 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: MT88E46AS | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

1
MT88E46
Bellcore Compliant Calling Number
Identification Circuit
Advance Information
Features
∑
Compatible with Bellcore GR-30-CORE,
SR-TSV-002476; TIA/EIA-716 and TIA/EIA-777
∑
Pin compatible with MT88E45
∑
Differential input amplifiers with adjustable
gains for Tip/Ring and 4-wire side connections
∑
TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association)
MEI (Multiple Extension Interworking)
compatible architecture: CAS (CPE Alerting
Signal) detection is selectable between Tip/
Ring and 4-wire side
∑
4-wire side CAS detection is Bellcore talkoff
and talkdown compliant when near end speech
is attenuated 8dB or better, and is close to
talkoff compliant even without near end speech
attenuation
∑
Tip/Ring side CAS detection typically meets
talkdown condition 1 (the average case)
∑
1200 baud Bell 202 and CCITT V.23 FSK
demodulation
∑
Selectable 3-wire FSK data interface (serial bit
stream or 1 byte buffer) with facility to monitor
stop bit for framing error check
∑
FSK carrier detect status output
∑
3 to 5V
±
10% supply voltage
∑
Uses 3.579545MHz crystal
∑
Low power CMOS with power down mode
Applications
∑
Bellcore compliant CIDCW (Calling Identity
Delivery on Call Waiting) and CWD (Call
Waiting Deluxe) telephones
∑
CIDCW and CWD telephone adjunct boxes
∑
Computer Telephony Integrated (CTI) systems
Description
The MT88E46 is a CMOS integrated circuit suitable
for receiving the FSK and CAS signals in North
American (Bellcore) CIDCW, CWD and CID (Calling
Identity Delivery) services. It provides an optimal
solution for the CIDCW (also known as Type 2) and
CWD (Type 2.5) telephone set applications by
providing separate input op-amps for Tip/Ring and 4-
wire side (receive pair of the telephone hybrid or
speech IC) connections. The Tip/Ring connection is
compatible with TIA's MEI scheme and can be used
for FSK demodulation and `on hook mode' CAS
