = 0, SR2 = 0, SR1 = 1, SR0 =
0.The ADC will then be exactly 8kHz ( derived from 12MHz/250 x 1/6 ) and the DAC expects
data at exactly 48kHz ( derived from 12MHz/250 ).
2.
with a requirement that ADC data rate is 8kHz and DAC data rate is 44.1kHz the device is
programmed with BOSR = 0 (272fs), SR3 = 0, SR2 = 0, SR1 = 1, SR0 = 0. The ADC will not
output data at exactly 8kHz, instead it will be 8.021kHz ( derived from 12MHz/272 x 2/11 ) and
the DAC at 44.118kHz ( derived from 12MHz/272 ). A slight (sub 0.5%) pitch shift will therefore
results in the 8kHz and 44.1kHz audio data and (more importantly) the user must ensure that
the data across the digital interface is correctly synchronised at the 8.021kHz and 44.117kHz
rates.
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
41
The exact sample rates supported for all combinations are defined by the relationships in Table 21
below.
ACTUAL SAMPLING RATE
TARGET
SAMPLING
RATE
BOSR=0
( 250fs)
BOSR=1
(272fs)
kHz
kHz
kHz
8
8.021
8
12MHz/(250 x 48/8)
12MHz/(272 x 11/2)
32
32
12MHz/(250 x 48/32)
not available
44.117
44.1
not available
12MHz/272
48
48
12MHz/250
not available
88.235
88.2
not available
12MHz/136
96
96
12MHz/125
not available
Table 21 USB Mode Actual Sample Rates
ACTIVATING DSP AND DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE
To prevent any communication problems from arising across the Digital Audio Interface the Audio
Interface is disabled (tristate with weak 100k pulldown). Once the Audio Interface and the Sampling
Control has been programmed it is activated by setting the ACTIVE bit under Software Control.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0001001
Active Control
0
ACTIVE
0
Activate Interface
1 = Active
0 = Inactive
Table 22 Activating DSP and Digital Audio Interface
It is recommended that between changing any content of Digital Audio Interface or Sampling Control
Register that the active bit is reset then set.
SOFTWARE CONTROL INTERFACE
The software control interface may be operated using either a 3-wire (SPI-compatible) or 2-wire MPU