detection. The 4-wire side connection is for `off hook
mode' CAS detection. The CAS detection modes - on
hook and off hook - use different algorithms which
are optimized for the CPE states. In `off hook mode'
the CAS detector is Bellcore compliant when near
end speech is attenuated 8dB or better. `On hook
mode' is optimized for talkdown only and typically
meets talkdown condition 1 (the average case)
without speech attenuation at Tip/Ring such as in the
on hook state MEI CPE.
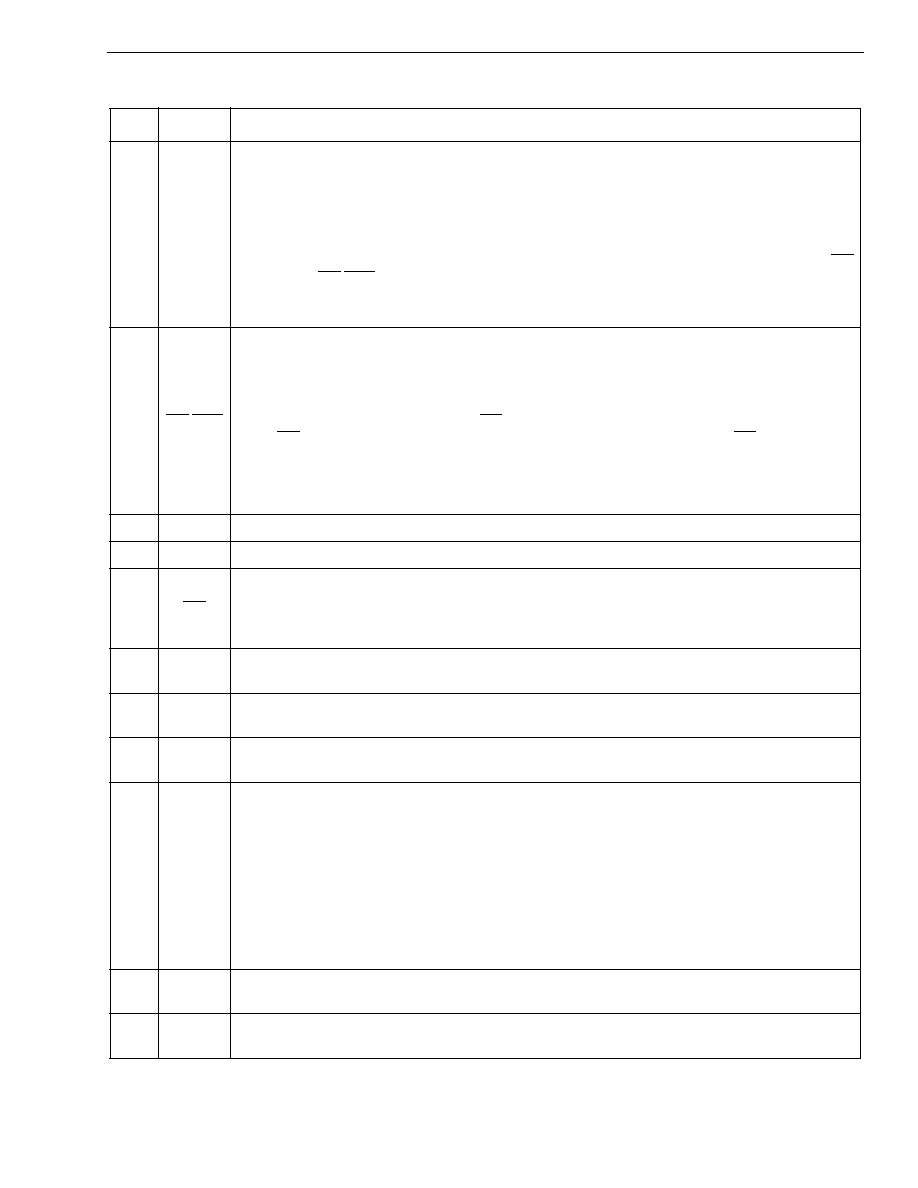
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
Anti-Alias
Filter
FSK
Bandpass
FSK
Demod
+
-
+
-
Data Timing
Recovery
Carrier
Detector
2130Hz
Bandpass
2750Hz
Bandpass
Tone
Detection
Algorithm
GS1en
GS1en
Mux
DR
DET
Bias
Generator
Oscillator
Control Bit
Decode
FSKen
CASen
PWDN
IN1+
IN1-
GS1
IN2+
IN2-
GS2
V
REF
OSC1
OSC2
CB0
CB2
CB1
DATA
DCLK
CD
DR/DET
Vdd
Vss
On/Off Hook mode
MODE
MODE
FSKen
CASen
CASen
GS1en
PWDN
PWDN
PWDN
Patent pending
DS5350
ISSUE 1
March 2000
Ordering Information
MT88E46AS
20 Pin SOIC
-40 to +85
∞
C

MT88E46
Advance Information
2
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin #
Name
Description
1
V
REF
Voltage Reference (Output).
Nominally Vdd/2. It is used to bias the GS1 (Tip/Ring
connection) and GS2 (telephone hybrid or speech IC receive pair connection) input op-amps.
2
IN1+
GS1 Op-Amp Non-inverting Input.
The op-amp is for connecting the MT88E46 to Tip/Ring.
3
IN1-
GS1 Op-Amp Inverting Input.
The op-amp is for connecting the MT88E46 to Tip/Ring.
4
GS1
Gain Select 1 (Output).
This is the output of the GS1 op-amp. The op-amp should be used to
connect the MT88E46 to Tip and Ring. The Tip/Ring signal can be amplified or attenuated at
GS1 via selection of the feedback resistor between GS1 and IN1-.
FSK demodulation or `on hook mode' CAS detection of the GS1 signal can be selected via the
CB1 and CB2 pins. See Tables 1 and 2.
5
Vss
Power Supply Ground.
6
OSC1
Oscillator Input.
Crystal connection. This pin can also be driven directly from an external
clock source.