interface. Selection of interface format is achieved by setting the state of the MODE pin.
In 3-wire mode, SDIN is used for the program data, SCLK is used to clock in the program data and
CSB is used to latch in the program data. In 2-wire mode, SDIN is used for serial data and SCLK is
used for the serial clock. In 2-wire mode, the state of CSB pin allows the user to select one of two
addresses.
SELECTION OF SERIAL CONTROL MODE
The serial control interface may be selected to operate in either 2 or 3-wire modes. This is achieved
by setting the state of the MODE pin.
MODE
INTERFACE
FORMAT
0
2 wire
1
3 wire
Table 23 Control Interface Mode Selection
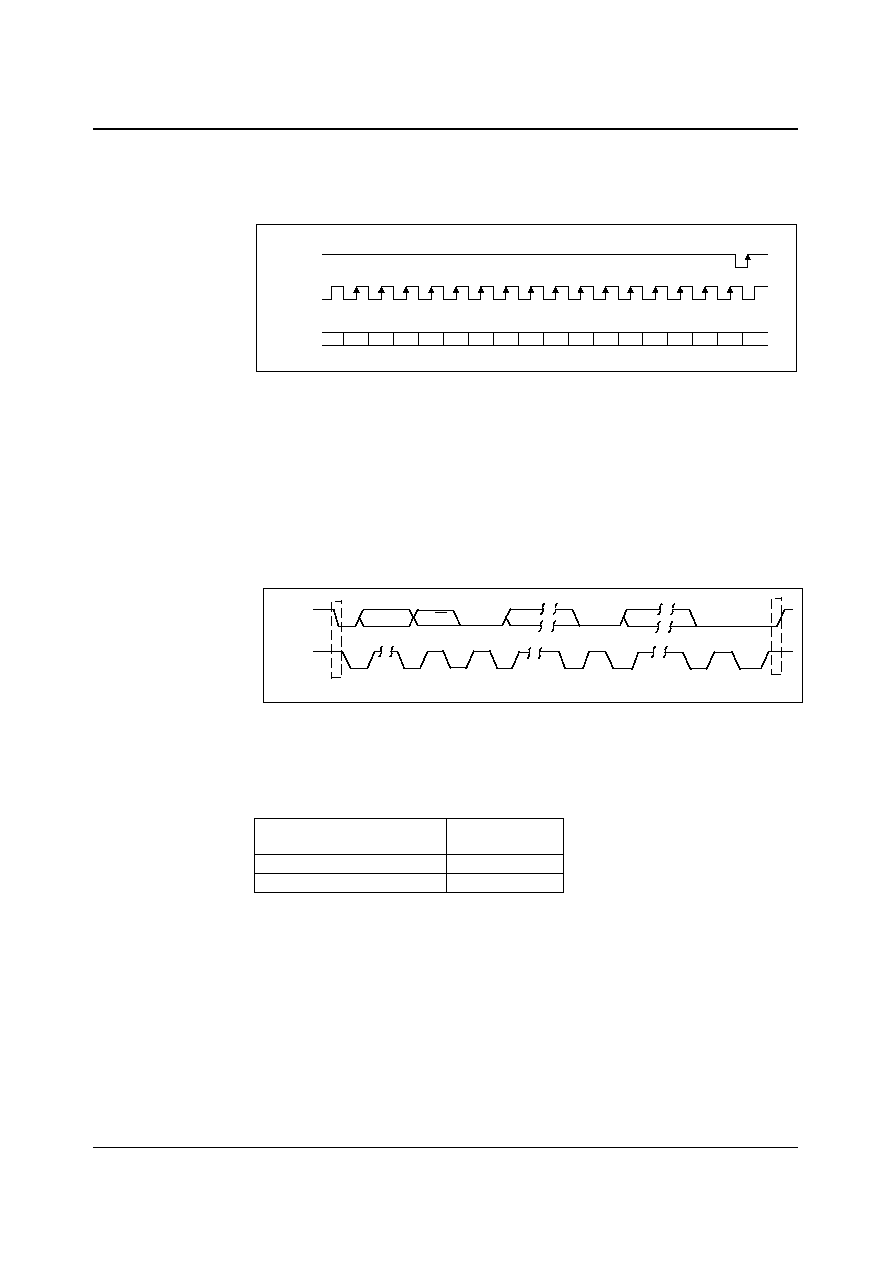
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
42
3-WIRE (SPI COMPATIBLE) SERIAL CONTROL MODE
The WM8731 can be controlled using a 3-wire serial interface. SDIN is used for the program data,
SCLK is used to clock in the program data and CSB is use to latch in the program data. The 3-wire
interface protocol is shown in Figure 31.
CSB
SCLK
SDIN
B15
B6
B7
B8
B9
B10
B11
B12
B13
B14
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B0
Figure 31 3-Wire Serial Interface
Notes:
1.
B[15:9] are Control Address Bits
2.
B[8:0] are Control Data Bits
3.
CSB is edge sensitive not level sensitive. The data is latched on the rising edge of CSB.
2-WIRE SERIAL CONTROL MODE
The WM8731 supports a 2-wire MPU serial interface. The device operates as a slave device only.
The WM8731 has one of two slave addresses that are selected by setting the state of pin 10, (CSB).
SDIN
SCLK
ACK
R ADDR
ACK
DATA B15-8
STOP
START
DATA B7-0
R/W
ACK
Figure 32 2-Wire Serial Interface
Notes:
1.
B[15:9] are Control Address Bits
2.
B[8:0] are Control Data Bits
CSB STATE
(Default = LOW)
Address
0
0011010
1
0011011
Table 24 2-Wire MPU Interface Address Selection

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
43
To control the WM8731 on the 2-wire bus the master control device must initiate a data transfer by
establishing a start condition, defined by a high to low transition on SDIN while SCLK remains high.