7
OSC2
Oscillator Output.
Crystal connection. When OSC1 is driven by an external clock, this pin
should be left open circuit.
8
CB0
Control Bit 0 (CMOS Logic Input).
This pin is used primarily to select the 3-wire FSK data
interface mode. When it is low, interface mode 0 is selected where the FSK bit stream is output
directly at the DATA pin. When it is high, interface mode 1 is selected where the FSK byte is
stored in a 1 byte buffer which can be read serially by the application's microcontroller.
The FSK interface is consisted of the DATA, DCLK and DR/DET pins. See the 3 pin
descriptions to understand how CB0 affects the FSK interface.
This pin is also used with CB1 and CB2 to put the MT88E46 into a power down state drawing
virtually no power supply current. See Tables 1 and 2.
9
DCLK
3-Wire FSK Interface Data Clock (Schmitt Logic Input/CMOS Logic Output).
In interface
mode 0 (when the CB0 pin is logic low) this is a CMOS output whose rising edge denotes the
nominal mid-point of a bit in the FSK data byte.
In interface mode 1 (when the CB0 pin is logic high) this is a Schmitt trigger input used to shift
the FSK data byte out of an on chip buffer to the DATA pin.
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
V
REF
IN1+
IN1-
GS1
Vss
OSC1
DCLK
DATA
IN2+
IN2-
GS2
CB2
CB1
Vdd
CD
NC
MT88E46
7
OSC2
8
CB0
12
11
IC
DR/DET
Advance Information
MT88E46
3
10
DATA
3-Wire FSK Interface Data (CMOS Logic Output).
Mark frequency corresponds to logical 1.
Space frequency corresponds to logical 0.
In interface mode 0 (when the CB0 pin is logic low) the FSK serial bit stream is output to DATA
directly.
In interface mode 1 (when the CB0 pin is logic high) the start bit is stripped off, the data byte
and the trailing stop bit are stored in a 9 bit buffer. At the end of each word indicated by the DR
signal at the DR/DET pin, the microcontroller should shift the byte out to DATA by applying 8
read pulses to the DCLK pin. A 9th DCLK pulse will shift out the trailing stop bit for framing
error checking.
11
DR/DET
3-Wire FSK Interface Data Ready/CAS Detect (CMOS Logic Output).
Active low.
This is a dual purpose pin which indicates the end of an FSK word or the end of CAS.
Data Ready:
When FSK demodulation is enabled this pin denotes the end of a word. In both
FSK interface modes 0 and 1, it is normally high and goes low for half a bit time at the end of a
word. In mode 1 if DCLK starts while DR is low, the first rising edge of the DCLK input will
return DR to high. This feature allows an interrupt requested by a low going DR to be cleared
upon reading the first DATA bit.
CAS Detect:
When CAS detection is enabled, this pin goes low after the end of CAS for 416
µ
s
(nominal) to indicate that CAS has been detected.
12
IC
Internal Connection.
Must be left open circuit.
13
NC
No Connection.
This pin is not bonded to the die and is unaffected by external connections.
14
CD
Carrier Detect (CMOS Logic Output).
Active low.
A logic low indicates that an FSK signal is present. A 10ms time hysteresis has been provided
to allow for momentary signal discontinuity. The demodulated FSK data is ignored until carrier
detect has been activated.
15
Vdd
Positive Power Supply.
A decoupling capacitor should be connected directly across the Vdd
and Vss pins.
16
CB1
Control Bit 1 (CMOS Logic Input).
Together with CB2 this pin enables FSK demodulation or
CAS detection. See Tables 1 and 2.
17
CB2
Control Bit 2 (CMOS Logic Input).
Together with CB1 this pin enables FSK demodulation or
CAS detection. See Tables 1 and 2.
18
GS2
Gain Select 2 (Output).
This is the output of the GS2 op-amp. The op-amp should be used to
connect the MT88E46 to the receive pair of the telephone hybrid or speech IC. The signal can
be amplified or attenuated at GS2 via selection of the feedback resistor between GS2 and IN2-
.