This indicates that an address and data transfer will follow. All peripherals on the 2-wire bus respond
to the start condition and shift in the next eight bits (7-bit address + R/W bit). The transfer is MSB
first. The 7-bit address consists of a 6-bit base address + a single programmable bit to select one of
two available addresses for this device (see table 24). If the correct address is received and the R/W
bit is `0', indicating a write, then the WM8731 will respond by pulling SDIN low on the next clock pulse
(ACK). The WM8731 is a write only device and will only respond to the R/W bit indicating a write. If
the address is not recognised the device will return to the idle condition and wait for a new start
condition and valid address.
Once the WM8731 has acknowledged a correct address, the controller will send eight data bits (bits
B[15]-B[8]). WM8731 will then acknowledge the sent data by pulling SDIN low for one clock pulse.
The controller will then send the remaining eight data bits (bits B[7]-B[0]) and the WM8731 will then
acknowledge again by pulling SDIN low.
A stop condition is defined when there is a low to high transition on SDIN while SCLK is high. If a
start or stop condition is detected out of sequence at any point in the data transfer then the device
will jump to the idle condition.
After receiving a complete address and data sequence the WM8731 returns to the idle state and
waits for another start condition. Each write to a register requires the complete sequence of start
condition, device address and R/W bit followed by the 16 register address and data bits.
POWER DOWN MODES
The WM8731 contains power conservation modes in which various circuit blocks may be safely
powered down in order to conserve power. This is software programmable as shown in the table
below.
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0
LINEINPD
1
Line Input Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
1
MICPD
1
Microphone Input an Bias
Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
2
ADCPD
1
ADC Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
3
DACPD
1
DAC Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
4
OUTPD
1
Line Output Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
5
OSCPD
0
Oscillator Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
6
CLKOUTPD
0
CLKOUT power down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
0000110
Power Down
Control
7
POWEROFF
1
Power Off Device
1 = Device Power Off
0 = Device Power On
Table 25 Power Conservation Modes Software Control
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
44
The power down control can be used to either a) permanently disable functions when not required in
certain applications or b) to dynamically power up and down functions depending on the operating
mode, e.g.: during playback or record. Please follow the special instructions below if dynamic
implementations are being used.
LINEINPD: Simultaneously powers down both the Line Inputs. This can be done dynamically without
any audible effects either on the ADC or to the Line Outputs in Bypass mode. This is of use when the
device enters Playback, Pause or Stop modes or the Microphone input has been selected.
MICPD: Simultaneously powers down both the Microphone Input and Microphone Bias. If this is done
dynamically, audible pops through the ADC will result. This will only be audible if the Microphone
Input is selected to the ADC at the time. If the state of MICPD is changed then the controlling DSP or
microprocessor should switch to select the Line Inputs as input to the ADC (INSEL) before changing
MICPD. This is of use when the device enters Playback, Pause or Stop modes or the Microphone
Input is not selected.
ADCPD: Powers down the ADC and ADC Filters. If this is done dynamically then audible pops will
result if any signals were present through the ADC. To overcome this whenever the ADC is to be
powered down, either mute the Microphone Input (MUTEIN) or MUTELINEIN, then change ADCPD.
This is of use when the device enters Playback, Pause or Stop modes regardless of whether
Microphone or Line Inputs are selected.
DACPD: Powers down the DAC and DAC Digital Filters. If this is done dynamically then audible pops
will result unless the following guidelines are followed. In order to prevent pops, the DAC should first
be soft-muted (DACMU), the output should then be de-selected from the line and headphone output
(DACSEL), then the DAC powered down (DACPD). This is of use when the device enters Record,
Pause, Stop or Bypass modes.
OUTPD: Powers down the Line Headphone Output. If this is done dynamically then audible pops
may result unless the DAC is first soft-muted (DACMU). This is of use when the device enters
Record, Pause or Stop modes.
OSCPD: Powers off the on board crystal oscillator. The MCLK input will function independently of the
Oscillator being powered down.
CLKOUTPD: Powers down the CLOCKOUT pin. This conserves power, reduces digital noise and RF
emissions if not required. CLKOUT is tied low when powered down.
The device can be put into a standby mode (STANDBY) by powering down all the audio circuitry
under software control as shown in Table 18. If the crystal oscillator and/or CLOKOUT pins are being
used to derive the system master clock, these should probably never be powered off in standby.
Provision has been made to independently power off these areas according to Table 26.
PO
W
E
R
O
F
F
CL
KOUT
P
D
OS
CP
D
OUTP
D
DACP
D
ADCP
D
MIC
P
D
LIN
E
IN
PD
DESCRIPTION
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
STANDBY, but with Crystal
Oscillator OS and CLKOUT
available
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
STANDBY, but with Crystal
Oscillator OS available,
CLKOUT not-available
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
STANDBY, Crystal
oscillator and CLKOUT not-
available.
Table 26 Standby Mode
In STANDBY mode the Control Interface, a small portion of the digital and areas of the analogue
circuitry remain active. The active analogue includes the analogue VMID reference so that the
analogue line inputs, line outputs and headphone outputs remain biased to VMID. This reduces any
audible effects caused by DC glitches when entering or leaving STANDBY mode.
The device can be powered off by writing to the POWEROFF bit of the Power Down register. In
POWEROFF mode the Control Interface and a small portion of the digital remain active. The

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
45
analogue VMID reference is disabled. As in STANDBY mode the crystal oscillator and/or CLKOUT
pin can be independently controlled. Refer to Table 27.
PO
W
E
R
O
F
F
CL
KOUT
P
D
OS
CP
D
OUTP
D
DACP
D
ADCP
D
MIC
P
D
LIN
E
IN
PD
DESCRIPTION
1
0
0
X
1
1
X
X
POWEROFF, but with Crystal
Oscillator OS and CLKOUT
available
1
1
0
X
1
1
X
X
POWEROFF, but with Crystal
Oscillator OS available, CLKOUT
not-available
1
1
1
X
1
1
X
X
POWEROFF, Crystal oscillator
and CLKOUT not-available.
Table 27 Poweroff Mode
REGISTER MAP
The complete register map is shown in Table 28. The detailed description can be found in Table 29
and in the relevant text of the device description. There are 11 registers with 16 bits per register (7 bit
address + 9 bits of data). These can be controlled using either the 2 wire or 3 wire MPU interface.
REGISTER
B
15
B
14
B
13
B
12
B
11
B
10
B
9
B8
B7
B6
B5
B4
B3
B2
B1
B0
R0 (00h)
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
LRIN
BOTH
LIN
MUTE
0
0
LINVOL
R1 (02h)
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
RLIN
BOTH
RIN
MUTE
0
0
RINVOL
R2 (04h)
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
LRHP
BOTH
LZCEN
LHPVOL
R3 (06h)
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
RLHP
BOTH
RZCEN
RHPVOL
R4 (08h)
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
SIDEATT
IDE TONE DAC SEL BY PASS
INSEL
UTE MIC IC BOOST
R5 (0Ah)
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
DAC MU
DEEMPH
ADC HPD
R6 (0Ch)
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
PWR
OFF
CLK
OUTPD
OSCPD
OUTPD
DACPD
ADCPD
MICPD
LINEINPD
R7 (0Eh)
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
BCLK
INV
MS
LR SWAP
LRP
IWL
FORMAT
R8 (10h)
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
CLKO
DIV2
CLKI
DIV2
SR
BOSR
SB/ NORM
R9 (12h)
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
ACTIVE
R15(1Eh)
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
RESET
ADDRESS
DATA
Table 28 Mapping of Program Registers