When the application is a telephone adjunct box where there is no hybrid or speech IC, if the
GS2 gain with respect to Tip/Ring is to be set to the same as that of GS1, the GS2 op-amp can
be connected as a voltage follower to the GS1 op-amp output (see Figure 5).
The GS2 signal is used for `off hook mode' CAS detection only as selected via the CB1 and
CB2 pins. See Tables 1 and 2.
19
IN2-
GS2 Op-Amp Inverting Input.
The op-amp is for connecting the MT88E46 to the receive pair
of the telephone hybrid or speech IC.
20
IN2+
GS2 Op-Amp Non-Inverting Input.
The op-amp is for connecting the MT88E46 to the receive
pair of the telephone hybrid or speech IC.
Pin Description
Pin #
Name
Description

MT88E46
Advance Information
4
Control Bit (CB0/1/2) Functionality
Table 1. CB0/1/2 Function Table
The number of control bits (CB) required to interface the MT88E46 to the microcontroller depends on the
functionality of the application.
Table 2. Control Bit Functionality Groups
CB0 CB1 CB2
FSK
Interface
Input
Op-Amp
Function
0/1
1
1
Set by CB0
GS1
FSK Demodulation.
DR/DET pin is the DR signal.
0/1
1
0
Set by CB0
GS2
`Off hook mode' CAS Detection.
DR/DET pin is the DET signal.
The off hook mode algorithm is Bellcore talkoff and talkdown compliant
when near end speech level is attenuated 8dB or better. It should be used
for the off hook state CPE.
0/1
0
1
Set by CB0
GS1
`On hook mode' CAS Detection.
DR/DET pin is the DET signal.
When the line is in use, a TIA Multiple Extension Interworking (MEI)
compatible Type 2 CPE must be able to detect CAS even though the CPE
itself is on hook. Since in most telephone designs the hybrid or speech IC
is not operational when the CPE itself is on hook, this mode provides Tip
Ring CAS detection for the on hook state MEI CPE.
The on hook mode algorithm is optimized for talkdown only and typically
meets talkdown condition 1 (the average case) without near end speech
attenuation. It must not be used when the CPE itself is off hook. See `On
Hook Mode CAS Detection' section in `Functional Description'.
1
0
0
Mode 1
-
Power Down.
DR/DET pin is logic high.
The MT88E46 is disabled and draws virtually no power supply current.
Note that the DCLK pin becomes an input pin because FSK interface
mode 1 is selected by CB0=1.
0
0
0
Mode 0
-
Reserved for factory testing.
Functionality Group
Controls
Description
FSK,
Off Hook mode CAS
(Non MEI compatible)
CB2
CB0 is connected to Vdd or Vss to select the FSK interface mode.
CB1 connected to Vdd.
The microcontroller uses CB2 to select between the 2 functions.
FSK,
Off Hook mode CAS,
On Hook mode CAS
CB1
CB2
CB0 is connected to Vdd or Vss to select the FSK interface mode.
The microcontroller uses CB1 and CB2 to select between the 3
functions.
FSK (Interface mode 1),
Off Hook mode CAS,
On Hook mode CAS,
Power Down
CB1
CB2
CB0 is connected to Vdd to select FSK interface mode 1.
The microcontroller uses CB1 and CB2 to select between the 4
functions.
FSK (Interface mode 0),
Off Hook mode CAS,
On Hook mode CAS,
Power Down
CB0
CB1
CB2
All 3 pins are required.

Advance Information
MT88E46
5
Functional Overview
In the Calling Identity Delivery on Call Waiting
(CIDCW) and Call Waiting Deluxe (CWD) services
offered by North American telephone operating
companies, a dual tone known as CAS (CPE Alerting
Signal) is sent from the central office to notify the
near end CPE, which is already engaged in an
established call, that the central office wishes to
deliver calling identity information of a waited call.
The signalling protocol is specified in Bellcore GR-
30-CORE, the CPE (Customer Premises Equipment)
requirements in SR-TSV-002476.
In the GR-30-CORE off hook protocol, the central
office mutes the far end connection (the other end of
the established call) just before CAS is transmitted.