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
46
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
4:0
LINVOL[4:0]
10111
( 0dB )
Left Channel Line Input Volume
Control
11111 = +12dB . . 1.5dB steps down
to 00000 = -34.5dB
7
LINMUTE
1
Left Channel Line Input Mute to ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
0000000
Left Line In
8
LRINBOTH
0
Left to Right Channel Line Input
Volume and Mute Data Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
LINVOL[4:0] and LINMUTE to
RINVOL[4:0] and RINMUTE
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
4:0
RINVOL[4:0]
10111
( 0dB )
Right Channel Line Input Volume
Control
11111 = +12dB . .1.5dB steps down
to 00000 = -34.5dB
7
RINMUTE
1
Right Channel Line Input Mute to
ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
0000001
Right Line In
8
RLINBOTH
0
Right to Left Channel Line Input
Volume and Mute Data Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
RINVOL[4:0] and RINMUTE to
LINVOL[4:0] and LINMUTE
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
6:0
LHPVOL
[6:0]
1111001
( 0dB )
Left Channel Headphone Output
Volume Control
1111111 = +6dB
. . 1dB steps down to
0110000 = -73dB
0000000 to 0101111 = MUTE
7
LZCEN
0
Left Channel Zero Cross detect
Enable
1 = Enable
0 = Disable
0000010
Left Headphone
Out
8
LRHPBOTH
0
Left to Right Channel Headphone
Volume, Mute and Zero Cross Data
Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
LHPVOL[6:0] and LZCEN to
RHPVOL[6:0] and RZCEN
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
47
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
6:0
RHPVOL
[6:0]
1111001
( 0dB )
Right Channel Headphone Output
Volume Control
1111111 = +6dB
. . 1dB steps down to
0110000 = -73dB
0000000 to 0101111 = MUTE
7
RZCEN
0
Right Channel Zero Cross detect
Enable
1 = Enable
0 = Disable
0000011
Right
Headphone Out
8
RLHPBOTH
0
Right to Left Channel Headphone
Volume, Mute and Zero Cross Data
Load Control
1 = Enable Simultaneous Load of
RHPVOL[6:0] and RZCEN to
LHPVOL[6:0] and LZCEN
0 = Disable Simultaneous Load
0
MICBOOST
0
Microphone Input Level Boost
1 = Enable Boost
0 = Disable Boost
1
MUTEMIC
1
Line Input Mute to ADC
1 = Enable Mute
0 = Disable Mute
2
INSEL
0
Microphone/Line Input Select to ADC
1 = Microphone Input Select to ADC
0 = Line Input Select to ADC
3
BYPASS
1
Bypass Switch
1 = Enable Bypass
0 = Disable Bypass
4
DACSEL
0
DAC Select
1 =Select DAC
0 = Don't select DAC
5
SIDETONE
0
Side Tone Switch
1 = Enable Side Tone
0 = Disable Side Tone
0000100
Analogue Audio
Path Control
7:6
SIDEATT[1:0]
00
Side Tone Attenuation
11 = -15dB
10 = -12dB
01 = -9dB
00 = -6dB
0
ADCHPD
0
ADC High Pass Filter Enable
1 = Enable High Pass Filter
0 = Disable High Pass Filter
2:1
DEEMP[1:0]
00
De-emphasis Control
11 = 48kHz
10 = 44.1kHz
01 = 32kHz
00 = Disable
0000101
Digital Audio
Path Control
3
DACMU
1
DAC Soft Mute Control
1 = Enable soft mute
0 = Disable soft mute

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
48
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0
LINEINPD
1
Line Input Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
1
MICPD
1
Microphone Input an Bias Power
Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
2
ADCPD
1
ADC Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
3
DACPD
1
DAC Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
4
OUTPD
1
Outputs Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
5
OSCPD
0
Oscillator Power Down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
6
CLKOUTPD
0
CLKOUT power down
1 = Enable Power Down
0 = Disable Power Down
0000110
Power Down
Control
7
POWEROFF
1
POWEROFF mode
1 = Enable POWEROFF
0 = Disable POWEROFF

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
49
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
1:0
FORMAT[1:0]
10
Audio Data Format Select
11 = DSP Mode, frame sync + 2 data
packed words
10 = I
2
S Format, MSB-First left-1
justified
01 = MSB-First, left justified
00 = MSB-First, right justified
3:2
IWL[1:0]
10
Input Audio Data Bit Length Select
11 = 32 bits
10 = 24 bits
01 = 20 bits
00 = 16 bits
4
LRP
0
DACLRC phase control (in left, right
or I
2
S modes)
1 = Right Channel DAC data when
DACLRC high
0 = Right Channel DAC data when
DACLRC low
(opposite phasing in I
2
S mode)
or
DSP mode A/B select (in DSP mode
only)
1 = MSB is available on 2nd BCLK
rising edge after DACLRC rising edge
0 = MSB is available on 1st BCLK
rising edge after DACLRC rising edge
5
LRSWAP
0
DAC Left Right Clock Swap
1 = Right Channel DAC Data Left
0 = Right Channel DAC Data Right
6
MS
0
Master Slave Mode Control
1 = Enable Master Mode
0 = Enable Slave Mode
0000111
Digital Audio
Interface
Format
7
BCLKINV
0
Bit Clock Invert
1 = Invert BCLK
0 = Don't invert BCLK
0
USB/
NORMAL
0
Mode Select
1 = USB mode (250/272fs)
0 = Normal mode (256/384fs)
Base Over-Sampling Rate
1
BOSR
0
USB Mode
0 = 250fs
1 = 272fs
Normal Mode
0 = 256fs
1 = 384fs
5:2
SR[3:0]
0000
ADC and DAC sample rate control;
See USB Mode and Normal Mode
Sample Rate sections for operation
6
CLKIDIV2
0
Core Clock divider select
1 = Core Clock is MCLK divided by 2
0 = Core Clock is MCLK
0001000
Sampling
Control
7
CLKODIV2
0
CLKOUT divider select
1 = CLOCKOUT is Core Clock
divided by 2
0 = CLOCKOUT is Core Clock

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
50
REGISTER
ADDRESS
BIT
LABEL
DEFAULT
DESCRIPTION
0001001
Active Control
0
ACTIVE
0
Activate Interface
1 = Active
0 = Inactive
0001111
Reset Register
8:0
RESET
not reset
Reset Register
Writing 00000000 to register resets
device
Table 29 Register Map Description
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
The ADC and DAC employ different digital filters. There are 4 types of digital filter, called Type 0, 1, 2
and 3. The performance of Types 0 and 1 is listed in the table below, the responses of all filters is
shown in the proceeding pages.
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
ADC Filter Type 0 (USB Mode, 250fs operation)
+/- 0.05dB
0
0.416fs
Passband
-6dB
0.5fs
Passband Ripple
+/- 0.05
dB
Stopband
0.584fs
Stopband Attenuation
f > 0.584fs
-60
dB
ADC Filter Type 1 (USB mode, 272fs or Normal mode operation)
+/- 0.05dB
0
0.4535fs
Passband
-6dB
0.5fs
Passband Ripple
+/- 0.05
dB
Stopband
0.5465fs
Stopband Attenuation
f > 0.5465fs
-60
dB
High Pass Filter Corner
Frequency
-3dB
-0.5dB
-0.1dB
3.7
10.4
21.6
Hz
DAC Filter Type 0 (USB mode, 250fs operation)
+/- 0.03dB
0
0.416fs
Passband
-6dB
0.5fs
Passband Ripple
+/-0.03
dB
Stopband
0.584fs
Stopband Attenuation
f > 0.584fs
-50
dB
DAC Filter Type 1 (USB mode, 272fs or Normal mode operation)
+/- 0.03dB
0
0.4535fs
Passband
-6dB
0.5fs
Passband Ripple
+/- 0.03
dB
Stopband
0.5465fs
Stopband Attenuation
f > 0.5465fs
-50
dB
Table 30 Digital Filter Characteristics
TERMINOLOGY
1.