When the near end CPE detects the CAS, it mutes
the handset and checks whether there is any parallel
off hook CPE. If there is no parallel off hook CPE, it
acknowledges CAS reception by sending ACK,
which is a predefined DTMF digit, back to the central
office. When the central office receives ACK, it
transmits the calling party information in 1200 baud
Bell 202 format FSK to the near end CPE which then
typically displays the information to the user.
When CAS is transmitted from the central office,
even though the far end has been muted the near
end user (the end which is to receive the caller ID
information) may be speaking. Therefore, the CAS
must be detected in the presence of near end
speech, noise or music. Failure to detect the CAS
and reply with ACK within a defined interval is known
as `talkdown'. Talkdown is undesirable because the
central office will not deliver the calling information,
hence the quality of the CIDCW or CWD service will
be degraded.
Since CAS can be transmitted anytime during an
established call, the CAS detector is therefore
subjected to speech, noise or music - which can
imitate CAS - from both the near end and the far end
throughout the call. False detection followed by ACK
is known as `talkoff'. Talkoff is undesirable because it
annoys the far end user by the near end CPE's
sending ACK and because the near end CPE is
muted in anticipation of the FSK signal.
Bellcore has specified talkdown and talkoff immunity
performance requirements in SR-TSV-002476. If the
CPE is a telephone, one way to achieve good CAS
speech immunity is to put CAS detection on the
receive pair of the telephone hybrid or speech IC
instead of on Tip and Ring. Compared to a Tip/Ring
connection, talkdown immunity improves because
the near end speech is attenuated on the hybrid /
speech IC receive pair while the CAS level is the
same as on Tip/Ring. Talkoff immunity is also better
because the near end speech is attenuated.
In the GR-30-CORE issue 1 off hook protocol, the
near end CPE must not ACK if there is a parallel off
hook CPE. Otherwise the ACK will not be detected
reliably at the central office. This restriction is
modified by a protocol known as MEI (Multiple
Extension Interworking) developed by the TIA
(Telecommunications Industry Association) in
conjunction with Bellcore. MEI allows a CPE to ACK
if all off hook CPEs are MEI compatible. MEI is
described in the TIA/EIA-777 standard.
MEI introduces the concept of the ACK-Sender and
the Backup ACK-Sender.
∑
On a per call basis, the ACK-Sender is the first
CPE to go off hook for the call. It retains its
status even if it returned on hook while the line
remains in use. The ACK-Sender must give up
its status if a Type 3 (Analog Display Services
Interface) CPE asserts its ACK-Sender status.
∑
The Backup ACK-Sender is the CPE to last
respond to CAS with an ACK and successfully
received FSK data. It retains its status from call
to call but must give up its Backup ACK-Sender
status when another CPE successfully
completes the CAS-ACK-FSK sequence.
When CAS is sent from the central office, all MEI
compatible off hook CPEs detect CAS and go back
on hook. After the ACK-Sender detected CAS, it
monitors the line voltage. When the line voltage has
returned to the HIGH state (the voltage when the line
is not terminated by any CPE), it goes off hook and
sends the ACK. If there is no ACK-Sender because
the first CPE to go off hook is not MEI compatible,
the Backup ACK-Sender takes over and sends the
ACK. Note that both the ACK-Sender and the
Backup ACK-Sender can be on hook or off hook.
Because it may be the ACK-Sender or Backup ACK-
Sender, an MEI compatible on hook state CPE must
be able to detect CAS when the line is in use.
Additionally, the TIA/EIA-777 standard requires an
MEI on hook state CPE to detect CAS during a call
so that it can listen in on the FSK to keep its call log
consistent with the off hook CPEs. However, a CAS
detector connected only to the hybrid / speech IC
cannot detect CAS when the CPE itself is on hook
because either the hybrid / speech IC is not
operational or the signal level is severely attenuated.
Therefore an MEI compatible CPE must be able to
detect CAS from Tip/Ring when the CPE is on hook,
and be able to detect CAS from the hybrid / speech
IC when the CPE is off hook.