Stop Band Attenuation (dB) - the degree to which the frequency spectrum is attenuated (outside audio band)
2. Pass-band
Ripple
≠ any variation of the frequency response in the pass-band region

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
51
DAC FILTER RESPONSES
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 33 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 0
Figure 34 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 0
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 35 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 1
Figure 36 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 1
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 37 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 2
Figure 38 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 2

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
52
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.25
-0.2
-0.15
-0.1
-0.05
0
0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 39 DAC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 3
Figure 40 DAC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 3
ADC FILTER RESPONSES
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 41 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 0
Figure 42 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 0
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 43 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 1
Figure 44 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 1

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
53
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 45 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 2
Figure 46 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 2
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.06
-0.05
-0.04
-0.03
-0.02
-0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 47 ADC Digital Filter Frequency Response ≠Type 3
Figure 48 ADC Digital Filter Ripple ≠Type 3
ADC HIGH PASS FILTER
The WM8731 has a selectable digital high pass filter to remove DC offsets. The filter response is
characterised by the following polynomial.
H(z) = 1 ≠ z
-1
1 ≠ 0.9995 z
-1

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
54
DIGITAL DE-EMPHASIS CHARACTERISTICS
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
14000
16000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
14000
16000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 49 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (32kHz)
Figure 50 De-Emphasis Error (32kHz)
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 51 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (44.1kHz)
Figure 52 De-Emphasis Error (44.1kHz)
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
Response (dB)
Frequency (Fs)
Figure 53 De-Emphasis Frequency Response (48kHz)
Figure 54 De-Emphasis Error (48kHz)

WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
55
RECOMMENDED EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
WM8731
Codec
RHPOUT
VMID
100
CLKOUT
LOUT
+
47k
100
12
LHPOUT
+
47k
220
µ
F
9
AVDD
AGND
14
15
3.3V
HPVDD
HPGND
11
8
3.3V
ROUT
+
47k
100
13
+
47k
220
µ
F
10
2
0.1
µ
F
10
µ
F
+
16
RLINEIN
MICBIAS
DACLRC
DACDAT
ADCLRC
ADCDAT
5.6k
5.6k
+
19
LLINEIN
5.6k
5.6k
220pF
+
20
MICIN
DBVDD
DCVDD
3.3V
DGND
1.5V - 3.3V
+
+
1
28
27
BCLK
3
Audio Serial Data I/F
5
4
7
6
3-wire or 2-wire
MPU Interface
3-wire Interface
2-wire Interface
SDIN
23
CSB
22
SCLK
24
MODE
21
+
1
µ
F
Rmic
680
220pF
47k
17
18
10
µ
F
0.1
µ
F
10k
3.3V
XTO
XTI/MCLK
15pF
15pF
26
25
+
10
µ
F
+
Note:
1. Rmic - The value of this resistor is dependent on the gain setting. Refer to Page 20 for Rmic calculation.
2. Where possible, it is recommended that NPO or COG type capacitors should be used for best performance.
10
µ
F
0.1
µ
F
0.1
µ
F
0.1
µ
F
10
µ
F
1
µ
F
1
µ
F
1
µ
F
1
µ
F
220pF
Figure 55 External Components Diagram
WM8731
Advanced Information
WOLFSON MICROELECTRONICS LTD
AI Rev 2.0 February 2001
56
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
NOTES:
A. ALL LINEAR DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
B. THIS DRAWING IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
C. BODY DIMENSIONS DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH OR PROTRUSION, NOT TO EXCEED 0.20MM.
D. MEETS JEDEC.95 MO-150, VARIATION = AH. REFER TO THIS SPECIFICATION FOR FURTHER DETAILS.
DM007.C
DS: 28 PIN SSOP (10.2 x 5.3 x 1.75 mm)
Symbols
Dimensions
(mm)
MIN
NOM
MAX
A
-----
-----
2.0
A
1
0.05
-----
-----
A
2
1.62
1.75
1.85
b
0.22
-----
0.38
c
0.09
-----
0.25
D
9.90
10.20
10.50
e
0.65 BSC
E
7.40
7.80
8.20
E
1
5.00
5.30
5.60
L
0.55
0.75
0.95
0
o
4
o
8
o
REF:
JEDEC.95, MO-150
A A2
A1
14
1
15
28
E1
E
c
L
GAUGE
PLANE
0.25
e
b
D
SEATING PLANE
-C-
0.10 C























































